Trevor Wood
Universal Semantic Disentangled Privacy-preserving Speech Representation Learning
May 19, 2025Abstract:The use of audio recordings of human speech to train LLMs poses privacy concerns due to these models' potential to generate outputs that closely resemble artifacts in the training data. In this study, we propose a speaker privacy-preserving representation learning method through the Universal Speech Codec (USC), a computationally efficient encoder-decoder model that disentangles speech into: $\textit{(i)}$ privacy-preserving semantically rich representations, capturing content and speech paralinguistics, and $\textit{(ii)}$ residual acoustic and speaker representations that enables high-fidelity reconstruction. Extensive evaluations presented show that USC's semantic representation preserves content, prosody, and sentiment, while removing potentially identifiable speaker attributes. Combining both representations, USC achieves state-of-the-art speech reconstruction. Additionally, we introduce an evaluation methodology for measuring privacy-preserving properties, aligning with perceptual tests. We compare USC against other codecs in the literature and demonstrate its effectiveness on privacy-preserving representation learning, illustrating the trade-offs of speaker anonymization, paralinguistics retention and content preservation in the learned semantic representations. Audio samples are shared in $\href{https://www.amazon.science/usc-samples}{https://www.amazon.science/usc-samples}$.
Analysis and Utilization of Entrainment on Acoustic and Emotion Features in User-agent Dialogue
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:Entrainment is the phenomenon by which an interlocutor adapts their speaking style to align with their partner in conversations. It has been found in different dimensions as acoustic, prosodic, lexical or syntactic. In this work, we explore and utilize the entrainment phenomenon to improve spoken dialogue systems for voice assistants. We first examine the existence of the entrainment phenomenon in human-to-human dialogues in respect to acoustic feature and then extend the analysis to emotion features. The analysis results show strong evidence of entrainment in terms of both acoustic and emotion features. Based on this findings, we implement two entrainment policies and assess if the integration of entrainment principle into a Text-to-Speech (TTS) system improves the synthesis performance and the user experience. It is found that the integration of the entrainment principle into a TTS system brings performance improvement when considering acoustic features, while no obvious improvement is observed when considering emotion features.
Distribution augmentation for low-resource expressive text-to-speech
Feb 19, 2022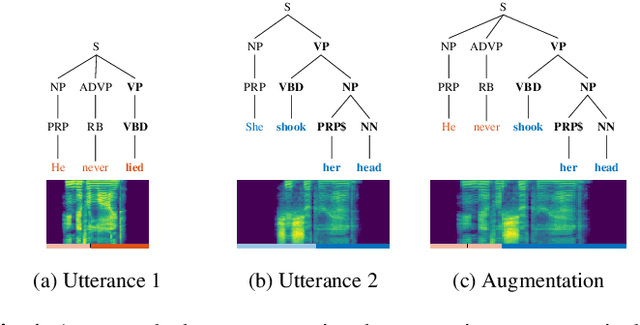
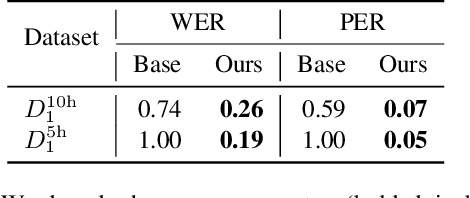
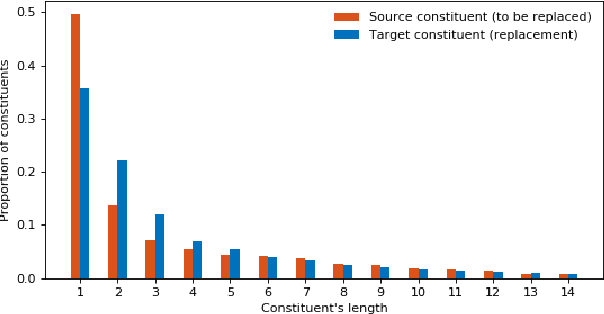
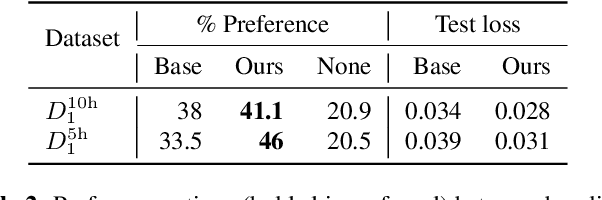
Abstract:This paper presents a novel data augmentation technique for text-to-speech (TTS), that allows to generate new (text, audio) training examples without requiring any additional data. Our goal is to increase diversity of text conditionings available during training. This helps to reduce overfitting, especially in low-resource settings. Our method relies on substituting text and audio fragments in a way that preserves syntactical correctness. We take additional measures to ensure that synthesized speech does not contain artifacts caused by combining inconsistent audio samples. The perceptual evaluations show that our method improves speech quality over a number of datasets, speakers, and TTS architectures. We also demonstrate that it greatly improves robustness of attention-based TTS models.
Discrete acoustic space for an efficient sampling in neural text-to-speech
Oct 24, 2021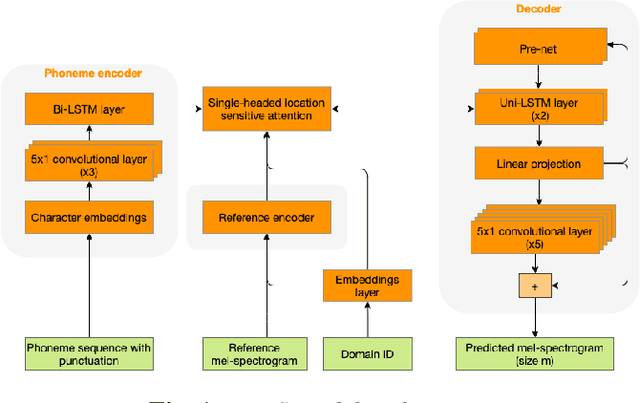
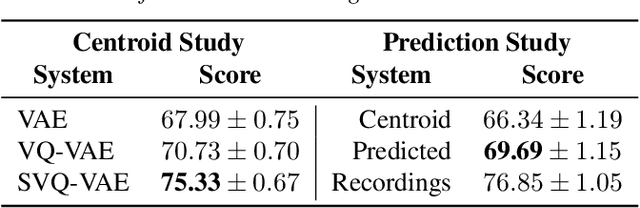
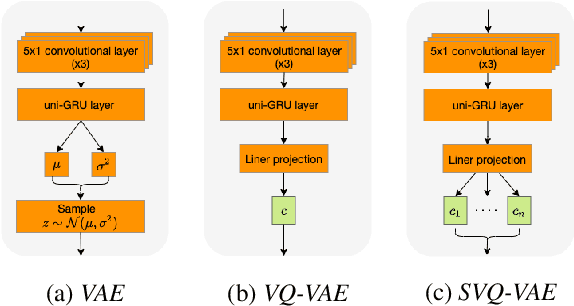
Abstract:We present an SVQ-VAE architecture using a split vector quantizer for NTTS, as an enhancement to the well-known VAE and VQ-VAE architectures. Compared to these previous architectures, our proposed model retains the benefits of using an utterance-level bottleneck, while reducing the associated loss of representation power. We train the model on recordings in the highly expressive task-oriented dialogues domain and show that SVQ-VAE achieves a statistically significant improvement in naturalness over the VAE and VQ-VAE models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the SVQ-VAE acoustic space is predictable from text, reducing the gap between the standard constant vector synthesis and vocoded recordings by 32%.
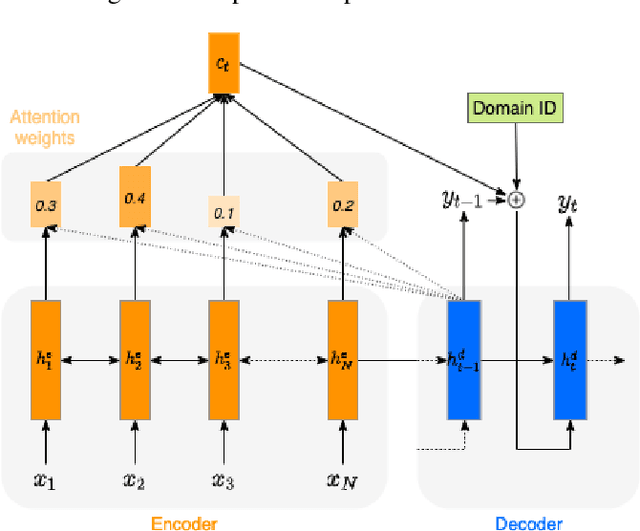
In Other News: A Bi-style Text-to-speech Model for Synthesizing Newscaster Voice with Limited Data
Apr 04, 2019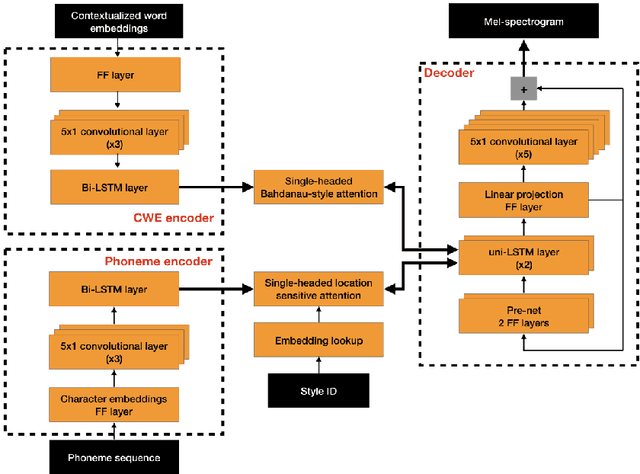
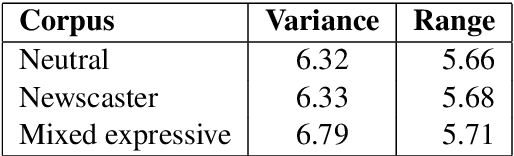

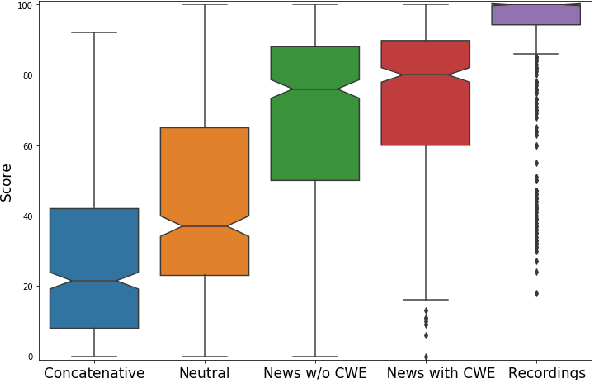
Abstract:Neural text-to-speech synthesis (NTTS) models have shown significant progress in generating high-quality speech, however they require a large quantity of training data. This makes creating models for multiple styles expensive and time-consuming. In this paper different styles of speech are analysed based on prosodic variations, from this a model is proposed to synthesise speech in the style of a newscaster, with just a few hours of supplementary data. We pose the problem of synthesising in a target style using limited data as that of creating a bi-style model that can synthesise both neutral-style and newscaster-style speech via a one-hot vector which factorises the two styles. We also propose conditioning the model on contextual word embeddings, and extensively evaluate it against neutral NTTS, and neutral concatenative-based synthesis. This model closes the gap in perceived style-appropriateness between natural recordings for newscaster-style of speech, and neutral speech synthesis by approximately two-thirds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge