Hao Gong
A Deep Learning Approach to Anomaly Detection in High-Frequency Trading Data
Mar 31, 2025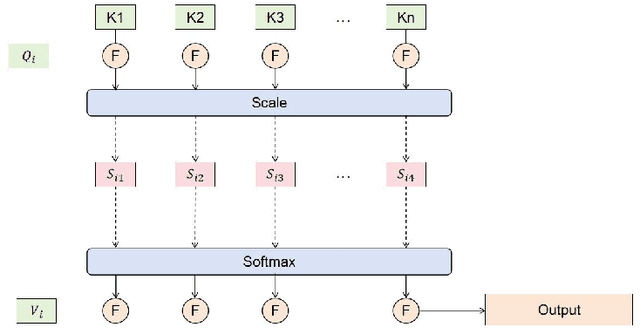
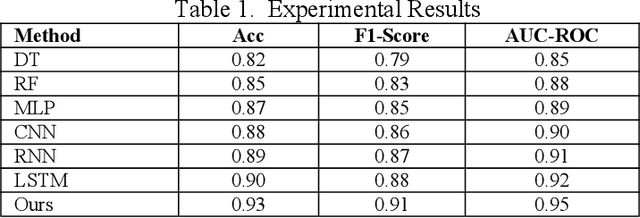
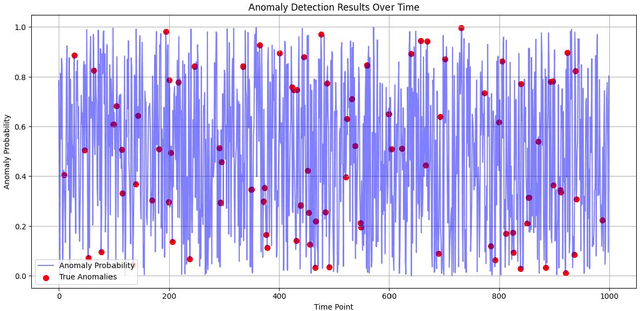
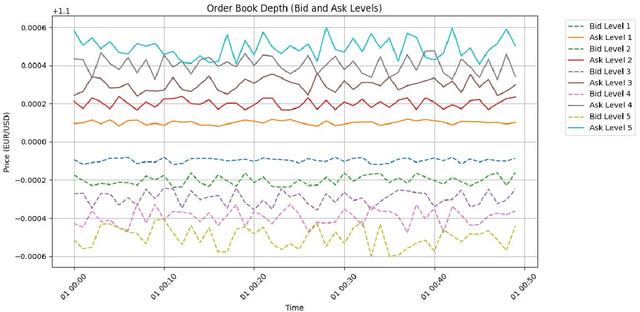
Abstract:This paper proposes an algorithm based on a staged sliding window Transformer architecture to detect abnormal behaviors in the microstructure of the foreign exchange market, focusing on high-frequency EUR/USD trading data. The method captures multi-scale temporal features through a staged sliding window, extracts global and local dependencies by combining the self-attention mechanism and weighted attention mechanism of the Transformer, and uses a classifier to identify abnormal events. Experimental results on a real high-frequency dataset containing order book depth, spread, and trading volume show that the proposed method significantly outperforms traditional machine learning (such as decision trees and random forests) and deep learning methods (such as MLP, CNN, RNN, LSTM) in terms of accuracy (0.93), F1-Score (0.91), and AUC-ROC (0.95). Ablation experiments verify the contribution of each component, and the visualization of order book depth and anomaly detection further reveals the effectiveness of the model under complex market dynamics. Despite the false positive problem, the model still provides important support for market supervision. In the future, noise processing can be optimized and extended to other markets to improve generalization and real-time performance.
Hunyuan-Large: An Open-Source MoE Model with 52 Billion Activated Parameters by Tencent
Nov 05, 2024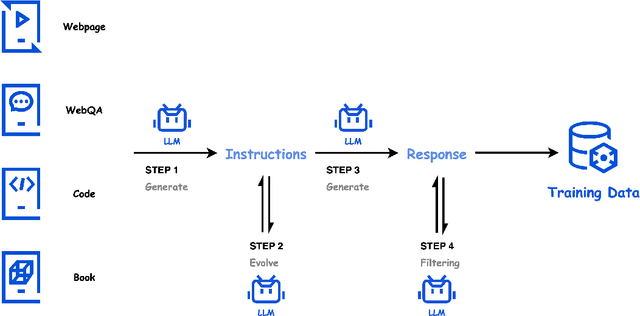
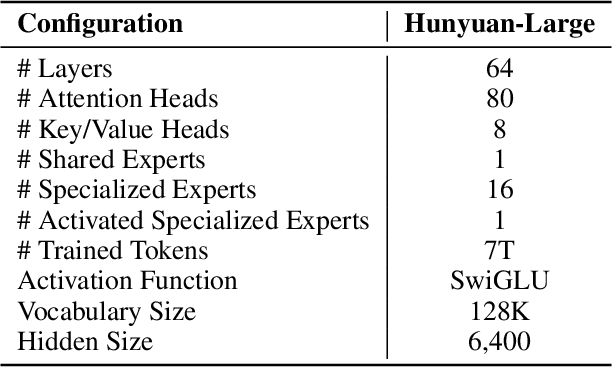
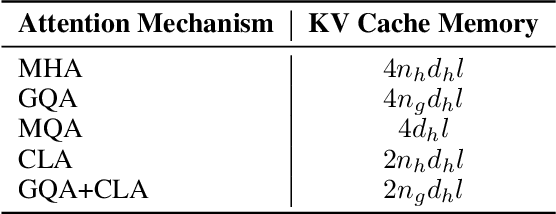
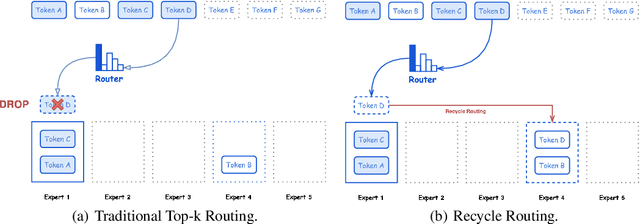
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Hunyuan-Large, which is currently the largest open-source Transformer-based mixture of experts model, with a total of 389 billion parameters and 52 billion activation parameters, capable of handling up to 256K tokens. We conduct a thorough evaluation of Hunyuan-Large's superior performance across various benchmarks including language understanding and generation, logical reasoning, mathematical problem-solving, coding, long-context, and aggregated tasks, where it outperforms LLama3.1-70B and exhibits comparable performance when compared to the significantly larger LLama3.1-405B model. Key practice of Hunyuan-Large include large-scale synthetic data that is orders larger than in previous literature, a mixed expert routing strategy, a key-value cache compression technique, and an expert-specific learning rate strategy. Additionally, we also investigate the scaling laws and learning rate schedule of mixture of experts models, providing valuable insights and guidances for future model development and optimization. The code and checkpoints of Hunyuan-Large are released to facilitate future innovations and applications. Codes: https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan-Large Models: https://huggingface.co/tencent/Tencent-Hunyuan-Large
Comparison of Methods in Human Skin Decomposition
Mar 31, 2024



Abstract:Decomposition of skin pigment plays an important role in medical fields. Human skin can be decomposed into two primitive components, hemoglobin and melanin. It is our goal to apply these results for diagnosis of skin cancer. In this paper, various methods for skin pigment decomposition are reviewed comparatively and the performance of each method is evaluated both theoretically and experimentally. In addition, isometric feature mapping (Isomap) is introduced in order to improve the dimensionality reduction performance in context of skin decomposition.
Modelling Power Consumptions for Multi-rotor UAVs
Sep 09, 2022



Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have various advantages, but their practical applications are influenced by their limited energy. Therefore, it is important to manage their power consumption and also important to establish corresponding power consumption models. However, most of existing works either establish theoretical power consumption models for fixed-wing UAVs and single-rotor UAVs, or provide heuristic power consumption models for multi-rotor UAVs without rigorous mathematical derivations. This paper aims to establish theoretical power consumption models for multi-rotor UAVs. To be specific, the closed-form power consumption models for a multi-rotor UAV in three flight statuses, i.e., forward flight, vertical ascent and vertical descent, are derived by leveraging the relationship between single-rotor UAVs and multi-rotor UAVs in terms of power consumptions. On this basis, a generic flight power consumption model for the UAV in a three-dimensional (3-D) scenario is obtained. Extensive experiments are conducted by using DJI M210 and a mobile app made by DJI Mobile SDK in real scenarios, and confirm the correctness and effectiveness of these models; in addition, simulations are performed to further investigate the effect of the rotor numbers on the power consumption for the UAV. The proposed power consumption models not only reveal how the power consumption of multi-rotor UAVs are affected by various factors, but also pave the way for introducing other novel applications.
UserBERT: Modeling Long- and Short-Term User Preferences via Self-Supervision
Feb 14, 2022



Abstract:E-commerce platforms generate vast amounts of customer behavior data, such as clicks and purchases, from millions of unique users every day. However, effectively using this data for behavior understanding tasks is challenging because there are usually not enough labels to learn from all users in a supervised manner. This paper extends the BERT model to e-commerce user data for pre-training representations in a self-supervised manner. By viewing user actions in sequences as analogous to words in sentences, we extend the existing BERT model to user behavior data. Further, our model adopts a unified structure to simultaneously learn from long-term and short-term user behavior, as well as user attributes. We propose methods for the tokenization of different types of user behavior sequences, the generation of input representation vectors, and a novel pretext task to enable the pre-trained model to learn from its own input, eliminating the need for labeled training data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the learned representations result in significant improvements when transferred to three different real-world tasks, particularly compared to task-specific modeling and multi-task representation learning
Learning to Profile: User Meta-Profile Network for Few-Shot Learning
Aug 21, 2020



Abstract:Meta-learning approaches have shown great success in vision and language domains. However, few studies discuss the practice of meta-learning for large-scale industrial applications. Although e-commerce companies have spent many efforts on learning representations to provide a better user experience, we argue that such efforts cannot be stopped at this step. In addition to learning a strong profile, the challenging question about how to effectively transfer the learned representation is raised simultaneously. This paper introduces the contributions that we made to address these challenges from three aspects. 1) Meta-learning model: In the context of representation learning with e-commerce user behavior data, we propose a meta-learning framework called the Meta-Profile Network, which extends the ideas of matching network and relation network for knowledge transfer and fast adaptation; 2) Encoding strategy: To keep high fidelity of large-scale long-term sequential behavior data, we propose a time-heatmap encoding strategy that allows the model to encode data effectively; 3) Deep network architecture: A multi-modal model combined with multi-task learning architecture is utilized to address the cross-domain knowledge learning and insufficient label problems. Moreover, we argue that an industrial model should not only have good performance in terms of accuracy, but also have better robustness and uncertainty performance under extreme conditions. We evaluate the performance of our model with extensive control experiments in various extreme scenarios, i.e. out-of-distribution detection, data insufficiency and class imbalance scenarios. The Meta-Profile Network shows significant improvement in the model performance when compared to baseline models.
Learning low-dimensional state embeddings and metastable clusters from time series data
Jun 01, 2019



Abstract:This paper studies how to find compact state embeddings from high-dimensional Markov state trajectories, where the transition kernel has a small intrinsic rank. In the spirit of diffusion map, we propose an efficient method for learning a low-dimensional state embedding and capturing the process's dynamics. This idea also leads to a kernel reshaping method for more accurate nonparametric estimation of the transition function. State embedding can be used to cluster states into metastable sets, thereby identifying the slow dynamics. Sharp statistical error bounds and misclassification rate are proved. Experiment on a simulated dynamical system shows that the state clustering method indeed reveals metastable structures. We also experiment with time series generated by layers of a Deep-Q-Network when playing an Atari game. The embedding method identifies game states to be similar if they share similar future events, even though their raw data are far different.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge