Martin A. Giese
Another BRIXEL in the Wall: Towards Cheaper Dense Features
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Vision foundation models achieve strong performance on both global and locally dense downstream tasks. Pretrained on large images, the recent DINOv3 model family is able to produce very fine-grained dense feature maps, enabling state-of-the-art performance. However, computing these feature maps requires the input image to be available at very high resolution, as well as large amounts of compute due to the squared complexity of the transformer architecture. To address these issues, we propose BRIXEL, a simple knowledge distillation approach that has the student learn to reproduce its own feature maps at higher resolution. Despite its simplicity, BRIXEL outperforms the baseline DINOv3 models by large margins on downstream tasks when the resolution is kept fixed. Moreover, it is able to produce feature maps that are very similar to those of the teacher at a fraction of the computational cost. Code and model weights are available at https://github.com/alexanderlappe/BRIXEL.
Single-Example Learning in a Mixture of GPDMs with Latent Geometries
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:We present the Gaussian process dynamical mixture model (GPDMM) and show its utility in single-example learning of human motion data. The Gaussian process dynamical model (GPDM) is a form of the Gaussian process latent variable model (GPLVM), but optimized with a hidden Markov model dynamical prior. The GPDMM combines multiple GPDMs in a probabilistic mixture-of-experts framework, utilizing embedded geometric features to allow for diverse sequences to be encoded in a single latent space, enabling the categorization and generation of each sequence class. GPDMs and our mixture model are particularly advantageous in addressing the challenges of modeling human movement in scenarios where data is limited and model interpretability is vital, such as in patient-specific medical applications like prosthesis control. We score the GPDMM on classification accuracy and generative ability in single-example learning, showcase model variations, and benchmark it against LSTMs, VAEs, and transformers.
Register and CLS tokens yield a decoupling of local and global features in large ViTs
May 09, 2025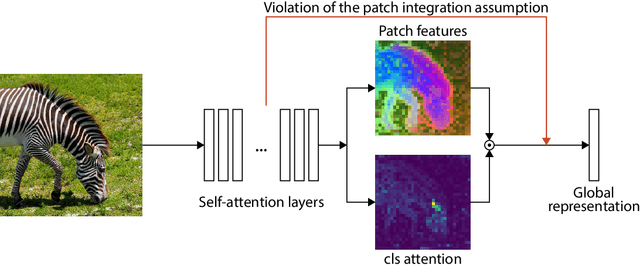
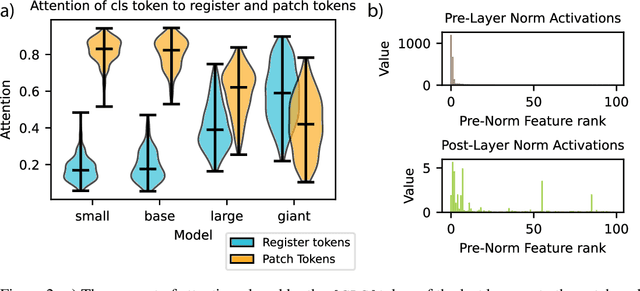
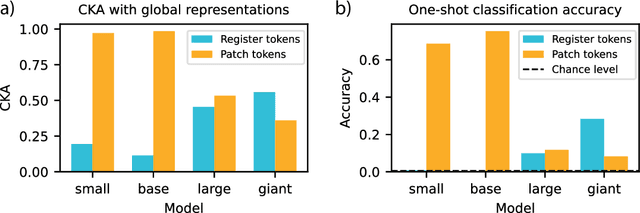
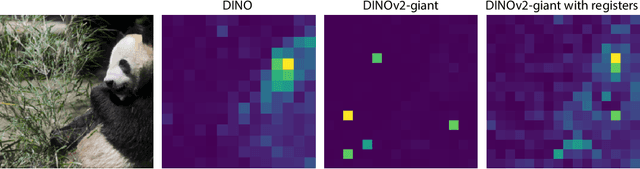
Abstract:Recent work has shown that the attention maps of the widely popular DINOv2 model exhibit artifacts, which hurt both model interpretability and performance on dense image tasks. These artifacts emerge due to the model repurposing patch tokens with redundant local information for the storage of global image information. To address this problem, additional register tokens have been incorporated in which the model can store such information instead. We carefully examine the influence of these register tokens on the relationship between global and local image features, showing that while register tokens yield cleaner attention maps, these maps do not accurately reflect the integration of local image information in large models. Instead, global information is dominated by information extracted from register tokens, leading to a disconnect between local and global features. Inspired by these findings, we show that the CLS token itself, which can be interpreted as a register, leads to a very similar phenomenon in models without explicit register tokens. Our work shows that care must be taken when interpreting attention maps of large ViTs. Further, by clearly attributing the faulty behaviour to register and CLS tokens, we show a path towards more interpretable vision models.
Parallel Backpropagation for Shared-Feature Visualization
May 16, 2024



Abstract:High-level visual brain regions contain subareas in which neurons appear to respond more strongly to examples of a particular semantic category, like faces or bodies, rather than objects. However, recent work has shown that while this finding holds on average, some out-of-category stimuli also activate neurons in these regions. This may be due to visual features common among the preferred class also being present in other images. Here, we propose a deep-learning-based approach for visualizing these features. For each neuron, we identify relevant visual features driving its selectivity by modelling responses to images based on latent activations of a deep neural network. Given an out-of-category image which strongly activates the neuron, our method first identifies a reference image from the preferred category yielding a similar feature activation pattern. We then backpropagate latent activations of both images to the pixel level, while enhancing the identified shared dimensions and attenuating non-shared features. The procedure highlights image regions containing shared features driving responses of the model neuron. We apply the algorithm to novel recordings from body-selective regions in macaque IT cortex in order to understand why some images of objects excite these neurons. Visualizations reveal object parts which resemble parts of a macaque body, shedding light on neural preference of these objects.
Early Recognition of Ball Catching Success in Clinical Trials with RNN-Based Predictive Classification
Jul 06, 2021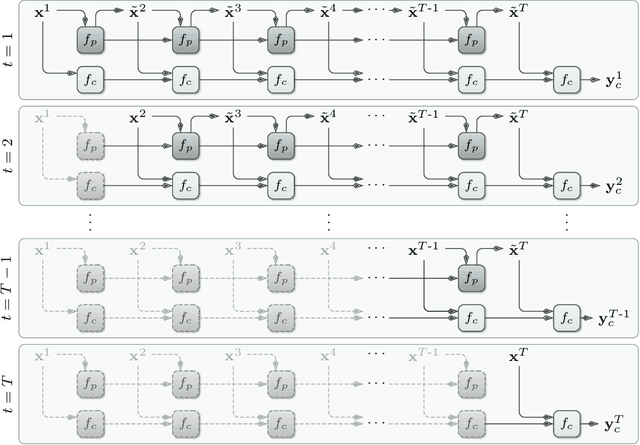
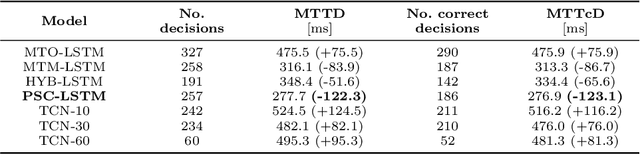
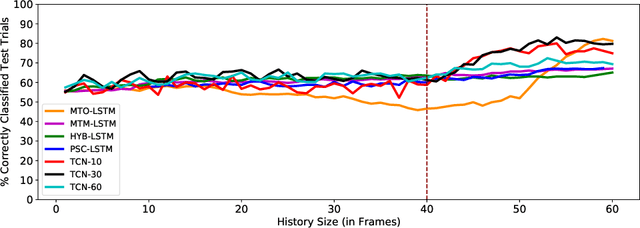
Abstract:Motor disturbances can affect the interaction with dynamic objects, such as catching a ball. A classification of clinical catching trials might give insight into the existence of pathological alterations in the relation of arm and ball movements. Accurate, but also early decisions are required to classify a catching attempt before the catcher's first ball contact. To obtain clinically valuable results, a significant decision confidence of at least 75% is required. Hence, three competing objectives have to be optimized at the same time: accuracy, earliness and decision-making confidence. Here we propose a coupled classification and prediction approach for early time series classification: a predictive, generative recurrent neural network (RNN) forecasts the next data points of ball trajectories based on already available observations; a discriminative RNN continuously generates classification guesses based on the available data points and the unrolled sequence predictions. We compare our approach, which we refer to as predictive sequential classification (PSC), to state-of-the-art sequence learners, including various RNN and temporal convolutional network (TCN) architectures. On this hard real-world task we can consistently demonstrate the superiority of PSC over all other models in terms of accuracy and confidence with respect to earliness of recognition. Specifically, PSC is able to confidently classify the success of catching trials as early as 123 milliseconds before the first ball contact. We conclude that PSC is a promising approach for early time series classification, when accurate and confident decisions are required.
Continuous Decoding of Daily-Life Hand Movements from Forearm Muscle Activity for Enhanced Myoelectric Control of Hand Prostheses
Apr 29, 2021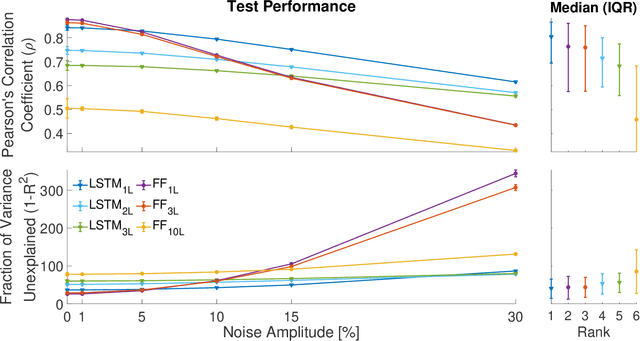
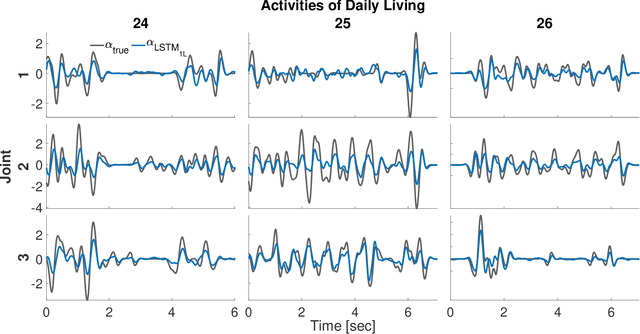
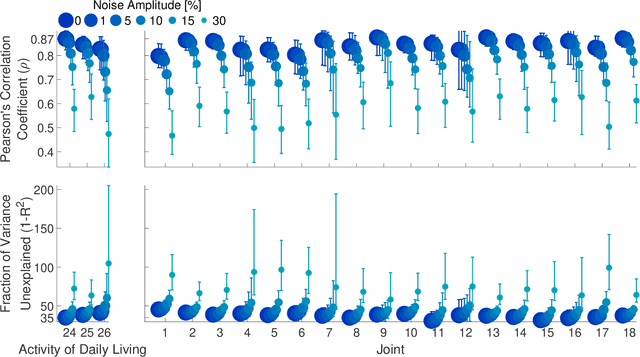

Abstract:State-of-the-art motorized hand prostheses are endowed with actuators able to provide independent and proportional control of as many as six degrees of freedom (DOFs). The control signals are derived from residual electromyographic (EMG) activity, recorded concurrently from relevant forearm muscles. Nevertheless, the functional mapping between forearm EMG activity and hand kinematics is only known with limited accuracy. Therefore, no robust method exists for the reliable computation of control signals for the independent and proportional actuation of more than two DOFs. A common approach to deal with this limitation is to pre-program the prostheses for the execution of a restricted number of behaviors (e.g., pinching, grasping, and wrist rotation) that are activated by the detection of specific EMG activation patterns. However, this approach severely limits the range of activities users can perform with the prostheses during their daily living. In this work, we introduce a novel method, based on a long short-term memory (LSTM) network, to continuously map forearm EMG activity onto hand kinematics. Critically, unlike previous work, which often focuses on simple and highly controlled motor tasks, we tested our method on a dataset of activities of daily living (ADLs): the KIN-MUS UJI dataset. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first reported work on the prediction of hand kinematics that uses this challenging dataset. Remarkably, we show that our network is able to generalize to novel untrained ADLs. Our results suggest that the presented method is suitable for the generation of control signals for the independent and proportional actuation of the multiple DOFs of state-of-the-art hand prostheses.
Recurrent Neural Network Learning of Performance and Intrinsic Population Dynamics from Sparse Neural Data
May 05, 2020
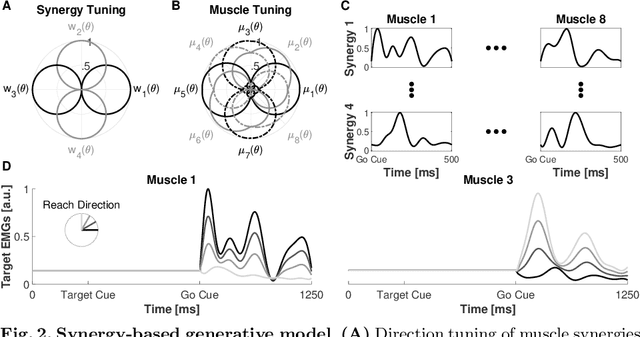
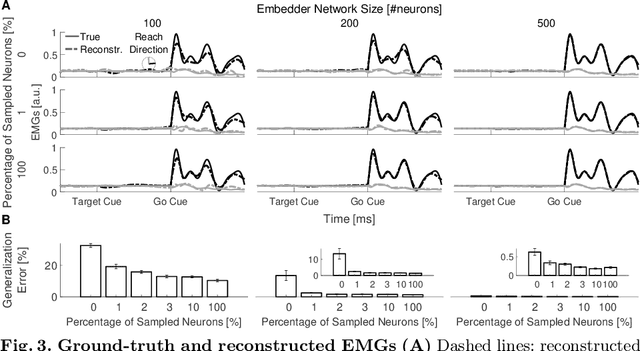

Abstract:Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are popular models of brain function. The typical training strategy is to adjust their input-output behavior so that it matches that of the biological circuit of interest. Even though this strategy ensures that the biological and artificial networks perform the same computational task, it does not guarantee that their internal activity dynamics match. This suggests that the trained RNNs might end up performing the task employing a different internal computational mechanism, which would make them a suboptimal model of the biological circuit. In this work, we introduce a novel training strategy that allows learning not only the input-output behavior of an RNN but also its internal network dynamics, based on sparse neural recordings. We test the proposed method by training an RNN to simultaneously reproduce internal dynamics and output signals of a physiologically-inspired neural model. Specifically, this model generates the multiphasic muscle-like activity patterns typically observed during the execution of reaching movements, based on the oscillatory activation patterns concurrently observed in the motor cortex. Remarkably, we show that the reproduction of the internal dynamics is successful even when the training algorithm relies on the activities of a small subset of neurons sampled from the biological network. Furthermore, we show that training the RNNs with this method significantly improves their generalization performance. Overall, our results suggest that the proposed method is suitable for building powerful functional RNN models, which automatically capture important computational properties of the biological circuit of interest from sparse neural recordings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge