Shreyas Shetty
A Teacher Is Worth A Million Instructions
Jun 27, 2024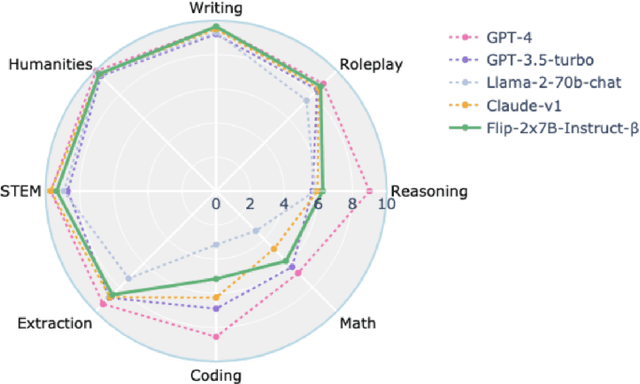
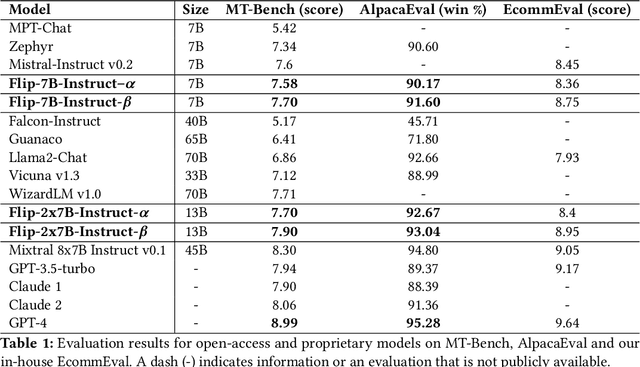
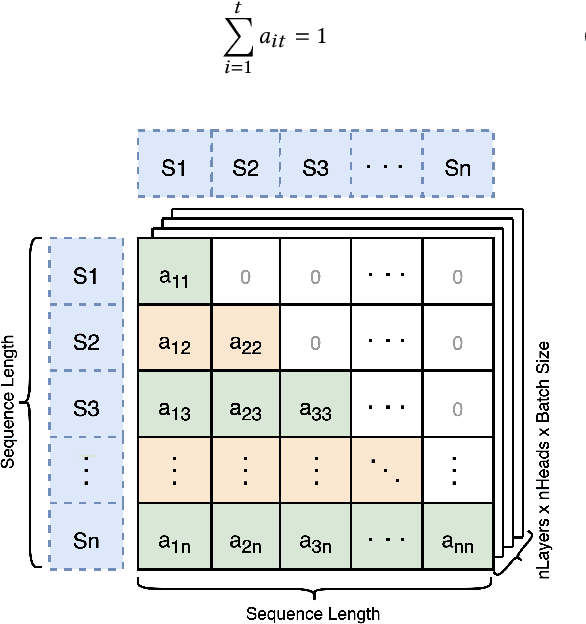
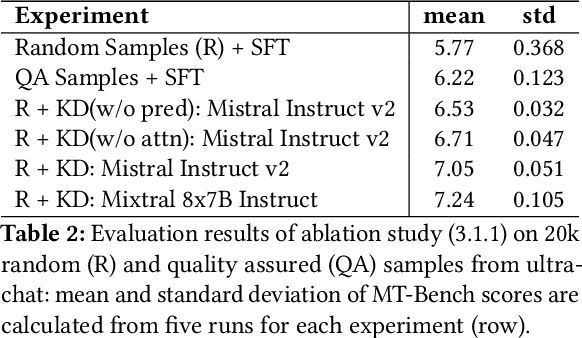
Abstract:Large Language Models(LLMs) have shown exceptional abilities, yet training these models can be quite challenging. There is a strong dependence on the quality of data and finding the best instruction tuning set. Further, the inherent limitations in training methods create substantial difficulties to train relatively smaller models with 7B and 13B parameters. In our research, we suggest an improved training method for these models by utilising knowledge from larger models, such as a mixture of experts (8x7B) architectures. The scale of these larger models allows them to capture a wide range of variations from data alone, making them effective teachers for smaller models. Moreover, we implement a novel post-training domain alignment phase that employs domain-specific expert models to boost domain-specific knowledge during training while preserving the model's ability to generalise. Fine-tuning Mistral 7B and 2x7B with our method surpasses the performance of state-of-the-art language models with more than 7B and 13B parameters: achieving up to $7.9$ in MT-Bench and $93.04\%$ on AlpacaEval.
Reproducibility, Replicability and Beyond: Assessing Production Readiness of Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis in the Wild
Jan 23, 2021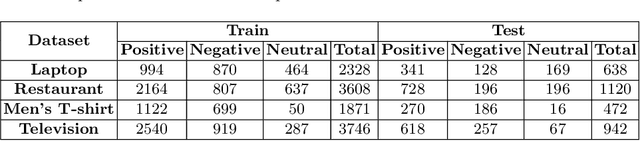
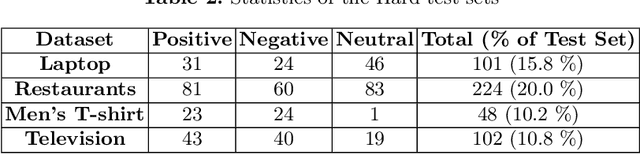
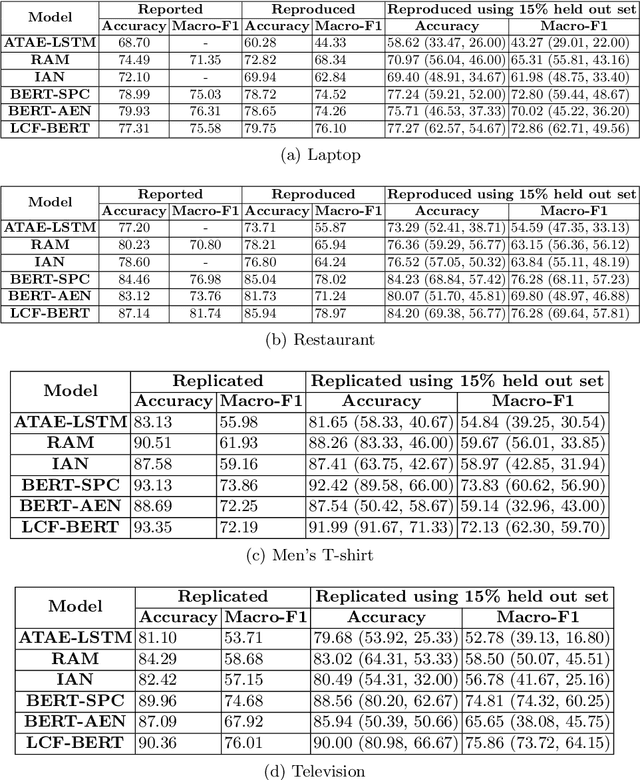
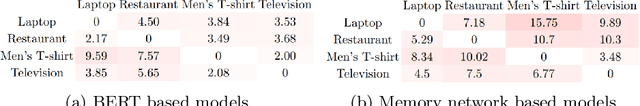
Abstract:With the exponential growth of online marketplaces and user-generated content therein, aspect-based sentiment analysis has become more important than ever. In this work, we critically review a representative sample of the models published during the past six years through the lens of a practitioner, with an eye towards deployment in production. First, our rigorous empirical evaluation reveals poor reproducibility: an average 4-5% drop in test accuracy across the sample. Second, to further bolster our confidence in empirical evaluation, we report experiments on two challenging data slices, and observe a consistent 12-55% drop in accuracy. Third, we study the possibility of transfer across domains and observe that as little as 10-25% of the domain-specific training dataset, when used in conjunction with datasets from other domains within the same locale, largely closes the gap between complete cross-domain and complete in-domain predictive performance. Lastly, we open-source two large-scale annotated review corpora from a large e-commerce portal in India in order to aid the study of replicability and transfer, with the hope that it will fuel further growth of the field.
A Mixed Hierarchical Attention based Encoder-Decoder Approach for Standard Table Summarization
Apr 20, 2018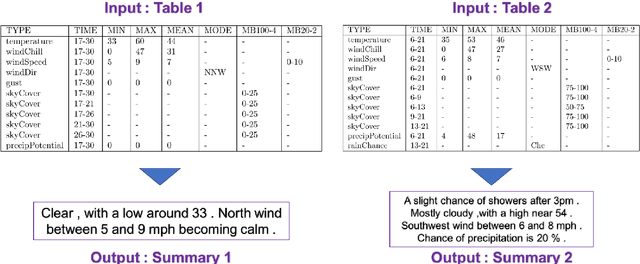
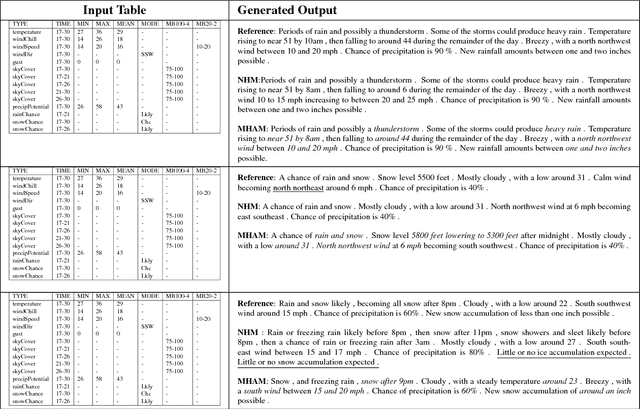
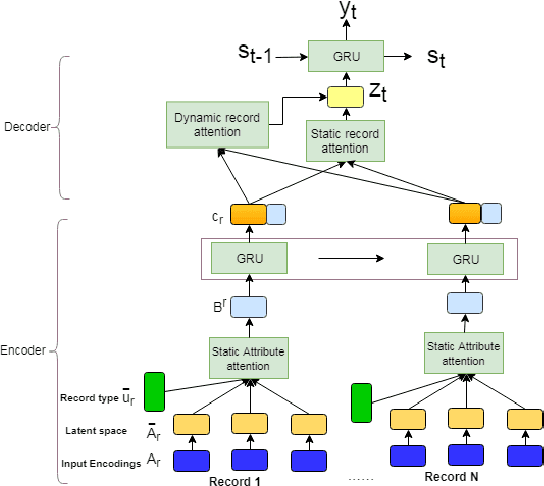
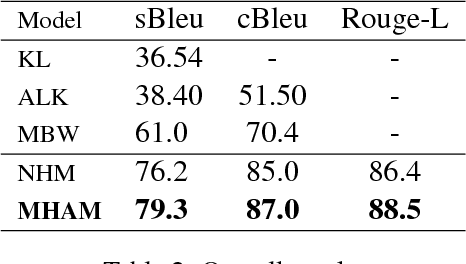
Abstract:Structured data summarization involves generation of natural language summaries from structured input data. In this work, we consider summarizing structured data occurring in the form of tables as they are prevalent across a wide variety of domains. We formulate the standard table summarization problem, which deals with tables conforming to a single predefined schema. To this end, we propose a mixed hierarchical attention based encoder-decoder model which is able to leverage the structure in addition to the content of the tables. Our experiments on the publicly available WEATHERGOV dataset show around 18 BLEU (~ 30%) improvement over the current state-of-the-art.
Generating Descriptions from Structured Data Using a Bifocal Attention Mechanism and Gated Orthogonalization
Apr 20, 2018
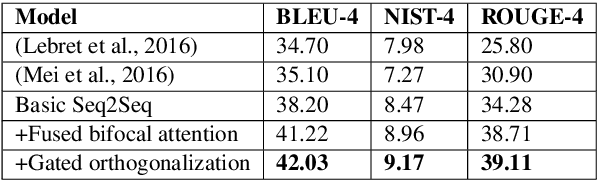
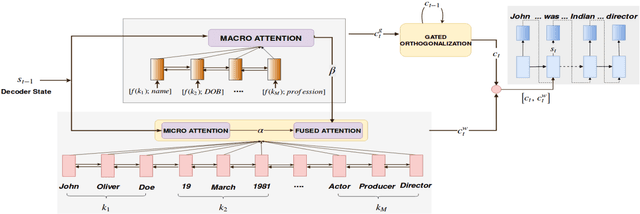

Abstract:In this work, we focus on the task of generating natural language descriptions from a structured table of facts containing fields (such as nationality, occupation, etc) and values (such as Indian, actor, director, etc). One simple choice is to treat the table as a sequence of fields and values and then use a standard seq2seq model for this task. However, such a model is too generic and does not exploit task-specific characteristics. For example, while generating descriptions from a table, a human would attend to information at two levels: (i) the fields (macro level) and (ii) the values within the field (micro level). Further, a human would continue attending to a field for a few timesteps till all the information from that field has been rendered and then never return back to this field (because there is nothing left to say about it). To capture this behavior we use (i) a fused bifocal attention mechanism which exploits and combines this micro and macro level information and (ii) a gated orthogonalization mechanism which tries to ensure that a field is remembered for a few time steps and then forgotten. We experiment with a recently released dataset which contains fact tables about people and their corresponding one line biographical descriptions in English. In addition, we also introduce two similar datasets for French and German. Our experiments show that the proposed model gives 21% relative improvement over a recently proposed state of the art method and 10% relative improvement over basic seq2seq models. The code and the datasets developed as a part of this work are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge