Bajibabu Bollepalli
Distribution augmentation for low-resource expressive text-to-speech
Feb 19, 2022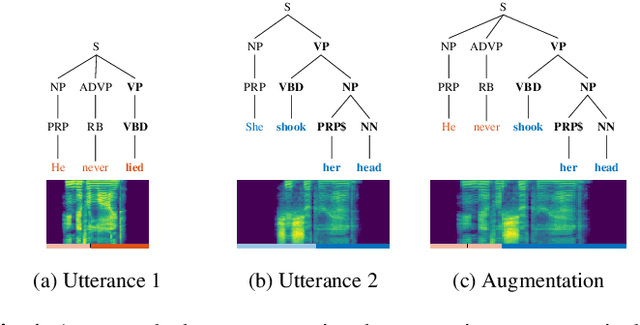
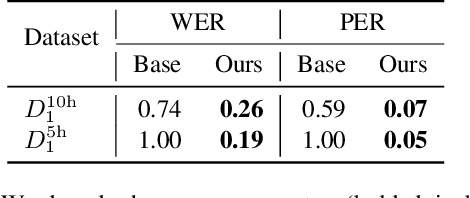
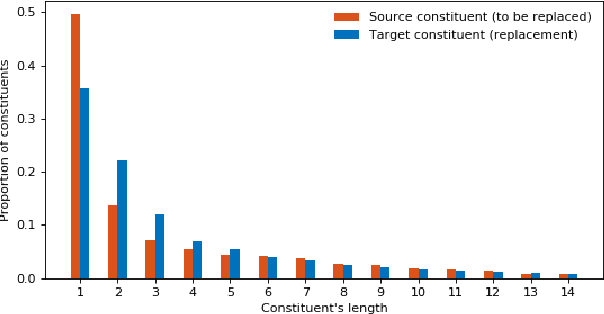
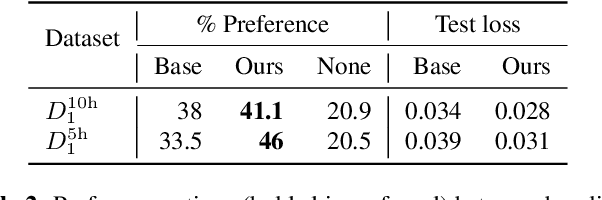
Abstract:This paper presents a novel data augmentation technique for text-to-speech (TTS), that allows to generate new (text, audio) training examples without requiring any additional data. Our goal is to increase diversity of text conditionings available during training. This helps to reduce overfitting, especially in low-resource settings. Our method relies on substituting text and audio fragments in a way that preserves syntactical correctness. We take additional measures to ensure that synthesized speech does not contain artifacts caused by combining inconsistent audio samples. The perceptual evaluations show that our method improves speech quality over a number of datasets, speakers, and TTS architectures. We also demonstrate that it greatly improves robustness of attention-based TTS models.
Formant Tracking Using Quasi-Closed Phase Forward-Backward Linear Prediction Analysis and Deep Neural Networks
Jan 05, 2022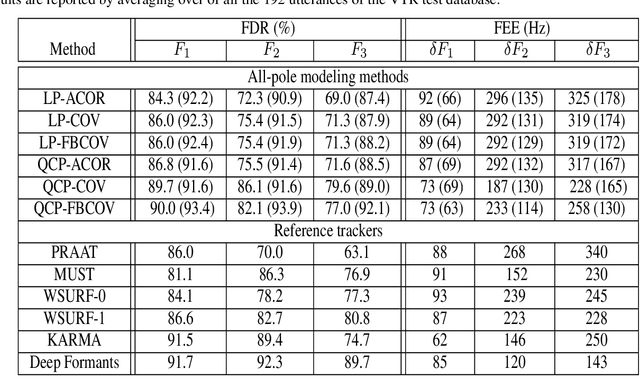
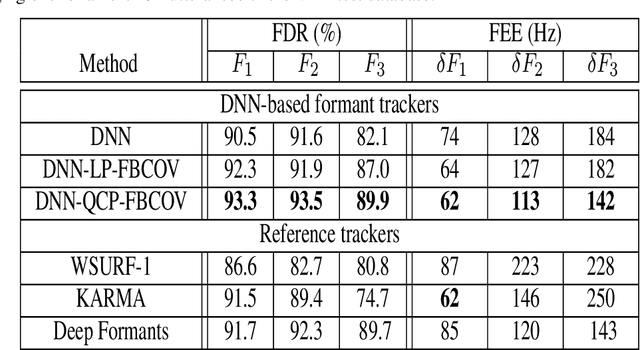
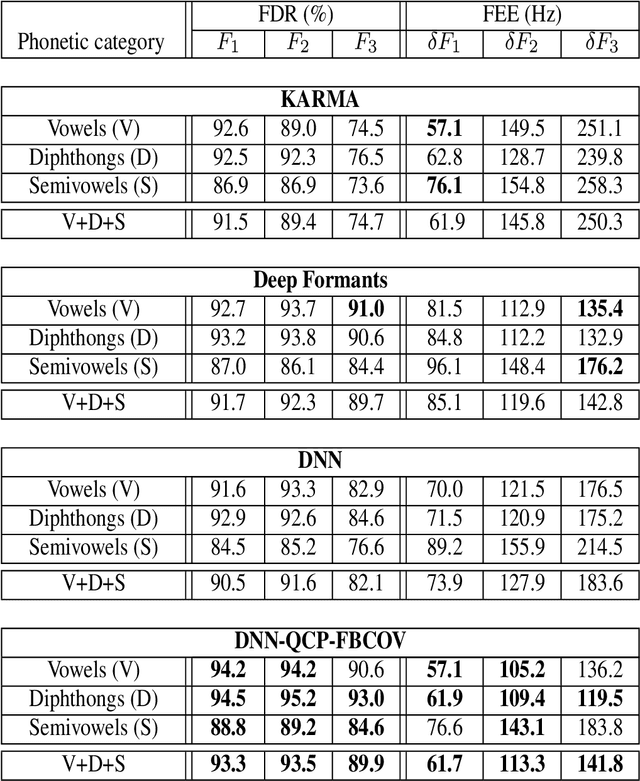
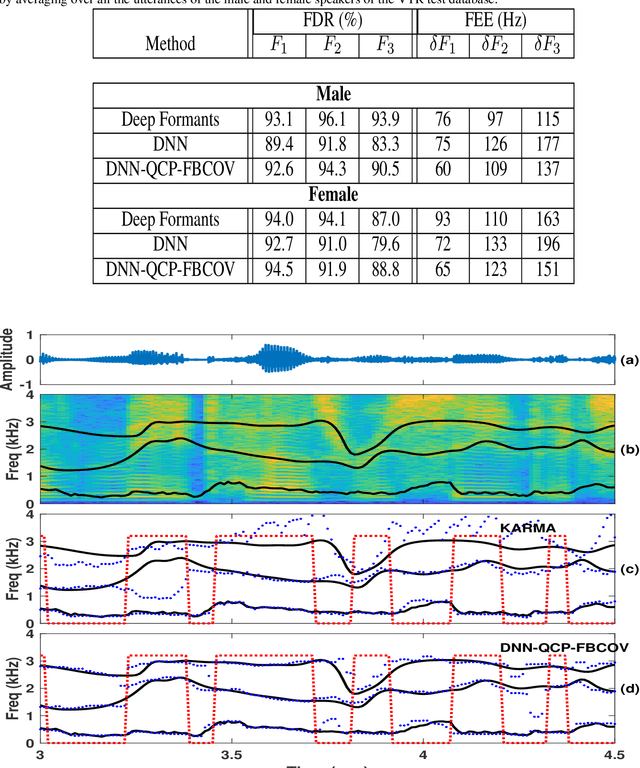
Abstract:Formant tracking is investigated in this study by using trackers based on dynamic programming (DP) and deep neural nets (DNNs). Using the DP approach, six formant estimation methods were first compared. The six methods include linear prediction (LP) algorithms, weighted LP algorithms and the recently developed quasi-closed phase forward-backward (QCP-FB) method. QCP-FB gave the best performance in the comparison. Therefore, a novel formant tracking approach, which combines benefits of deep learning and signal processing based on QCP-FB, was proposed. In this approach, the formants predicted by a DNN-based tracker from a speech frame are refined using the peaks of the all-pole spectrum computed by QCP-FB from the same frame. Results show that the proposed DNN-based tracker performed better both in detection rate and estimation error for the lowest three formants compared to reference formant trackers. Compared to the popular Wavesurfer, for example, the proposed tracker gave a reduction of 29%, 48% and 35% in the estimation error for the lowest three formants, respectively.
Multi-Scale Spectrogram Modelling for Neural Text-to-Speech
Jun 29, 2021
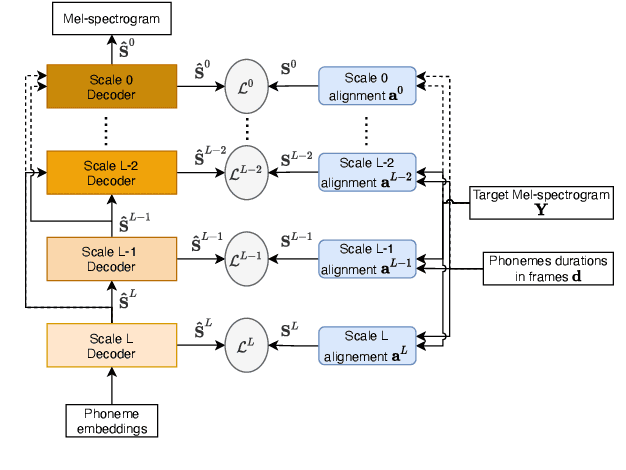
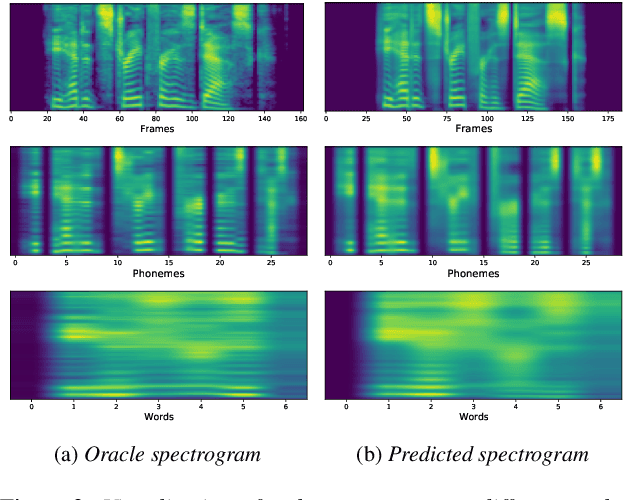
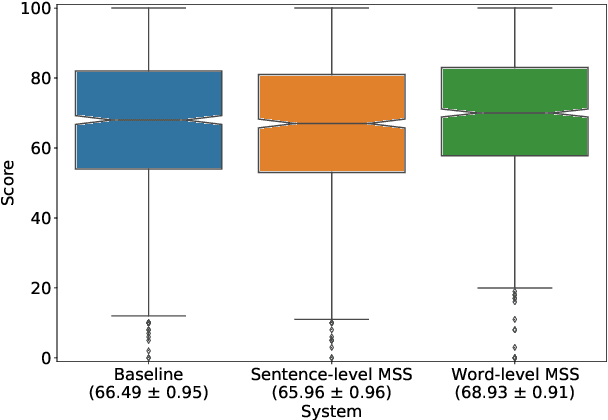
Abstract:We propose a novel Multi-Scale Spectrogram (MSS) modelling approach to synthesise speech with an improved coarse and fine-grained prosody. We present a generic multi-scale spectrogram prediction mechanism where the system first predicts coarser scale mel-spectrograms that capture the suprasegmental information in speech, and later uses these coarser scale mel-spectrograms to predict finer scale mel-spectrograms capturing fine-grained prosody. We present details for two specific versions of MSS called Word-level MSS and Sentence-level MSS where the scales in our system are motivated by the linguistic units. The Word-level MSS models word, phoneme, and frame-level spectrograms while Sentence-level MSS models sentence-level spectrogram in addition. Subjective evaluations show that Word-level MSS performs statistically significantly better compared to the baseline on two voices.
GELP: GAN-Excited Linear Prediction for Speech Synthesis from Mel-spectrogram
Apr 10, 2019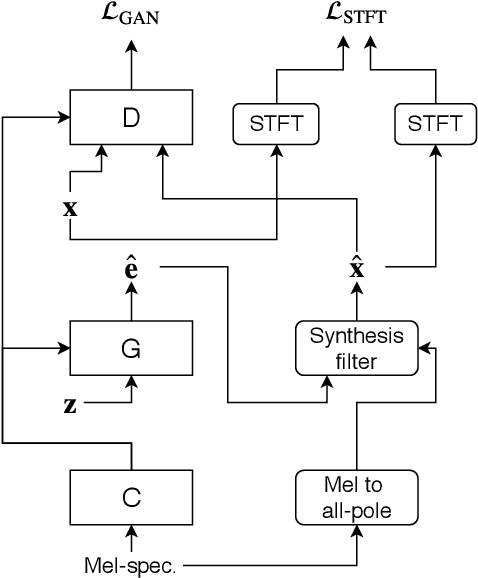
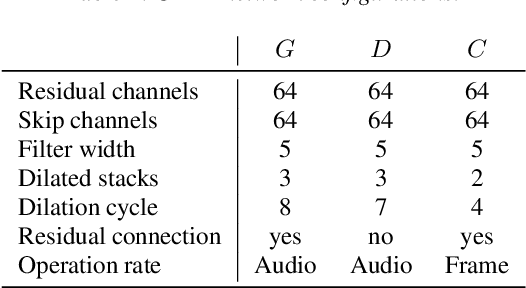
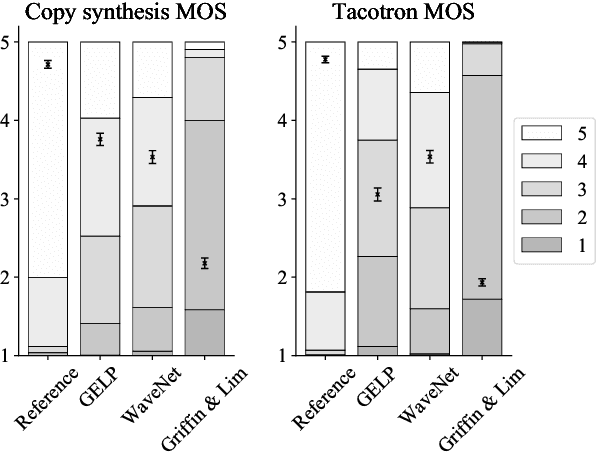
Abstract:Recent advances in neural network -based text-to-speech have reached human level naturalness in synthetic speech. The present sequence-to-sequence models can directly map text to mel-spectrogram acoustic features, which are convenient for modeling, but present additional challenges for vocoding (i.e., waveform generation from the acoustic features). High-quality synthesis can be achieved with neural vocoders, such as WaveNet, but such autoregressive models suffer from slow sequential inference. Meanwhile, their existing parallel inference counterparts are difficult to train and require increasingly large model sizes. In this paper, we propose an alternative training strategy for a parallel neural vocoder utilizing generative adversarial networks, and integrate a linear predictive synthesis filter into the model. Results show that the proposed model achieves significant improvement in inference speed, while outperforming a WaveNet in copy-synthesis quality.
Generative adversarial network-based glottal waveform model for statistical parametric speech synthesis
Mar 14, 2019



Abstract:Recent studies have shown that text-to-speech synthesis quality can be improved by using glottal vocoding. This refers to vocoders that parameterize speech into two parts, the glottal excitation and vocal tract, that occur in the human speech production apparatus. Current glottal vocoders generate the glottal excitation waveform by using deep neural networks (DNNs). However, the squared error-based training of the present glottal excitation models is limited to generating conditional average waveforms, which fails to capture the stochastic variation of the waveforms. As a result, shaped noise is added as post-processing. In this study, we propose a new method for predicting glottal waveforms by generative adversarial networks (GANs). GANs are generative models that aim to embed the data distribution in a latent space, enabling generation of new instances very similar to the original by randomly sampling the latent distribution. The glottal pulses generated by GANs show a stochastic component similar to natural glottal pulses. In our experiments, we compare synthetic speech generated using glottal waveforms produced by both DNNs and GANs. The results show that the newly proposed GANs achieve synthesis quality comparable to that of widely-used DNNs, without using an additive noise component.
* Accepted in Interspeech
Waveform generation for text-to-speech synthesis using pitch-synchronous multi-scale generative adversarial networks
Oct 30, 2018

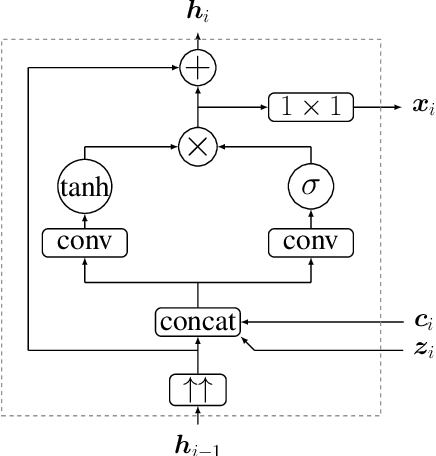
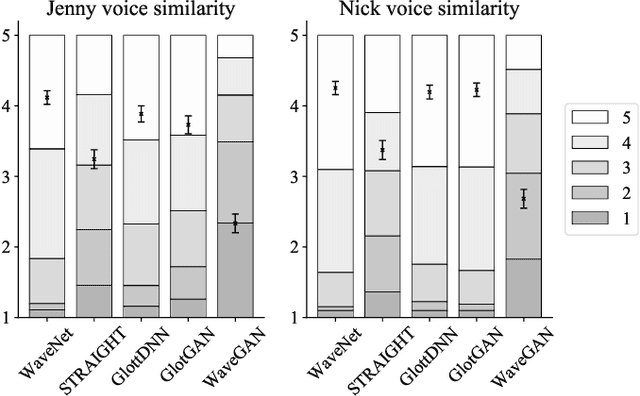
Abstract:The state-of-the-art in text-to-speech synthesis has recently improved considerably due to novel neural waveform generation methods, such as WaveNet. However, these methods suffer from their slow sequential inference process, while their parallel versions are difficult to train and even more expensive computationally. Meanwhile, generative adversarial networks (GANs) have achieved impressive results in image generation and are making their way into audio applications; parallel inference is among their lucrative properties. By adopting recent advances in GAN training techniques, this investigation studies waveform generation for TTS in two domains (speech signal and glottal excitation). Listening test results show that while direct waveform generation with GAN is still far behind WaveNet, a GAN-based glottal excitation model can achieve quality and voice similarity on par with a WaveNet vocoder.
Speaking style adaptation in Text-To-Speech synthesis using Sequence-to-sequence models with attention
Oct 29, 2018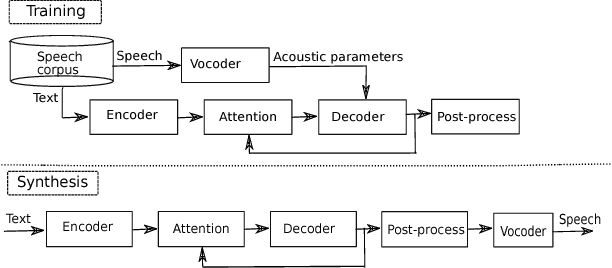
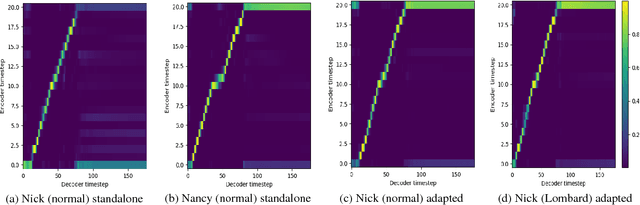

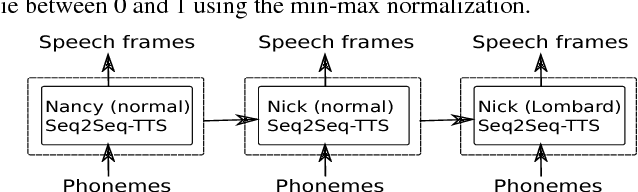
Abstract:Currently, there are increasing interests in text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis to use sequence-to-sequence models with attention. These models are end-to-end meaning that they learn both co-articulation and duration properties directly from text and speech. Since these models are entirely data-driven, they need large amounts of data to generate synthetic speech with good quality. However, in challenging speaking styles, such as Lombard speech, it is difficult to record sufficiently large speech corpora. Therefore, in this study we propose a transfer learning method to adapt a sequence-to-sequence based TTS system of normal speaking style to Lombard style. Moreover, we experiment with a WaveNet vocoder in synthesis of Lombard speech. We conducted subjective evaluations to assess the performance of the adapted TTS systems. The subjective evaluation results indicated that an adaptation system with the WaveNet vocoder clearly outperformed the conventional deep neural network based TTS system in synthesis of Lombard speech.
Speaker-independent raw waveform model for glottal excitation
Apr 25, 2018



Abstract:Recent speech technology research has seen a growing interest in using WaveNets as statistical vocoders, i.e., generating speech waveforms from acoustic features. These models have been shown to improve the generated speech quality over classical vocoders in many tasks, such as text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion. Furthermore, conditioning WaveNets with acoustic features allows sharing the waveform generator model across multiple speakers without additional speaker codes. However, multi-speaker WaveNet models require large amounts of training data and computation to cover the entire acoustic space. This paper proposes leveraging the source-filter model of speech production to more effectively train a speaker-independent waveform generator with limited resources. We present a multi-speaker 'GlotNet' vocoder, which utilizes a WaveNet to generate glottal excitation waveforms, which are then used to excite the corresponding vocal tract filter to produce speech. Listening tests show that the proposed model performs favourably to a direct WaveNet vocoder trained with the same model architecture and data.
Speech waveform synthesis from MFCC sequences with generative adversarial networks
Apr 03, 2018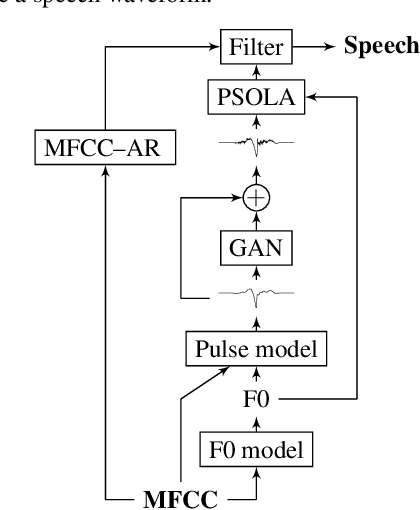


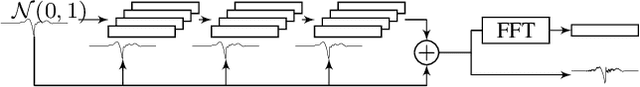
Abstract:This paper proposes a method for generating speech from filterbank mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC), which are widely used in speech applications, such as ASR, but are generally considered unusable for speech synthesis. First, we predict fundamental frequency and voicing information from MFCCs with an autoregressive recurrent neural net. Second, the spectral envelope information contained in MFCCs is converted to all-pole filters, and a pitch-synchronous excitation model matched to these filters is trained. Finally, we introduce a generative adversarial network -based noise model to add a realistic high-frequency stochastic component to the modeled excitation signal. The results show that high quality speech reconstruction can be obtained, given only MFCC information at test time.
DNN-based Speech Synthesis for Indian Languages from ASCII text
Aug 18, 2016
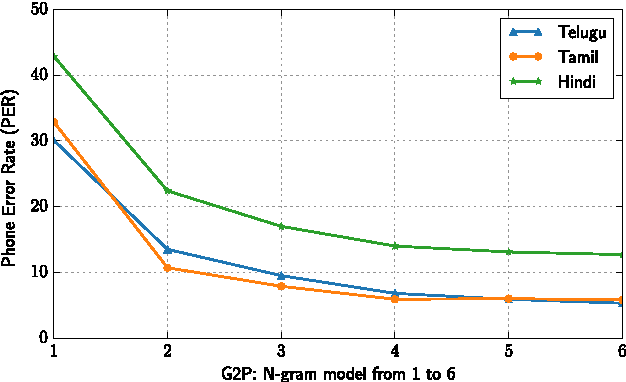
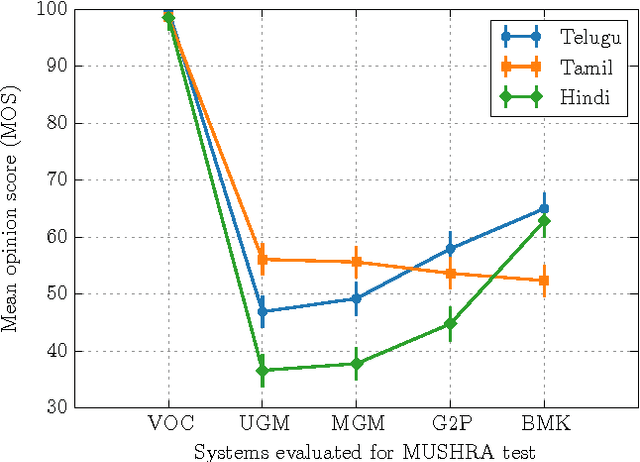

Abstract:Text-to-Speech synthesis in Indian languages has a seen lot of progress over the decade partly due to the annual Blizzard challenges. These systems assume the text to be written in Devanagari or Dravidian scripts which are nearly phonemic orthography scripts. However, the most common form of computer interaction among Indians is ASCII written transliterated text. Such text is generally noisy with many variations in spelling for the same word. In this paper we evaluate three approaches to synthesize speech from such noisy ASCII text: a naive Uni-Grapheme approach, a Multi-Grapheme approach, and a supervised Grapheme-to-Phoneme (G2P) approach. These methods first convert the ASCII text to a phonetic script, and then learn a Deep Neural Network to synthesize speech from that. We train and test our models on Blizzard Challenge datasets that were transliterated to ASCII using crowdsourcing. Our experiments on Hindi, Tamil and Telugu demonstrate that our models generate speech of competetive quality from ASCII text compared to the speech synthesized from the native scripts. All the accompanying transliterated datasets are released for public access.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge