Antonio Bonafonte
Universal Semantic Disentangled Privacy-preserving Speech Representation Learning
May 19, 2025Abstract:The use of audio recordings of human speech to train LLMs poses privacy concerns due to these models' potential to generate outputs that closely resemble artifacts in the training data. In this study, we propose a speaker privacy-preserving representation learning method through the Universal Speech Codec (USC), a computationally efficient encoder-decoder model that disentangles speech into: $\textit{(i)}$ privacy-preserving semantically rich representations, capturing content and speech paralinguistics, and $\textit{(ii)}$ residual acoustic and speaker representations that enables high-fidelity reconstruction. Extensive evaluations presented show that USC's semantic representation preserves content, prosody, and sentiment, while removing potentially identifiable speaker attributes. Combining both representations, USC achieves state-of-the-art speech reconstruction. Additionally, we introduce an evaluation methodology for measuring privacy-preserving properties, aligning with perceptual tests. We compare USC against other codecs in the literature and demonstrate its effectiveness on privacy-preserving representation learning, illustrating the trade-offs of speaker anonymization, paralinguistics retention and content preservation in the learned semantic representations. Audio samples are shared in $\href{https://www.amazon.science/usc-samples}{https://www.amazon.science/usc-samples}$.
Controllable Emphasis with zero data for text-to-speech
Jul 13, 2023Abstract:We present a scalable method to produce high quality emphasis for text-to-speech (TTS) that does not require recordings or annotations. Many TTS models include a phoneme duration model. A simple but effective method to achieve emphasized speech consists in increasing the predicted duration of the emphasised word. We show that this is significantly better than spectrogram modification techniques improving naturalness by $7.3\%$ and correct testers' identification of the emphasized word in a sentence by $40\%$ on a reference female en-US voice. We show that this technique significantly closes the gap to methods that require explicit recordings. The method proved to be scalable and preferred in all four languages tested (English, Spanish, Italian, German), for different voices and multiple speaking styles.
Analysis and Utilization of Entrainment on Acoustic and Emotion Features in User-agent Dialogue
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:Entrainment is the phenomenon by which an interlocutor adapts their speaking style to align with their partner in conversations. It has been found in different dimensions as acoustic, prosodic, lexical or syntactic. In this work, we explore and utilize the entrainment phenomenon to improve spoken dialogue systems for voice assistants. We first examine the existence of the entrainment phenomenon in human-to-human dialogues in respect to acoustic feature and then extend the analysis to emotion features. The analysis results show strong evidence of entrainment in terms of both acoustic and emotion features. Based on this findings, we implement two entrainment policies and assess if the integration of entrainment principle into a Text-to-Speech (TTS) system improves the synthesis performance and the user experience. It is found that the integration of the entrainment principle into a TTS system brings performance improvement when considering acoustic features, while no obvious improvement is observed when considering emotion features.
Distribution augmentation for low-resource expressive text-to-speech
Feb 19, 2022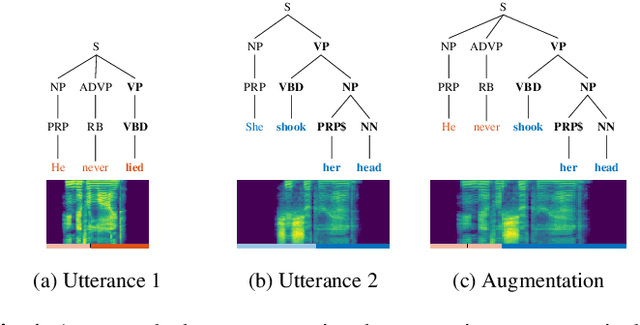
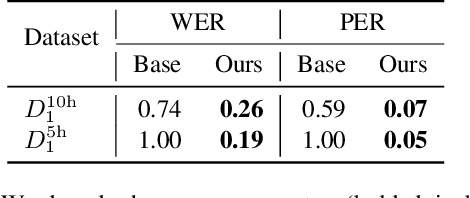
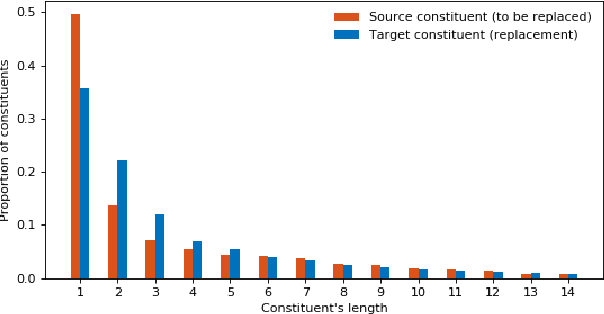
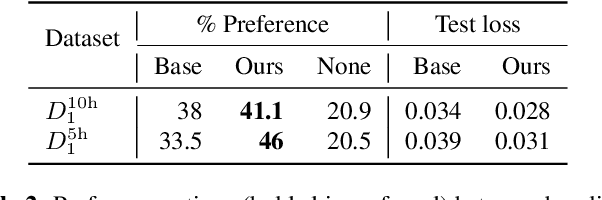
Abstract:This paper presents a novel data augmentation technique for text-to-speech (TTS), that allows to generate new (text, audio) training examples without requiring any additional data. Our goal is to increase diversity of text conditionings available during training. This helps to reduce overfitting, especially in low-resource settings. Our method relies on substituting text and audio fragments in a way that preserves syntactical correctness. We take additional measures to ensure that synthesized speech does not contain artifacts caused by combining inconsistent audio samples. The perceptual evaluations show that our method improves speech quality over a number of datasets, speakers, and TTS architectures. We also demonstrate that it greatly improves robustness of attention-based TTS models.
Discrete acoustic space for an efficient sampling in neural text-to-speech
Oct 24, 2021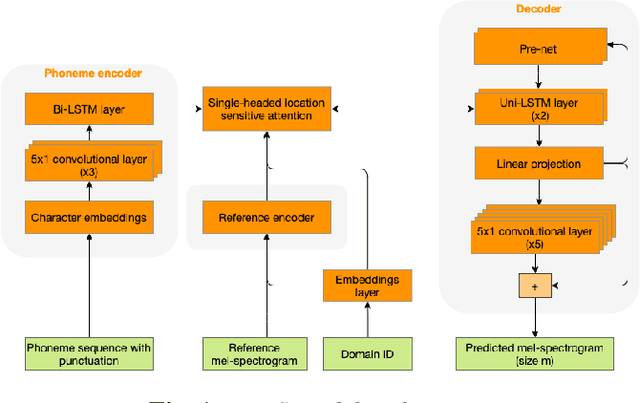
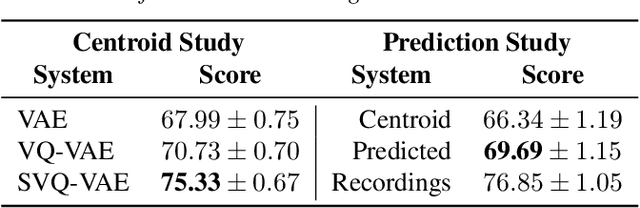
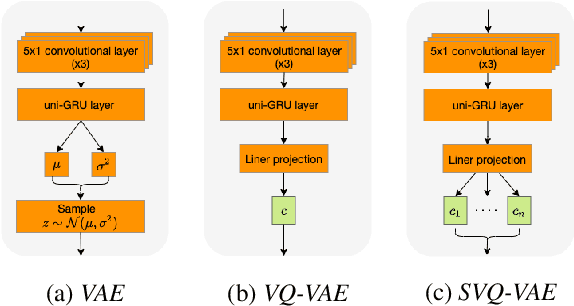
Abstract:We present an SVQ-VAE architecture using a split vector quantizer for NTTS, as an enhancement to the well-known VAE and VQ-VAE architectures. Compared to these previous architectures, our proposed model retains the benefits of using an utterance-level bottleneck, while reducing the associated loss of representation power. We train the model on recordings in the highly expressive task-oriented dialogues domain and show that SVQ-VAE achieves a statistically significant improvement in naturalness over the VAE and VQ-VAE models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the SVQ-VAE acoustic space is predictable from text, reducing the gap between the standard constant vector synthesis and vocoded recordings by 32%.
Proteno: Text Normalization with Limited Data for Fast Deployment in Text to Speech Systems
Apr 15, 2021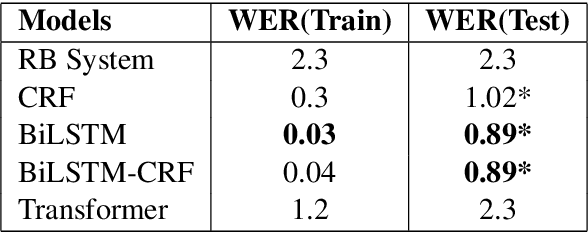
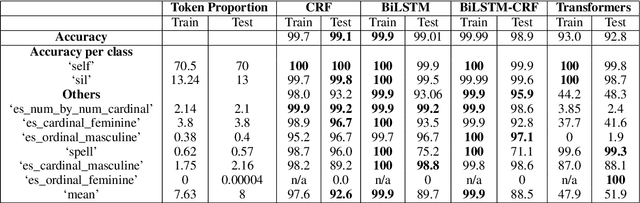
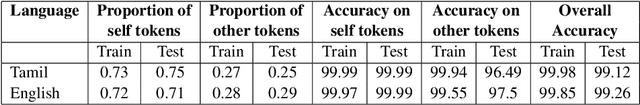
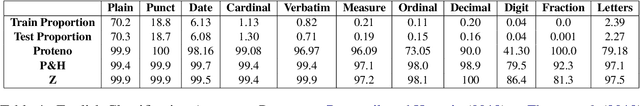
Abstract:Developing Text Normalization (TN) systems for Text-to-Speech (TTS) on new languages is hard. We propose a novel architecture to facilitate it for multiple languages while using data less than 3% of the size of the data used by the state of the art results on English. We treat TN as a sequence classification problem and propose a granular tokenization mechanism that enables the system to learn majority of the classes and their normalizations from the training data itself. This is further combined with minimal precoded linguistic knowledge for other classes. We publish the first results on TN for TTS in Spanish and Tamil and also demonstrate that the performance of the approach is comparable with the previous work done on English. All annotated datasets used for experimentation will be released at https://github.com/amazon-research/proteno.
Prosodic Phrase Alignment for Machine Dubbing
Aug 20, 2019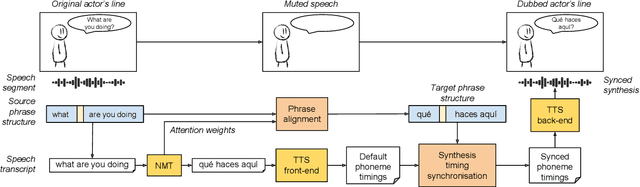

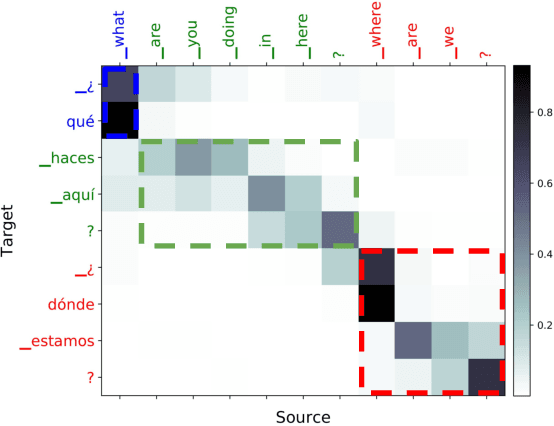
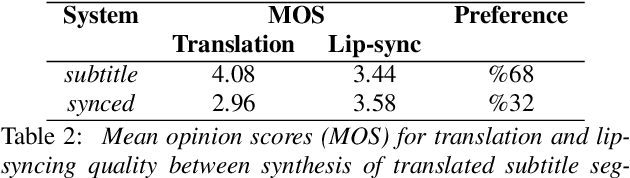
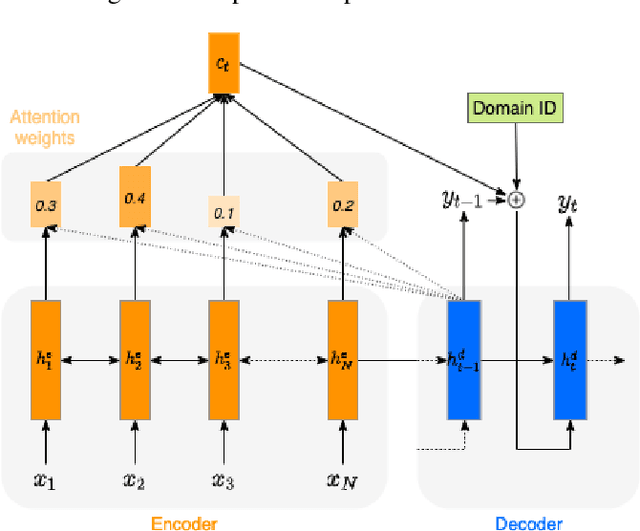
Abstract:Dubbing is a type of audiovisual translation where dialogues are translated and enacted so that they give the impression that the media is in the target language. It requires a careful alignment of dubbed recordings with the lip movements of performers in order to achieve visual coherence. In this paper, we deal with the specific problem of prosodic phrase synchronization within the framework of machine dubbing. Our methodology exploits the attention mechanism output in neural machine translation to find plausible phrasing for the translated dialogue lines and then uses them to condition their synthesis. Our initial work in this field records comparable speech rate ratio to professional dubbing translation, and improvement in terms of lip-syncing of long dialogue lines.
Towards Generalized Speech Enhancement with Generative Adversarial Networks
Apr 06, 2019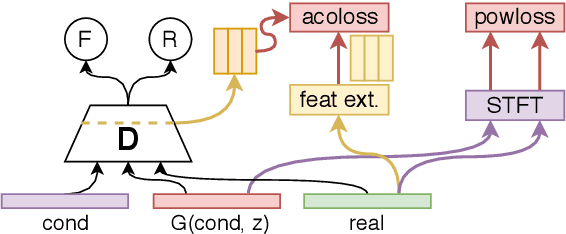
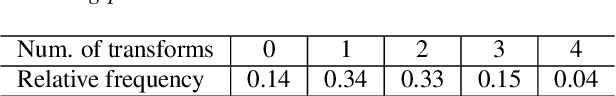
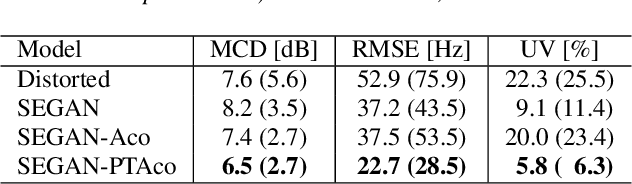
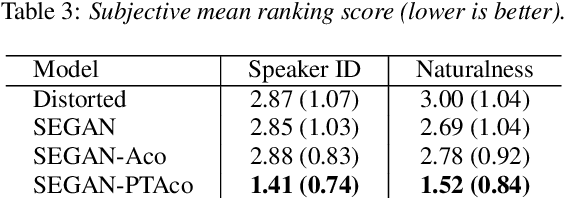
Abstract:The speech enhancement task usually consists of removing additive noise or reverberation that partially mask spoken utterances, affecting their intelligibility. However, little attention is drawn to other, perhaps more aggressive signal distortions like clipping, chunk elimination, or frequency-band removal. Such distortions can have a large impact not only on intelligibility, but also on naturalness or even speaker identity, and require of careful signal reconstruction. In this work, we give full consideration to this generalized speech enhancement task, and show it can be tackled with a time-domain generative adversarial network (GAN). In particular, we extend a previous GAN-based speech enhancement system to deal with mixtures of four types of aggressive distortions. Firstly, we propose the addition of an adversarial acoustic regression loss that promotes a richer feature extraction at the discriminator. Secondly, we also make use of a two-step adversarial training schedule, acting as a warm up-and-fine-tune sequence. Both objective and subjective evaluations show that these two additions bring improved speech reconstructions that better match the original speaker identity and naturalness.
Learning Problem-agnostic Speech Representations from Multiple Self-supervised Tasks
Apr 06, 2019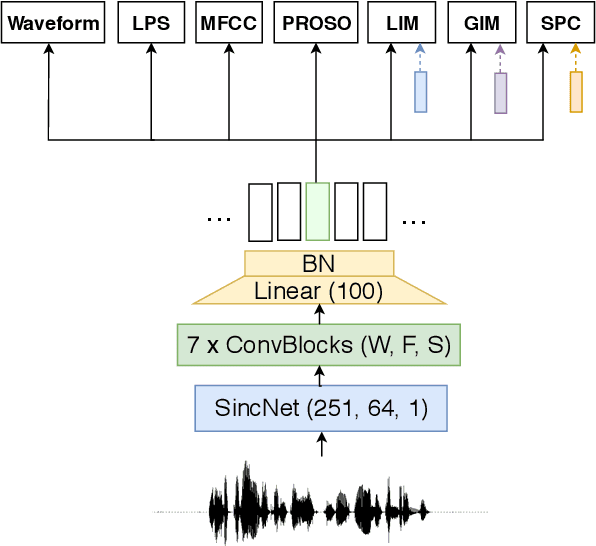
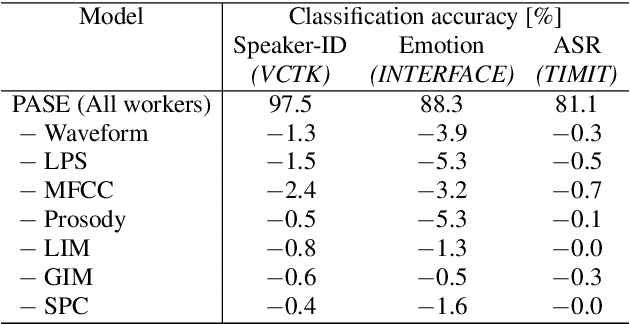
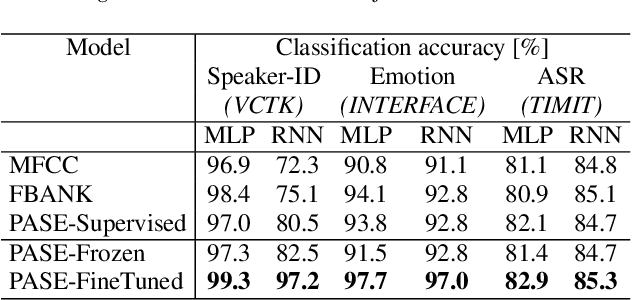
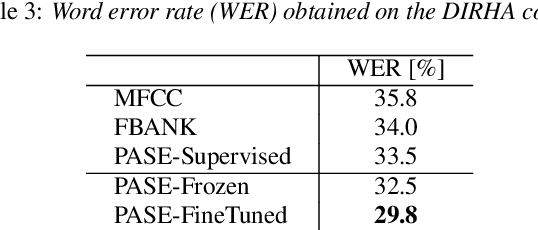
Abstract:Learning good representations without supervision is still an open issue in machine learning, and is particularly challenging for speech signals, which are often characterized by long sequences with a complex hierarchical structure. Some recent works, however, have shown that it is possible to derive useful speech representations by employing a self-supervised encoder-discriminator approach. This paper proposes an improved self-supervised method, where a single neural encoder is followed by multiple workers that jointly solve different self-supervised tasks. The needed consensus across different tasks naturally imposes meaningful constraints to the encoder, contributing to discover general representations and to minimize the risk of learning superficial ones. Experiments show that the proposed approach can learn transferable, robust, and problem-agnostic features that carry on relevant information from the speech signal, such as speaker identity, phonemes, and even higher-level features such as emotional cues. In addition, a number of design choices make the encoder easily exportable, facilitating its direct usage or adaptation to different problems.
Self-Attention Linguistic-Acoustic Decoder
Nov 05, 2018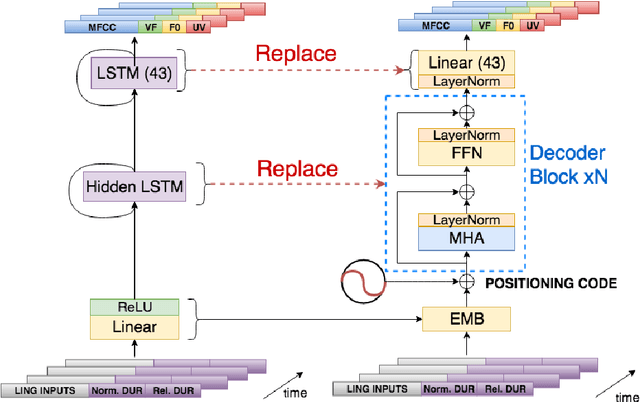
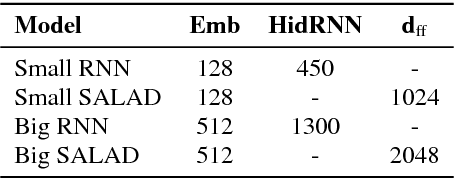
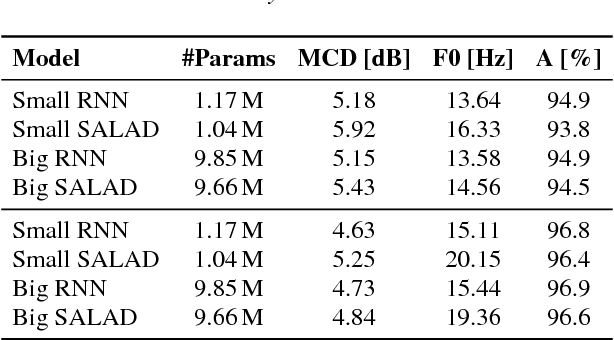
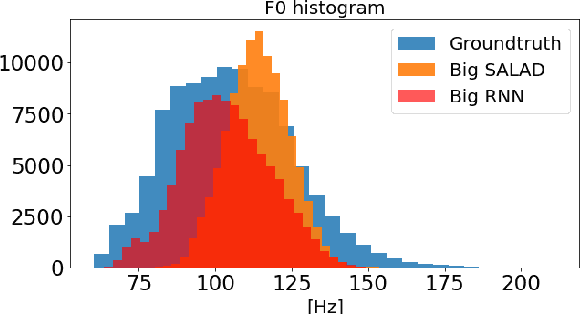
Abstract:The conversion from text to speech relies on the accurate mapping from linguistic to acoustic symbol sequences, for which current practice employs recurrent statistical models like recurrent neural networks. Despite the good performance of such models (in terms of low distortion in the generated speech), their recursive structure tends to make them slow to train and to sample from. In this work, we try to overcome the limitations of recursive structure by using a module based on the transformer decoder network, designed without recurrent connections but emulating them with attention and positioning codes. Our results show that the proposed decoder network is competitive in terms of distortion when compared to a recurrent baseline, whilst being significantly faster in terms of CPU inference time. On average, it increases Mel cepstral distortion between 0.1 and 0.3 dB, but it is over an order of magnitude faster on average. Fast inference is important for the deployment of speech synthesis systems on devices with restricted resources, like mobile phones or embedded systems, where speaking virtual assistants are gaining importance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge