Jonas Rohnke
Analysis and Utilization of Entrainment on Acoustic and Emotion Features in User-agent Dialogue
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:Entrainment is the phenomenon by which an interlocutor adapts their speaking style to align with their partner in conversations. It has been found in different dimensions as acoustic, prosodic, lexical or syntactic. In this work, we explore and utilize the entrainment phenomenon to improve spoken dialogue systems for voice assistants. We first examine the existence of the entrainment phenomenon in human-to-human dialogues in respect to acoustic feature and then extend the analysis to emotion features. The analysis results show strong evidence of entrainment in terms of both acoustic and emotion features. Based on this findings, we implement two entrainment policies and assess if the integration of entrainment principle into a Text-to-Speech (TTS) system improves the synthesis performance and the user experience. It is found that the integration of the entrainment principle into a TTS system brings performance improvement when considering acoustic features, while no obvious improvement is observed when considering emotion features.
Discrete acoustic space for an efficient sampling in neural text-to-speech
Oct 24, 2021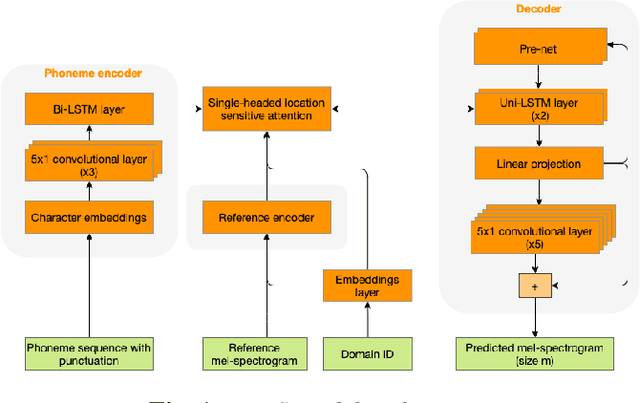
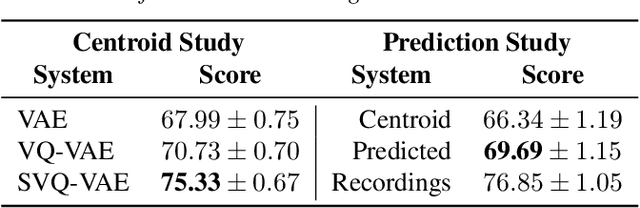
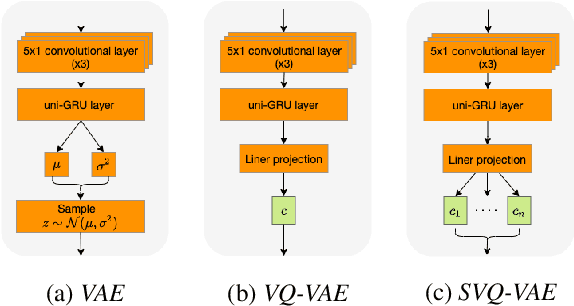
Abstract:We present an SVQ-VAE architecture using a split vector quantizer for NTTS, as an enhancement to the well-known VAE and VQ-VAE architectures. Compared to these previous architectures, our proposed model retains the benefits of using an utterance-level bottleneck, while reducing the associated loss of representation power. We train the model on recordings in the highly expressive task-oriented dialogues domain and show that SVQ-VAE achieves a statistically significant improvement in naturalness over the VAE and VQ-VAE models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the SVQ-VAE acoustic space is predictable from text, reducing the gap between the standard constant vector synthesis and vocoded recordings by 32%.
Dynamic Prosody Generation for Speech Synthesis using Linguistics-Driven Acoustic Embedding Selection
Dec 02, 2019



Abstract:Recent advances in Text-to-Speech (TTS) have improved quality and naturalness to near-human capabilities when considering isolated sentences. But something which is still lacking in order to achieve human-like communication is the dynamic variations and adaptability of human speech. This work attempts to solve the problem of achieving a more dynamic and natural intonation in TTS systems, particularly for stylistic speech such as the newscaster speaking style. We propose a novel embedding selection approach which exploits linguistic information, leveraging the speech variability present in the training dataset. We analyze the contribution of both semantic and syntactic features. Our results show that the approach improves the prosody and naturalness for complex utterances as well as in Long Form Reading (LFR).
Fine-grained robust prosody transfer for single-speaker neural text-to-speech
Jul 04, 2019



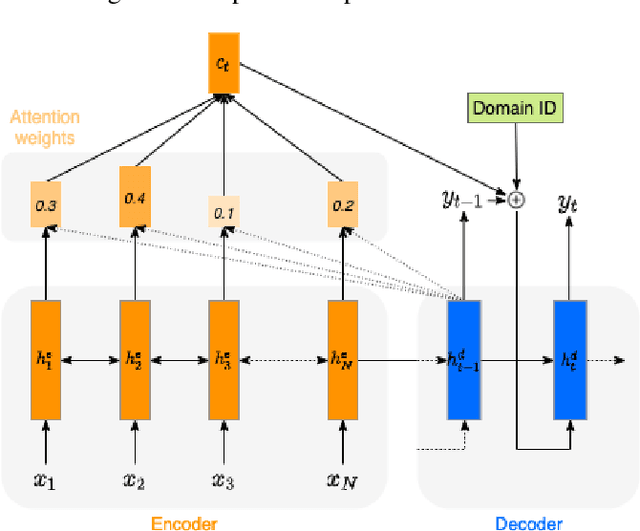
Abstract:We present a neural text-to-speech system for fine-grained prosody transfer from one speaker to another. Conventional approaches for end-to-end prosody transfer typically use either fixed-dimensional or variable-length prosody embedding via a secondary attention to encode the reference signal. However, when trained on a single-speaker dataset, the conventional prosody transfer systems are not robust enough to speaker variability, especially in the case of a reference signal coming from an unseen speaker. Therefore, we propose decoupling of the reference signal alignment from the overall system. For this purpose, we pre-compute phoneme-level time stamps and use them to aggregate prosodic features per phoneme, injecting them into a sequence-to-sequence text-to-speech system. We incorporate a variational auto-encoder to further enhance the latent representation of prosody embeddings. We show that our proposed approach is significantly more stable and achieves reliable prosody transplantation from an unseen speaker. We also propose a solution to the use case in which the transcription of the reference signal is absent. We evaluate all our proposed methods using both objective and subjective listening tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge