Arti Singh
Iowa State University
FloraForge: LLM-Assisted Procedural Generation of Editable and Analysis-Ready 3D Plant Geometric Models For Agricultural Applications
Dec 11, 2025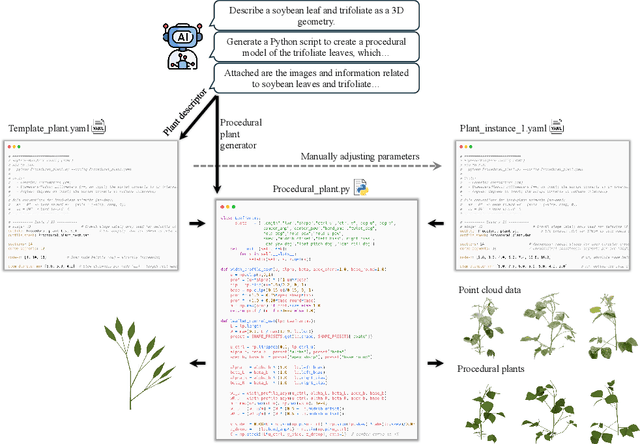
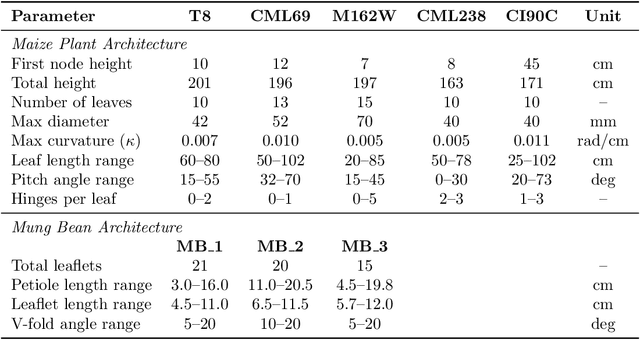
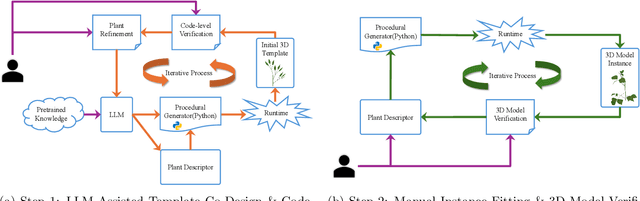
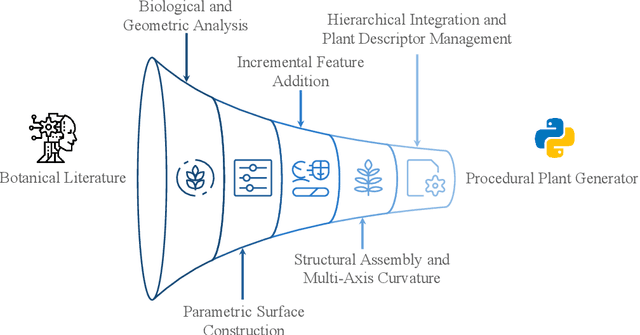
Abstract:Accurate 3D plant models are crucial for computational phenotyping and physics-based simulation; however, current approaches face significant limitations. Learning-based reconstruction methods require extensive species-specific training data and lack editability. Procedural modeling offers parametric control but demands specialized expertise in geometric modeling and an in-depth understanding of complex procedural rules, making it inaccessible to domain scientists. We present FloraForge, an LLM-assisted framework that enables domain experts to generate biologically accurate, fully parametric 3D plant models through iterative natural language Plant Refinements (PR), minimizing programming expertise. Our framework leverages LLM-enabled co-design to refine Python scripts that generate parameterized plant geometries as hierarchical B-spline surface representations with botanical constraints with explicit control points and parametric deformation functions. This representation can be easily tessellated into polygonal meshes with arbitrary precision, ensuring compatibility with functional structural plant analysis workflows such as light simulation, computational fluid dynamics, and finite element analysis. We demonstrate the framework on maize, soybean, and mung bean, fitting procedural models to empirical point cloud data through manual refinement of the Plant Descriptor (PD), human-readable files. The pipeline generates dual outputs: triangular meshes for visualization and triangular meshes with additional parametric metadata for quantitative analysis. This approach uniquely combines LLM-assisted template creation, mathematically continuous representations enabling both phenotyping and rendering, and direct parametric control through PD. The framework democratizes sophisticated geometric modeling for plant science while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Medical Image De-Identification Benchmark Challenge
Jul 31, 2025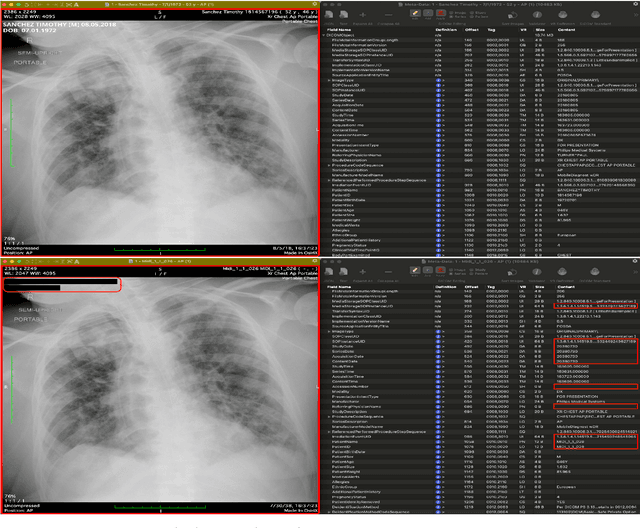
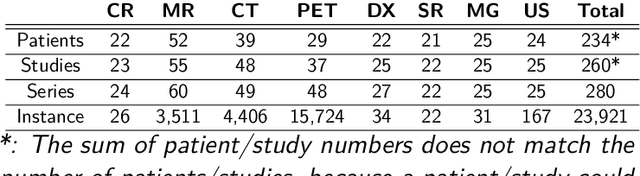
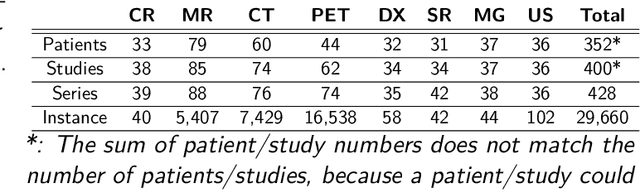
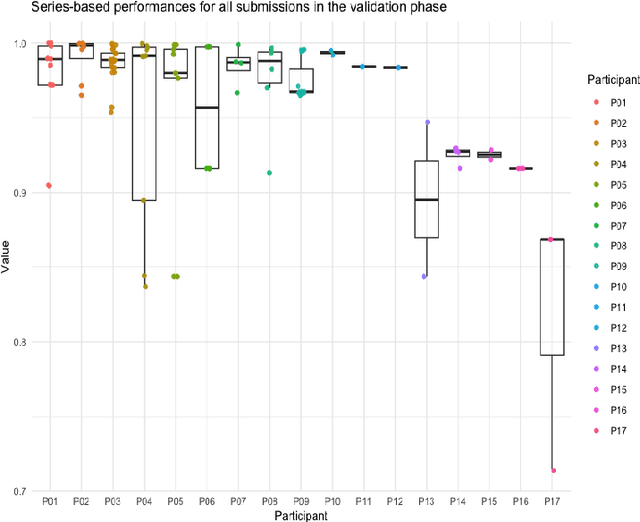
Abstract:The de-identification (deID) of protected health information (PHI) and personally identifiable information (PII) is a fundamental requirement for sharing medical images, particularly through public repositories, to ensure compliance with patient privacy laws. In addition, preservation of non-PHI metadata to inform and enable downstream development of imaging artificial intelligence (AI) is an important consideration in biomedical research. The goal of MIDI-B was to provide a standardized platform for benchmarking of DICOM image deID tools based on a set of rules conformant to the HIPAA Safe Harbor regulation, the DICOM Attribute Confidentiality Profiles, and best practices in preservation of research-critical metadata, as defined by The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA). The challenge employed a large, diverse, multi-center, and multi-modality set of real de-identified radiology images with synthetic PHI/PII inserted. The MIDI-B Challenge consisted of three phases: training, validation, and test. Eighty individuals registered for the challenge. In the training phase, we encouraged participants to tune their algorithms using their in-house or public data. The validation and test phases utilized the DICOM images containing synthetic identifiers (of 216 and 322 subjects, respectively). Ten teams successfully completed the test phase of the challenge. To measure success of a rule-based approach to image deID, scores were computed as the percentage of correct actions from the total number of required actions. The scores ranged from 97.91% to 99.93%. Participants employed a variety of open-source and proprietary tools with customized configurations, large language models, and optical character recognition (OCR). In this paper we provide a comprehensive report on the MIDI-B Challenge's design, implementation, results, and lessons learned.
Towards Large Reasoning Models for Agriculture
May 25, 2025Abstract:Agricultural decision-making involves complex, context-specific reasoning, where choices about crops, practices, and interventions depend heavily on geographic, climatic, and economic conditions. Traditional large language models (LLMs) often fall short in navigating this nuanced problem due to limited reasoning capacity. We hypothesize that recent advances in large reasoning models (LRMs) can better handle such structured, domain-specific inference. To investigate this, we introduce AgReason, the first expert-curated open-ended science benchmark with 100 questions for agricultural reasoning. Evaluations across thirteen open-source and proprietary models reveal that LRMs outperform conventional ones, though notable challenges persist, with the strongest Gemini-based baseline achieving 36% accuracy. We also present AgThoughts, a large-scale dataset of 44.6K question-answer pairs generated with human oversight and equipped with synthetically generated reasoning traces. Using AgThoughts, we develop AgThinker, a suite of small reasoning models that can be run on consumer-grade GPUs, and show that our dataset can be effective in unlocking agricultural reasoning abilities in LLMs. Our project page is here: https://baskargroup.github.io/Ag_reasoning/
WeedNet: A Foundation Model-Based Global-to-Local AI Approach for Real-Time Weed Species Identification and Classification
May 25, 2025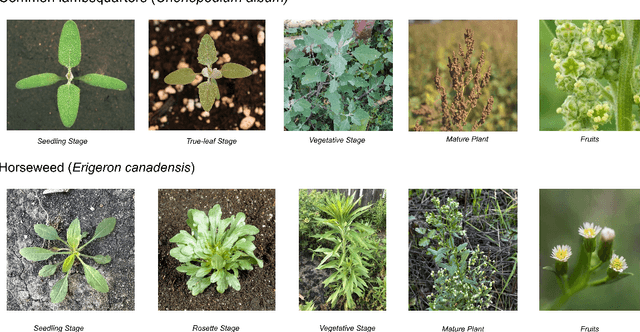
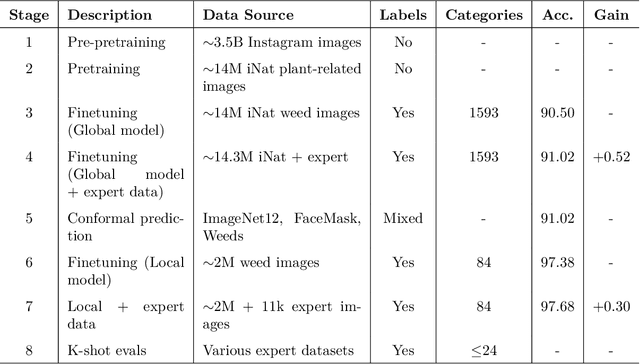
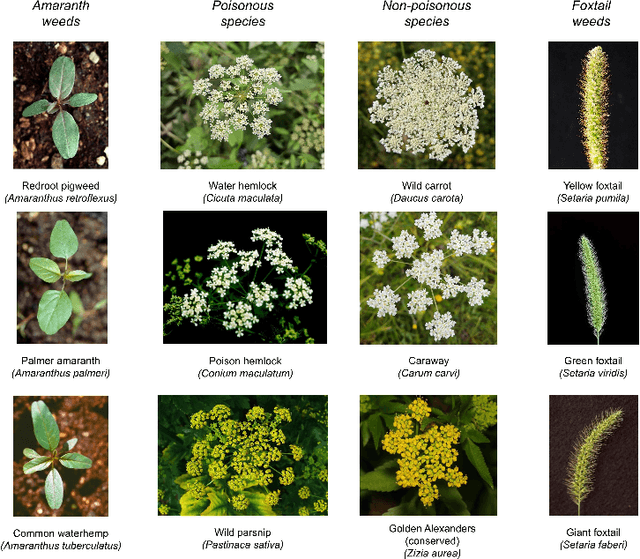

Abstract:Early identification of weeds is essential for effective management and control, and there is growing interest in automating the process using computer vision techniques coupled with AI methods. However, challenges associated with training AI-based weed identification models, such as limited expert-verified data and complexity and variability in morphological features, have hindered progress. To address these issues, we present WeedNet, the first global-scale weed identification model capable of recognizing an extensive set of weed species, including noxious and invasive plant species. WeedNet is an end-to-end real-time weed identification pipeline and uses self-supervised learning, fine-tuning, and enhanced trustworthiness strategies. WeedNet achieved 91.02% accuracy across 1,593 weed species, with 41% species achieving 100% accuracy. Using a fine-tuning strategy and a Global-to-Local approach, the local Iowa WeedNet model achieved an overall accuracy of 97.38% for 85 Iowa weeds, most classes exceeded a 90% mean accuracy per class. Testing across intra-species dissimilarity (developmental stages) and inter-species similarity (look-alike species) suggests that diversity in the images collected, spanning all the growth stages and distinguishable plant characteristics, is crucial in driving model performance. The generalizability and adaptability of the Global WeedNet model enable it to function as a foundational model, with the Global-to-Local strategy allowing fine-tuning for region-specific weed communities. Additional validation of drone- and ground-rover-based images highlights the potential of WeedNet for integration into robotic platforms. Furthermore, integration with AI for conversational use provides intelligent agricultural and ecological conservation consulting tools for farmers, agronomists, researchers, land managers, and government agencies across diverse landscapes.
Soybean Maturity Prediction using 2D Contour Plots from Drone based Time Series Imagery
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Plant breeding programs require assessments of days to maturity for accurate selection and placement of entries in appropriate tests. In the early stages of the breeding pipeline, soybean breeding programs assign relative maturity ratings to experimental varieties that indicate their suitable maturity zones. Traditionally, the estimation of maturity value for breeding varieties has involved breeders manually inspecting fields and assessing maturity value visually. This approach relies heavily on rater judgment, making it subjective and time-consuming. This study aimed to develop a machine-learning model for evaluating soybean maturity using UAV-based time-series imagery. Images were captured at three-day intervals, beginning as the earliest varieties started maturing and continuing until the last varieties fully matured. The data collected for this experiment consisted of 22,043 plots collected across three years (2021 to 2023) and represent relative maturity groups 1.6 - 3.9. We utilized contour plot images extracted from the time-series UAV RGB imagery as input for a neural network model. This contour plot approach encoded the temporal and spatial variation within each plot into a single image. A deep learning model was trained to utilize this contour plot to predict maturity ratings. This model significantly improves accuracy and robustness, achieving up to 85% accuracy. We also evaluate the model's accuracy as we reduce the number of time points, quantifying the trade-off between temporal resolution and maturity prediction. The predictive model offers a scalable, objective, and efficient means of assessing crop maturity, enabling phenomics and ML approaches to reduce the reliance on manual inspection and subjective assessment. This approach enables the automatic prediction of relative maturity ratings in a breeding program, saving time and resources.
Robust soybean seed yield estimation using high-throughput ground robot videos
Dec 03, 2024
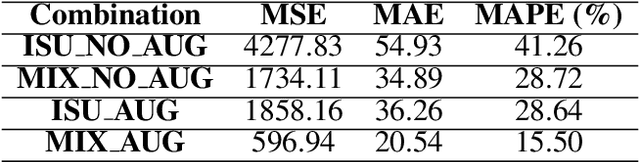
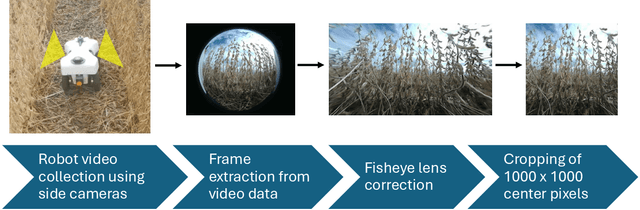

Abstract:We present a novel method for soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) yield estimation leveraging high throughput seed counting via computer vision and deep learning techniques. Traditional methods for collecting yield data are labor-intensive, costly, prone to equipment failures at critical data collection times, and require transportation of equipment across field sites. Computer vision, the field of teaching computers to interpret visual data, allows us to extract detailed yield information directly from images. By treating it as a computer vision task, we report a more efficient alternative, employing a ground robot equipped with fisheye cameras to capture comprehensive videos of soybean plots from which images are extracted in a variety of development programs. These images are processed through the P2PNet-Yield model, a deep learning framework where we combined a Feature Extraction Module (the backbone of the P2PNet-Soy) and a Yield Regression Module to estimate seed yields of soybean plots. Our results are built on three years of yield testing plot data - 8500 in 2021, 2275 in 2022, and 650 in 2023. With these datasets, our approach incorporates several innovations to further improve the accuracy and generalizability of the seed counting and yield estimation architecture, such as the fisheye image correction and data augmentation with random sensor effects. The P2PNet-Yield model achieved a genotype ranking accuracy score of up to 83%. It demonstrates up to a 32% reduction in time to collect yield data as well as costs associated with traditional yield estimation, offering a scalable solution for breeding programs and agricultural productivity enhancement.
AgGym: An agricultural biotic stress simulation environment for ultra-precision management planning
Sep 01, 2024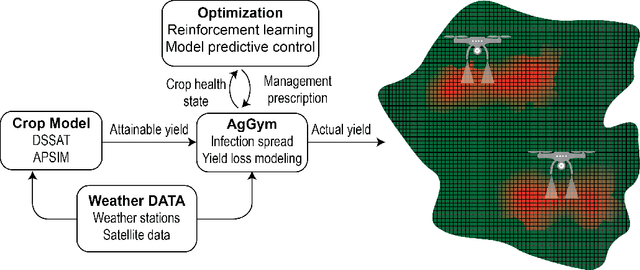
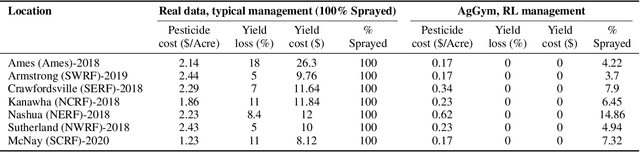
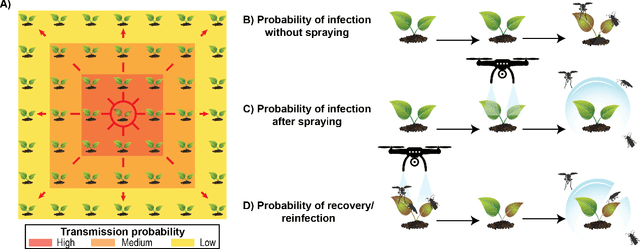
Abstract:Agricultural production requires careful management of inputs such as fungicides, insecticides, and herbicides to ensure a successful crop that is high-yielding, profitable, and of superior seed quality. Current state-of-the-art field crop management relies on coarse-scale crop management strategies, where entire fields are sprayed with pest and disease-controlling chemicals, leading to increased cost and sub-optimal soil and crop management. To overcome these challenges and optimize crop production, we utilize machine learning tools within a virtual field environment to generate localized management plans for farmers to manage biotic threats while maximizing profits. Specifically, we present AgGym, a modular, crop and stress agnostic simulation framework to model the spread of biotic stresses in a field and estimate yield losses with and without chemical treatments. Our validation with real data shows that AgGym can be customized with limited data to simulate yield outcomes under various biotic stress conditions. We further demonstrate that deep reinforcement learning (RL) policies can be trained using AgGym for designing ultra-precise biotic stress mitigation strategies with potential to increase yield recovery with less chemicals and lower cost. Our proposed framework enables personalized decision support that can transform biotic stress management from being schedule based and reactive to opportunistic and prescriptive. We also release the AgGym software implementation as a community resource and invite experts to contribute to this open-sourced publicly available modular environment framework. The source code can be accessed at: https://github.com/SCSLabISU/AgGym.
AgEval: A Benchmark for Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Plant Stress Phenotyping with Multimodal LLMs
Jul 29, 2024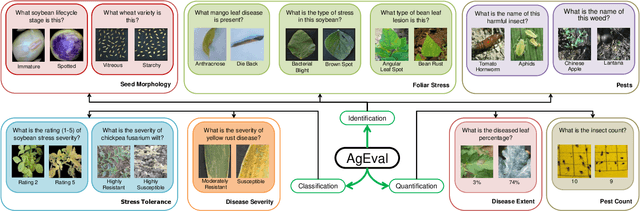
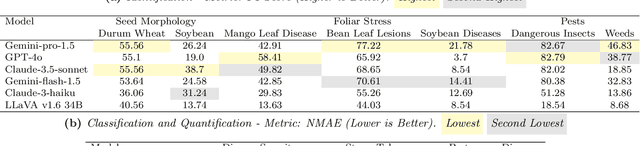
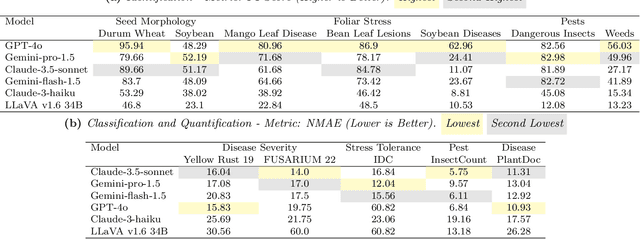
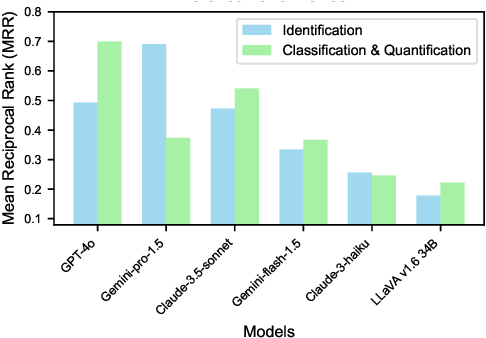
Abstract:Plant stress phenotyping traditionally relies on expert assessments and specialized models, limiting scalability in agriculture. Recent advances in multimodal large language models (LLMs) offer potential solutions to this challenge. We present AgEval, a benchmark comprising 12 diverse plant stress phenotyping tasks, to evaluate these models' capabilities. Our study assesses zero-shot and few-shot in-context learning performance of state-of-the-art models, including Claude, GPT, Gemini, and LLaVA. Results show significant performance improvements with few-shot learning, with F1 scores increasing from 46.24% to 73.37% in 8-shot identification for the best-performing model. Few-shot examples from other classes in the dataset have negligible or negative impacts, although having the exact category example helps to increase performance by 15.38%. We also quantify the consistency of model performance across different classes within each task, finding that the coefficient of variance (CV) ranges from 26.02% to 58.03% across models, implying that subject matter expertise is needed - of 'difficult' classes - to achieve reliability in performance. AgEval establishes baseline metrics for multimodal LLMs in agricultural applications, offering insights into their promise for enhancing plant stress phenotyping at scale. Benchmark and code can be accessed at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AgEval/
Arboretum: A Large Multimodal Dataset Enabling AI for Biodiversity
Jun 25, 2024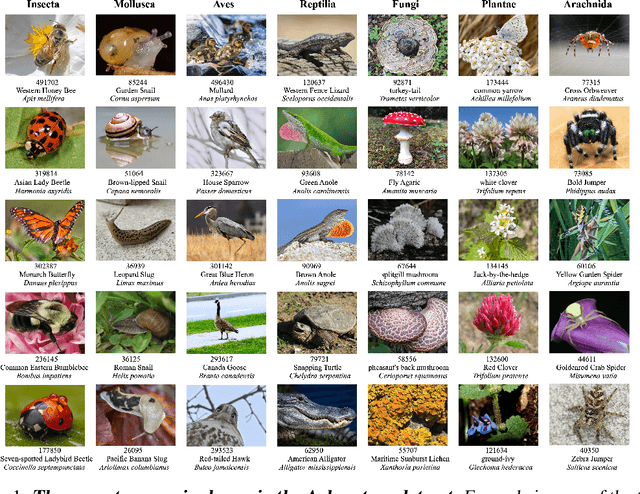

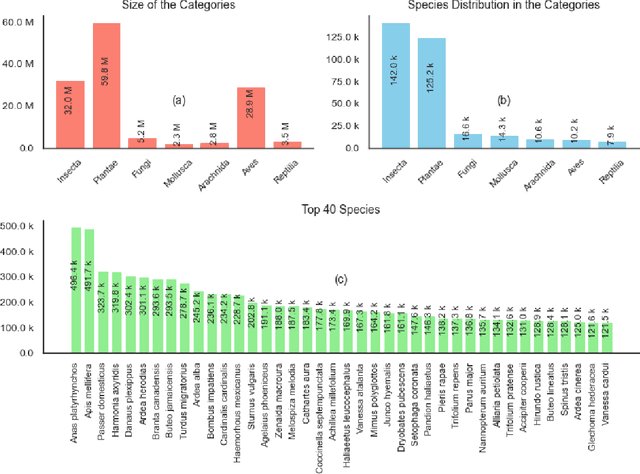
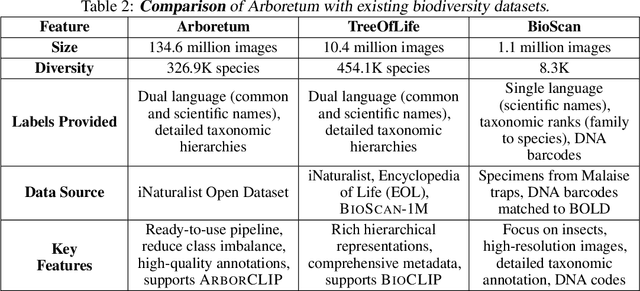
Abstract:We introduce Arboretum, the largest publicly accessible dataset designed to advance AI for biodiversity applications. This dataset, curated from the iNaturalist community science platform and vetted by domain experts to ensure accuracy, includes 134.6 million images, surpassing existing datasets in scale by an order of magnitude. The dataset encompasses image-language paired data for a diverse set of species from birds (Aves), spiders/ticks/mites (Arachnida), insects (Insecta), plants (Plantae), fungus/mushrooms (Fungi), snails (Mollusca), and snakes/lizards (Reptilia), making it a valuable resource for multimodal vision-language AI models for biodiversity assessment and agriculture research. Each image is annotated with scientific names, taxonomic details, and common names, enhancing the robustness of AI model training. We showcase the value of Arboretum by releasing a suite of CLIP models trained using a subset of 40 million captioned images. We introduce several new benchmarks for rigorous assessment, report accuracy for zero-shot learning, and evaluations across life stages, rare species, confounding species, and various levels of the taxonomic hierarchy. We anticipate that Arboretum will spur the development of AI models that can enable a variety of digital tools ranging from pest control strategies, crop monitoring, and worldwide biodiversity assessment and environmental conservation. These advancements are critical for ensuring food security, preserving ecosystems, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Arboretum is publicly available, easily accessible, and ready for immediate use. Please see the \href{https://baskargroup.github.io/Arboretum/}{project website} for links to our data, models, and code.
Class-specific Data Augmentation for Plant Stress Classification
Jun 18, 2024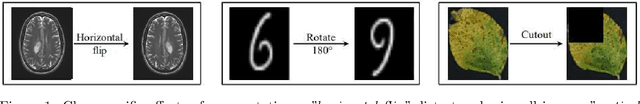
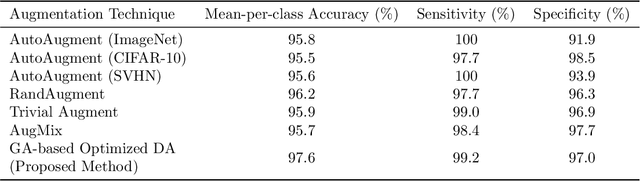
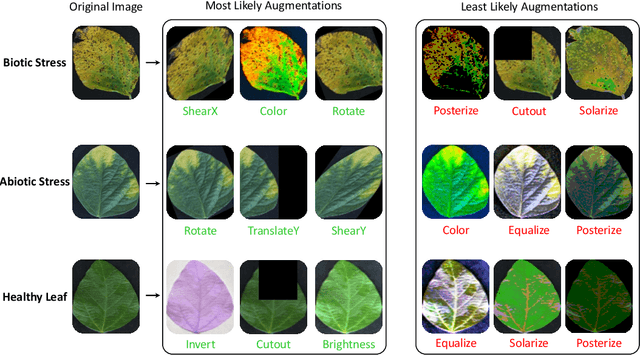
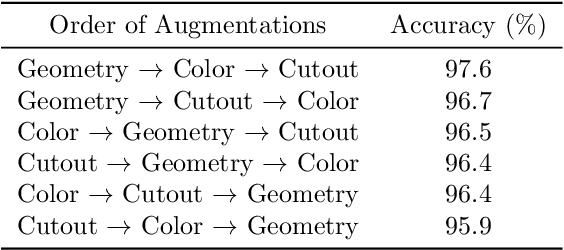
Abstract:Data augmentation is a powerful tool for improving deep learning-based image classifiers for plant stress identification and classification. However, selecting an effective set of augmentations from a large pool of candidates remains a key challenge, particularly in imbalanced and confounding datasets. We propose an approach for automated class-specific data augmentation using a genetic algorithm. We demonstrate the utility of our approach on soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr] stress classification where symptoms are observed on leaves; a particularly challenging problem due to confounding classes in the dataset. Our approach yields substantial performance, achieving a mean-per-class accuracy of 97.61% and an overall accuracy of 98% on the soybean leaf stress dataset. Our method significantly improves the accuracy of the most challenging classes, with notable enhancements from 83.01% to 88.89% and from 85.71% to 94.05%, respectively. A key observation we make in this study is that high-performing augmentation strategies can be identified in a computationally efficient manner. We fine-tune only the linear layer of the baseline model with different augmentations, thereby reducing the computational burden associated with training classifiers from scratch for each augmentation policy while achieving exceptional performance. This research represents an advancement in automated data augmentation strategies for plant stress classification, particularly in the context of confounding datasets. Our findings contribute to the growing body of research in tailored augmentation techniques and their potential impact on disease management strategies, crop yields, and global food security. The proposed approach holds the potential to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of deep learning-based tools for managing plant stresses in agriculture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge