Kalyani Roy
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
A Simple yet Efficient Ensemble Approach for AI-generated Text Detection
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:Recent Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating text that closely resembles human writing across wide range of styles and genres. However, such capabilities are prone to potential abuse, such as fake news generation, spam email creation, and misuse in academic assignments. Hence, it is essential to build automated approaches capable of distinguishing between artificially generated text and human-authored text. In this paper, we propose a simple yet efficient solution to this problem by ensembling predictions from multiple constituent LLMs. Compared to previous state-of-the-art approaches, which are perplexity-based or uses ensembles with a number of LLMs, our condensed ensembling approach uses only two constituent LLMs to achieve comparable performance. Experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets for generative text classification show performance improvements in the range of 0.5 to 100\% compared to previous state-of-the-art approaches. We also study the influence that the training data from individual LLMs have on model performance. We found that substituting commercially-restrictive Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) data with data generated from other open language models such as Falcon, Large Language Model Meta AI (LLaMA2), and Mosaic Pretrained Transformers (MPT) is a feasible alternative when developing generative text detectors. Furthermore, to demonstrate zero-shot generalization, we experimented with an English essays dataset, and results suggest that our ensembling approach can handle new data effectively.
Exploring Generative Models for Joint Attribute Value Extraction from Product Titles
Aug 15, 2022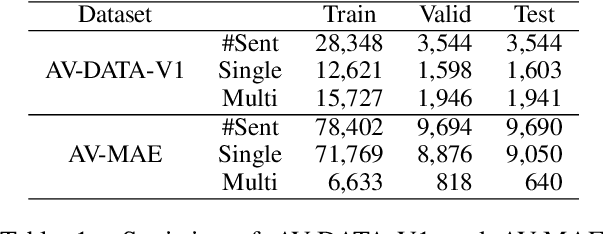
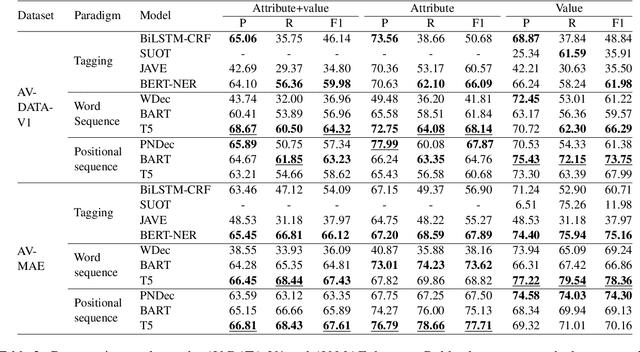
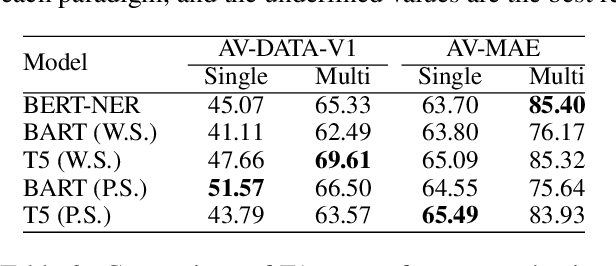

Abstract:Attribute values of the products are an essential component in any e-commerce platform. Attribute Value Extraction (AVE) deals with extracting the attributes of a product and their values from its title or description. In this paper, we propose to tackle the AVE task using generative frameworks. We present two types of generative paradigms, namely, word sequence-based and positional sequence-based, by formulating the AVE task as a generation problem. We conduct experiments on two datasets where the generative approaches achieve the new state-of-the-art results. This shows that we can use the proposed framework for AVE tasks without additional tagging or task-specific model design.
Logic Constrained Pointer Networks for Interpretable Textual Similarity
Jul 15, 2020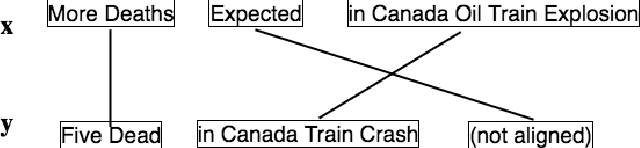

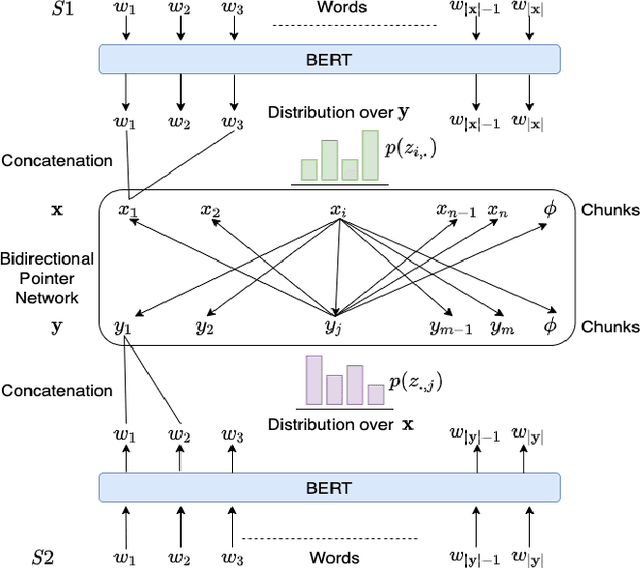
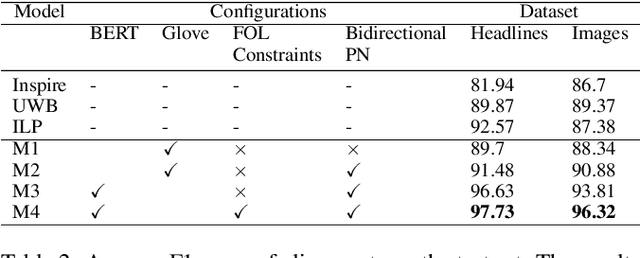
Abstract:Systematically discovering semantic relationships in text is an important and extensively studied area in Natural Language Processing, with various tasks such as entailment, semantic similarity, etc. Decomposability of sentence-level scores via subsequence alignments has been proposed as a way to make models more interpretable. We study the problem of aligning components of sentences leading to an interpretable model for semantic textual similarity. In this paper, we introduce a novel pointer network based model with a sentinel gating function to align constituent chunks, which are represented using BERT. We improve this base model with a loss function to equally penalize misalignments in both sentences, ensuring the alignments are bidirectional. Finally, to guide the network with structured external knowledge, we introduce first-order logic constraints based on ConceptNet and syntactic knowledge. The model achieves an F1 score of 97.73 and 96.32 on the benchmark SemEval datasets for the chunk alignment task, showing large improvements over the existing solutions. Source code is available at https://github.com/manishb89/interpretable_sentence_similarity
* Accepted at IJCAI 2020 Main Track. Sole copyright holder is IJCAI, all rights reserved. Available at https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/2020/333
Using Large Pretrained Language Models for Answering User Queries from Product Specifications
May 29, 2020



Abstract:While buying a product from the e-commerce websites, customers generally have a plethora of questions. From the perspective of both the e-commerce service provider as well as the customers, there must be an effective question answering system to provide immediate answers to the user queries. While certain questions can only be answered after using the product, there are many questions which can be answered from the product specification itself. Our work takes a first step in this direction by finding out the relevant product specifications, that can help answering the user questions. We propose an approach to automatically create a training dataset for this problem. We utilize recently proposed XLNet and BERT architectures for this problem and find that they provide much better performance than the Siamese model, previously applied for this problem. Our model gives a good performance even when trained on one vertical and tested across different verticals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge