Bjorn Stenger
Age Prediction From Face Images Via Contrastive Learning
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach for accurately estimating age from face images, which overcomes the challenge of collecting a large dataset of individuals with the same identity at different ages. Instead, we leverage readily available face datasets of different people at different ages and aim to extract age-related features using contrastive learning. Our method emphasizes these relevant features while suppressing identity-related features using a combination of cosine similarity and triplet margin losses. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach by achieving state-of-the-art performance on two public datasets, FG-NET and MORPH-II.
LLDiffusion: Learning Degradation Representations in Diffusion Models for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 27, 2023Abstract:Current deep learning methods for low-light image enhancement (LLIE) typically rely on pixel-wise mapping learned from paired data. However, these methods often overlook the importance of considering degradation representations, which can lead to sub-optimal outcomes. In this paper, we address this limitation by proposing a degradation-aware learning scheme for LLIE using diffusion models, which effectively integrates degradation and image priors into the diffusion process, resulting in improved image enhancement. Our proposed degradation-aware learning scheme is based on the understanding that degradation representations play a crucial role in accurately modeling and capturing the specific degradation patterns present in low-light images. To this end, First, a joint learning framework for both image generation and image enhancement is presented to learn the degradation representations. Second, to leverage the learned degradation representations, we develop a Low-Light Diffusion model (LLDiffusion) with a well-designed dynamic diffusion module. This module takes into account both the color map and the latent degradation representations to guide the diffusion process. By incorporating these conditioning factors, the proposed LLDiffusion can effectively enhance low-light images, considering both the inherent degradation patterns and the desired color fidelity. Finally, we evaluate our proposed method on several well-known benchmark datasets, including synthetic and real-world unpaired datasets. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks demonstrate that our LLDiffusion outperforms state-of-the-art LLIE methods both quantitatively and qualitatively. The source code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/TaoWangzj/LLDiffusion.
GridFormer: Residual Dense Transformer with Grid Structure for Image Restoration in Adverse Weather Conditions
May 29, 2023
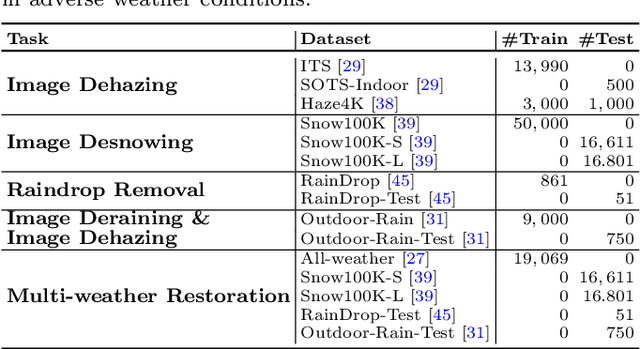

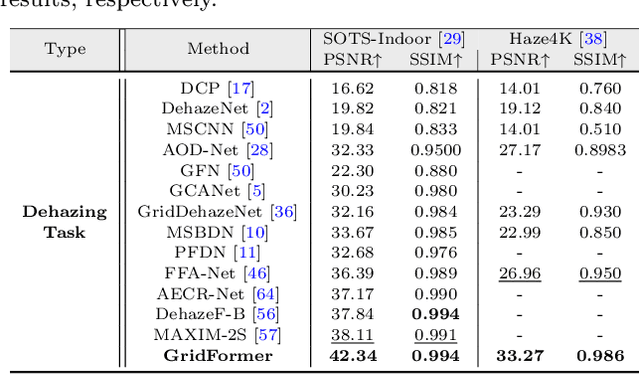
Abstract:Image restoration in adverse weather conditions is a difficult task in computer vision. In this paper, we propose a novel transformer-based framework called GridFormer which serves as a backbone for image restoration under adverse weather conditions. GridFormer is designed in a grid structure using a residual dense transformer block, and it introduces two core designs. First, it uses an enhanced attention mechanism in the transformer layer. The mechanism includes stages of the sampler and compact self-attention to improve efficiency, and a local enhancement stage to strengthen local information. Second, we introduce a residual dense transformer block (RDTB) as the final GridFormer layer. This design further improves the network's ability to learn effective features from both preceding and current local features. The GridFormer framework achieves state-of-the-art results on five diverse image restoration tasks in adverse weather conditions, including image deraining, dehazing, deraining & dehazing, desnowing, and multi-weather restoration. The source code and pre-trained models will be released.
Ultra-High-Definition Low-Light Image Enhancement: A Benchmark and Transformer-Based Method
Dec 22, 2022



Abstract:As the quality of optical sensors improves, there is a need for processing large-scale images. In particular, the ability of devices to capture ultra-high definition (UHD) images and video places new demands on the image processing pipeline. In this paper, we consider the task of low-light image enhancement (LLIE) and introduce a large-scale database consisting of images at 4K and 8K resolution. We conduct systematic benchmarking studies and provide a comparison of current LLIE algorithms. As a second contribution, we introduce LLFormer, a transformer-based low-light enhancement method. The core components of LLFormer are the axis-based multi-head self-attention and cross-layer attention fusion block, which significantly reduces the linear complexity. Extensive experiments on the new dataset and existing public datasets show that LLFormer outperforms state-of-the-art methods. We also show that employing existing LLIE methods trained on our benchmark as a pre-processing step significantly improves the performance of downstream tasks, e.g., face detection in low-light conditions. The source code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/TaoWangzj/LLFormer.
UserBERT: Modeling Long- and Short-Term User Preferences via Self-Supervision
Feb 14, 2022



Abstract:E-commerce platforms generate vast amounts of customer behavior data, such as clicks and purchases, from millions of unique users every day. However, effectively using this data for behavior understanding tasks is challenging because there are usually not enough labels to learn from all users in a supervised manner. This paper extends the BERT model to e-commerce user data for pre-training representations in a self-supervised manner. By viewing user actions in sequences as analogous to words in sentences, we extend the existing BERT model to user behavior data. Further, our model adopts a unified structure to simultaneously learn from long-term and short-term user behavior, as well as user attributes. We propose methods for the tokenization of different types of user behavior sequences, the generation of input representation vectors, and a novel pretext task to enable the pre-trained model to learn from its own input, eliminating the need for labeled training data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the learned representations result in significant improvements when transferred to three different real-world tasks, particularly compared to task-specific modeling and multi-task representation learning
Deep Image Deblurring: A Survey
Jan 26, 2022
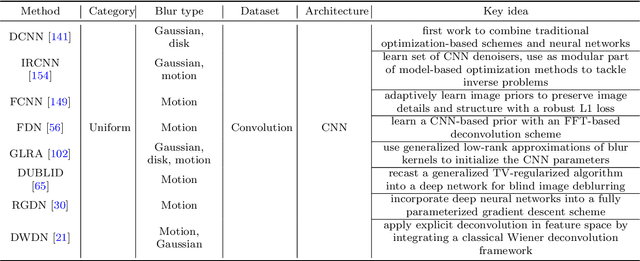
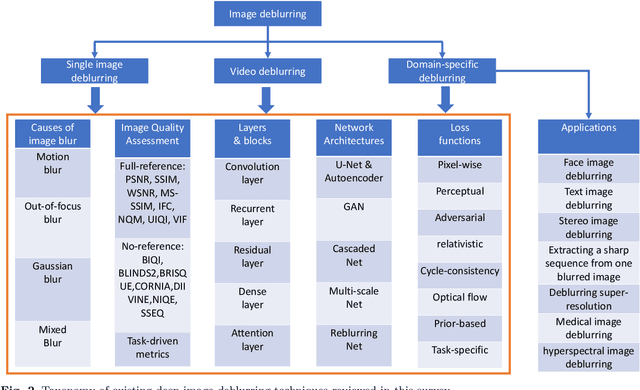
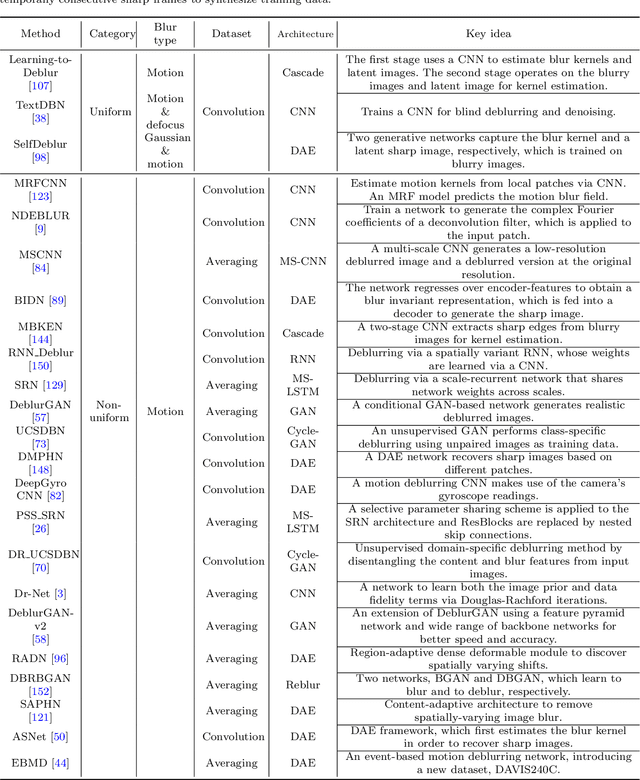
Abstract:Image deblurring is a classic problem in low-level computer vision, which aims to recover a sharp image from a blurred input image. Recent advances in deep learning have led to significant progress in solving this problem, and a large number of deblurring networks have been proposed. This paper presents a comprehensive and timely survey of recently published deep-learning based image deblurring approaches, aiming to serve the community as a useful literature review. We start by discussing common causes of image blur, introduce benchmark datasets and performance metrics, and summarize different problem formulations. Next we present a taxonomy of methods using convolutional neural networks (CNN) based on architecture, loss function, and application, offering a detailed review and comparison. In addition, we discuss some domain-specific deblurring applications including face images, text, and stereo image pairs. We conclude by discussing key challenges and future research directions.
Benchmarking Deep Deblurring Algorithms: A Large-Scale Multi-Cause Dataset and A New Baseline Model
Dec 01, 2021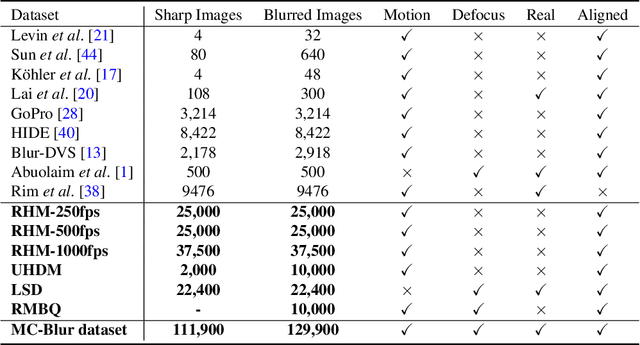
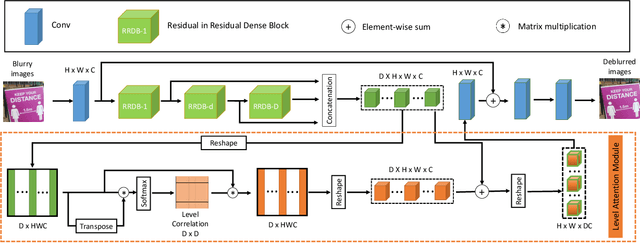
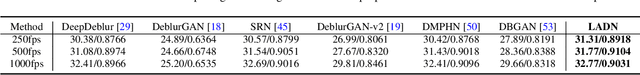
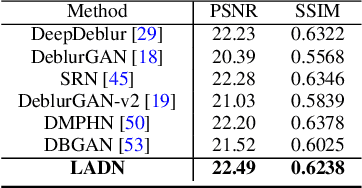
Abstract:Blur artifacts can seriously degrade the visual quality of images, and numerous deblurring methods have been proposed for specific scenarios. However, in most real-world images, blur is caused by different factors, e.g., motion and defocus. In this paper, we address how different deblurring methods perform on general types of blur. For in-depth performance evaluation, we construct a new large-scale multi-cause image deblurring dataset called (MC-Blur) including real-world and synthesized blurry images with mixed factors of blurs. The images in the proposed MC-Blur dataset are collected using different techniques: convolving Ultra-High-Definition (UHD) sharp images with large kernels, averaging sharp images captured by a 1000 fps high-speed camera, adding defocus to images, and real-world blurred images captured by various camera models. These results provide a comprehensive overview of the advantages and limitations of current deblurring methods. Further, we propose a new baseline model, level-attention deblurring network, to adapt to multiple causes of blurs. By including different weights of attention to the different levels of features, the proposed network derives more powerful features with larger weights assigned to more important levels, thereby enhancing the feature representation. Extensive experimental results on the new dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model for the multi-cause blur scenarios.
Deblurring by Realistic Blurring
Apr 04, 2020



Abstract:Existing deep learning methods for image deblurring typically train models using pairs of sharp images and their blurred counterparts. However, synthetically blurring images do not necessarily model the genuine blurring process in real-world scenarios with sufficient accuracy. To address this problem, we propose a new method which combines two GAN models, i.e., a learning-to-Blur GAN (BGAN) and learning-to-DeBlur GAN (DBGAN), in order to learn a better model for image deblurring by primarily learning how to blur images. The first model, BGAN, learns how to blur sharp images with unpaired sharp and blurry image sets, and then guides the second model, DBGAN, to learn how to correctly deblur such images. In order to reduce the discrepancy between real blur and synthesized blur, a relativistic blur loss is leveraged. As an additional contribution, this paper also introduces a Real-World Blurred Image (RWBI) dataset including diverse blurry images. Our experiments show that the proposed method achieves consistently superior quantitative performance as well as higher perceptual quality on both the newly proposed dataset and the public GOPRO dataset.
Learning Classifiers on Positive and Unlabeled Data with Policy Gradient
Oct 15, 2019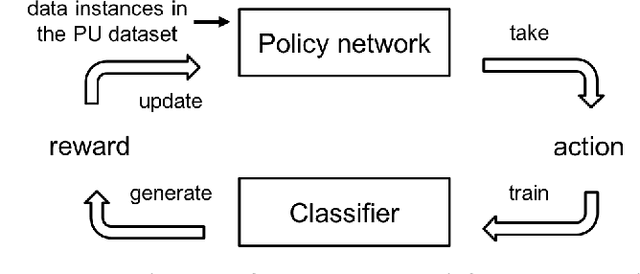
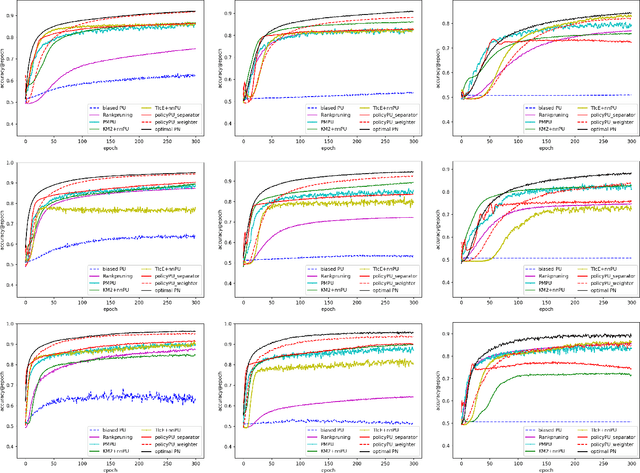
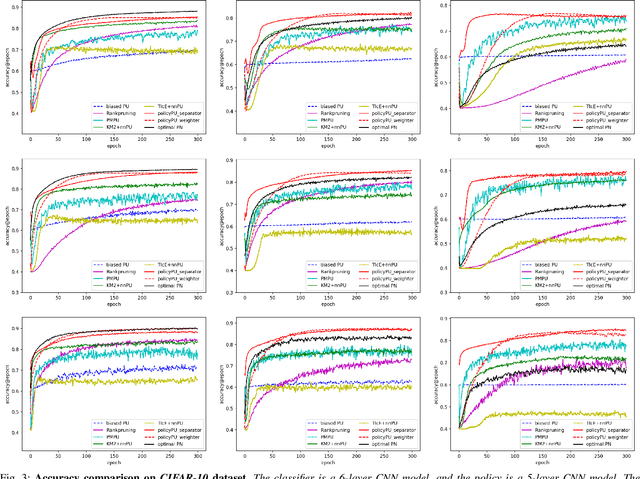
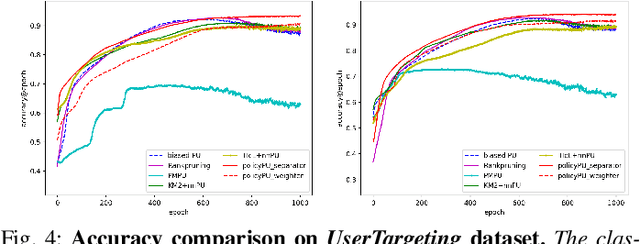
Abstract:Existing algorithms aiming to learn a binary classifier from positive (P) and unlabeled (U) data generally require estimating the class prior or label noises ahead of building a classification model. However, the estimation and classifier learning are normally conducted in a pipeline instead of being jointly optimized. In this paper, we propose to alternatively train the two steps using reinforcement learning. Our proposal adopts a policy network to adaptively make assumptions on the labels of unlabeled data, while a classifier is built upon the output of the policy network and provides rewards to learn a better strategy. The dynamic and interactive training between the policy maker and the classifier can exploit the unlabeled data in a more effective manner and yield a significant improvement on the classification performance. Furthermore, we present two different approaches to represent the actions sampled from the policy. The first approach considers continuous actions as soft labels, while the other uses discrete actions as hard assignment of labels for unlabeled examples.We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method on two benchmark datasets as well as one e-commerce dataset. The result shows the proposed method is able to consistently outperform state-of-the-art methods in various settings.
Deep Heterogeneous Autoencoders for Collaborative Filtering
Dec 17, 2018
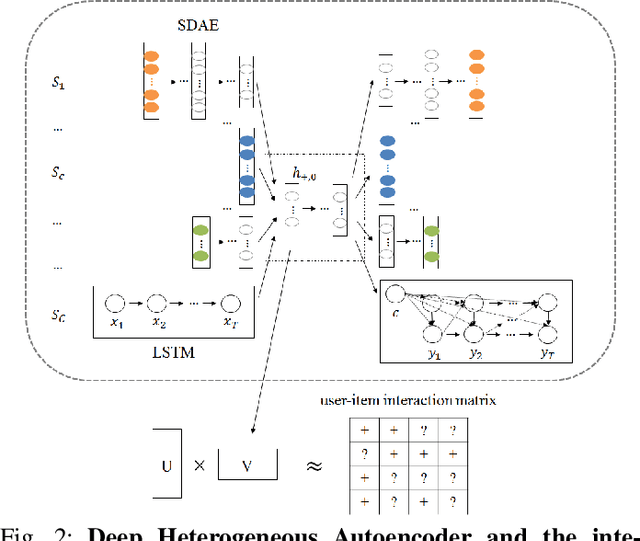
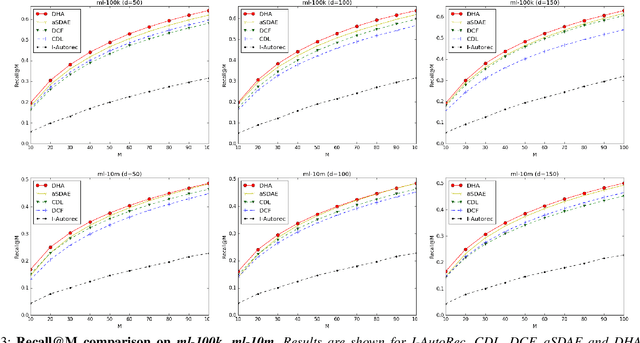
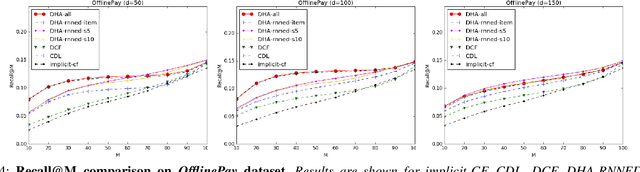
Abstract:This paper leverages heterogeneous auxiliary information to address the data sparsity problem of recommender systems. We propose a model that learns a shared feature space from heterogeneous data, such as item descriptions, product tags and online purchase history, to obtain better predictions. Our model consists of autoencoders, not only for numerical and categorical data, but also for sequential data, which enables capturing user tastes, item characteristics and the recent dynamics of user preference. We learn the autoencoder architecture for each data source independently in order to better model their statistical properties. Our evaluation on two MovieLens datasets and an e-commerce dataset shows that mean average precision and recall improve over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge