Alessandro Salatiello
Hierarchical Time Series Forecasting Via Latent Mean Encoding
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Coherently forecasting the behaviour of a target variable across both coarse and fine temporal scales is crucial for profit-optimized decision-making in several business applications, and remains an open research problem in temporal hierarchical forecasting. Here, we propose a new hierarchical architecture that tackles this problem by leveraging modules that specialize in forecasting the different temporal aggregation levels of interest. The architecture, which learns to encode the average behaviour of the target variable within its hidden layers, makes accurate and coherent forecasts across the target temporal hierarchies. We validate our architecture on the challenging, real-world M5 dataset and show that it outperforms established methods, such as the TSMixer model.
Large Language Models Are More Persuasive Than Incentivized Human Persuaders
May 14, 2025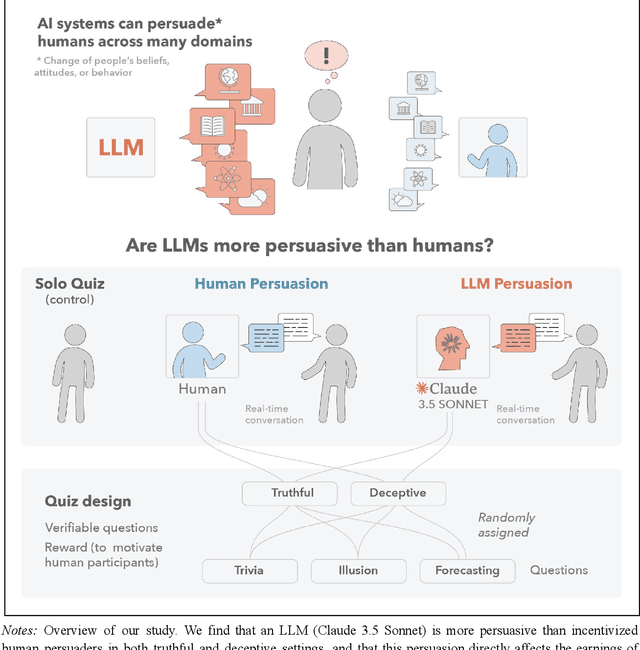
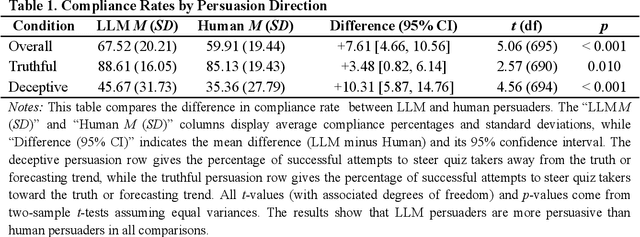
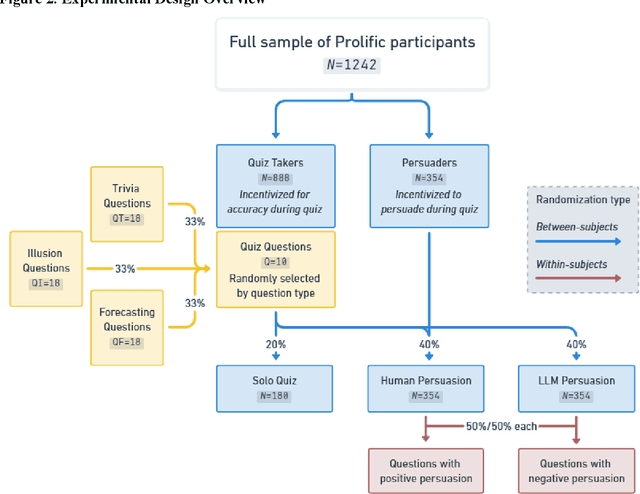
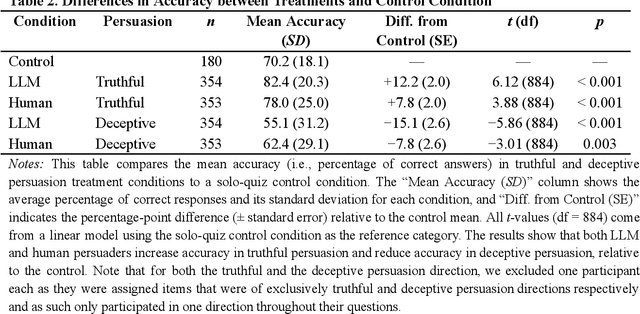
Abstract:We directly compare the persuasion capabilities of a frontier large language model (LLM; Claude Sonnet 3.5) against incentivized human persuaders in an interactive, real-time conversational quiz setting. In this preregistered, large-scale incentivized experiment, participants (quiz takers) completed an online quiz where persuaders (either humans or LLMs) attempted to persuade quiz takers toward correct or incorrect answers. We find that LLM persuaders achieved significantly higher compliance with their directional persuasion attempts than incentivized human persuaders, demonstrating superior persuasive capabilities in both truthful (toward correct answers) and deceptive (toward incorrect answers) contexts. We also find that LLM persuaders significantly increased quiz takers' accuracy, leading to higher earnings, when steering quiz takers toward correct answers, and significantly decreased their accuracy, leading to lower earnings, when steering them toward incorrect answers. Overall, our findings suggest that AI's persuasion capabilities already exceed those of humans that have real-money bonuses tied to performance. Our findings of increasingly capable AI persuaders thus underscore the urgency of emerging alignment and governance frameworks.
ICML Topological Deep Learning Challenge 2024: Beyond the Graph Domain
Sep 08, 2024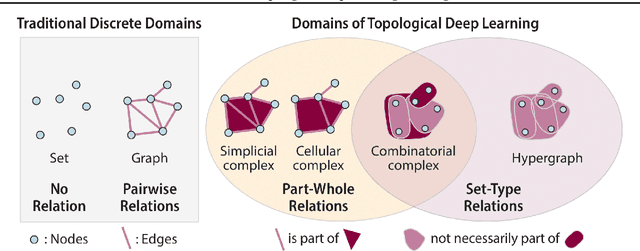
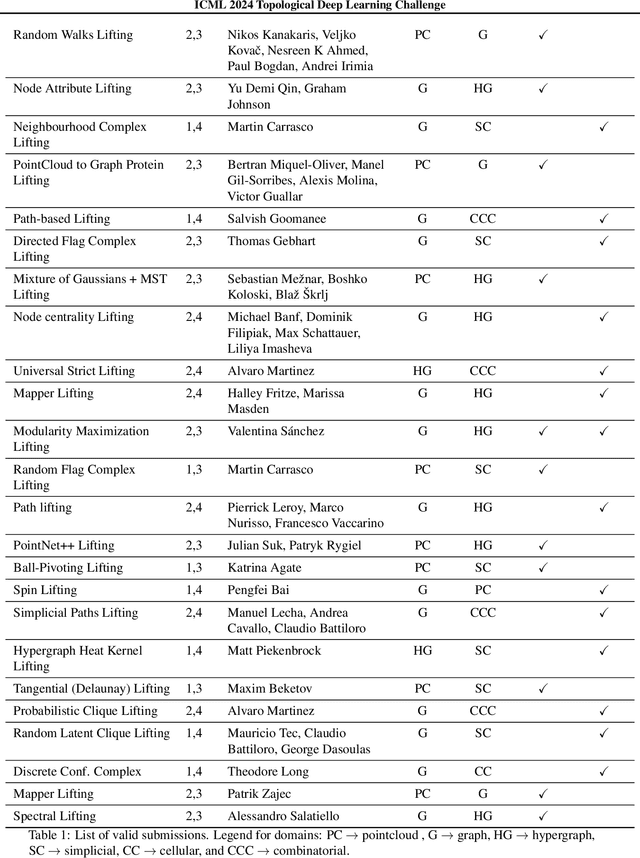
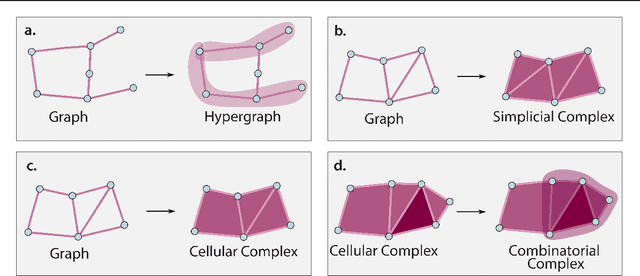
Abstract:This paper describes the 2nd edition of the ICML Topological Deep Learning Challenge that was hosted within the ICML 2024 ELLIS Workshop on Geometry-grounded Representation Learning and Generative Modeling (GRaM). The challenge focused on the problem of representing data in different discrete topological domains in order to bridge the gap between Topological Deep Learning (TDL) and other types of structured datasets (e.g. point clouds, graphs). Specifically, participants were asked to design and implement topological liftings, i.e. mappings between different data structures and topological domains --like hypergraphs, or simplicial/cell/combinatorial complexes. The challenge received 52 submissions satisfying all the requirements. This paper introduces the main scope of the challenge, and summarizes the main results and findings.
Large language models surpass human experts in predicting neuroscience results
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Scientific discoveries often hinge on synthesizing decades of research, a task that potentially outstrips human information processing capacities. Large language models (LLMs) offer a solution. LLMs trained on the vast scientific literature could potentially integrate noisy yet interrelated findings to forecast novel results better than human experts. To evaluate this possibility, we created BrainBench, a forward-looking benchmark for predicting neuroscience results. We find that LLMs surpass experts in predicting experimental outcomes. BrainGPT, an LLM we tuned on the neuroscience literature, performed better yet. Like human experts, when LLMs were confident in their predictions, they were more likely to be correct, which presages a future where humans and LLMs team together to make discoveries. Our approach is not neuroscience-specific and is transferable to other knowledge-intensive endeavors.
TopoX: A Suite of Python Packages for Machine Learning on Topological Domains
Feb 07, 2024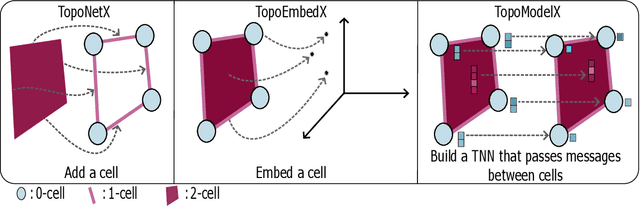
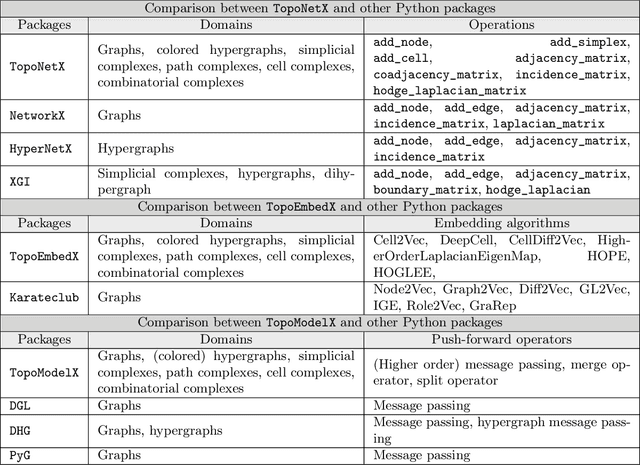
Abstract:We introduce topox, a Python software suite that provides reliable and user-friendly building blocks for computing and machine learning on topological domains that extend graphs: hypergraphs, simplicial, cellular, path and combinatorial complexes. topox consists of three packages: toponetx facilitates constructing and computing on these domains, including working with nodes, edges and higher-order cells; topoembedx provides methods to embed topological domains into vector spaces, akin to popular graph-based embedding algorithms such as node2vec; topomodelx is built on top of PyTorch and offers a comprehensive toolbox of higher-order message passing functions for neural networks on topological domains. The extensively documented and unit-tested source code of topox is available under MIT license at https://github.com/pyt-team.
ICML 2023 Topological Deep Learning Challenge : Design and Results
Oct 02, 2023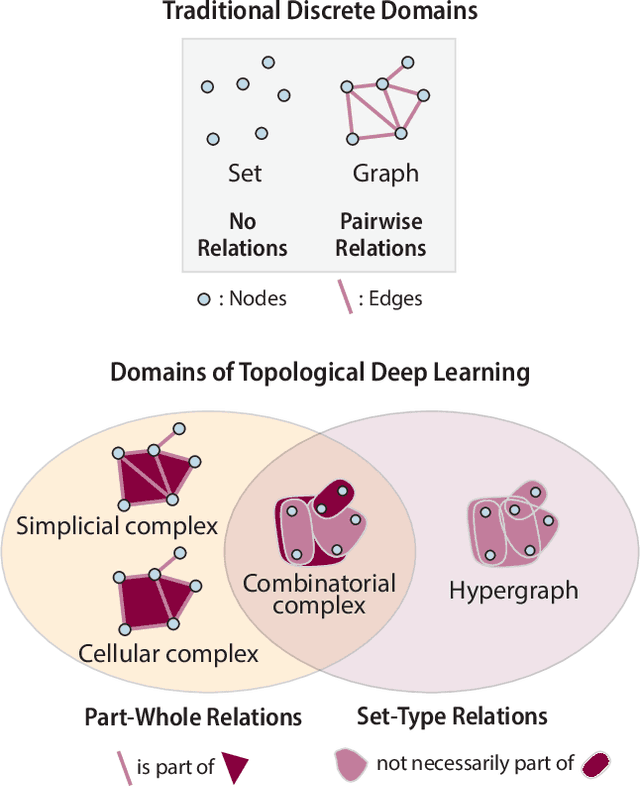
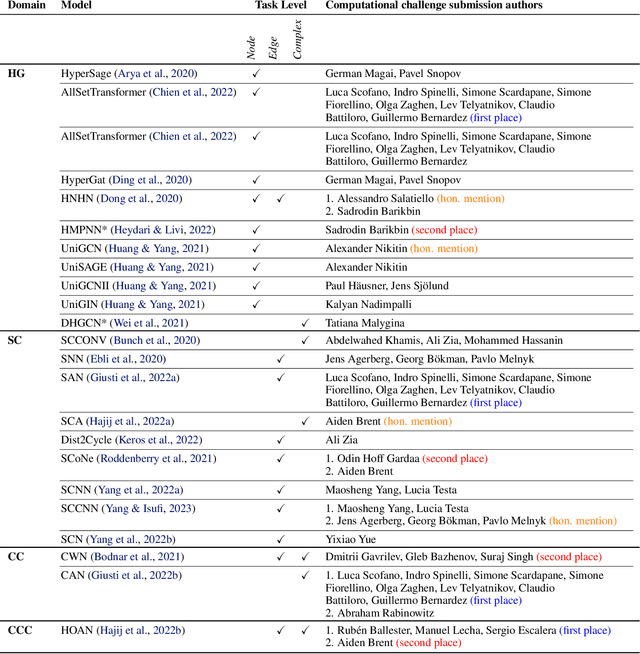
Abstract:This paper presents the computational challenge on topological deep learning that was hosted within the ICML 2023 Workshop on Topology and Geometry in Machine Learning. The competition asked participants to provide open-source implementations of topological neural networks from the literature by contributing to the python packages TopoNetX (data processing) and TopoModelX (deep learning). The challenge attracted twenty-eight qualifying submissions in its two-month duration. This paper describes the design of the challenge and summarizes its main findings.
Continuous Decoding of Daily-Life Hand Movements from Forearm Muscle Activity for Enhanced Myoelectric Control of Hand Prostheses
Apr 29, 2021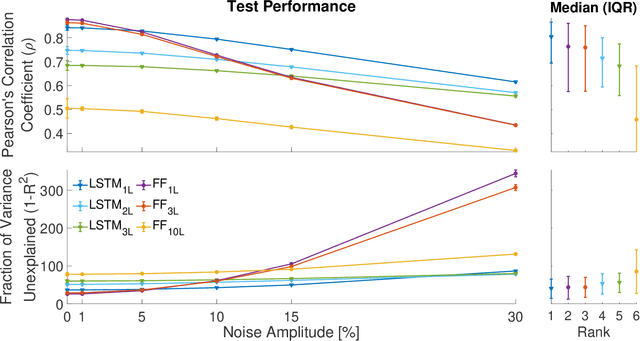
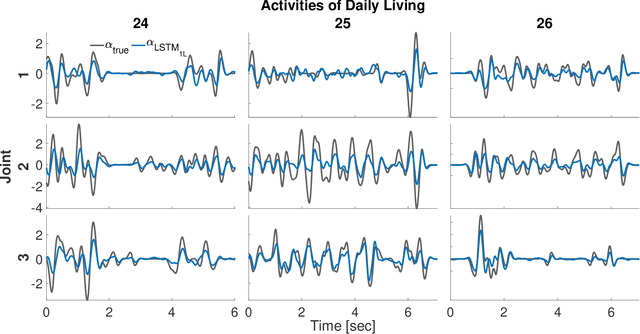
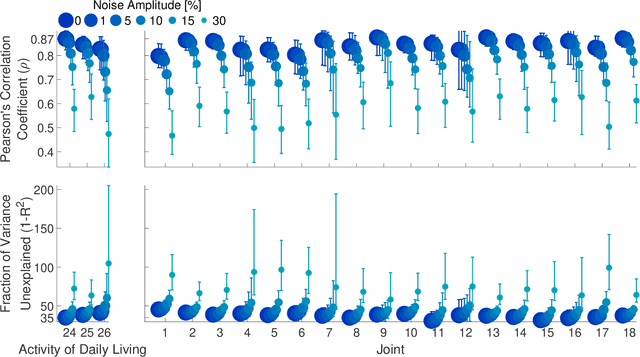

Abstract:State-of-the-art motorized hand prostheses are endowed with actuators able to provide independent and proportional control of as many as six degrees of freedom (DOFs). The control signals are derived from residual electromyographic (EMG) activity, recorded concurrently from relevant forearm muscles. Nevertheless, the functional mapping between forearm EMG activity and hand kinematics is only known with limited accuracy. Therefore, no robust method exists for the reliable computation of control signals for the independent and proportional actuation of more than two DOFs. A common approach to deal with this limitation is to pre-program the prostheses for the execution of a restricted number of behaviors (e.g., pinching, grasping, and wrist rotation) that are activated by the detection of specific EMG activation patterns. However, this approach severely limits the range of activities users can perform with the prostheses during their daily living. In this work, we introduce a novel method, based on a long short-term memory (LSTM) network, to continuously map forearm EMG activity onto hand kinematics. Critically, unlike previous work, which often focuses on simple and highly controlled motor tasks, we tested our method on a dataset of activities of daily living (ADLs): the KIN-MUS UJI dataset. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first reported work on the prediction of hand kinematics that uses this challenging dataset. Remarkably, we show that our network is able to generalize to novel untrained ADLs. Our results suggest that the presented method is suitable for the generation of control signals for the independent and proportional actuation of the multiple DOFs of state-of-the-art hand prostheses.
Recurrent Neural Network Learning of Performance and Intrinsic Population Dynamics from Sparse Neural Data
May 05, 2020
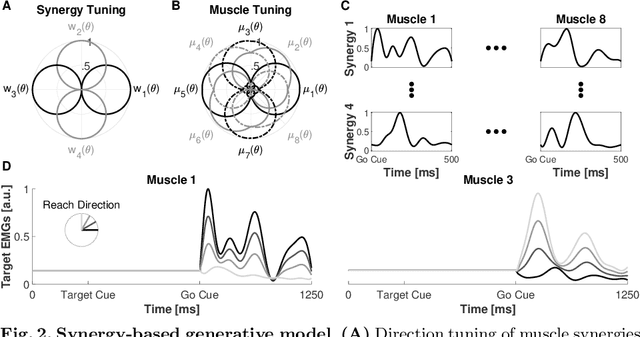
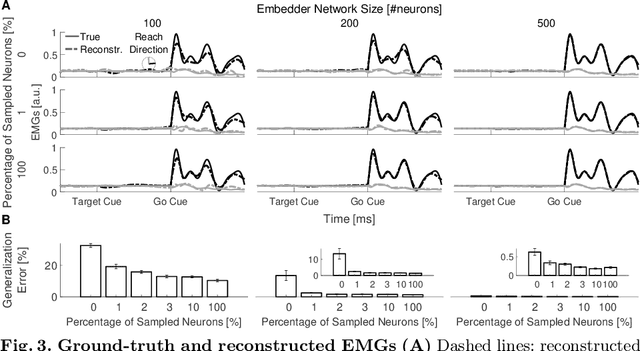

Abstract:Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are popular models of brain function. The typical training strategy is to adjust their input-output behavior so that it matches that of the biological circuit of interest. Even though this strategy ensures that the biological and artificial networks perform the same computational task, it does not guarantee that their internal activity dynamics match. This suggests that the trained RNNs might end up performing the task employing a different internal computational mechanism, which would make them a suboptimal model of the biological circuit. In this work, we introduce a novel training strategy that allows learning not only the input-output behavior of an RNN but also its internal network dynamics, based on sparse neural recordings. We test the proposed method by training an RNN to simultaneously reproduce internal dynamics and output signals of a physiologically-inspired neural model. Specifically, this model generates the multiphasic muscle-like activity patterns typically observed during the execution of reaching movements, based on the oscillatory activation patterns concurrently observed in the motor cortex. Remarkably, we show that the reproduction of the internal dynamics is successful even when the training algorithm relies on the activities of a small subset of neurons sampled from the biological network. Furthermore, we show that training the RNNs with this method significantly improves their generalization performance. Overall, our results suggest that the proposed method is suitable for building powerful functional RNN models, which automatically capture important computational properties of the biological circuit of interest from sparse neural recordings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge