Yibin Ying
Learn from Foundation Model: Fruit Detection Model without Manual Annotation
Nov 25, 2024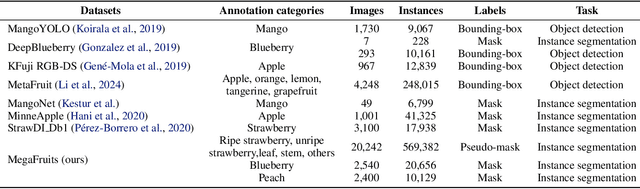
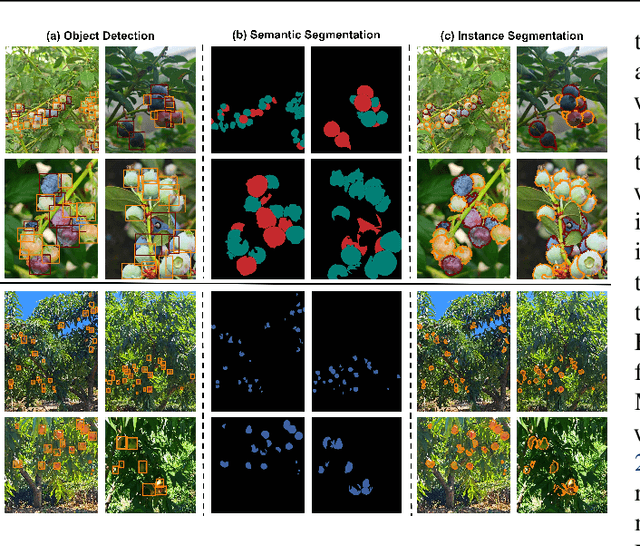
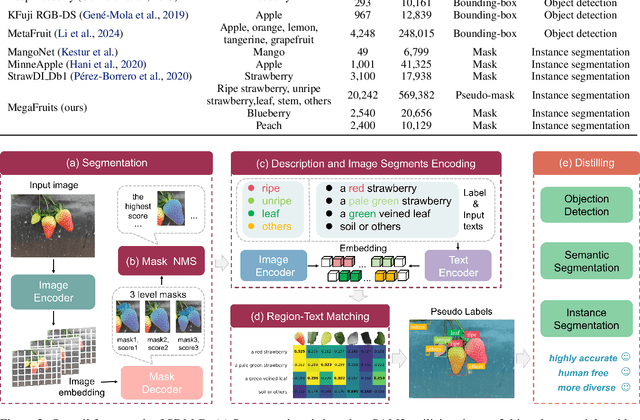
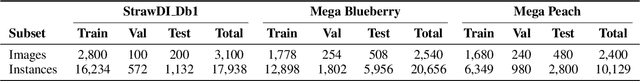

Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in large foundation models have enabled the possibility of transferring knowledge pre-trained on vast datasets to domains with limited data availability. Agriculture is one of the domains that lacks sufficient data. This study proposes a framework to train effective, domain-specific, small models from foundation models without manual annotation. Our approach begins with SDM (Segmentation-Description-Matching), a stage that leverages two foundation models: SAM2 (Segment Anything in Images and Videos) for segmentation and OpenCLIP (Open Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining) for zero-shot open-vocabulary classification. In the second stage, a novel knowledge distillation mechanism is utilized to distill compact, edge-deployable models from SDM, enhancing both inference speed and perception accuracy. The complete method, termed SDM-D (Segmentation-Description-Matching-Distilling), demonstrates strong performance across various fruit detection tasks object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation) without manual annotation. It nearly matches the performance of models trained with abundant labels. Notably, SDM-D outperforms open-set detection methods such as Grounding SAM and YOLO-World on all tested fruit detection datasets. Additionally, we introduce MegaFruits, a comprehensive fruit segmentation dataset encompassing over 25,000 images, and all code and datasets are made publicly available at https://github.com/AgRoboticsResearch/SDM-D.git.
PlantStereo: A Stereo Matching Benchmark for Plant Surface Dense Reconstruction
Nov 30, 2021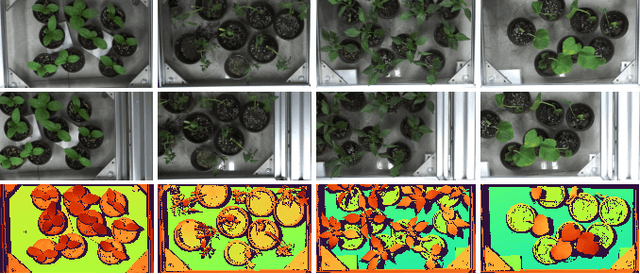


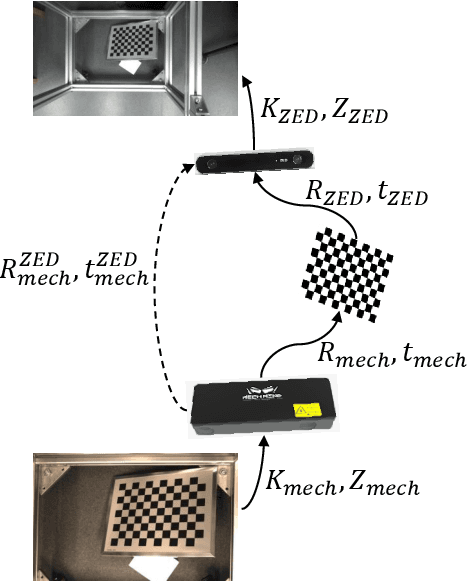
Abstract:Stereo matching is an important task in computer vision which has drawn tremendous research attention for decades. While in terms of disparity accuracy, density and data size, public stereo datasets are difficult to meet the requirements of models. In this paper, we aim to address the issue between datasets and models and propose a large scale stereo dataset with high accuracy disparity ground truth named PlantStereo. We used a semi-automatic way to construct the dataset: after camera calibration and image registration, high accuracy disparity images can be obtained from the depth images. In total, PlantStereo contains 812 image pairs covering a diverse set of plants: spinach, tomato, pepper and pumpkin. We firstly evaluated our PlantStereo dataset on four different stereo matching methods. Extensive experiments on different models and plants show that compared with ground truth in integer accuracy, high accuracy disparity images provided by PlantStereo can remarkably improve the training effect of deep learning models. This paper provided a feasible and reliable method to realize plant surface dense reconstruction. The PlantStereo dataset and relative code are available at: https://www.github.com/wangqingyu985/PlantStereo
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge