Mireia Farrús
MuSeD: A Multimodal Spanish Dataset for Sexism Detection in Social Media Videos
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Sexism is generally defined as prejudice and discrimination based on sex or gender, affecting every sector of society, from social institutions to relationships and individual behavior. Social media platforms amplify the impact of sexism by conveying discriminatory content not only through text but also across multiple modalities, highlighting the critical need for a multimodal approach to the analysis of sexism online. With the rise of social media platforms where users share short videos, sexism is increasingly spreading through video content. Automatically detecting sexism in videos is a challenging task, as it requires analyzing the combination of verbal, audio, and visual elements to identify sexist content. In this study, (1) we introduce MuSeD, a new Multimodal Spanish dataset for Sexism Detection consisting of $\approx$ 11 hours of videos extracted from TikTok and BitChute; (2) we propose an innovative annotation framework for analyzing the contribution of textual and multimodal labels in the classification of sexist and non-sexist content; and (3) we evaluate a range of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal LLMs on the task of sexism detection. We find that visual information plays a key role in labeling sexist content for both humans and models. Models effectively detect explicit sexism; however, they struggle with implicit cases, such as stereotypes, instances where annotators also show low agreement. This highlights the inherent difficulty of the task, as identifying implicit sexism depends on the social and cultural context.
Data Augmentation for Low-Resource Quechua ASR Improvement
Jul 14, 2022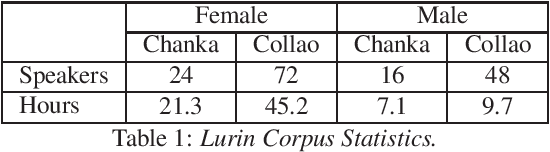
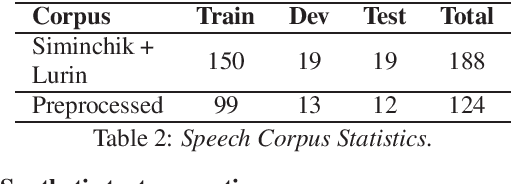
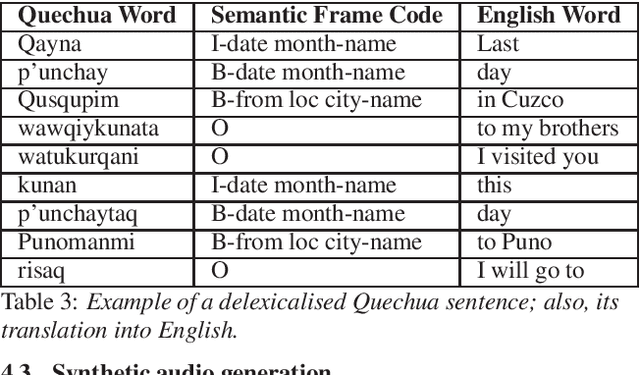
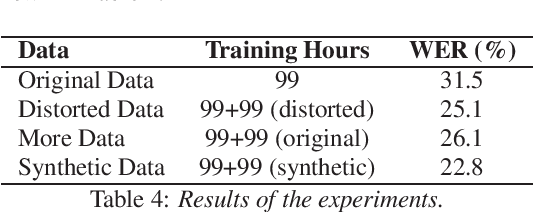
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is a key element in new services that helps users to interact with an automated system. Deep learning methods have made it possible to deploy systems with word error rates below 5% for ASR of English. However, the use of these methods is only available for languages with hundreds or thousands of hours of audio and their corresponding transcriptions. For the so-called low-resource languages to speed up the availability of resources that can improve the performance of their ASR systems, methods of creating new resources on the basis of existing ones are being investigated. In this paper we describe our data augmentation approach to improve the results of ASR models for low-resource and agglutinative languages. We carry out experiments developing an ASR for Quechua using the wav2letter++ model. We reduced WER by 8.73% through our approach to the base model. The resulting ASR model obtained 22.75% WER and was trained with 99 hours of original resources and 99 hours of synthetic data obtained with a combination of text augmentation and synthetic speech generati
Voice Quality and Pitch Features in Transformer-Based Speech Recognition
Dec 21, 2021
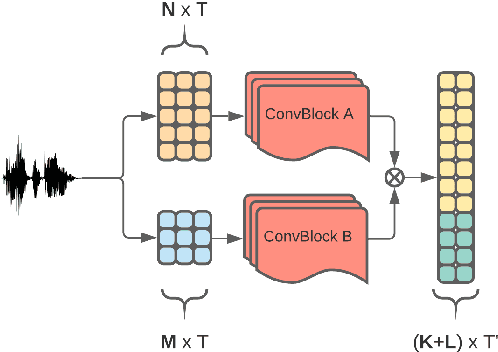
Abstract:Jitter and shimmer measurements have shown to be carriers of voice quality and prosodic information which enhance the performance of tasks like speaker recognition, diarization or automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, such features have been seldom used in the context of neural-based ASR, where spectral features often prevail. In this work, we study the effects of incorporating voice quality and pitch features altogether and separately to a Transformer-based ASR model, with the intuition that the attention mechanisms might exploit latent prosodic traits. For doing so, we propose separated convolutional front-ends for prosodic and spectral features, showing that this architectural choice yields better results than simple concatenation of such pitch and voice quality features to mel-spectrogram filterbanks. Furthermore, we find mean Word Error Rate relative reductions of up to 5.6% with the LibriSpeech benchmark. Such findings motivate further research on the application of prosody knowledge for increasing the robustness of Transformer-based ASR.
English Accent Accuracy Analysis in a State-of-the-Art Automatic Speech Recognition System
May 09, 2021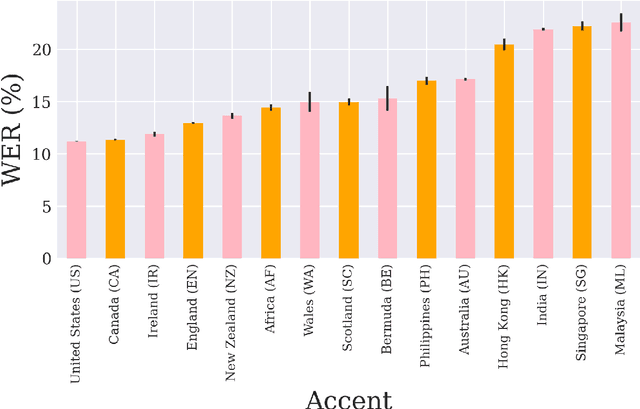
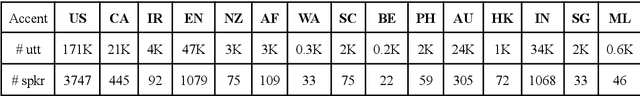
Abstract:Nowadays, research in speech technologies has gotten a lot out thanks to recently created public domain corpora that contain thousands of recording hours. These large amounts of data are very helpful for training the new complex models based on deep learning technologies. However, the lack of dialectal diversity in a corpus is known to cause performance biases in speech systems, mainly for underrepresented dialects. In this work, we propose to evaluate a state-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) deep learning-based model, using unseen data from a corpus with a wide variety of labeled English accents from different countries around the world. The model has been trained with 44.5K hours of English speech from an open access corpus called Multilingual LibriSpeech, showing remarkable results in popular benchmarks. We test the accuracy of such ASR against samples extracted from another public corpus that is continuously growing, the Common Voice dataset. Then, we present graphically the accuracy in terms of Word Error Rate of each of the different English included accents, showing that there is indeed an accuracy bias in terms of accentual variety, favoring the accents most prevalent in the training corpus.
BCN2BRNO: ASR System Fusion for Albayzin 2020 Speech to Text Challenge
Jan 29, 2021
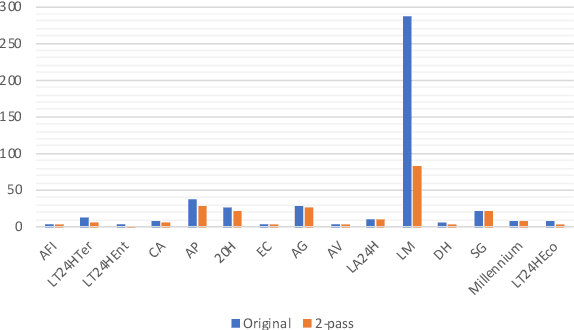
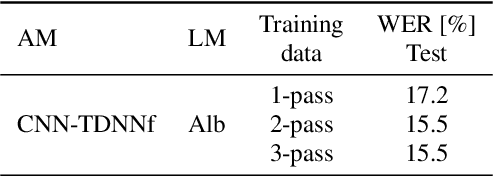
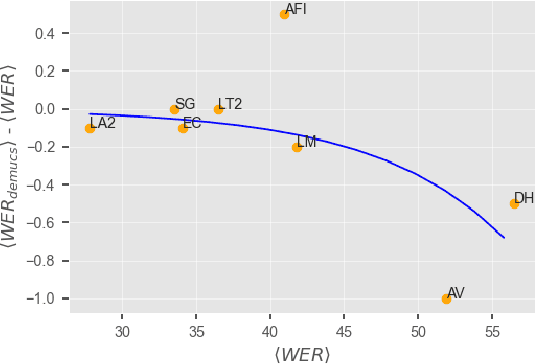
Abstract:This paper describes joint effort of BUT and Telef\'onica Research on development of Automatic Speech Recognition systems for Albayzin 2020 Challenge. We compare approaches based on either hybrid or end-to-end models. In hybrid modelling, we explore the impact of SpecAugment layer on performance. For end-to-end modelling, we used a convolutional neural network with gated linear units (GLUs). The performance of such model is also evaluated with an additional n-gram language model to improve word error rates. We further inspect source separation methods to extract speech from noisy environment (i.e. TV shows). More precisely, we assess the effect of using a neural-based music separator named Demucs. A fusion of our best systems achieved 23.33% WER in official Albayzin 2020 evaluations. Aside from techniques used in our final submitted systems, we also describe our efforts in retrieving high quality transcripts for training.
Combining Prosodic, Voice Quality and Lexical Features to Automatically Detect Alzheimer's Disease
Nov 18, 2020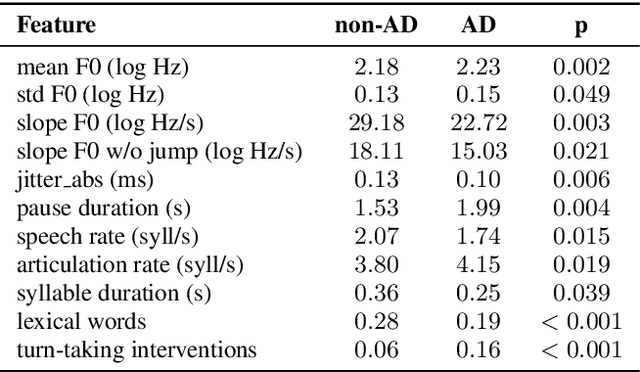
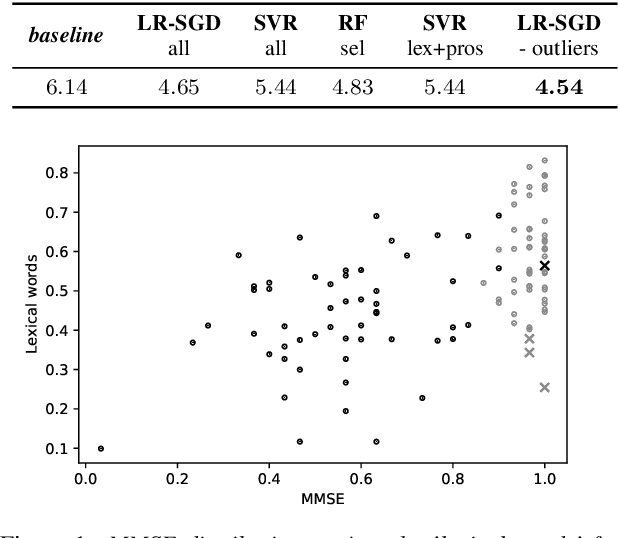
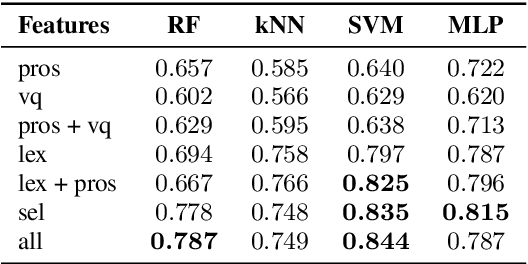
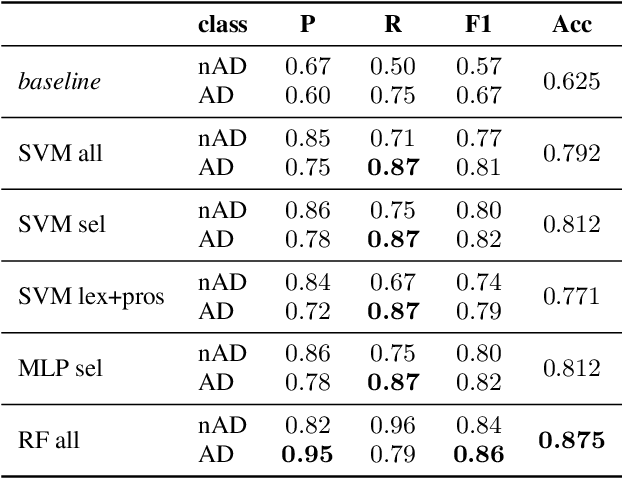
Abstract:Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is nowadays the most common form of dementia, and its automatic detection can help to identify symptoms at early stages, so that preventive actions can be carried out. Moreover, non-intrusive techniques based on spoken data are crucial for the development of AD automatic detection systems. In this light, this paper is presented as a contribution to the ADReSS Challenge, aiming at improving AD automatic detection from spontaneous speech. To this end, recordings from 108 participants, which are age-, gender-, and AD condition-balanced, have been used as training set to perform two different tasks: classification into AD/non-AD conditions, and regression over the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores. Both tasks have been performed extracting 28 features from speech -- based on prosody and voice quality -- and 51 features from the transcriptions -- based on lexical and turn-taking information. Our results achieved up to 87.5 % of classification accuracy using a Random Forest classifier, and 4.54 of RMSE using a linear regression with stochastic gradient descent over the provided test set. This shows promising results in the automatic detection of Alzheimer's Disease through speech and lexical features.
Convolutional Speech Recognition with Pitch and Voice Quality Features
Sep 02, 2020

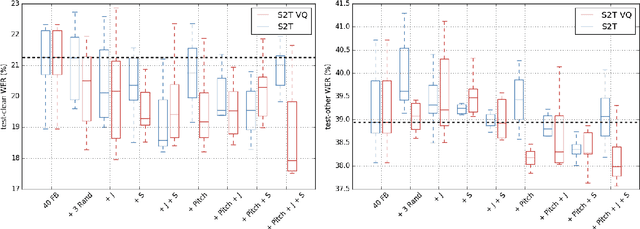
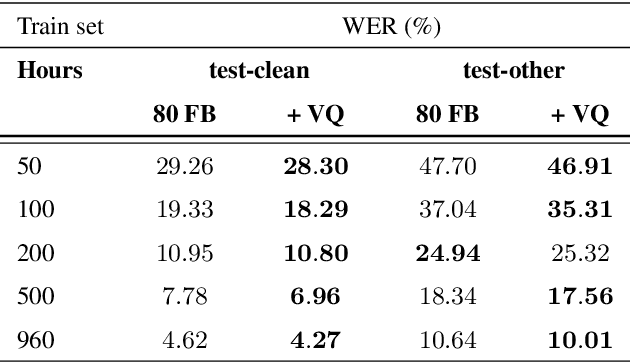
Abstract:The effects of adding pitch and voice quality features such as jitter and shimmer to a state-of-the-art CNN model for Automatic Speech Recognition are studied in this work. Pitch features have been previously used for improving classical HMM and DNN baselines, while jitter and shimmer parameters have proven to be useful for tasks like speaker or emotion recognition. Up to our knowledge, this is the first work combining such pitch and voice quality features with modern convolutional architectures, showing improvements up to 2% absolute WER points, for the publicly available Spanish Common Voice dataset. Particularly, our work combines these features with mel-frequency spectral coefficients (MFSCs) to train a convolutional architecture with Gated Linear Units (Conv GLUs). Such models have shown to yield small word error rates, while being very suitable for parallel processing for online streaming recognition use cases. We have added pitch and voice quality functionality to Facebook's wav2letter speech recognition framework, and we provide with such code and recipes to the community, to carry on with further experiments. Besides, to the best of our knowledge, our Spanish Common Voice recipe is the first public Spanish recipe for wav2letter.
Detection of speech events and speaker characteristics through photo-plethysmographic signal neural processing
Nov 12, 2019
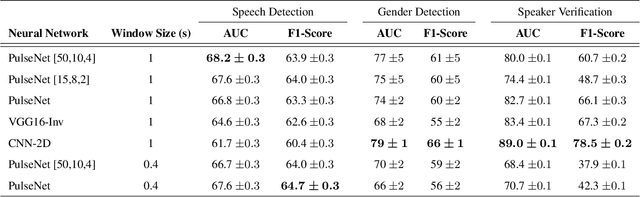
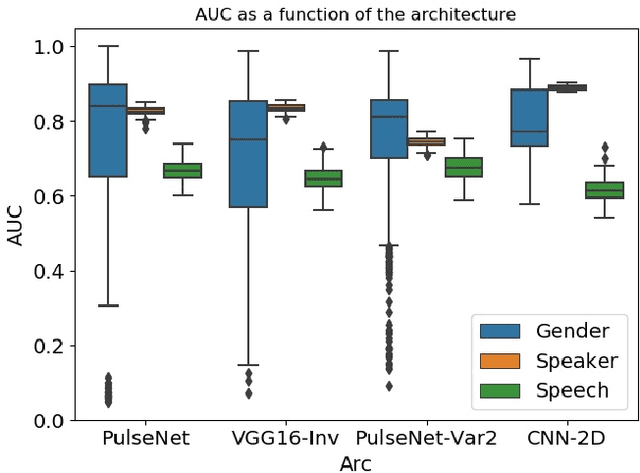
Abstract:The use of photoplethysmogram signal (PPG) for heart and sleep monitoring is commonly found nowadays in smartphones and wrist wearables. Besides common usages, it has been proposed and reported that person information can be extracted from PPG for other uses, like biometry tasks. In this work, we explore several end-to-end convolutional neural network architectures for detection of human's characteristics such as gender or person identity. In addition, we evaluate whether speech/non-speech events may be inferred from PPG signal, where speech might translate in fluctuations into the pulse signal. The obtained results are promising and clearly show the potential of fully end-to-end topologies for automatic extraction of meaningful biomarkers, even from a noisy signal sampled by a low-cost PPG sensor. The AUCs for best architectures put forward PPG wave as biological discriminant, reaching $79\%$ and $89.0\%$, respectively for gender and person verification tasks. Furthermore, speech detection experiments reporting AUCs around $69\%$ encourage us for further exploration about the feasibility of PPG for speech processing tasks.
Prosodic Phrase Alignment for Machine Dubbing
Aug 20, 2019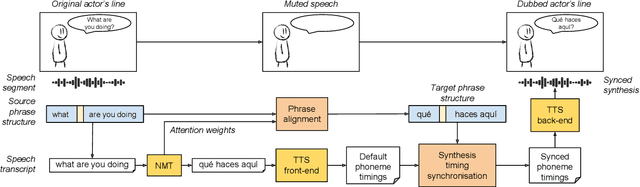

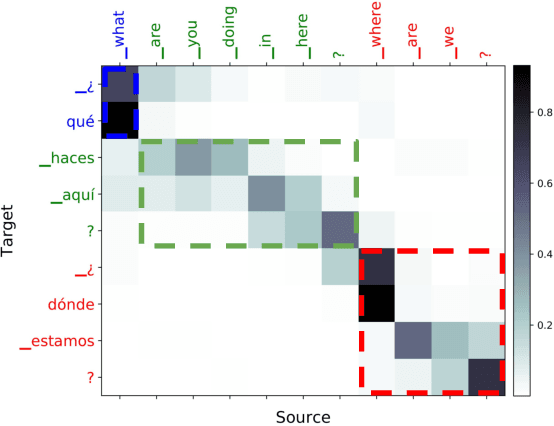
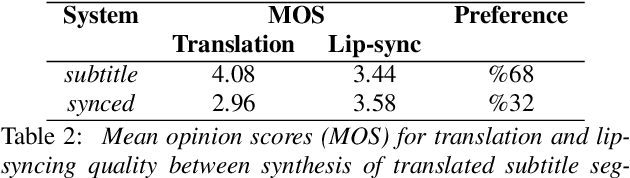
Abstract:Dubbing is a type of audiovisual translation where dialogues are translated and enacted so that they give the impression that the media is in the target language. It requires a careful alignment of dubbed recordings with the lip movements of performers in order to achieve visual coherence. In this paper, we deal with the specific problem of prosodic phrase synchronization within the framework of machine dubbing. Our methodology exploits the attention mechanism output in neural machine translation to find plausible phrasing for the translated dialogue lines and then uses them to condition their synthesis. Our initial work in this field records comparable speech rate ratio to professional dubbing translation, and improvement in terms of lip-syncing of long dialogue lines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge