Baskar Ganapathysubramanian
Iowa State University
FloraForge: LLM-Assisted Procedural Generation of Editable and Analysis-Ready 3D Plant Geometric Models For Agricultural Applications
Dec 11, 2025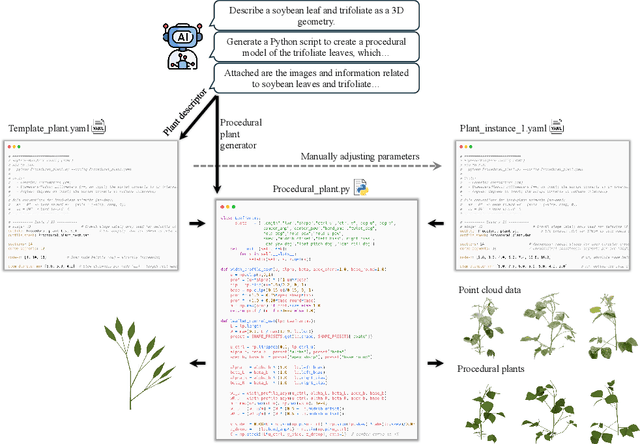
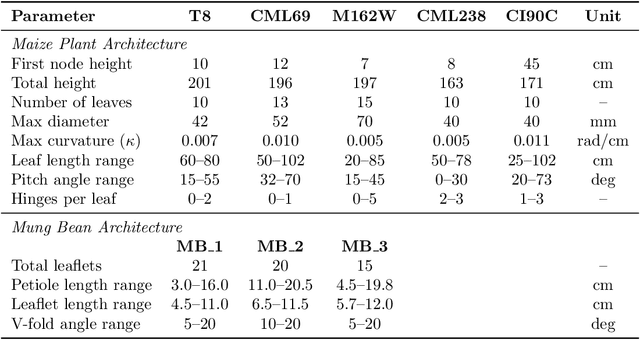
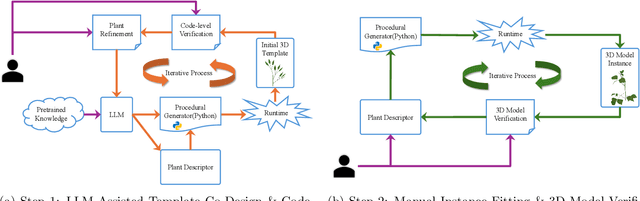
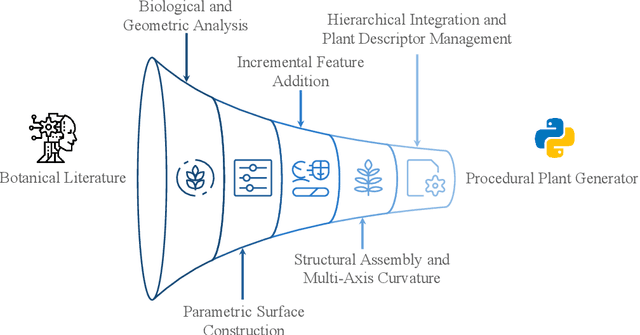
Abstract:Accurate 3D plant models are crucial for computational phenotyping and physics-based simulation; however, current approaches face significant limitations. Learning-based reconstruction methods require extensive species-specific training data and lack editability. Procedural modeling offers parametric control but demands specialized expertise in geometric modeling and an in-depth understanding of complex procedural rules, making it inaccessible to domain scientists. We present FloraForge, an LLM-assisted framework that enables domain experts to generate biologically accurate, fully parametric 3D plant models through iterative natural language Plant Refinements (PR), minimizing programming expertise. Our framework leverages LLM-enabled co-design to refine Python scripts that generate parameterized plant geometries as hierarchical B-spline surface representations with botanical constraints with explicit control points and parametric deformation functions. This representation can be easily tessellated into polygonal meshes with arbitrary precision, ensuring compatibility with functional structural plant analysis workflows such as light simulation, computational fluid dynamics, and finite element analysis. We demonstrate the framework on maize, soybean, and mung bean, fitting procedural models to empirical point cloud data through manual refinement of the Plant Descriptor (PD), human-readable files. The pipeline generates dual outputs: triangular meshes for visualization and triangular meshes with additional parametric metadata for quantitative analysis. This approach uniquely combines LLM-assisted template creation, mathematically continuous representations enabling both phenotyping and rendering, and direct parametric control through PD. The framework democratizes sophisticated geometric modeling for plant science while maintaining mathematical rigor.
WeedNet: A Foundation Model-Based Global-to-Local AI Approach for Real-Time Weed Species Identification and Classification
May 25, 2025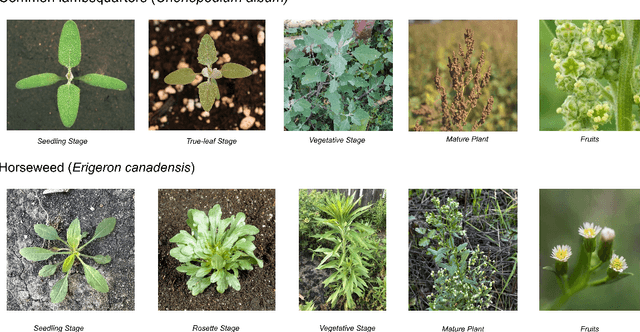
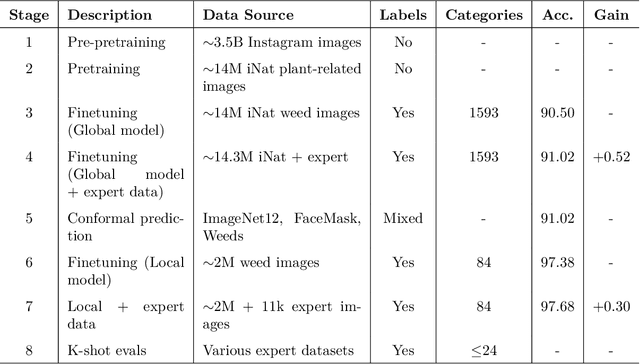
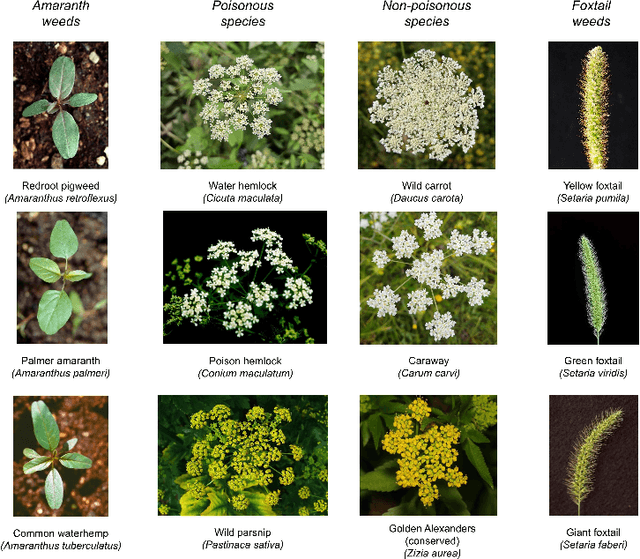

Abstract:Early identification of weeds is essential for effective management and control, and there is growing interest in automating the process using computer vision techniques coupled with AI methods. However, challenges associated with training AI-based weed identification models, such as limited expert-verified data and complexity and variability in morphological features, have hindered progress. To address these issues, we present WeedNet, the first global-scale weed identification model capable of recognizing an extensive set of weed species, including noxious and invasive plant species. WeedNet is an end-to-end real-time weed identification pipeline and uses self-supervised learning, fine-tuning, and enhanced trustworthiness strategies. WeedNet achieved 91.02% accuracy across 1,593 weed species, with 41% species achieving 100% accuracy. Using a fine-tuning strategy and a Global-to-Local approach, the local Iowa WeedNet model achieved an overall accuracy of 97.38% for 85 Iowa weeds, most classes exceeded a 90% mean accuracy per class. Testing across intra-species dissimilarity (developmental stages) and inter-species similarity (look-alike species) suggests that diversity in the images collected, spanning all the growth stages and distinguishable plant characteristics, is crucial in driving model performance. The generalizability and adaptability of the Global WeedNet model enable it to function as a foundational model, with the Global-to-Local strategy allowing fine-tuning for region-specific weed communities. Additional validation of drone- and ground-rover-based images highlights the potential of WeedNet for integration into robotic platforms. Furthermore, integration with AI for conversational use provides intelligent agricultural and ecological conservation consulting tools for farmers, agronomists, researchers, land managers, and government agencies across diverse landscapes.
Towards Large Reasoning Models for Agriculture
May 25, 2025Abstract:Agricultural decision-making involves complex, context-specific reasoning, where choices about crops, practices, and interventions depend heavily on geographic, climatic, and economic conditions. Traditional large language models (LLMs) often fall short in navigating this nuanced problem due to limited reasoning capacity. We hypothesize that recent advances in large reasoning models (LRMs) can better handle such structured, domain-specific inference. To investigate this, we introduce AgReason, the first expert-curated open-ended science benchmark with 100 questions for agricultural reasoning. Evaluations across thirteen open-source and proprietary models reveal that LRMs outperform conventional ones, though notable challenges persist, with the strongest Gemini-based baseline achieving 36% accuracy. We also present AgThoughts, a large-scale dataset of 44.6K question-answer pairs generated with human oversight and equipped with synthetically generated reasoning traces. Using AgThoughts, we develop AgThinker, a suite of small reasoning models that can be run on consumer-grade GPUs, and show that our dataset can be effective in unlocking agricultural reasoning abilities in LLMs. Our project page is here: https://baskargroup.github.io/Ag_reasoning/
NeRF-based Point Cloud Reconstruction using a Stationary Camera for Agricultural Applications
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a NeRF-based framework for point cloud (PCD) reconstruction, specifically designed for indoor high-throughput plant phenotyping facilities. Traditional NeRF-based reconstruction methods require cameras to move around stationary objects, but this approach is impractical for high-throughput environments where objects are rapidly imaged while moving on conveyors or rotating pedestals. To address this limitation, we develop a variant of NeRF-based PCD reconstruction that uses a single stationary camera to capture images as the object rotates on a pedestal. Our workflow comprises COLMAP-based pose estimation, a straightforward pose transformation to simulate camera movement, and subsequent standard NeRF training. A defined Region of Interest (ROI) excludes irrelevant scene data, enabling the generation of high-resolution point clouds (10M points). Experimental results demonstrate excellent reconstruction fidelity, with precision-recall analyses yielding an F-score close to 100.00 across all evaluated plant objects. Although pose estimation remains computationally intensive with a stationary camera setup, overall training and reconstruction times are competitive, validating the method's feasibility for practical high-throughput indoor phenotyping applications. Our findings indicate that high-quality NeRF-based 3D reconstructions are achievable using a stationary camera, eliminating the need for complex camera motion or costly imaging equipment. This approach is especially beneficial when employing expensive and delicate instruments, such as hyperspectral cameras, for 3D plant phenotyping. Future work will focus on optimizing pose estimation techniques and further streamlining the methodology to facilitate seamless integration into automated, high-throughput 3D phenotyping pipelines.
3D Neural Operator-Based Flow Surrogates around 3D geometries: Signed Distance Functions and Derivative Constraints
Mar 21, 2025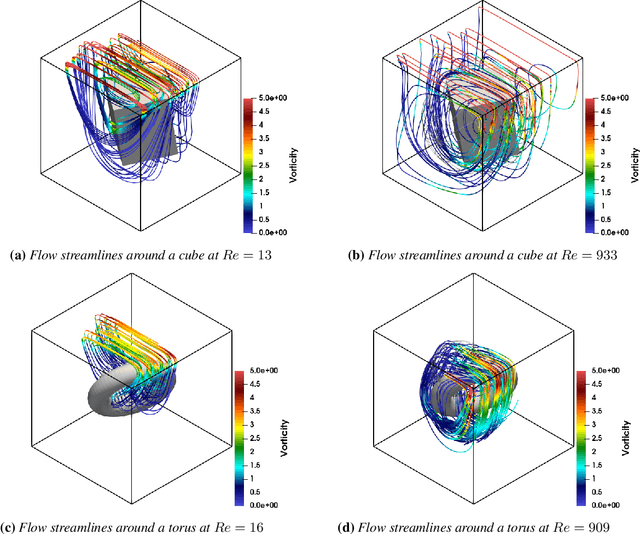
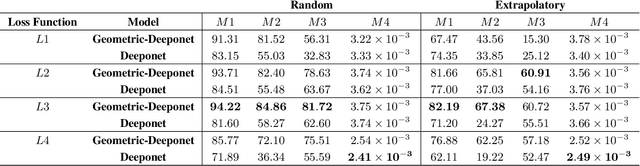
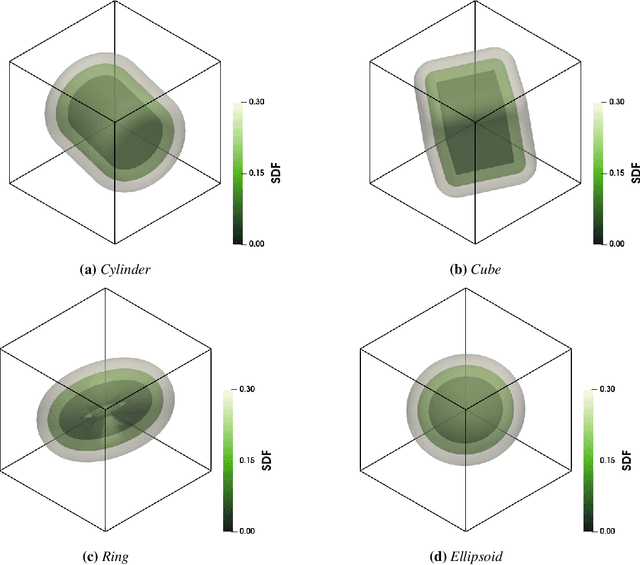
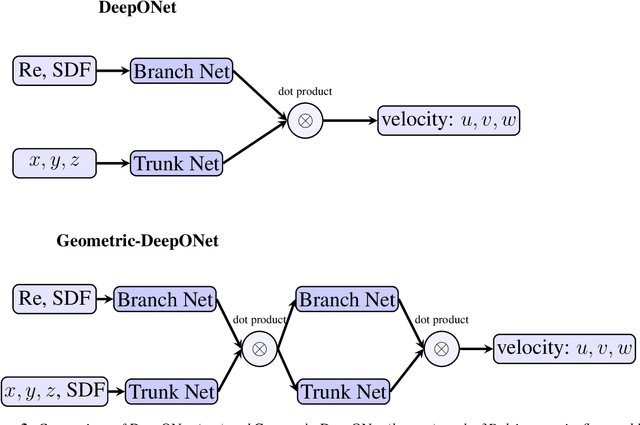
Abstract:Accurate modeling of fluid dynamics around complex geometries is critical for applications such as aerodynamic optimization and biomedical device design. While advancements in numerical methods and high-performance computing have improved simulation capabilities, the computational cost of high-fidelity 3D flow simulations remains a significant challenge. Scientific machine learning (SciML) offers an efficient alternative, enabling rapid and reliable flow predictions. In this study, we evaluate Deep Operator Networks (DeepONet) and Geometric-DeepONet, a variant that incorporates geometry information via signed distance functions (SDFs), on steady-state 3D flow over complex objects. Our dataset consists of 1,000 high-fidelity simulations spanning Reynolds numbers from 10 to 1,000, enabling comprehensive training and evaluation across a range of flow regimes. To assess model generalization, we test our models on a random and extrapolatory train-test splitting. Additionally, we explore a derivative-informed training strategy that augments standard loss functions with velocity gradient penalties and incompressibility constraints, improving physics consistency in 3D flow prediction. Our results show that Geometric-DeepONet improves boundary-layer accuracy by up to 32% compared to standard DeepONet. Moreover, incorporating derivative constraints enhances gradient accuracy by 25% in interpolation tasks and up to 45% in extrapolatory test scenarios, suggesting significant improvement in generalization capabilities to unseen 3D Reynolds numbers.
Accessing the Effect of Phyllotaxy and Planting Density on Light Use Efficiency in Field-Grown Maize using 3D Reconstructions
Mar 10, 2025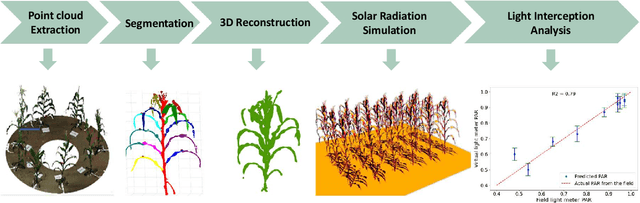
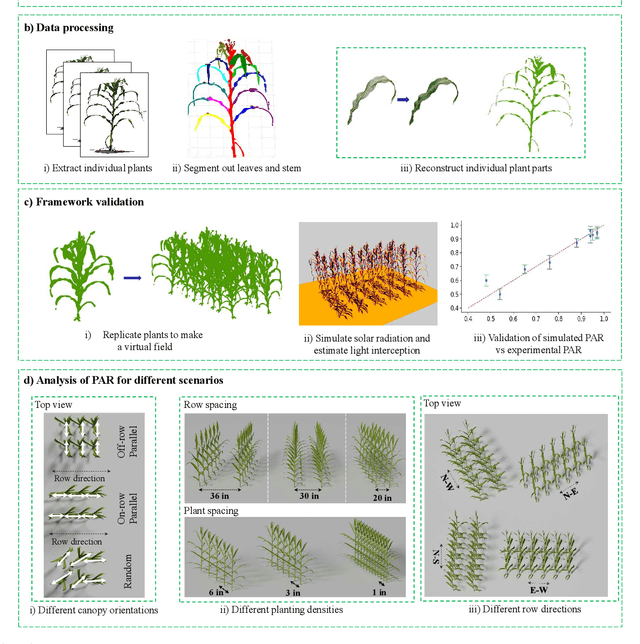
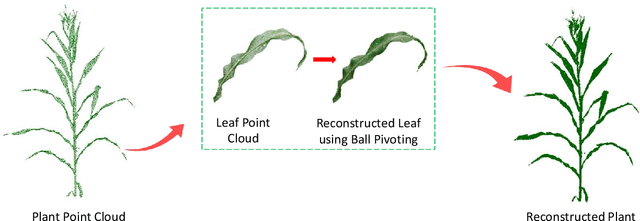
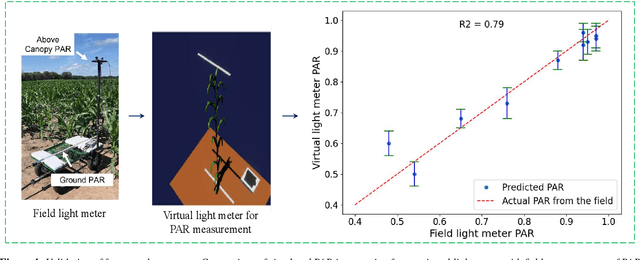
Abstract:High-density planting is a widely adopted strategy to enhance maize productivity, yet it introduces challenges such as increased interplant competition and shading, which can limit light capture and overall yield potential. In response, some maize plants naturally reorient their canopies to optimize light capture, a process known as canopy reorientation. Understanding this adaptive response and its impact on light capture is crucial for maximizing agricultural yield potential. This study introduces an end-to-end framework that integrates realistic 3D reconstructions of field-grown maize with photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) modeling to assess the effects of phyllotaxy and planting density on light interception. In particular, using 3D point clouds derived from field data, virtual fields for a diverse set of maize genotypes were constructed and validated against field PAR measurements. Using this framework, we present detailed analyses of the impact of canopy orientations, plant and row spacings, and planting row directions on PAR interception throughout a typical growing season. Our findings highlight significant variations in light interception efficiency across different planting densities and canopy orientations. By elucidating the relationship between canopy architecture and light capture, this study offers valuable guidance for optimizing maize breeding and cultivation strategies across diverse agricultural settings.
AgriField3D: A Curated 3D Point Cloud and Procedural Model Dataset of Field-Grown Maize from a Diversity Panel
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in three-dimensional (3D) agricultural research, particularly for maize, has been limited by the scarcity of large-scale, diverse datasets. While 2D image datasets are abundant, they fail to capture essential structural details such as leaf architecture, plant volume, and spatial arrangements that 3D data provide. To address this limitation, we present AgriField3D (https://baskargroup.github.io/AgriField3D/), a curated dataset of 3D point clouds of field-grown maize plants from a diverse genetic panel, designed to be AI-ready for advancing agricultural research. Our dataset comprises over 1,000 high-quality point clouds collected using a Terrestrial Laser Scanner, complemented by procedural models that provide structured, parametric representations of maize plants. These procedural models, generated using Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) and optimized via a two-step process combining Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and differentiable programming, enable precise, scalable reconstructions of leaf surfaces and plant architectures. To enhance usability, we performed graph-based segmentation to isolate individual leaves and stalks, ensuring consistent labeling across all samples. We also conducted rigorous manual quality control on all datasets, correcting errors in segmentation, ensuring accurate leaf ordering, and validating metadata annotations. The dataset further includes metadata detailing plant morphology and quality, alongside multi-resolution subsampled versions (100k, 50k, 10k points) optimized for various computational needs. By integrating point cloud data of field grown plants with high-fidelity procedural models and ensuring meticulous manual validation, AgriField3D provides a comprehensive foundation for AI-driven phenotyping, plant structural analysis, and 3D applications in agricultural research.
MaizeEar-SAM: Zero-Shot Maize Ear Phenotyping
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Quantifying the variation in yield component traits of maize (Zea mays L.), which together determine the overall productivity of this globally important crop, plays a critical role in plant genetics research, plant breeding, and the development of improved farming practices. Grain yield per acre is calculated by multiplying the number of plants per acre, ears per plant, number of kernels per ear, and the average kernel weight. The number of kernels per ear is determined by the number of kernel rows per ear multiplied by the number of kernels per row. Traditional manual methods for measuring these two traits are time-consuming, limiting large-scale data collection. Recent automation efforts using image processing and deep learning encounter challenges such as high annotation costs and uncertain generalizability. We tackle these issues by exploring Large Vision Models for zero-shot, annotation-free maize kernel segmentation. By using an open-source large vision model, the Segment Anything Model (SAM), we segment individual kernels in RGB images of maize ears and apply a graph-based algorithm to calculate the number of kernels per row. Our approach successfully identifies the number of kernels per row across a wide range of maize ears, showing the potential of zero-shot learning with foundation vision models combined with image processing techniques to improve automation and reduce subjectivity in agronomic data collection. All our code is open-sourced to make these affordable phenotyping methods accessible to everyone.
Geometry Matters: Benchmarking Scientific ML Approaches for Flow Prediction around Complex Geometries
Dec 31, 2024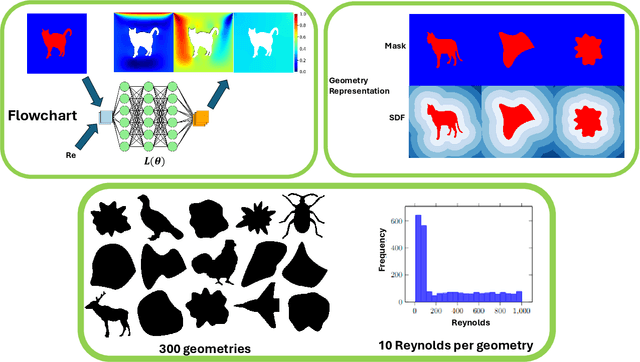
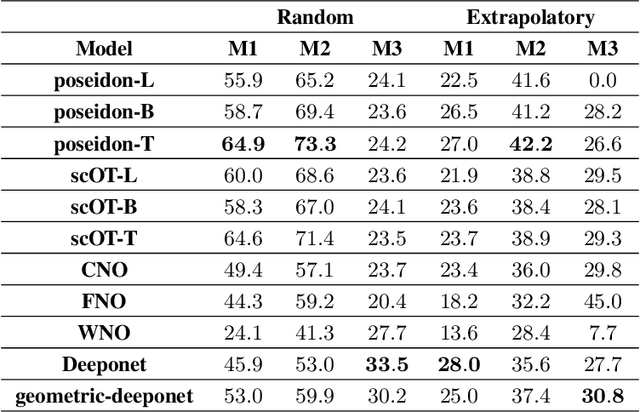
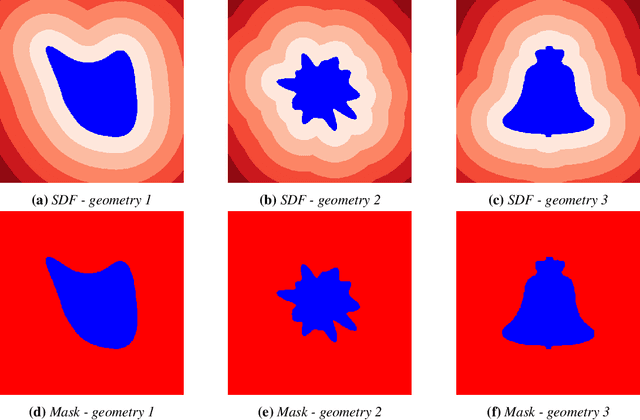
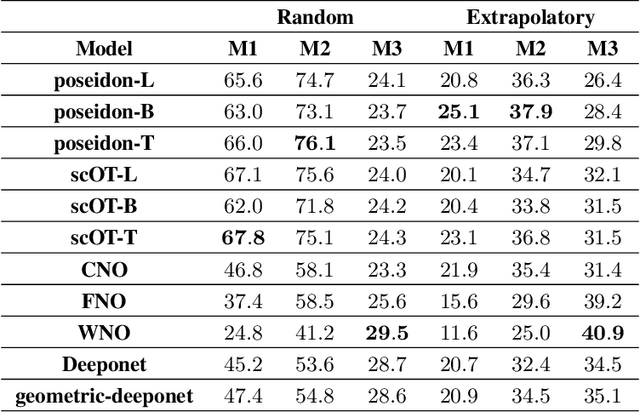
Abstract:Rapid yet accurate simulations of fluid dynamics around complex geometries is critical in a variety of engineering and scientific applications, including aerodynamics and biomedical flows. However, while scientific machine learning (SciML) has shown promise, most studies are constrained to simple geometries, leaving complex, real-world scenarios underexplored. This study addresses this gap by benchmarking diverse SciML models, including neural operators and vision transformer-based foundation models, for fluid flow prediction over intricate geometries. Using a high-fidelity dataset of steady-state flows across various geometries, we evaluate the impact of geometric representations -- Signed Distance Fields (SDF) and binary masks -- on model accuracy, scalability, and generalization. Central to this effort is the introduction of a novel, unified scoring framework that integrates metrics for global accuracy, boundary layer fidelity, and physical consistency to enable a robust, comparative evaluation of model performance. Our findings demonstrate that foundation models significantly outperform neural operators, particularly in data-limited scenarios, and that SDF representations yield superior results with sufficient training data. Despite these advancements, all models struggle with out-of-distribution generalization, highlighting a critical challenge for future SciML applications. By advancing both evaluation methodologies and modeling capabilities, this work paves the way for robust and scalable ML solutions for fluid dynamics across complex geometries.
STITCH: Surface reconstrucTion using Implicit neural representations with Topology Constraints and persistent Homology
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:We present STITCH, a novel approach for neural implicit surface reconstruction of a sparse and irregularly spaced point cloud while enforcing topological constraints (such as having a single connected component). We develop a new differentiable framework based on persistent homology to formulate topological loss terms that enforce the prior of a single 2-manifold object. Our method demonstrates excellent performance in preserving the topology of complex 3D geometries, evident through both visual and empirical comparisons. We supplement this with a theoretical analysis, and provably show that optimizing the loss with stochastic (sub)gradient descent leads to convergence and enables reconstructing shapes with a single connected component. Our approach showcases the integration of differentiable topological data analysis tools for implicit surface reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge