Automated Pulmonary Nodule Detection
Papers and Code
Hybrid CNN with Chebyshev Polynomial Expansion for Medical Image Analysis
Apr 09, 2025Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with early and accurate diagnosis playing a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography (CT) scans is a challenging task due to variability in nodule size, shape, texture, and location. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown considerable promise in medical image analysis; however, their limited ability to capture fine-grained spatial-spectral variations restricts their performance in complex diagnostic scenarios. In this study, we propose a novel hybrid deep learning architecture that incorporates Chebyshev polynomial expansions into CNN layers to enhance expressive power and improve the representation of underlying anatomical structures. The proposed Chebyshev-CNN leverages the orthogonality and recursive properties of Chebyshev polynomials to extract high-frequency features and approximate complex nonlinear functions with greater fidelity. The model is trained and evaluated on benchmark lung cancer imaging datasets, including LUNA16 and LIDC-IDRI, achieving superior performance in classifying pulmonary nodules as benign or malignant. Quantitative results demonstrate significant improvements in accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity compared to traditional CNN-based approaches. This integration of polynomial-based spectral approximation within deep learning provides a robust framework for enhancing automated medical diagnostics and holds potential for broader applications in clinical decision support systems.
AttentNet: Fully Convolutional 3D Attention for Lung Nodule Detection
Jul 19, 2024



Motivated by the increasing popularity of attention mechanisms, we observe that popular convolutional (conv.) attention models like Squeeze-and-Excite (SE) and Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) rely on expensive multi-layer perception (MLP) layers. These MLP layers significantly increase computational complexity, making such models less applicable to 3D image contexts, where data dimensionality and computational costs are higher. In 3D medical imaging, such as 3D pulmonary CT scans, efficient processing is crucial due to the large data volume. Traditional 2D attention generalized to 3D increases the computational load, creating demand for more efficient attention mechanisms for 3D tasks. We investigate the possibility of incorporating fully convolutional (conv.) attention in 3D context. We present two 3D fully conv. attention blocks, demonstrating their effectiveness in 3D context. Using pulmonary CT scans for 3D lung nodule detection, we present AttentNet, an automated lung nodule detection framework from CT images, performing detection as an ensemble of two stages, candidate proposal and false positive (FP) reduction. We compare the proposed 3D attention blocks to popular 2D conv. attention methods generalized to 3D modules and to self-attention units. For the FP reduction stage, we also use a joint analysis approach to aggregate spatial information from different contextual levels. We use LUNA-16 lung nodule detection dataset to demonstrate the benefits of the proposed fully conv. attention blocks compared to baseline popular lung nodule detection methods when no attention is used. Our work does not aim at achieving state-of-the-art results in the lung nodule detection task, rather to demonstrate the benefits of incorporating fully conv. attention within a 3D context.
Incorporation of Eye-Tracking and Gaze Feedback to Characterize and Improve Radiologist Search Patterns of Chest X-rays: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Aug 04, 2023Diagnostic errors in radiology often occur due to incomplete visual assessments by radiologists, despite their knowledge of predicting disease classes. This insufficiency is possibly linked to the absence of required training in search patterns. Additionally, radiologists lack consistent feedback on their visual search patterns, relying on ad-hoc strategies and peer input to minimize errors and enhance efficiency, leading to suboptimal patterns and potential false negatives. This study aimed to use eye-tracking technology to analyze radiologist search patterns, quantify performance using established metrics, and assess the impact of an automated feedback-driven educational framework on detection accuracy. Ten residents participated in a controlled trial focused on detecting suspicious pulmonary nodules. They were divided into an intervention group (received automated feedback) and a control group. Results showed that the intervention group exhibited a 38.89% absolute improvement in detecting suspicious-for-cancer nodules, surpassing the control group's improvement (5.56%, p-value=0.006). Improvement was more rapid over the four training sessions (p-value=0.0001). However, other metrics such as speed, search pattern heterogeneity, distractions, and coverage did not show significant changes. In conclusion, implementing an automated feedback-driven educational framework improved radiologist accuracy in detecting suspicious nodules. The study underscores the potential of such systems in enhancing diagnostic performance and reducing errors. Further research and broader implementation are needed to consolidate these promising results and develop effective training strategies for radiologists, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.
Dual Skip Connections Minimize the False Positive Rate of Lung Nodule Detection in CT images
Oct 25, 2021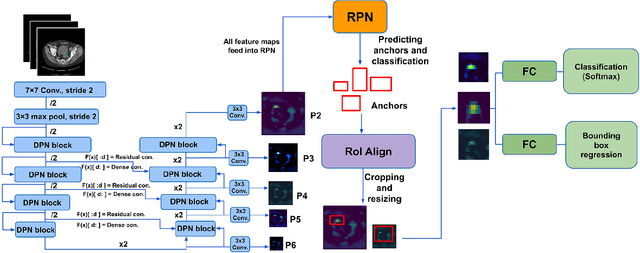
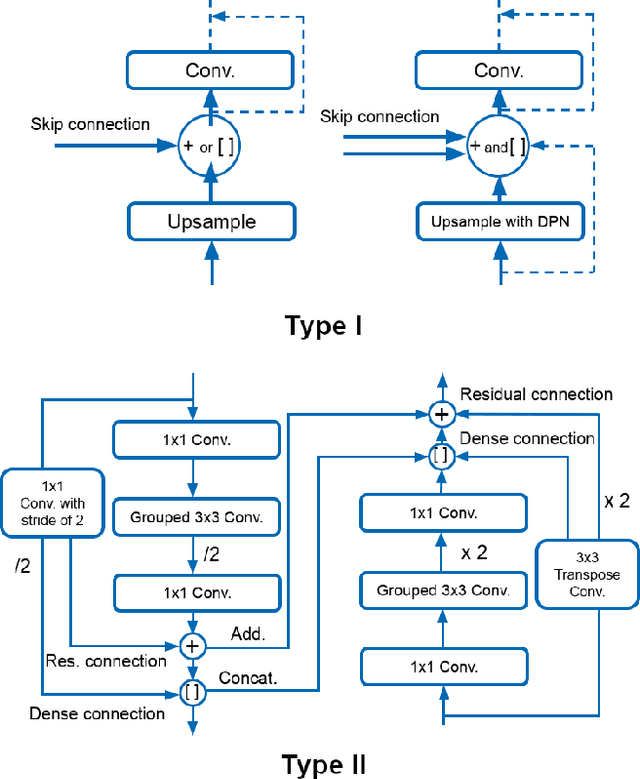
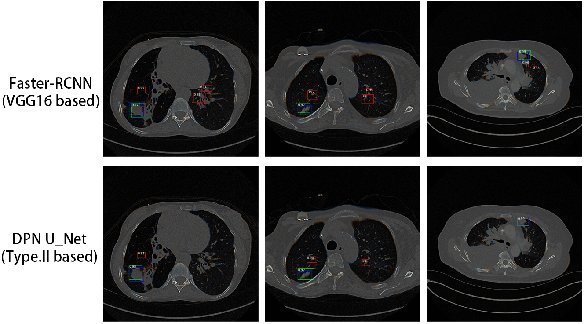
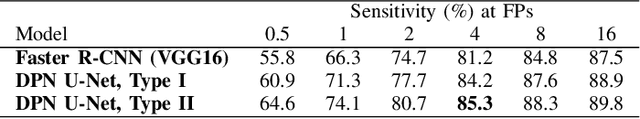
Pulmonary cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed and fatal cancers and is often diagnosed by incidental findings on computed tomography. Automated pulmonary nodule detection is an essential part of computer-aided diagnosis, which is still facing great challenges and difficulties to quickly and accurately locate the exact nodules' positions. This paper proposes a dual skip connection upsampling strategy based on Dual Path network in a U-Net structure generating multiscale feature maps, which aims to minimize the ratio of false positives and maximize the sensitivity for lesion detection of nodules. The results show that our new upsampling strategy improves the performance by having 85.3% sensitivity at 4 FROC per image compared to 84.2% for the regular upsampling strategy or 81.2% for VGG16-based Faster-R-CNN.
AI-based software for lung nodule detection in chest X-rays -- Time for a second reader approach?
Jun 22, 2022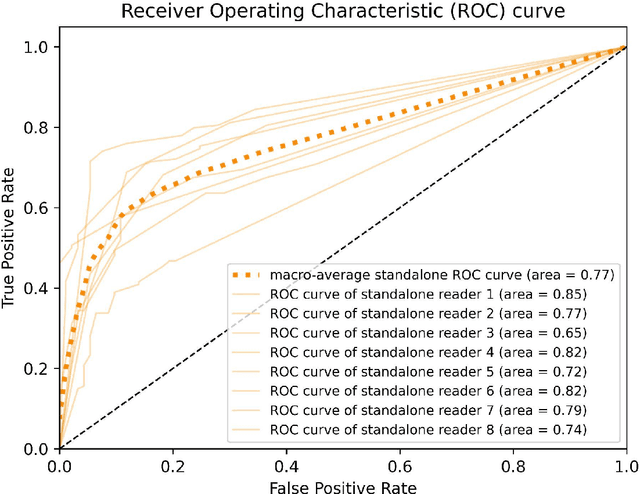
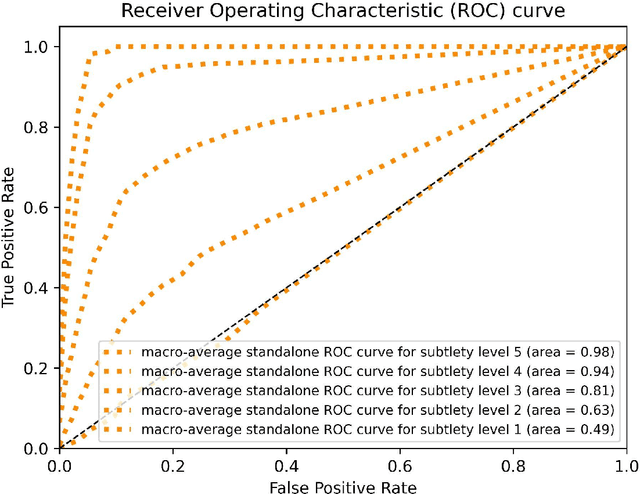

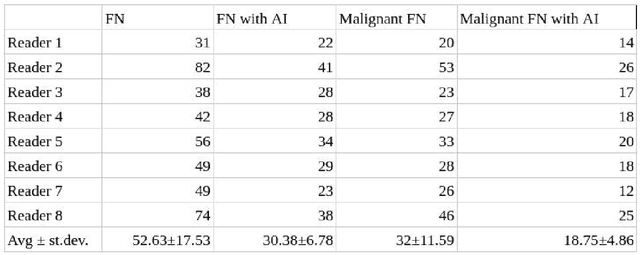
Objectives: To compare artificial intelligence (AI) as a second reader in detecting lung nodules on chest X-rays (CXR) versus radiologists of two binational institutions, and to evaluate AI performance when using two different modes: automated versus assisted (additional remote radiologist review). Methods: The CXR public database (n = 247) of the Japanese Society of Radiological Technology with various types and sizes of lung nodules was analyzed. Eight radiologists evaluated the CXR images with regard to the presence of lung nodules and nodule conspicuity. After radiologist review, the AI software processed and flagged the CXR with the highest probability of missed nodules. The calculated accuracy metrics were the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, F1 score, false negative case number (FN), and the effect of different AI modes (automated/assisted) on the accuracy of nodule detection. Results: For radiologists, the average AUC value was 0.77 $\pm$ 0.07, while the average FN was 52.63 $\pm$ 17.53 (all studies) and 32 $\pm$ 11.59 (studies containing a nodule of malignant etiology = 32% rate of missed malignant nodules). Both AI modes -- automated and assisted -- produced an average increase in sensitivity (by 14% and 12%) and of F1-score (5% and 6%) and a decrease in specificity (by 10% and 3%, respectively). Conclusions: Both AI modes flagged the pulmonary nodules missed by radiologists in a significant number of cases. AI as a second reader has a high potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and radiology workflow. AI might detect certain pulmonary nodules earlier than radiologists, with a potentially significant impact on patient outcomes.
Automated pulmonary nodule detection using 3D deep convolutional neural networks
Mar 23, 2019



Early detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography (CT) images is essential for successful outcomes among lung cancer patients. Much attention has been given to deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based approaches to this task, but models have relied at least partly on 2D or 2.5D components for inherently 3D data. In this paper, we introduce a novel DCNN approach, consisting of two stages, that is fully three-dimensional end-to-end and utilizes the state-of-the-art in object detection. First, nodule candidates are identified with a U-Net-inspired 3D Faster R-CNN trained using online hard negative mining. Second, false positive reduction is performed by 3D DCNN classifiers trained on difficult examples produced during candidate screening. Finally, we introduce a method to ensemble models from both stages via consensus to give the final predictions. By using this framework, we ranked first of 2887 teams in Season One of Alibaba's 2017 TianChi AI Competition for Healthcare.
Extracting and Leveraging Nodule Features with Lung Inpainting for Local Feature Augmentation
Aug 05, 2020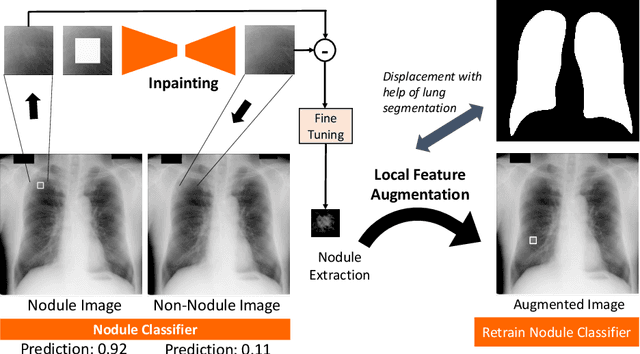
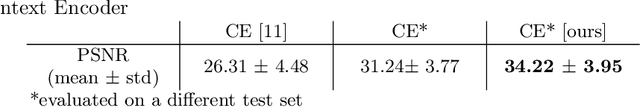
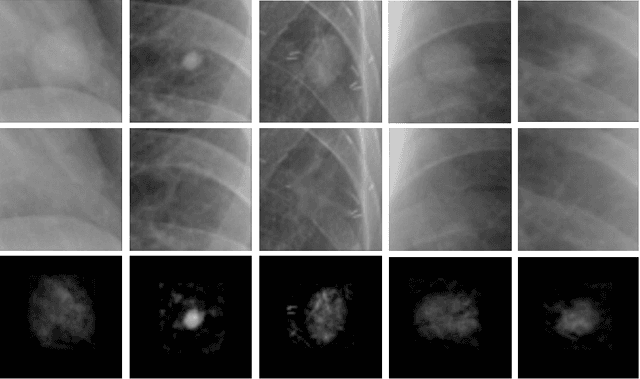
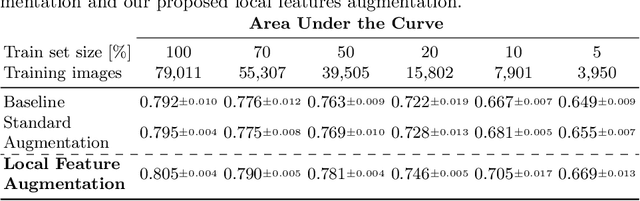
Chest X-ray (CXR) is the most common examination for fast detection of pulmonary abnormalities. Recently, automated algorithms have been developed to classify multiple diseases and abnormalities in CXR scans. However, because of the limited availability of scans containing nodules and the subtle properties of nodules in CXRs, state-of-the-art methods do not perform well on nodule classification. To create additional data for the training process, standard augmentation techniques are applied. However, the variance introduced by these methods are limited as the images are typically modified globally. In this paper, we propose a method for local feature augmentation by extracting local nodule features using a generative inpainting network. The network is applied to generate realistic, healthy tissue and structures in patches containing nodules. The nodules are entirely removed in the inpainted representation. The extraction of the nodule features is processed by subtraction of the inpainted patch from the nodule patch. With arbitrary displacement of the extracted nodules in the lung area across different CXR scans and further local modifications during training, we significantly increase the nodule classification performance and outperform state-of-the-art augmentation methods.
Discriminative Localization in CNNs for Weakly-Supervised Segmentation of Pulmonary Nodules
Feb 22, 2018



Automated detection and segmentation of pulmonary nodules on lung computed tomography (CT) scans can facilitate early lung cancer diagnosis. Existing supervised approaches for automated nodule segmentation on CT scans require voxel-based annotations for training, which are labor- and time-consuming to obtain. In this work, we propose a weakly-supervised method that generates accurate voxel-level nodule segmentation trained with image-level labels only. By adapting a convolutional neural network (CNN) trained for image classification, our proposed method learns discriminative regions from the activation maps of convolution units at different scales, and identifies the true nodule location with a novel candidate-screening framework. Experimental results on the public LIDC-IDRI dataset demonstrate that, our weakly-supervised nodule segmentation framework achieves competitive performance compared to a fully-supervised CNN-based segmentation method.
A Pulmonary Nodule Detection Model Based on Progressive Resolution and Hierarchical Saliency
Jul 02, 2018



Detection of pulmonary nodules on chest CT is an essential step in the early diagnosis of lung cancer, which is critical for best patient care. Although a number of computer-aided nodule detection methods have been published in the literature, these methods still have two major drawbacks: missing out true nodules during the detection of nodule candidates and less-accurate identification of nodules from non-nodule. In this paper, we propose an automated pulmonary nodule detection algorithm that jointly combines progressive resolution and hierarchical saliency. Specifically, we design a 3D progressive resolution-based densely dilated FCN, namely the progressive resolution network (PRN), to detect nodule candidates inside the lung, and construct a densely dilated 3D CNN with hierarchical saliency, namely the hierarchical saliency network (HSN), to simultaneously identify genuine nodules from those candidates and estimate the diameters of nodules. We evaluated our algorithm on the benchmark LUng Nodule Analysis 2016 (LUNA16) dataset and achieved a state-of-the-art detection score. Our results suggest that the proposed algorithm can effectively detect pulmonary nodules on chest CT and accurately estimate their diameters.
DeepLung: Deep 3D Dual Path Nets for Automated Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Classification
Jan 25, 2018

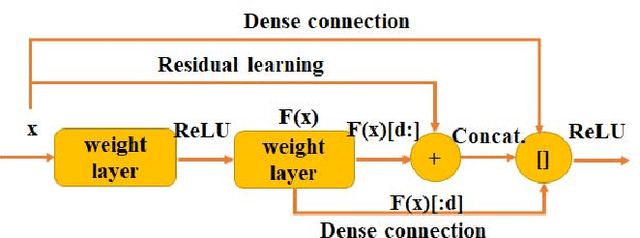
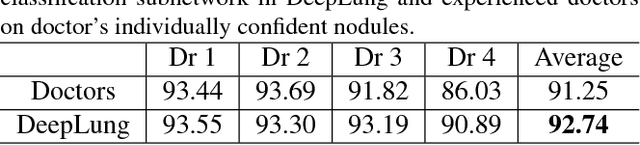
In this work, we present a fully automated lung computed tomography (CT) cancer diagnosis system, DeepLung. DeepLung consists of two components, nodule detection (identifying the locations of candidate nodules) and classification (classifying candidate nodules into benign or malignant). Considering the 3D nature of lung CT data and the compactness of dual path networks (DPN), two deep 3D DPN are designed for nodule detection and classification respectively. Specifically, a 3D Faster Regions with Convolutional Neural Net (R-CNN) is designed for nodule detection with 3D dual path blocks and a U-net-like encoder-decoder structure to effectively learn nodule features. For nodule classification, gradient boosting machine (GBM) with 3D dual path network features is proposed. The nodule classification subnetwork was validated on a public dataset from LIDC-IDRI, on which it achieved better performance than state-of-the-art approaches and surpassed the performance of experienced doctors based on image modality. Within the DeepLung system, candidate nodules are detected first by the nodule detection subnetwork, and nodule diagnosis is conducted by the classification subnetwork. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that DeepLung has performance comparable to experienced doctors both for the nodule-level and patient-level diagnosis on the LIDC-IDRI dataset.\footnote{https://github.com/uci-cbcl/DeepLung.git}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge