Aditya Prakash
How Do I Do That? Synthesizing 3D Hand Motion and Contacts for Everyday Interactions
Apr 16, 2025



Abstract:We tackle the novel problem of predicting 3D hand motion and contact maps (or Interaction Trajectories) given a single RGB view, action text, and a 3D contact point on the object as input. Our approach consists of (1) Interaction Codebook: a VQVAE model to learn a latent codebook of hand poses and contact points, effectively tokenizing interaction trajectories, (2) Interaction Predictor: a transformer-decoder module to predict the interaction trajectory from test time inputs by using an indexer module to retrieve a latent affordance from the learned codebook. To train our model, we develop a data engine that extracts 3D hand poses and contact trajectories from the diverse HoloAssist dataset. We evaluate our model on a benchmark that is 2.5-10X larger than existing works, in terms of diversity of objects and interactions observed, and test for generalization of the model across object categories, action categories, tasks, and scenes. Experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach over transformer & diffusion baselines across all settings.
Weakly Supervised Learning on Large Graphs
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Graph classification plays a pivotal role in various domains, including pathology, where images can be represented as graphs.In this domain, images can be represented as graphs, where nodes might represent individual nuclei, and edges capture the spatial or functional relationships between them. Often, the overall label of the graph, such as a cancer type or disease state, is determined by patterns within smaller, localized regions of the image. This work introduces a weakly-supervised graph classification framework leveraging two subgraph extraction techniques: (1) Sliding-window approach (2) BFS-based approach. Subgraphs are processed using a Graph Attention Network (GAT), which employs attention mechanisms to identify the most informative subgraphs for classification. Weak supervision is achieved by propagating graph-level labels to subgraphs, eliminating the need for detailed subgraph annotations.
Benchmarks and Challenges in Pose Estimation for Egocentric Hand Interactions with Objects
Mar 25, 2024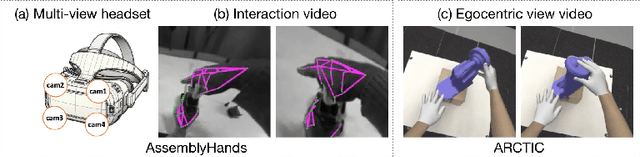
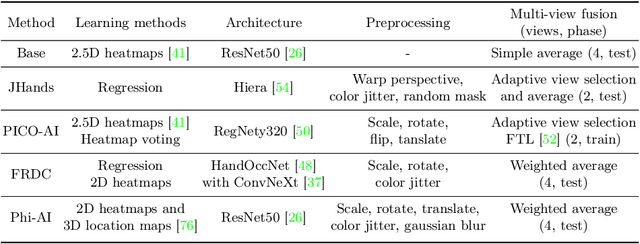
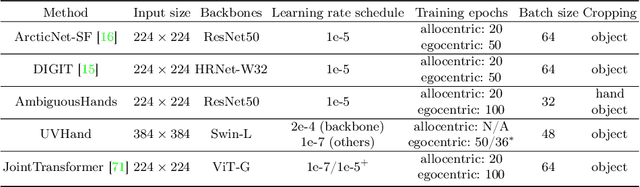
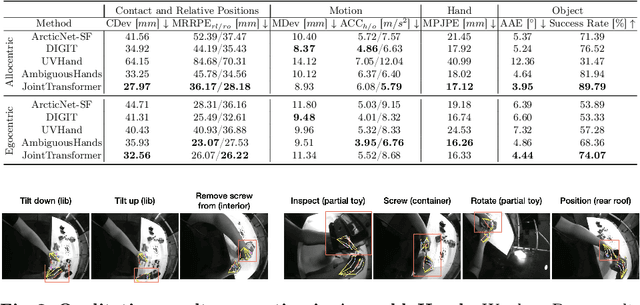
Abstract:We interact with the world with our hands and see it through our own (egocentric) perspective. A holistic 3D understanding of such interactions from egocentric views is important for tasks in robotics, AR/VR, action recognition and motion generation. Accurately reconstructing such interactions in 3D is challenging due to heavy occlusion, viewpoint bias, camera distortion, and motion blur from the head movement. To this end, we designed the HANDS23 challenge based on the AssemblyHands and ARCTIC datasets with carefully designed training and testing splits. Based on the results of the top submitted methods and more recent baselines on the leaderboards, we perform a thorough analysis on 3D hand(-object) reconstruction tasks. Our analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of addressing distortion specific to egocentric cameras, adopting high-capacity transformers to learn complex hand-object interactions, and fusing predictions from different views. Our study further reveals challenging scenarios intractable with state-of-the-art methods, such as fast hand motion, object reconstruction from narrow egocentric views, and close contact between two hands and objects. Our efforts will enrich the community's knowledge foundation and facilitate future hand studies on egocentric hand-object interactions.
Mitigating Perspective Distortion-induced Shape Ambiguity in Image Crops
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Objects undergo varying amounts of perspective distortion as they move across a camera's field of view. Models for predicting 3D from a single image often work with crops around the object of interest and ignore the location of the object in the camera's field of view. We note that ignoring this location information further exaggerates the inherent ambiguity in making 3D inferences from 2D images and can prevent models from even fitting to the training data. To mitigate this ambiguity, we propose Intrinsics-Aware Positional Encoding (KPE), which incorporates information about the location of crops in the image and camera intrinsics. Experiments on three popular 3D-from-a-single-image benchmarks: depth prediction on NYU, 3D object detection on KITTI & nuScenes, and predicting 3D shapes of articulated objects on ARCTIC, show the benefits of KPE.
3D Hand Pose Estimation in Egocentric Images in the Wild
Dec 11, 2023

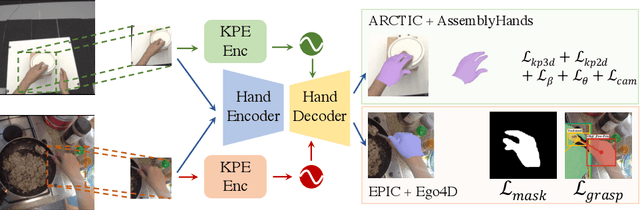

Abstract:We present WildHands, a method for 3D hand pose estimation in egocentric images in the wild. This is challenging due to (a) lack of 3D hand pose annotations for images in the wild, and (b) a form of perspective distortion-induced shape ambiguity that arises in the analysis of crops around hands. For the former, we use auxiliary supervision on in-the-wild data in the form of segmentation masks & grasp labels in addition to 3D supervision available in lab datasets. For the latter, we provide spatial cues about the location of the hand crop in the camera's field of view. Our approach achieves the best 3D hand pose on the ARCTIC leaderboard and outperforms FrankMocap, a popular and robust approach for estimating hand pose in the wild, by 45.3% when evaluated on 2D hand pose on our EPIC-HandKps dataset.
Look Ma, No Hands! Agent-Environment Factorization of Egocentric Videos
May 25, 2023



Abstract:The analysis and use of egocentric videos for robotic tasks is made challenging by occlusion due to the hand and the visual mismatch between the human hand and a robot end-effector. In this sense, the human hand presents a nuisance. However, often hands also provide a valuable signal, e.g. the hand pose may suggest what kind of object is being held. In this work, we propose to extract a factored representation of the scene that separates the agent (human hand) and the environment. This alleviates both occlusion and mismatch while preserving the signal, thereby easing the design of models for downstream robotics tasks. At the heart of this factorization is our proposed Video Inpainting via Diffusion Model (VIDM) that leverages both a prior on real-world images (through a large-scale pre-trained diffusion model) and the appearance of the object in earlier frames of the video (through attention). Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of VIDM at improving inpainting quality on egocentric videos and the power of our factored representation for numerous tasks: object detection, 3D reconstruction of manipulated objects, and learning of reward functions, policies, and affordances from videos.
Learning Hand-Held Object Reconstruction from In-The-Wild Videos
May 04, 2023Abstract:Prior works for reconstructing hand-held objects from a single image rely on direct 3D shape supervision which is challenging to gather in real world at scale. Consequently, these approaches do not generalize well when presented with novel objects in in-the-wild settings. While 3D supervision is a major bottleneck, there is an abundance of in-the-wild raw video data showing hand-object interactions. In this paper, we automatically extract 3D supervision (via multiview 2D supervision) from such raw video data to scale up the learning of models for hand-held object reconstruction. This requires tackling two key challenges: unknown camera pose and occlusion. For the former, we use hand pose (predicted from existing techniques, e.g. FrankMocap) as a proxy for object pose. For the latter, we learn data-driven 3D shape priors using synthetic objects from the ObMan dataset. We use these indirect 3D cues to train occupancy networks that predict the 3D shape of objects from a single RGB image. Our experiments on the MOW and HO3D datasets show the effectiveness of these supervisory signals at predicting the 3D shape for real-world hand-held objects without any direct real-world 3D supervision.
TransFuser: Imitation with Transformer-Based Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving
May 31, 2022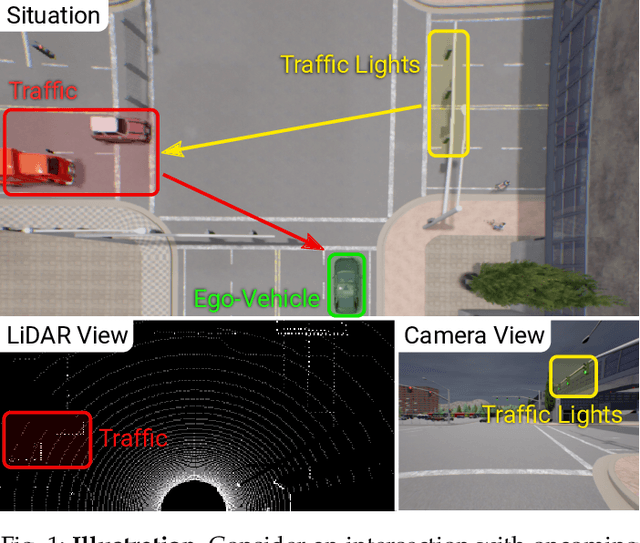
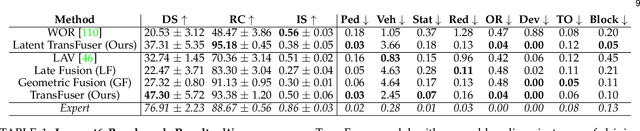
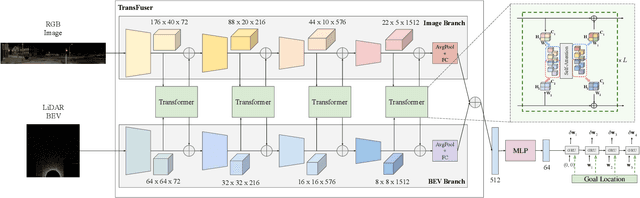
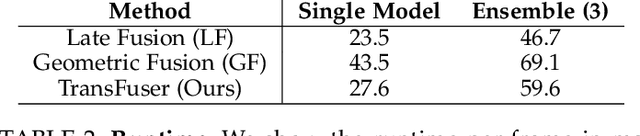
Abstract:How should we integrate representations from complementary sensors for autonomous driving? Geometry-based fusion has shown promise for perception (e.g. object detection, motion forecasting). However, in the context of end-to-end driving, we find that imitation learning based on existing sensor fusion methods underperforms in complex driving scenarios with a high density of dynamic agents. Therefore, we propose TransFuser, a mechanism to integrate image and LiDAR representations using self-attention. Our approach uses transformer modules at multiple resolutions to fuse perspective view and bird's eye view feature maps. We experimentally validate its efficacy on a challenging new benchmark with long routes and dense traffic, as well as the official leaderboard of the CARLA urban driving simulator. At the time of submission, TransFuser outperforms all prior work on the CARLA leaderboard in terms of driving score by a large margin. Compared to geometry-based fusion, TransFuser reduces the average collisions per kilometer by 48%.
NEAT: Neural Attention Fields for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Sep 09, 2021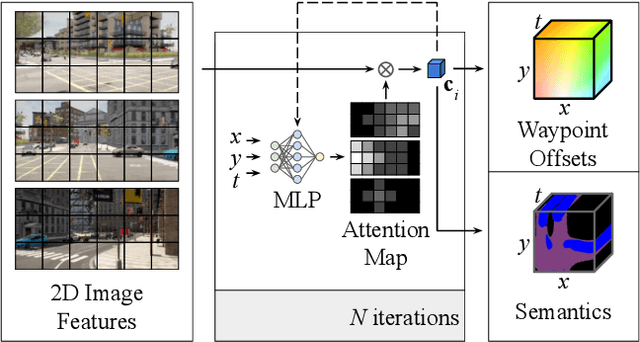
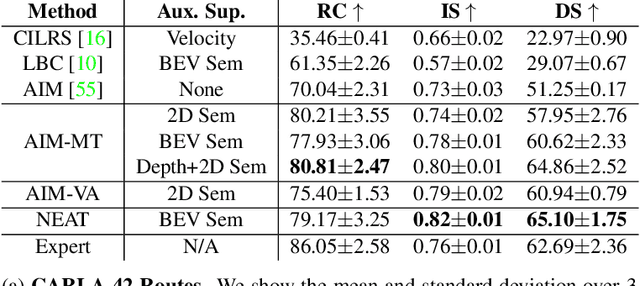
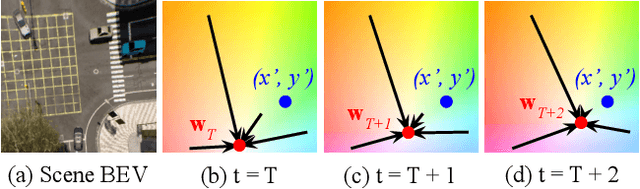
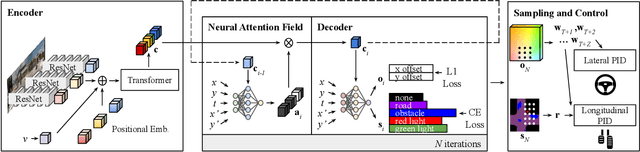
Abstract:Efficient reasoning about the semantic, spatial, and temporal structure of a scene is a crucial prerequisite for autonomous driving. We present NEural ATtention fields (NEAT), a novel representation that enables such reasoning for end-to-end imitation learning models. NEAT is a continuous function which maps locations in Bird's Eye View (BEV) scene coordinates to waypoints and semantics, using intermediate attention maps to iteratively compress high-dimensional 2D image features into a compact representation. This allows our model to selectively attend to relevant regions in the input while ignoring information irrelevant to the driving task, effectively associating the images with the BEV representation. In a new evaluation setting involving adverse environmental conditions and challenging scenarios, NEAT outperforms several strong baselines and achieves driving scores on par with the privileged CARLA expert used to generate its training data. Furthermore, visualizing the attention maps for models with NEAT intermediate representations provides improved interpretability.
Multi-Modal Fusion Transformer for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Apr 19, 2021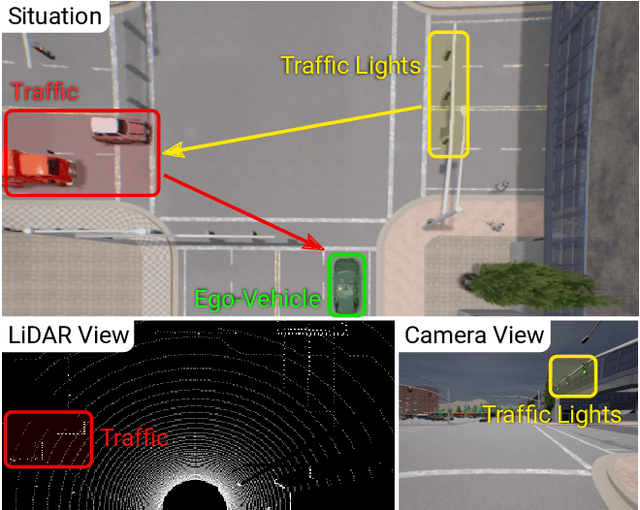
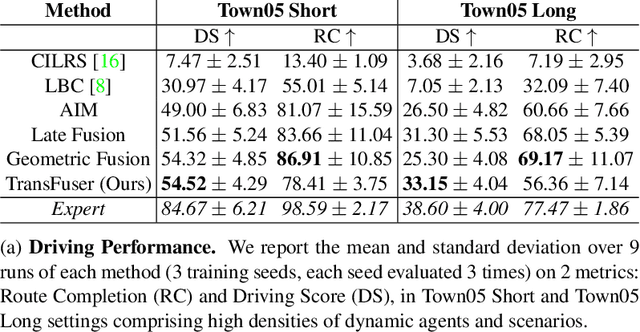
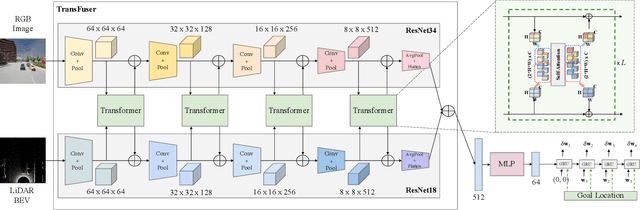
Abstract:How should representations from complementary sensors be integrated for autonomous driving? Geometry-based sensor fusion has shown great promise for perception tasks such as object detection and motion forecasting. However, for the actual driving task, the global context of the 3D scene is key, e.g. a change in traffic light state can affect the behavior of a vehicle geometrically distant from that traffic light. Geometry alone may therefore be insufficient for effectively fusing representations in end-to-end driving models. In this work, we demonstrate that imitation learning policies based on existing sensor fusion methods under-perform in the presence of a high density of dynamic agents and complex scenarios, which require global contextual reasoning, such as handling traffic oncoming from multiple directions at uncontrolled intersections. Therefore, we propose TransFuser, a novel Multi-Modal Fusion Transformer, to integrate image and LiDAR representations using attention. We experimentally validate the efficacy of our approach in urban settings involving complex scenarios using the CARLA urban driving simulator. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art driving performance while reducing collisions by 76% compared to geometry-based fusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge