Bong-Jin Lee
Rethinking Session Variability: Leveraging Session Embeddings for Session Robustness in Speaker Verification
Sep 26, 2023
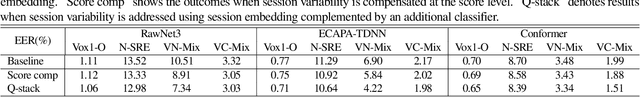
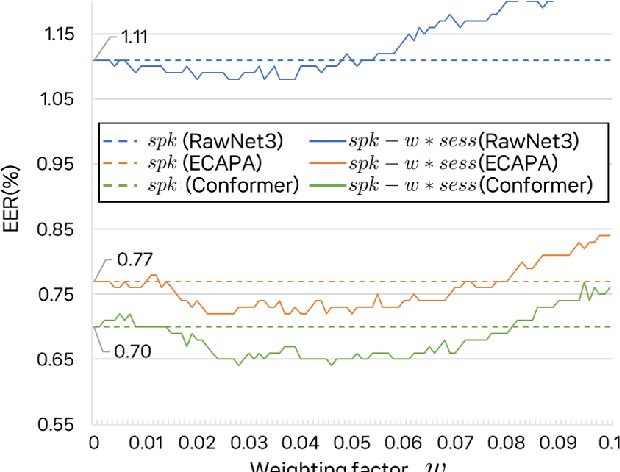
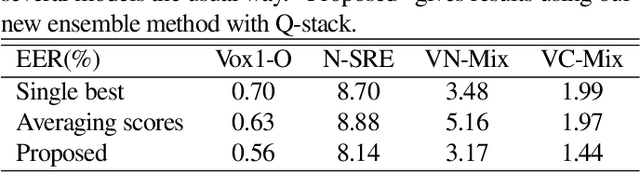
Abstract:In the field of speaker verification, session or channel variability poses a significant challenge. While many contemporary methods aim to disentangle session information from speaker embeddings, we introduce a novel approach using an additional embedding to represent the session information. This is achieved by training an auxiliary network appended to the speaker embedding extractor which remains fixed in this training process. This results in two similarity scores: one for the speakers information and one for the session information. The latter score acts as a compensator for the former that might be skewed due to session variations. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that session information can be effectively compensated without retraining of the embedding extractor.
Encoder-decoder multimodal speaker change detection
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:The task of speaker change detection (SCD), which detects points where speakers change in an input, is essential for several applications. Several studies solved the SCD task using audio inputs only and have shown limited performance. Recently, multimodal SCD (MMSCD) models, which utilise text modality in addition to audio, have shown improved performance. In this study, the proposed model are built upon two main proposals, a novel mechanism for modality fusion and the adoption of a encoder-decoder architecture. Different to previous MMSCD works that extract speaker embeddings from extremely short audio segments, aligned to a single word, we use a speaker embedding extracted from 1.5s. A transformer decoder layer further improves the performance of an encoder-only MMSCD model. The proposed model achieves state-of-the-art results among studies that report SCD performance and is also on par with recent work that combines SCD with automatic speech recognition via human transcription.
Absolute decision corrupts absolutely: conservative online speaker diarisation
Nov 09, 2022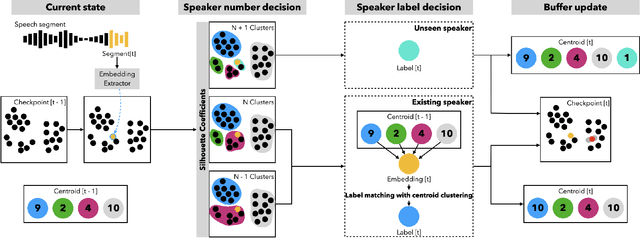
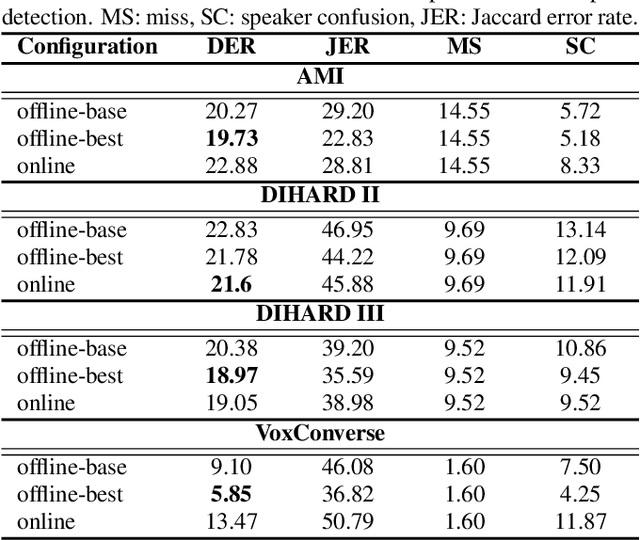
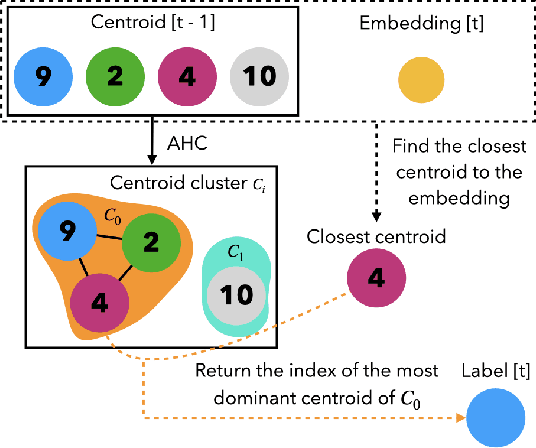
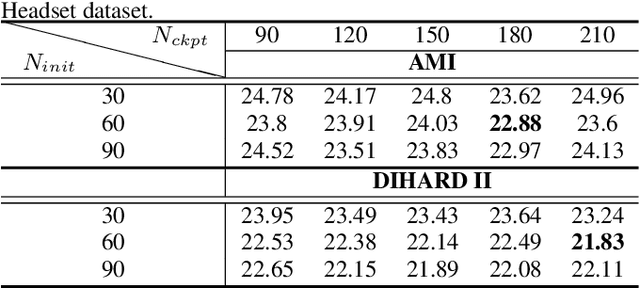
Abstract:Our focus lies in developing an online speaker diarisation framework which demonstrates robust performance across diverse domains. In online speaker diarisation, outputs generated in real-time are irreversible, and a few misjudgements in the early phase of an input session can lead to catastrophic results. We hypothesise that cautiously increasing the number of estimated speakers is of paramount importance among many other factors. Thus, our proposed framework includes decreasing the number of speakers by one when the system judges that an increase in the past was faulty. We also adopt dual buffers, checkpoints and centroids, where checkpoints are combined with silhouette coefficients to estimate the number of speakers and centroids represent speakers. Again, we believe that more than one centroid can be generated from one speaker. Thus we design a clustering-based label matching technique to assign labels in real-time. The resulting system is lightweight yet surprisingly effective. The system demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on DIHARD 2 and 3 datasets, where it is also competitive in AMI and VoxConverse test sets.
High-resolution embedding extractor for speaker diarisation
Nov 08, 2022
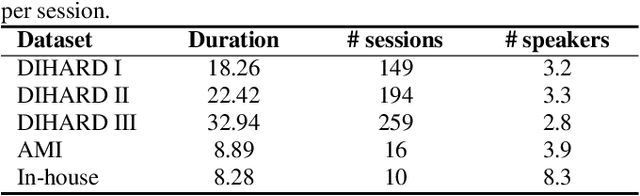

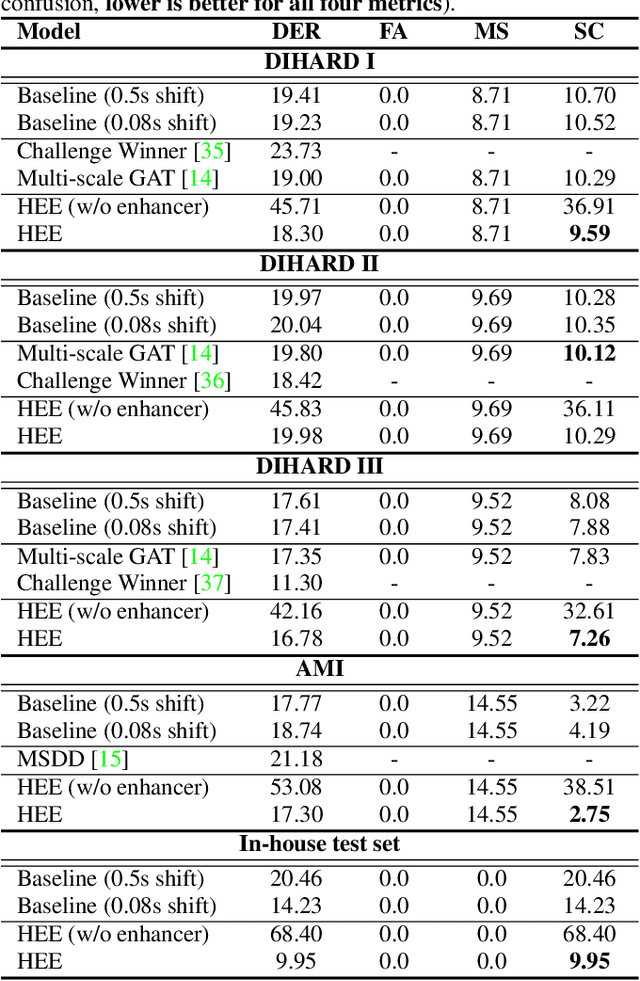
Abstract:Speaker embedding extractors significantly influence the performance of clustering-based speaker diarisation systems. Conventionally, only one embedding is extracted from each speech segment. However, because of the sliding window approach, a segment easily includes two or more speakers owing to speaker change points. This study proposes a novel embedding extractor architecture, referred to as a high-resolution embedding extractor (HEE), which extracts multiple high-resolution embeddings from each speech segment. Hee consists of a feature-map extractor and an enhancer, where the enhancer with the self-attention mechanism is the key to success. The enhancer of HEE replaces the aggregation process; instead of a global pooling layer, the enhancer combines relative information to each frame via attention leveraging the global context. Extracted dense frame-level embeddings can each represent a speaker. Thus, multiple speakers can be represented by different frame-level features in each segment. We also propose an artificially generating mixture data training framework to train the proposed HEE. Through experiments on five evaluation sets, including four public datasets, the proposed HEE demonstrates at least 10% improvement on each evaluation set, except for one dataset, which we analyse that rapid speaker changes less exist.
In search of strong embedding extractors for speaker diarisation
Oct 26, 2022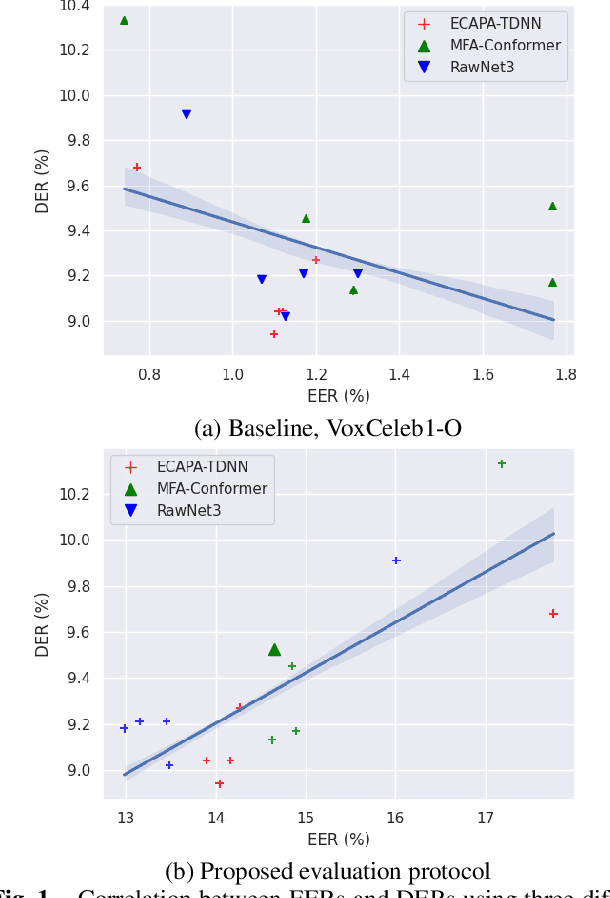
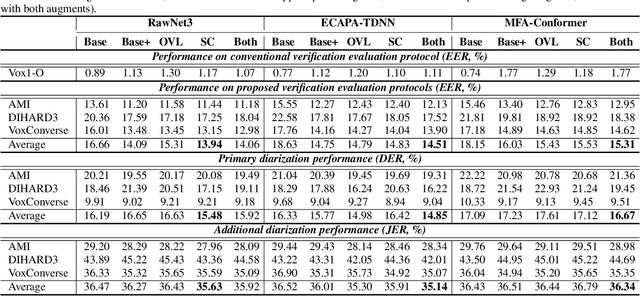
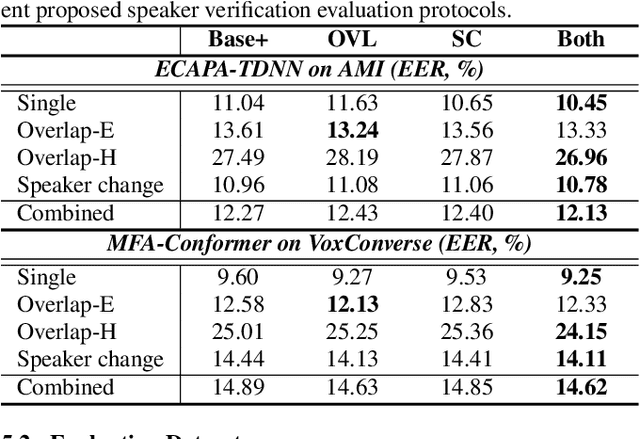
Abstract:Speaker embedding extractors (EEs), which map input audio to a speaker discriminant latent space, are of paramount importance in speaker diarisation. However, there are several challenges when adopting EEs for diarisation, from which we tackle two key problems. First, the evaluation is not straightforward because the features required for better performance differ between speaker verification and diarisation. We show that better performance on widely adopted speaker verification evaluation protocols does not lead to better diarisation performance. Second, embedding extractors have not seen utterances in which multiple speakers exist. These inputs are inevitably present in speaker diarisation because of overlapped speech and speaker changes; they degrade the performance. To mitigate the first problem, we generate speaker verification evaluation protocols that mimic the diarisation scenario better. We propose two data augmentation techniques to alleviate the second problem, making embedding extractors aware of overlapped speech or speaker change input. One technique generates overlapped speech segments, and the other generates segments where two speakers utter sequentially. Extensive experimental results using three state-of-the-art speaker embedding extractors demonstrate that both proposed approaches are effective.
Baseline Systems for the First Spoofing-Aware Speaker Verification Challenge: Score and Embedding Fusion
Apr 21, 2022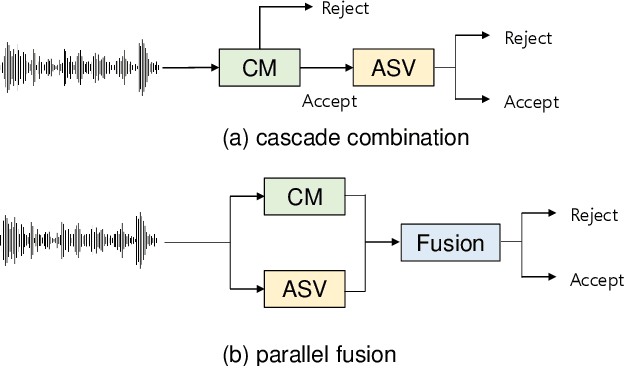

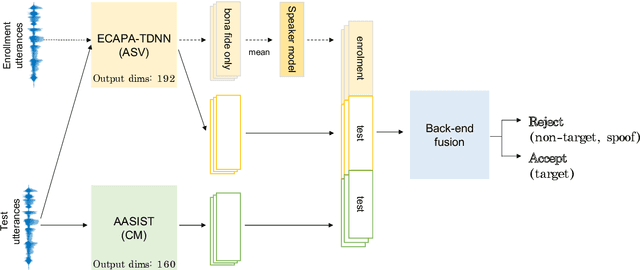
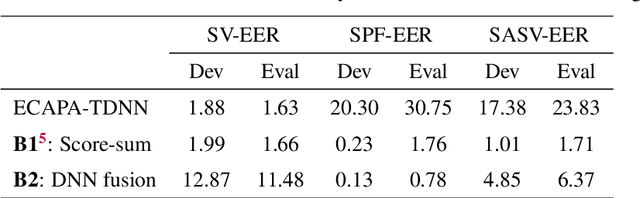
Abstract:Deep learning has brought impressive progress in the study of both automatic speaker verification (ASV) and spoofing countermeasures (CM). Although solutions are mutually dependent, they have typically evolved as standalone sub-systems whereby CM solutions are usually designed for a fixed ASV system. The work reported in this paper aims to gauge the improvements in reliability that can be gained from their closer integration. Results derived using the popular ASVspoof2019 dataset indicate that the equal error rate (EER) of a state-of-the-art ASV system degrades from 1.63% to 23.83% when the evaluation protocol is extended with spoofed trials.%subjected to spoofing attacks. However, even the straightforward integration of ASV and CM systems in the form of score-sum and deep neural network-based fusion strategies reduce the EER to 1.71% and 6.37%, respectively. The new Spoofing-Aware Speaker Verification (SASV) challenge has been formed to encourage greater attention to the integration of ASV and CM systems as well as to provide a means to benchmark different solutions.
Self-supervised curriculum learning for speaker verification
Apr 05, 2022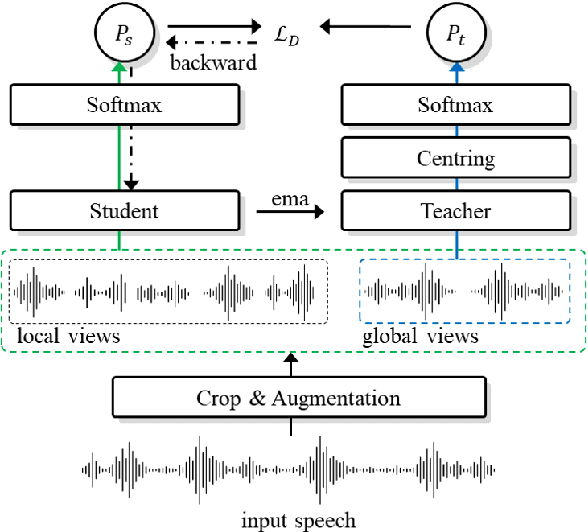
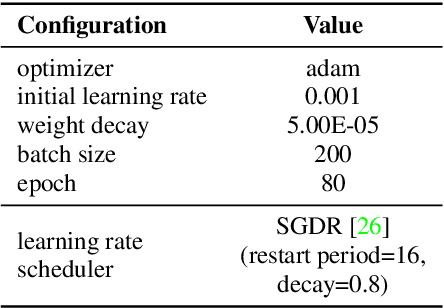
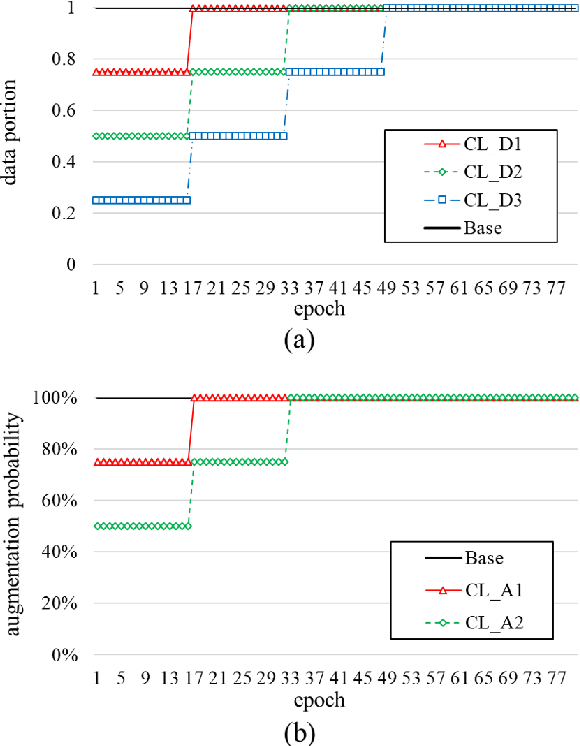
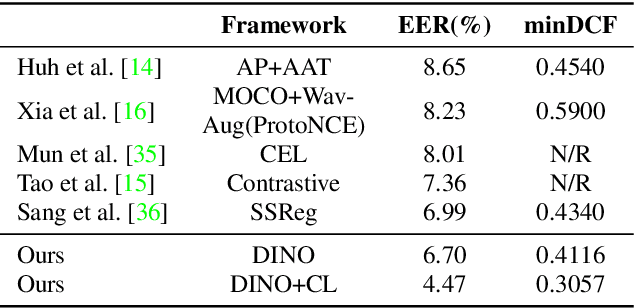
Abstract:Self-supervised learning is one of the emerging approaches to machine learning today, and has been successfully applied to vision, speech and natural processing tasks. There is a range of frameworks within self-supervised learning literature, but the speaker recognition literature has particularly adopted self-supervision via contrastive loss functions. Our work adapts the DINO framework for speaker recognition, in which the model is trained without exploiting negative utterance pairs. We introduce a curriculum learning strategy to the self-supervised framework, which guides effective training of speaker recognition models. In particular, we propose two curriculum strategies where one gradually increases the number of speakers in training dataset, and the other gradually applies augmentations to more utterances within a mini-batch as the training proceeds. A range of experiments conducted on the VoxCeleb1 evaluation protocol demonstrate the effectiveness of both the DINO framework on speaker verification and our proposed curriculum learning strategies. We report the state-of-the-art equal error rate of 4.47% with a single-phase training.
Pushing the limits of raw waveform speaker recognition
Mar 29, 2022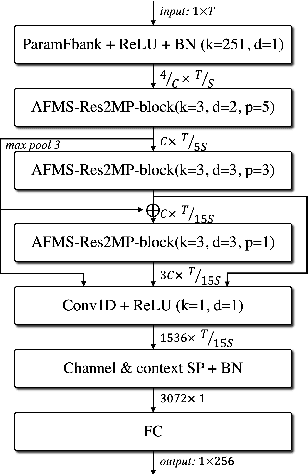
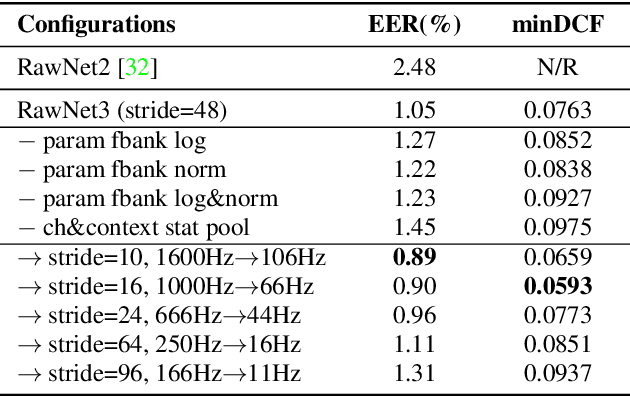
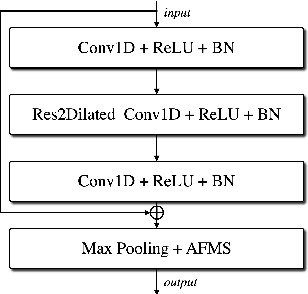
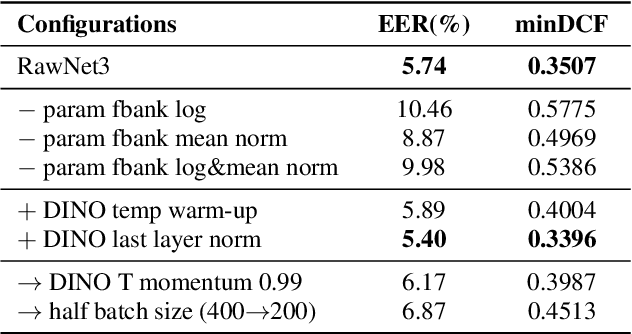
Abstract:In recent years, speaker recognition systems based on raw waveform inputs have received increasing attention. However, the performance of such systems are typically inferior to the state-of-the-art handcrafted feature-based counterparts, which demonstrate equal error rates under 1% on the popular VoxCeleb1 test set. This paper proposes a novel speaker recognition model based on raw waveform inputs. The model incorporates recent advances in machine learning and speaker verification, including the Res2Net backbone module and multi-layer feature aggregation. Our best model achieves an equal error rate of 0.89%, which is competitive with the state-of-the-art models based on handcrafted features, and outperforms the best model based on raw waveform inputs by a large margin. We also explore the application of the proposed model in the context of self-supervised learning framework. Our self-supervised model outperforms single phase-based existing works in this line of research. Finally, we show that self-supervised pre-training is effective for the semi-supervised scenario where we only have a small set of labelled training data, along with a larger set of unlabelled examples.
SASV 2022: The First Spoofing-Aware Speaker Verification Challenge
Mar 28, 2022



Abstract:The first spoofing-aware speaker verification (SASV) challenge aims to integrate research efforts in speaker verification and anti-spoofing. We extend the speaker verification scenario by introducing spoofed trials to the usual set of target and impostor trials. In contrast to the established ASVspoof challenge where the focus is upon separate, independently optimised spoofing detection and speaker verification sub-systems, SASV targets the development of integrated and jointly optimised solutions. Pre-trained spoofing detection and speaker verification models are provided as open source and are used in two baseline SASV solutions. Both models and baselines are freely available to participants and can be used to develop back-end fusion approaches or end-to-end solutions. Using the provided common evaluation protocol, 23 teams submitted SASV solutions. When assessed with target, bona fide non-target and spoofed non-target trials, the top-performing system reduces the equal error rate of a conventional speaker verification system from 23.83% to 0.13%. SASV challenge results are a testament to the reliability of today's state-of-the-art approaches to spoofing detection and speaker verification.
SASV Challenge 2022: A Spoofing Aware Speaker Verification Challenge Evaluation Plan
Jan 25, 2022
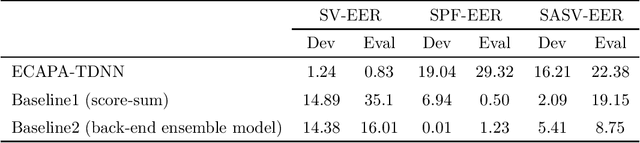
Abstract:ASV (automatic speaker verification) systems are intrinsically required to reject both non-target (e.g., voice uttered by different speaker) and spoofed (e.g., synthesised or converted) inputs. However, there is little consideration for how ASV systems themselves should be adapted when they are expected to encounter spoofing attacks, nor when they operate in tandem with CMs (spoofing countermeasures), much less how both systems should be jointly optimised. The goal of the first SASV (spoofing-aware speaker verification) challenge, a special sesscion in ISCA INTERSPEECH 2022, is to promote development of integrated systems that can perform ASV and CM simultaneously.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge