Subhadeep Maji
Universal Semantic Disentangled Privacy-preserving Speech Representation Learning
May 19, 2025Abstract:The use of audio recordings of human speech to train LLMs poses privacy concerns due to these models' potential to generate outputs that closely resemble artifacts in the training data. In this study, we propose a speaker privacy-preserving representation learning method through the Universal Speech Codec (USC), a computationally efficient encoder-decoder model that disentangles speech into: $\textit{(i)}$ privacy-preserving semantically rich representations, capturing content and speech paralinguistics, and $\textit{(ii)}$ residual acoustic and speaker representations that enables high-fidelity reconstruction. Extensive evaluations presented show that USC's semantic representation preserves content, prosody, and sentiment, while removing potentially identifiable speaker attributes. Combining both representations, USC achieves state-of-the-art speech reconstruction. Additionally, we introduce an evaluation methodology for measuring privacy-preserving properties, aligning with perceptual tests. We compare USC against other codecs in the literature and demonstrate its effectiveness on privacy-preserving representation learning, illustrating the trade-offs of speaker anonymization, paralinguistics retention and content preservation in the learned semantic representations. Audio samples are shared in $\href{https://www.amazon.science/usc-samples}{https://www.amazon.science/usc-samples}$.
Efficient data selection employing Semantic Similarity-based Graph Structures for model training
Feb 22, 2024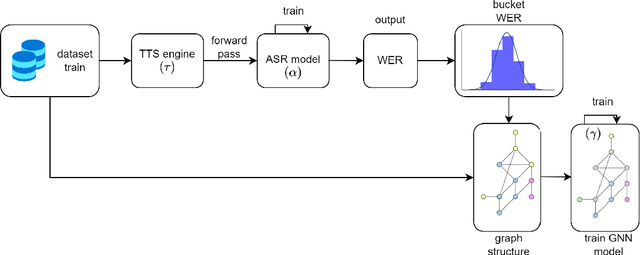
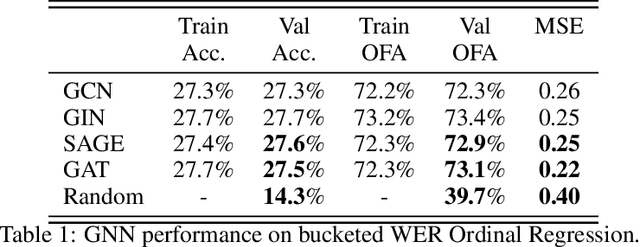
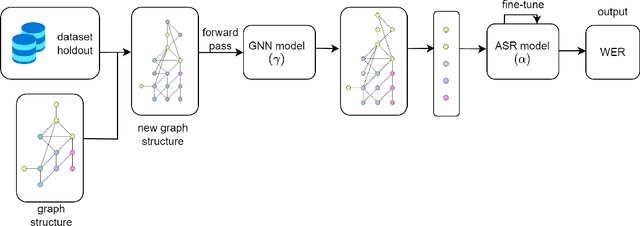
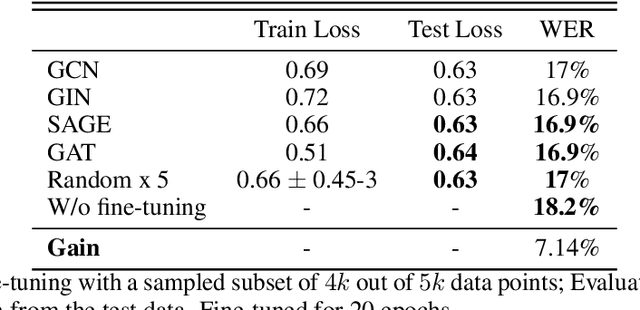
Abstract:Recent developments in natural language processing (NLP) have highlighted the need for substantial amounts of data for models to capture textual information accurately. This raises concerns regarding the computational resources and time required for training such models. This paper introduces Semantics for data SAliency in Model performance Estimation (SeSaME). It is an efficient data sampling mechanism solely based on textual information without passing the data through a compute-heavy model or other intensive pre-processing transformations. The application of this approach is demonstrated in the use case of low-resource automated speech recognition (ASR) models, which excessively rely on text-to-speech (TTS) calls when using augmented data. SeSaME learns to categorize new incoming data points into speech recognition difficulty buckets by employing semantic similarity-based graph structures and discrete ASR information from homophilous neighbourhoods through message passing. The results indicate reliable projections of ASR performance, with a 93% accuracy increase when using the proposed method compared to random predictions, bringing non-trivial information on the impact of textual representations in speech models. Furthermore, a series of experiments show both the benefits and challenges of using the ASR information on incoming data to fine-tune the model. We report a 7% drop in validation loss compared to random sampling, 7% WER drop with non-local aggregation when evaluating against a highly difficult dataset, and 1.8% WER drop with local aggregation and high semantic similarity between datasets.
Graph Neural Network Enhanced Language Models for Efficient Multilingual Text Classification
Mar 06, 2022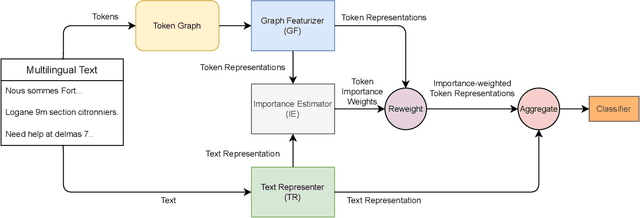
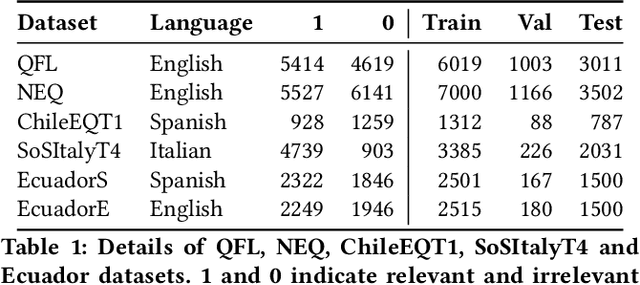
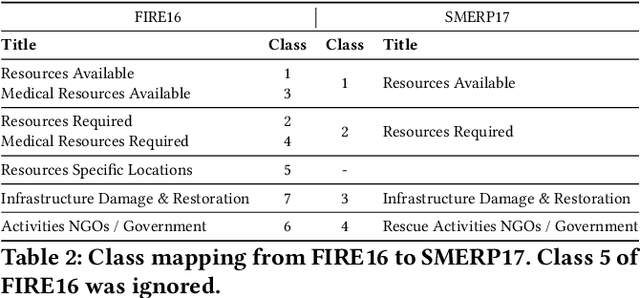
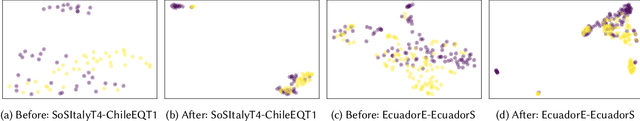
Abstract:Online social media works as a source of various valuable and actionable information during disasters. These information might be available in multiple languages due to the nature of user generated content. An effective system to automatically identify and categorize these actionable information should be capable to handle multiple languages and under limited supervision. However, existing works mostly focus on English language only with the assumption that sufficient labeled data is available. To overcome these challenges, we propose a multilingual disaster related text classification system which is capable to work under \{mono, cross and multi\} lingual scenarios and under limited supervision. Our end-to-end trainable framework combines the versatility of graph neural networks, by applying over the corpus, with the power of transformer based large language models, over examples, with the help of cross-attention between the two. We evaluate our framework over total nine English, Non-English and monolingual datasets in \{mono, cross and multi\} lingual classification scenarios. Our framework outperforms state-of-the-art models in disaster domain and multilingual BERT baseline in terms of Weighted F$_1$ score. We also show the generalizability of the proposed model under limited supervision.
Supervised Graph Contrastive Pretraining for Text Classification
Dec 21, 2021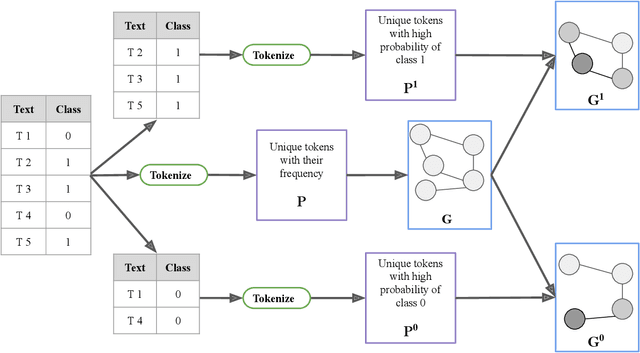
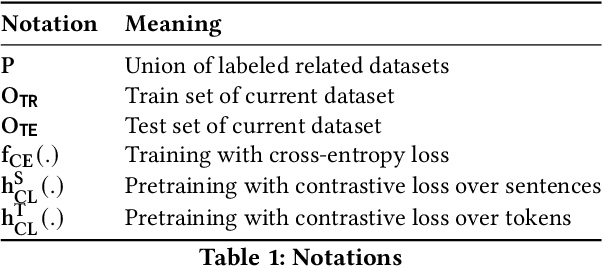
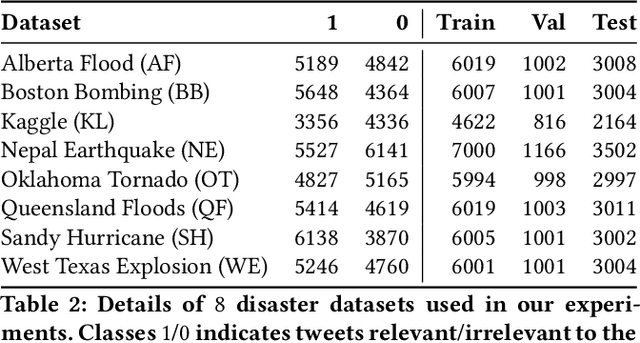
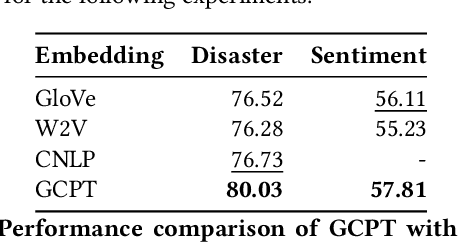
Abstract:Contrastive pretraining techniques for text classification has been largely studied in an unsupervised setting. However, oftentimes labeled data from related tasks which share label semantics with current task is available. We hypothesize that using this labeled data effectively can lead to better generalization on current task. In this paper, we propose a novel way to effectively utilize labeled data from related tasks with a graph based supervised contrastive learning approach. We formulate a token-graph by extrapolating the supervised information from examples to tokens. Our formulation results in an embedding space where tokens with high/low probability of belonging to same class are near/further-away from one another. We also develop detailed theoretical insights which serve as a motivation for our method. In our experiments with $13$ datasets, we show our method outperforms pretraining schemes by $2.5\%$ and also example-level contrastive learning based formulation by $1.8\%$ on average. In addition, we show cross-domain effectiveness of our method in a zero-shot setting by $3.91\%$ on average. Lastly, we also demonstrate our method can be used as a noisy teacher in a knowledge distillation setting to significantly improve performance of transformer based models in low labeled data regime by $4.57\%$ on average.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Global and Local Graph Neural Networks in Limited Labeled Data Scenario: Application to Disaster Management
Apr 03, 2021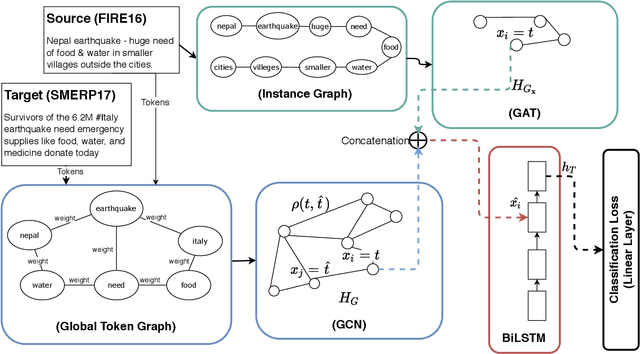
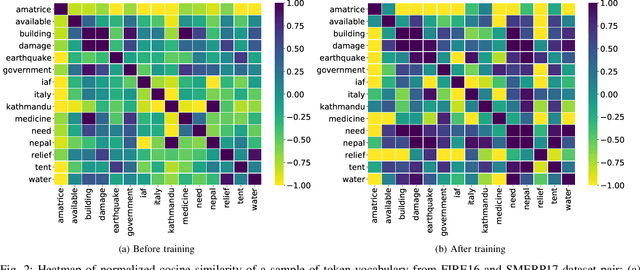
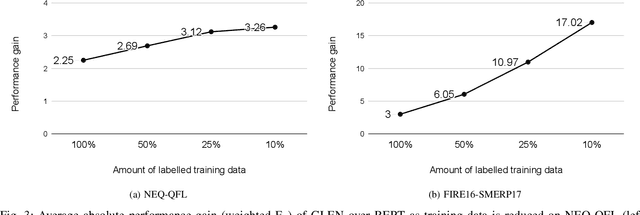

Abstract:Identification and categorization of social media posts generated during disasters are crucial to reduce the sufferings of the affected people. However, lack of labeled data is a significant bottleneck in learning an effective categorization system for a disaster. This motivates us to study the problem as unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) between a previous disaster with labeled data (source) and a current disaster (target). However, if the amount of labeled data available is limited, it restricts the learning capabilities of the model. To handle this challenge, we utilize limited labeled data along with abundantly available unlabeled data, generated during a source disaster to propose a novel two-part graph neural network. The first-part extracts domain-agnostic global information by constructing a token level graph across domains and the second-part preserves local instance-level semantics. In our experiments, we show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques by $2.74\%$ weighted F$_1$ score on average on two standard public dataset in the area of disaster management. We also report experimental results for granular actionable multi-label classification datasets in disaster domain for the first time, on which we outperform BERT by $3.00\%$ on average w.r.t weighted F$_1$. Additionally, we show that our approach can retain performance when very limited labeled data is available.
Reproducibility, Replicability and Beyond: Assessing Production Readiness of Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis in the Wild
Jan 23, 2021
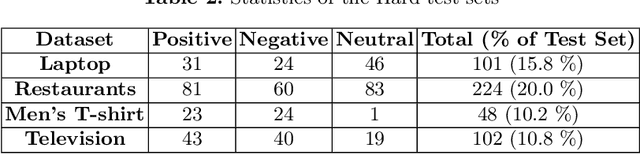
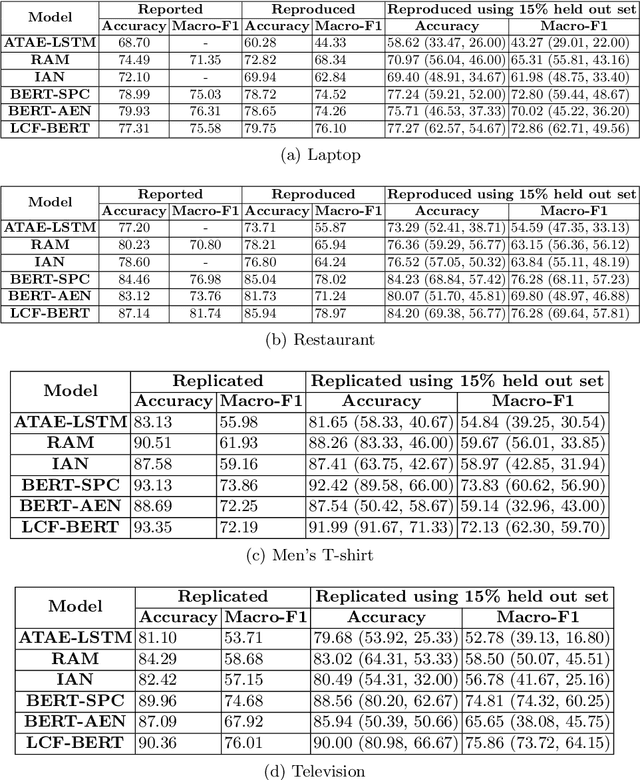
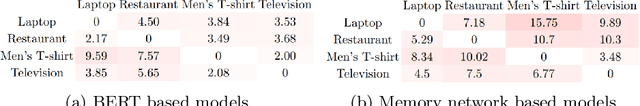
Abstract:With the exponential growth of online marketplaces and user-generated content therein, aspect-based sentiment analysis has become more important than ever. In this work, we critically review a representative sample of the models published during the past six years through the lens of a practitioner, with an eye towards deployment in production. First, our rigorous empirical evaluation reveals poor reproducibility: an average 4-5% drop in test accuracy across the sample. Second, to further bolster our confidence in empirical evaluation, we report experiments on two challenging data slices, and observe a consistent 12-55% drop in accuracy. Third, we study the possibility of transfer across domains and observe that as little as 10-25% of the domain-specific training dataset, when used in conjunction with datasets from other domains within the same locale, largely closes the gap between complete cross-domain and complete in-domain predictive performance. Lastly, we open-source two large-scale annotated review corpora from a large e-commerce portal in India in order to aid the study of replicability and transfer, with the hope that it will fuel further growth of the field.
Logic Constrained Pointer Networks for Interpretable Textual Similarity
Jul 15, 2020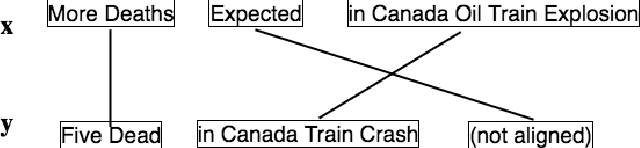

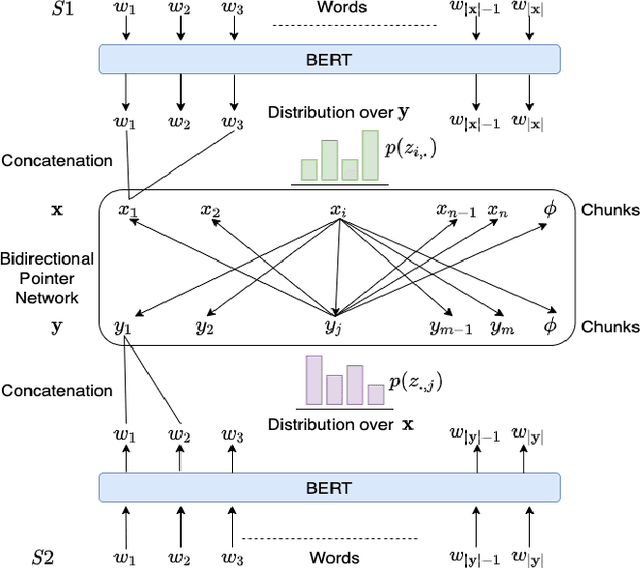
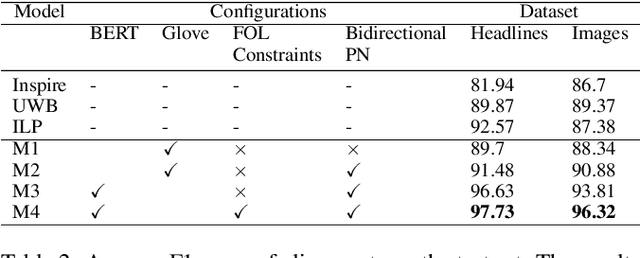
Abstract:Systematically discovering semantic relationships in text is an important and extensively studied area in Natural Language Processing, with various tasks such as entailment, semantic similarity, etc. Decomposability of sentence-level scores via subsequence alignments has been proposed as a way to make models more interpretable. We study the problem of aligning components of sentences leading to an interpretable model for semantic textual similarity. In this paper, we introduce a novel pointer network based model with a sentinel gating function to align constituent chunks, which are represented using BERT. We improve this base model with a loss function to equally penalize misalignments in both sentences, ensuring the alignments are bidirectional. Finally, to guide the network with structured external knowledge, we introduce first-order logic constraints based on ConceptNet and syntactic knowledge. The model achieves an F1 score of 97.73 and 96.32 on the benchmark SemEval datasets for the chunk alignment task, showing large improvements over the existing solutions. Source code is available at https://github.com/manishb89/interpretable_sentence_similarity
* Accepted at IJCAI 2020 Main Track. Sole copyright holder is IJCAI, all rights reserved. Available at https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/2020/333
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge