Benchmarking Deep Deblurring Algorithms: A Large-Scale Multi-Cause Dataset and A New Baseline Model
Paper and Code
Dec 01, 2021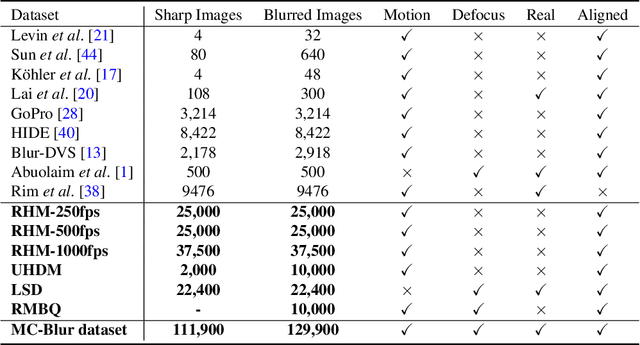
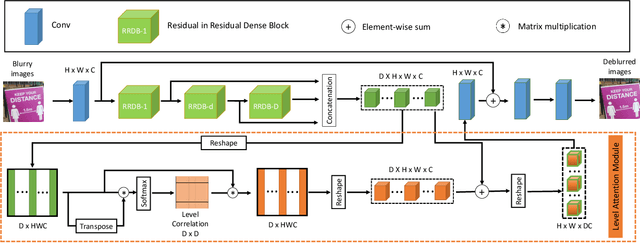
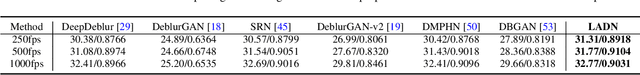
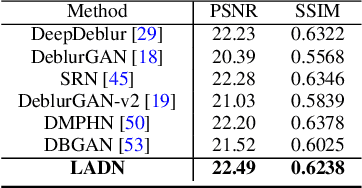
Blur artifacts can seriously degrade the visual quality of images, and numerous deblurring methods have been proposed for specific scenarios. However, in most real-world images, blur is caused by different factors, e.g., motion and defocus. In this paper, we address how different deblurring methods perform on general types of blur. For in-depth performance evaluation, we construct a new large-scale multi-cause image deblurring dataset called (MC-Blur) including real-world and synthesized blurry images with mixed factors of blurs. The images in the proposed MC-Blur dataset are collected using different techniques: convolving Ultra-High-Definition (UHD) sharp images with large kernels, averaging sharp images captured by a 1000 fps high-speed camera, adding defocus to images, and real-world blurred images captured by various camera models. These results provide a comprehensive overview of the advantages and limitations of current deblurring methods. Further, we propose a new baseline model, level-attention deblurring network, to adapt to multiple causes of blurs. By including different weights of attention to the different levels of features, the proposed network derives more powerful features with larger weights assigned to more important levels, thereby enhancing the feature representation. Extensive experimental results on the new dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model for the multi-cause blur scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge