Xinyang Feng
Convolutional Transformer based Dual Discriminator Generative Adversarial Networks for Video Anomaly Detection
Jul 29, 2021



Abstract:Detecting abnormal activities in real-world surveillance videos is an important yet challenging task as the prior knowledge about video anomalies is usually limited or unavailable. Despite that many approaches have been developed to resolve this problem, few of them can capture the normal spatio-temporal patterns effectively and efficiently. Moreover, existing works seldom explicitly consider the local consistency at frame level and global coherence of temporal dynamics in video sequences. To this end, we propose Convolutional Transformer based Dual Discriminator Generative Adversarial Networks (CT-D2GAN) to perform unsupervised video anomaly detection. Specifically, we first present a convolutional transformer to perform future frame prediction. It contains three key components, i.e., a convolutional encoder to capture the spatial information of the input video clips, a temporal self-attention module to encode the temporal dynamics, and a convolutional decoder to integrate spatio-temporal features and predict the future frame. Next, a dual discriminator based adversarial training procedure, which jointly considers an image discriminator that can maintain the local consistency at frame-level and a video discriminator that can enforce the global coherence of temporal dynamics, is employed to enhance the future frame prediction. Finally, the prediction error is used to identify abnormal video frames. Thoroughly empirical studies on three public video anomaly detection datasets, i.e., UCSD Ped2, CUHK Avenue, and Shanghai Tech Campus, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed adversarial spatio-temporal modeling framework.
Deep Learning Identifies Neuroimaging Signatures of Alzheimer's Disease Using Structural and Synthesized Functional MRI Data
Apr 10, 2021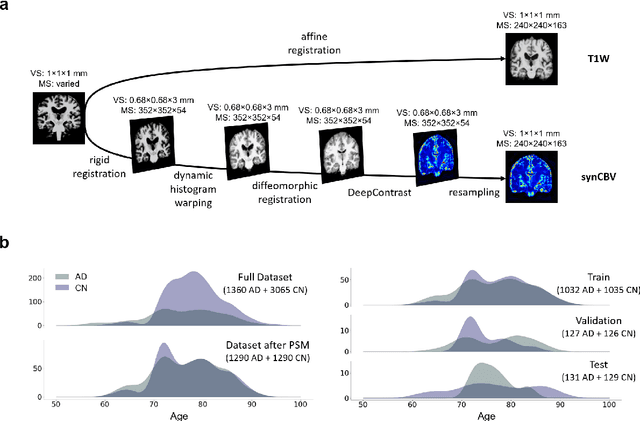
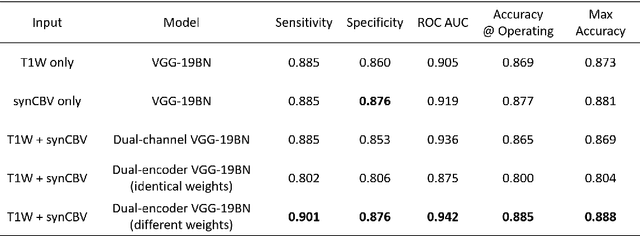
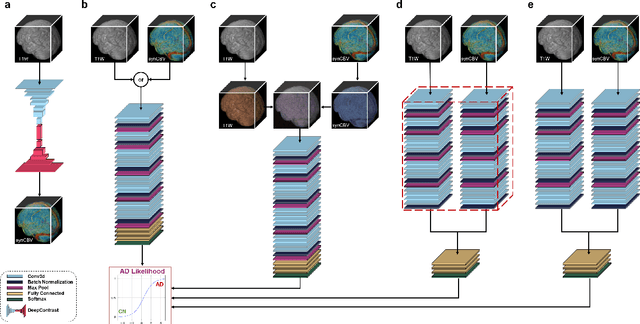
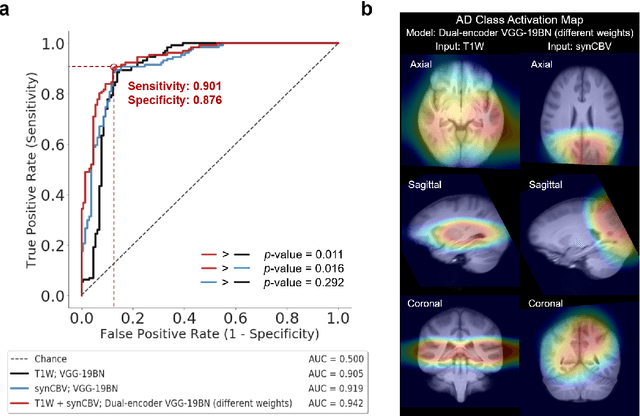
Abstract:Current neuroimaging techniques provide paths to investigate the structure and function of the brain in vivo and have made great advances in understanding Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the group-level analyses prevalently used for investigation and understanding of the disease are not applicable for diagnosis of individuals. More recently, deep learning, which can efficiently analyze large-scale complex patterns in 3D brain images, has helped pave the way for computer-aided individual diagnosis by providing accurate and automated disease classification. Great progress has been made in classifying AD with deep learning models developed upon increasingly available structural MRI data. The lack of scale-matched functional neuroimaging data prevents such models from being further improved by observing functional changes in pathophysiology. Here we propose a potential solution by first learning a structural-to-functional transformation in brain MRI, and further synthesizing spatially matched functional images from large-scale structural scans. We evaluated our approach by building computational models to discriminate patients with AD from healthy normal subjects and demonstrated a performance boost after combining the structural and synthesized functional brain images into the same model. Furthermore, our regional analyses identified the temporal lobe to be the most predictive structural-region and the parieto-occipital lobe to be the most predictive functional-region of our model, which are both in concordance with previous group-level neuroimaging findings. Together, we demonstrate the potential of deep learning with large-scale structural and synthesized functional MRI to impact AD classification and to identify AD's neuroimaging signatures.
Substituting Gadolinium in Brain MRI Using DeepContrast
Jan 15, 2020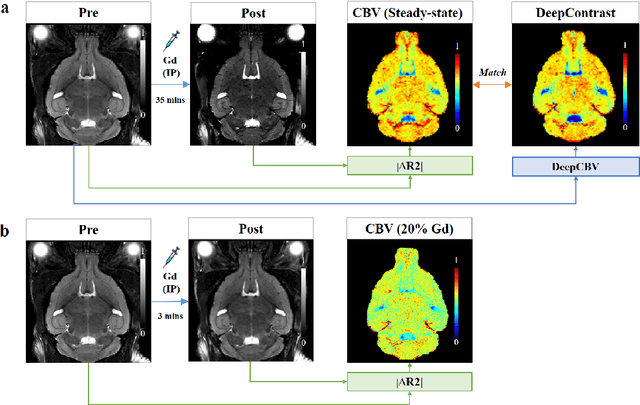
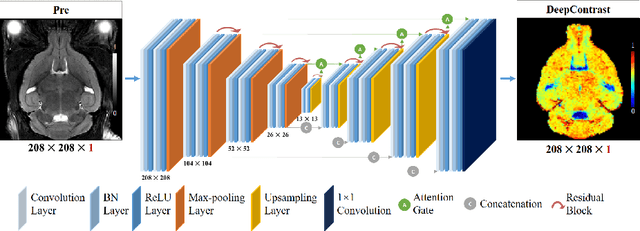
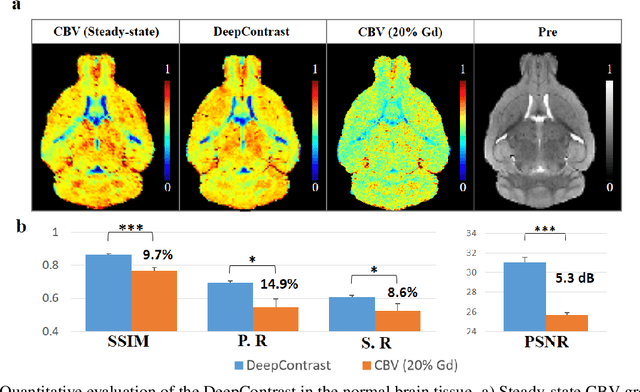
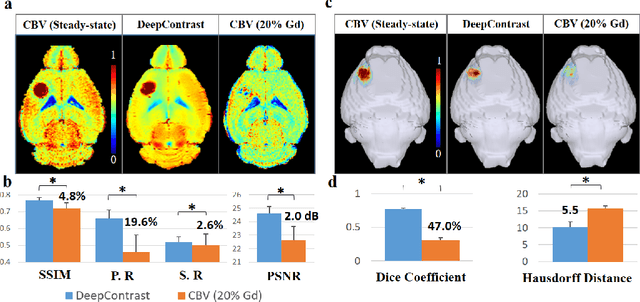
Abstract:Cerebral blood volume (CBV) is a hemodynamic correlate of oxygen metabolism and reflects brain activity and function. High-resolution CBV maps can be generated using the steady-state gadolinium-enhanced MRI technique. Such a technique requires an intravenous injection of exogenous gadolinium based contrast agent (GBCA) and recent studies suggest that the GBCA can accumulate in the brain after frequent use. We hypothesize that endogenous sources of contrast might exist within the most conventional and commonly acquired structural MRI, potentially obviating the need for exogenous contrast. Here, we test this hypothesis by developing and optimizing a deep learning algorithm, which we call DeepContrast, in mice. We find that DeepContrast performs equally well as exogenous GBCA in mapping CBV of the normal brain tissue and enhancing glioblastoma. Together, these studies validate our hypothesis that a deep learning approach can potentially replace the need for GBCAs in brain MRI.
Estimating brain age based on a healthy population with deep learning and structural MRI
Jul 01, 2019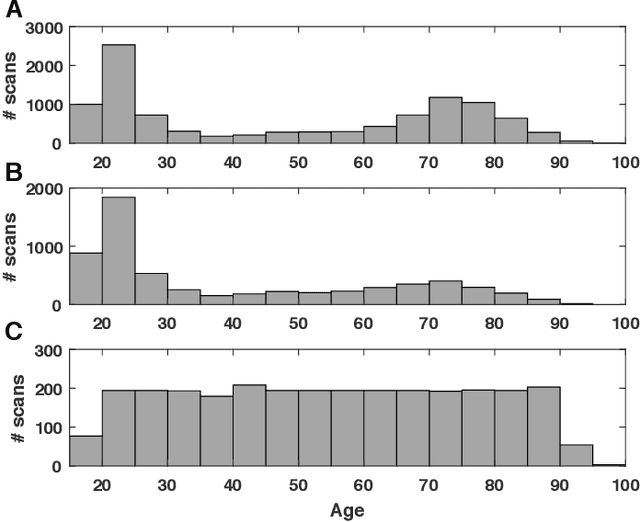
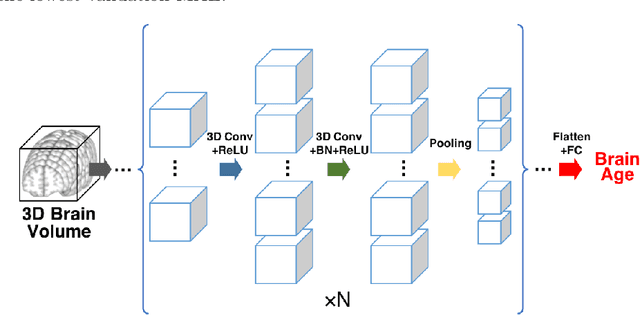
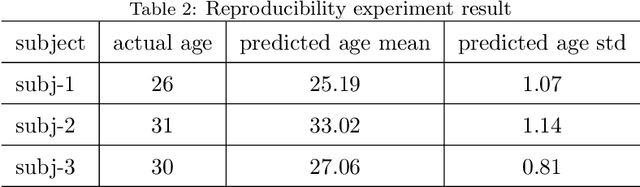
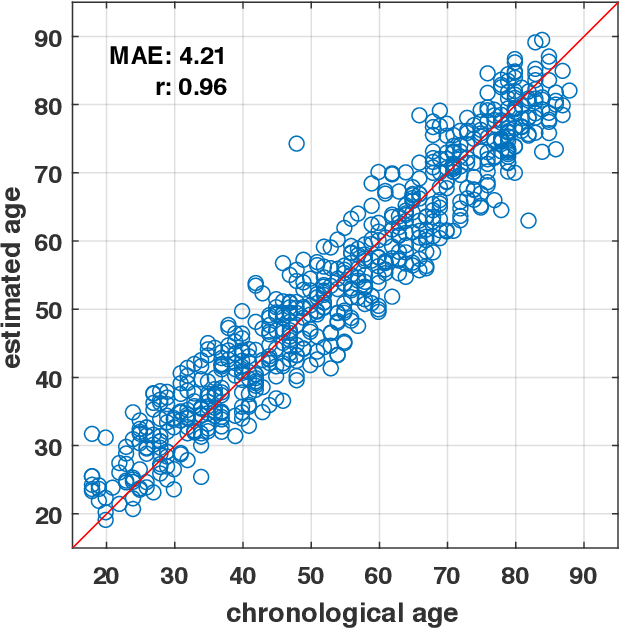
Abstract:Numerous studies have established that estimated brain age, as derived from statistical models trained on healthy populations, constitutes a valuable biomarker that is predictive of cognitive decline and various neurological diseases. In this work, we curate a large-scale heterogeneous dataset (N = 10,158, age range 18 - 97) of structural brain MRIs in a healthy population from multiple publicly-available sources, upon which we train a deep learning model for brain age estimation. The availability of the large-scale dataset enables a more uniform age distribution across adult life-span for effective age estimation with no bias toward certain age groups. We demonstrate that the age estimation accuracy, evaluated with mean absolute error (MAE) and correlation coefficient (r), outperforms previously reported methods in both a hold-out test set reflective of the custom population (MAE = 4.06 years, r = 0.970) and an independent life-span evaluation dataset (MAE = 4.21 years, r = 0.960) on which a previous study has evaluated. We further demonstrate the utility of the estimated age in life-span aging analysis of cognitive functions. Furthermore, we conduct extensive ablation tests and employ feature-attribution techniques to analyze which regions contribute the most predictive value, demonstrating the prominence of the frontal lobe as well as pattern shift across life-span. In summary, we achieve superior age estimation performance confirming the efficacy of deep learning and the added utility of training with data both in larger number and more uniformly distributed than in previous studies. We demonstrate the regional contribution to our brain age predictions through multiple routes and confirm the association of divergence between estimated and chronological brain age with neuropsychological measures.
Discriminative analysis of the human cortex using spherical CNNs - a study on Alzheimer's disease diagnosis
Dec 19, 2018



Abstract:In neuroimaging studies, the human cortex is commonly modeled as a sphere to preserve the topological structure of the cortical surface. Cortical neuroimaging measures hence can be modeled in spherical representation. In this work, we explore analyzing the human cortex using spherical CNNs in an Alzheimer's disease (AD) classification task using cortical morphometric measures derived from structural MRI. Our results show superior performance in classifying AD versus cognitively normal and in predicting MCI progression within two years, using structural MRI information only. This work demonstrates for the first time the potential of the spherical CNNs framework in the discriminative analysis of the human cortex and could be extended to other modalities and other neurological diseases.
A Deep Neural Network for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection and Diagnosis in Multivariate Time Series Data
Nov 20, 2018



Abstract:Nowadays, multivariate time series data are increasingly collected in various real world systems, e.g., power plants, wearable devices, etc. Anomaly detection and diagnosis in multivariate time series refer to identifying abnormal status in certain time steps and pinpointing the root causes. Building such a system, however, is challenging since it not only requires to capture the temporal dependency in each time series, but also need encode the inter-correlations between different pairs of time series. In addition, the system should be robust to noise and provide operators with different levels of anomaly scores based upon the severity of different incidents. Despite the fact that a number of unsupervised anomaly detection algorithms have been developed, few of them can jointly address these challenges. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Scale Convolutional Recurrent Encoder-Decoder (MSCRED), to perform anomaly detection and diagnosis in multivariate time series data. Specifically, MSCRED first constructs multi-scale (resolution) signature matrices to characterize multiple levels of the system statuses in different time steps. Subsequently, given the signature matrices, a convolutional encoder is employed to encode the inter-sensor (time series) correlations and an attention based Convolutional Long-Short Term Memory (ConvLSTM) network is developed to capture the temporal patterns. Finally, based upon the feature maps which encode the inter-sensor correlations and temporal information, a convolutional decoder is used to reconstruct the input signature matrices and the residual signature matrices are further utilized to detect and diagnose anomalies. Extensive empirical studies based on a synthetic dataset and a real power plant dataset demonstrate that MSCRED can outperform state-of-the-art baseline methods.
Discriminative Localization in CNNs for Weakly-Supervised Segmentation of Pulmonary Nodules
Feb 22, 2018



Abstract:Automated detection and segmentation of pulmonary nodules on lung computed tomography (CT) scans can facilitate early lung cancer diagnosis. Existing supervised approaches for automated nodule segmentation on CT scans require voxel-based annotations for training, which are labor- and time-consuming to obtain. In this work, we propose a weakly-supervised method that generates accurate voxel-level nodule segmentation trained with image-level labels only. By adapting a convolutional neural network (CNN) trained for image classification, our proposed method learns discriminative regions from the activation maps of convolution units at different scales, and identifies the true nodule location with a novel candidate-screening framework. Experimental results on the public LIDC-IDRI dataset demonstrate that, our weakly-supervised nodule segmentation framework achieves competitive performance compared to a fully-supervised CNN-based segmentation method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge