Mahsa Khosravi
Zero-shot Sim-to-Real Transfer for Reinforcement Learning-based Visual Servoing of Soft Continuum Arms
Apr 23, 2025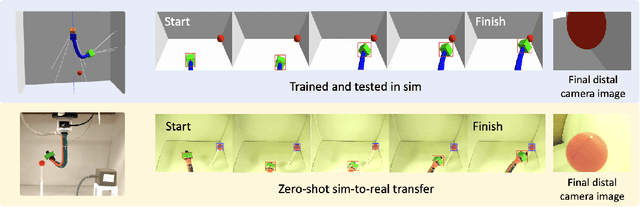
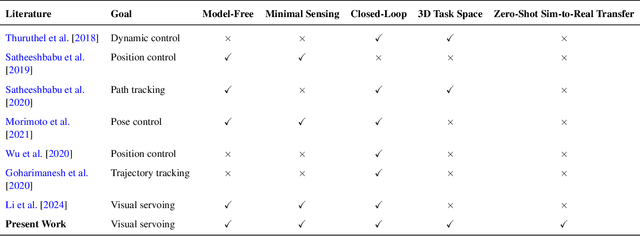
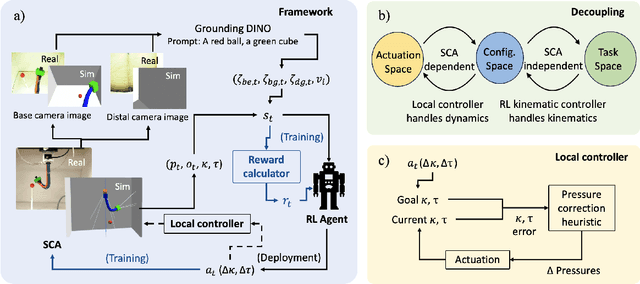
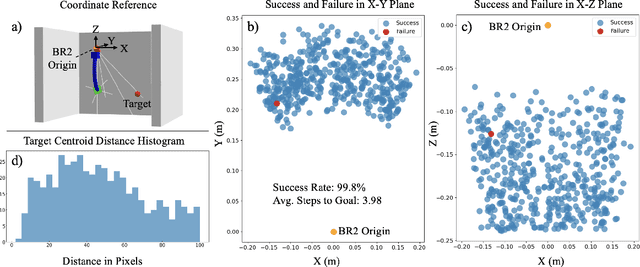
Abstract:Soft continuum arms (SCAs) soft and deformable nature presents challenges in modeling and control due to their infinite degrees of freedom and non-linear behavior. This work introduces a reinforcement learning (RL)-based framework for visual servoing tasks on SCAs with zero-shot sim-to-real transfer capabilities, demonstrated on a single section pneumatic manipulator capable of bending and twisting. The framework decouples kinematics from mechanical properties using an RL kinematic controller for motion planning and a local controller for actuation refinement, leveraging minimal sensing with visual feedback. Trained entirely in simulation, the RL controller achieved a 99.8% success rate. When deployed on hardware, it achieved a 67% success rate in zero-shot sim-to-real transfer, demonstrating robustness and adaptability. This approach offers a scalable solution for SCAs in 3D visual servoing, with potential for further refinement and expanded applications.
Enhancing PPO with Trajectory-Aware Hybrid Policies
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Proximal policy optimization (PPO) is one of the most popular state-of-the-art on-policy algorithms that has become a standard baseline in modern reinforcement learning with applications in numerous fields. Though it delivers stable performance with theoretical policy improvement guarantees, high variance, and high sample complexity still remain critical challenges in on-policy algorithms. To alleviate these issues, we propose Hybrid-Policy Proximal Policy Optimization (HP3O), which utilizes a trajectory replay buffer to make efficient use of trajectories generated by recent policies. Particularly, the buffer applies the "first in, first out" (FIFO) strategy so as to keep only the recent trajectories to attenuate the data distribution drift. A batch consisting of the trajectory with the best return and other randomly sampled ones from the buffer is used for updating the policy networks. The strategy helps the agent to improve its capability on top of the most recent best performance and in turn reduce variance empirically. We theoretically construct the policy improvement guarantees for the proposed algorithm. HP3O is validated and compared against several baseline algorithms using multiple continuous control environments. Our code is available here.
AgGym: An agricultural biotic stress simulation environment for ultra-precision management planning
Sep 01, 2024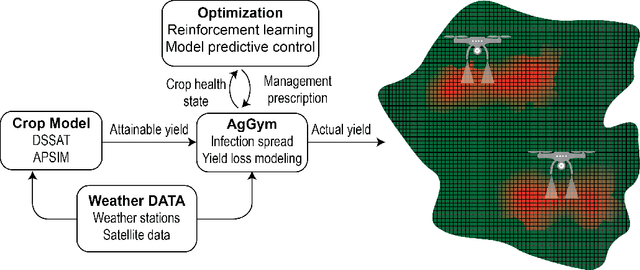
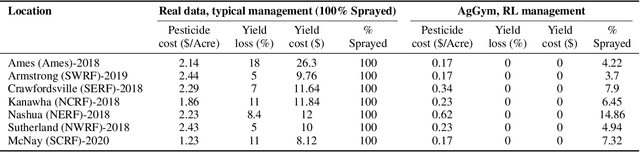
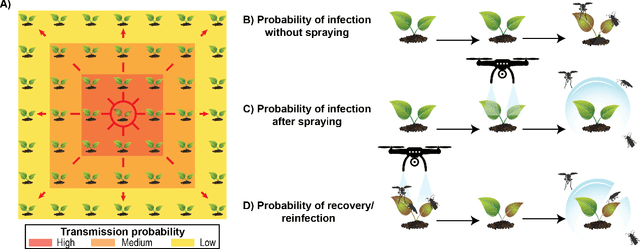
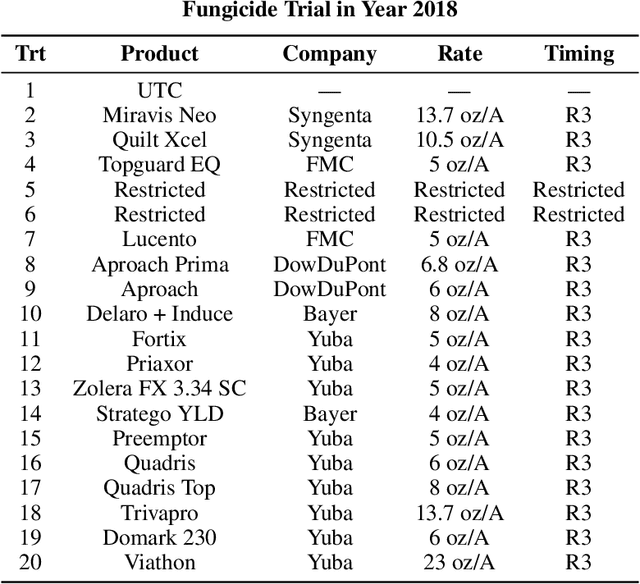
Abstract:Agricultural production requires careful management of inputs such as fungicides, insecticides, and herbicides to ensure a successful crop that is high-yielding, profitable, and of superior seed quality. Current state-of-the-art field crop management relies on coarse-scale crop management strategies, where entire fields are sprayed with pest and disease-controlling chemicals, leading to increased cost and sub-optimal soil and crop management. To overcome these challenges and optimize crop production, we utilize machine learning tools within a virtual field environment to generate localized management plans for farmers to manage biotic threats while maximizing profits. Specifically, we present AgGym, a modular, crop and stress agnostic simulation framework to model the spread of biotic stresses in a field and estimate yield losses with and without chemical treatments. Our validation with real data shows that AgGym can be customized with limited data to simulate yield outcomes under various biotic stress conditions. We further demonstrate that deep reinforcement learning (RL) policies can be trained using AgGym for designing ultra-precise biotic stress mitigation strategies with potential to increase yield recovery with less chemicals and lower cost. Our proposed framework enables personalized decision support that can transform biotic stress management from being schedule based and reactive to opportunistic and prescriptive. We also release the AgGym software implementation as a community resource and invite experts to contribute to this open-sourced publicly available modular environment framework. The source code can be accessed at: https://github.com/SCSLabISU/AgGym.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge