Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Global and Local Graph Neural Networks in Limited Labeled Data Scenario: Application to Disaster Management
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2021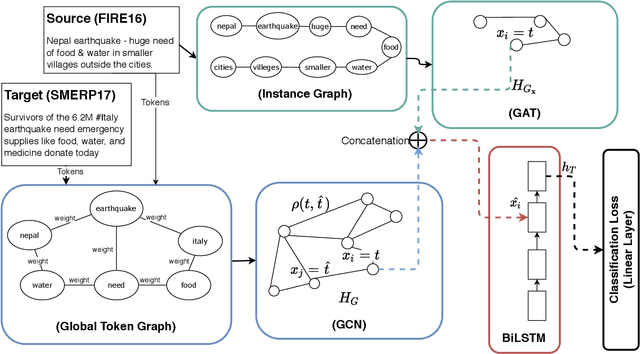
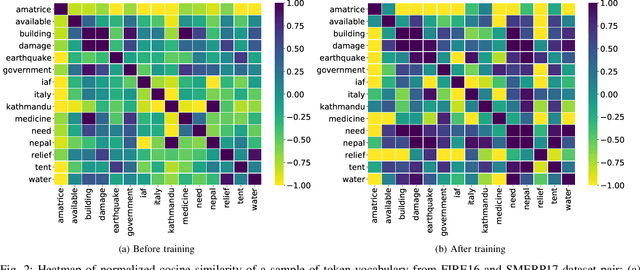
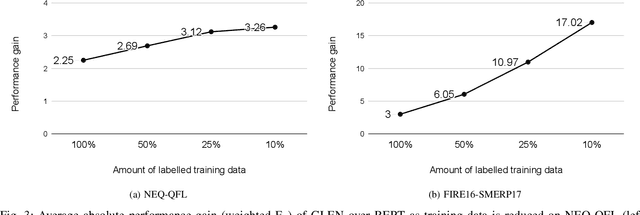

Identification and categorization of social media posts generated during disasters are crucial to reduce the sufferings of the affected people. However, lack of labeled data is a significant bottleneck in learning an effective categorization system for a disaster. This motivates us to study the problem as unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) between a previous disaster with labeled data (source) and a current disaster (target). However, if the amount of labeled data available is limited, it restricts the learning capabilities of the model. To handle this challenge, we utilize limited labeled data along with abundantly available unlabeled data, generated during a source disaster to propose a novel two-part graph neural network. The first-part extracts domain-agnostic global information by constructing a token level graph across domains and the second-part preserves local instance-level semantics. In our experiments, we show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques by $2.74\%$ weighted F$_1$ score on average on two standard public dataset in the area of disaster management. We also report experimental results for granular actionable multi-label classification datasets in disaster domain for the first time, on which we outperform BERT by $3.00\%$ on average w.r.t weighted F$_1$. Additionally, we show that our approach can retain performance when very limited labeled data is available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge