Zhongzhou Zhao
VK-G2T: Vision and Context Knowledge enhanced Gloss2Text
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Existing sign language translation methods follow a two-stage pipeline: first converting the sign language video to a gloss sequence (i.e. Sign2Gloss) and then translating the generated gloss sequence into a spoken language sentence (i.e. Gloss2Text). While previous studies have focused on boosting the performance of the Sign2Gloss stage, we emphasize the optimization of the Gloss2Text stage. However, this task is non-trivial due to two distinct features of Gloss2Text: (1) isolated gloss input and (2) low-capacity gloss vocabulary. To address these issues, we propose a vision and context knowledge enhanced Gloss2Text model, named VK-G2T, which leverages the visual content of the sign language video to learn the properties of the target sentence and exploit the context knowledge to facilitate the adaptive translation of gloss words. Extensive experiments conducted on a Chinese benchmark validate the superiority of our model.
CASEIN: Cascading Explicit and Implicit Control for Fine-grained Emotion Intensity Regulation
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:Existing fine-grained intensity regulation methods rely on explicit control through predicted emotion probabilities. However, these high-level semantic probabilities are often inaccurate and unsmooth at the phoneme level, leading to bias in learning. Especially when we attempt to mix multiple emotion intensities for specific phonemes, resulting in markedly reduced controllability and naturalness of the synthesis. To address this issue, we propose the CAScaded Explicit and Implicit coNtrol framework (CASEIN), which leverages accurate disentanglement of emotion manifolds from the reference speech to learn the implicit representation at a lower semantic level. This representation bridges the semantical gap between explicit probabilities and the synthesis model, reducing bias in learning. In experiments, our CASEIN surpasses existing methods in both controllability and naturalness. Notably, we are the first to achieve fine-grained control over the mixed intensity of multiple emotions.
Stylized Data-to-Text Generation: A Case Study in the E-Commerce Domain
May 05, 2023



Abstract:Existing data-to-text generation efforts mainly focus on generating a coherent text from non-linguistic input data, such as tables and attribute-value pairs, but overlook that different application scenarios may require texts of different styles. Inspired by this, we define a new task, namely stylized data-to-text generation, whose aim is to generate coherent text for the given non-linguistic data according to a specific style. This task is non-trivial, due to three challenges: the logic of the generated text, unstructured style reference, and biased training samples. To address these challenges, we propose a novel stylized data-to-text generation model, named StyleD2T, comprising three components: logic planning-enhanced data embedding, mask-based style embedding, and unbiased stylized text generation. In the first component, we introduce a graph-guided logic planner for attribute organization to ensure the logic of generated text. In the second component, we devise feature-level mask-based style embedding to extract the essential style signal from the given unstructured style reference. In the last one, pseudo triplet augmentation is utilized to achieve unbiased text generation, and a multi-condition based confidence assignment function is designed to ensure the quality of pseudo samples. Extensive experiments on a newly collected dataset from Taobao have been conducted, and the results show the superiority of our model over existing methods.
Towards Zero-Shot Personalized Table-to-Text Generation with Contrastive Persona Distillation
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Existing neural methods have shown great potentials towards generating informative text from structured tabular data as well as maintaining high content fidelity. However, few of them shed light on generating personalized expressions, which often requires well-aligned persona-table-text datasets that are difficult to obtain. To overcome these obstacles, we explore personalized table-to-text generation under a zero-shot setting, by assuming no well-aligned persona-table-text triples are required during training. To this end, we firstly collect a set of unpaired persona information and then propose a semi-supervised approach with contrastive persona distillation (S2P-CPD) to generate personalized context. Specifically, tabular data and persona information are firstly represented as latent variables separately. Then, we devise a latent space fusion technique to distill persona information into the table representation. Besides, a contrastive-based discriminator is employed to guarantee the style consistency between the generated context and its corresponding persona. Experimental results on two benchmarks demonstrate S2P-CPD's ability on keeping both content fidelity and personalized expressions.
Dual Preference Distribution Learning for Item Recommendation
Jan 24, 2022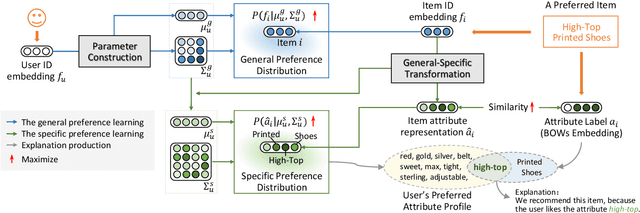
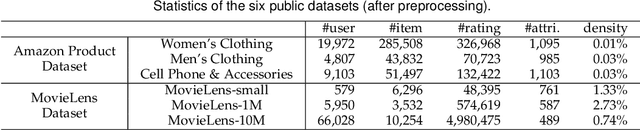
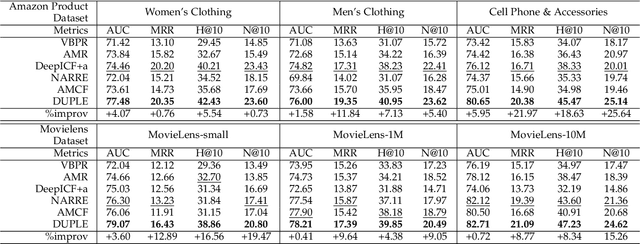
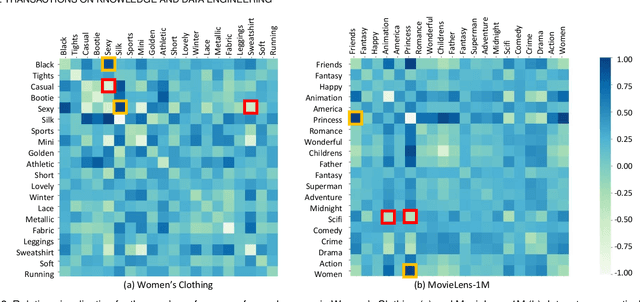
Abstract:Recommender systems can automatically recommend users items that they probably like, for which the goal is to represent the user and item as well as model their interaction. Existing methods have primarily learned the user's preferences and item's features with vectorized representations, and modeled the user-item interaction by the similarity of their representations. In fact, the user's different preferences are related and capturing such relations could better understand the user's preferences for a better recommendation. Toward this end, we propose to represent the user's preference with multi-variant Gaussian distribution, and model the user-item interaction by calculating the probability density at the item in the user's preference distribution. In this manner, the mean vector of the Gaussian distribution is able to capture the center of the user's preferences, while its covariance matrix captures the relations of these preferences. In particular, in this work, we propose a dual preference distribution learning framework (DUPLE), which captures the user's preferences to both the items and attributes by a Gaussian distribution, respectively. As a byproduct, identifying the user's preference to specific attributes enables us to provide the explanation of recommending an item to the user. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments on six public datasets show that DUPLE achieves the best performance over all state-of-the-art recommendation methods.
AliMe MKG: A Multi-modal Knowledge Graph for Live-streaming E-commerce
Sep 13, 2021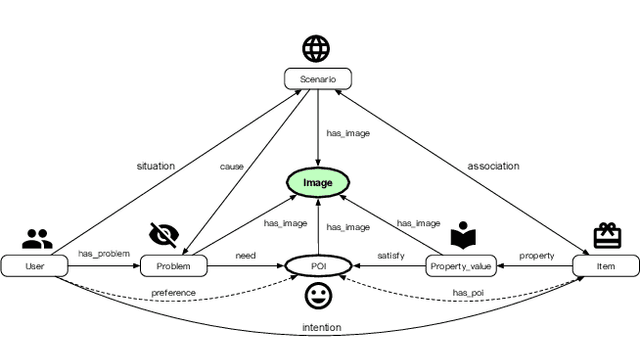
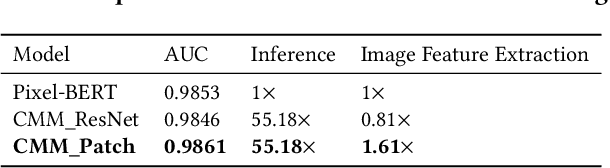
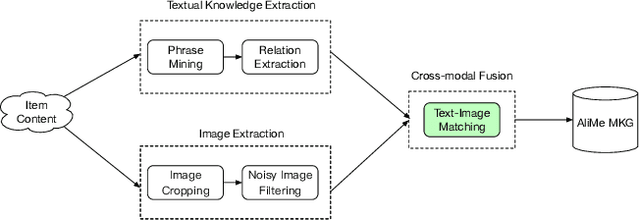
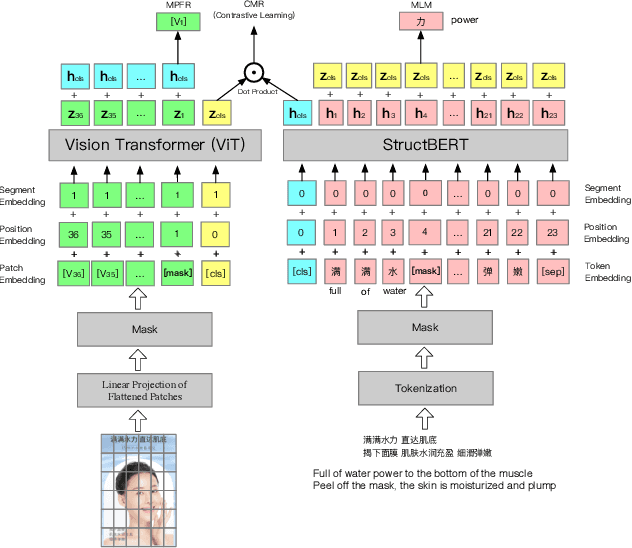
Abstract:Live streaming is becoming an increasingly popular trend of sales in E-commerce. The core of live-streaming sales is to encourage customers to purchase in an online broadcasting room. To enable customers to better understand a product without jumping out, we propose AliMe MKG, a multi-modal knowledge graph that aims at providing a cognitive profile for products, through which customers are able to seek information about and understand a product. Based on the MKG, we build an online live assistant that highlights product search, product exhibition and question answering, allowing customers to skim over item list, view item details, and ask item-related questions. Our system has been launched online in the Taobao app, and currently serves hundreds of thousands of customers per day.
GGP: A Graph-based Grouping Planner for Explicit Control of Long Text Generation
Aug 18, 2021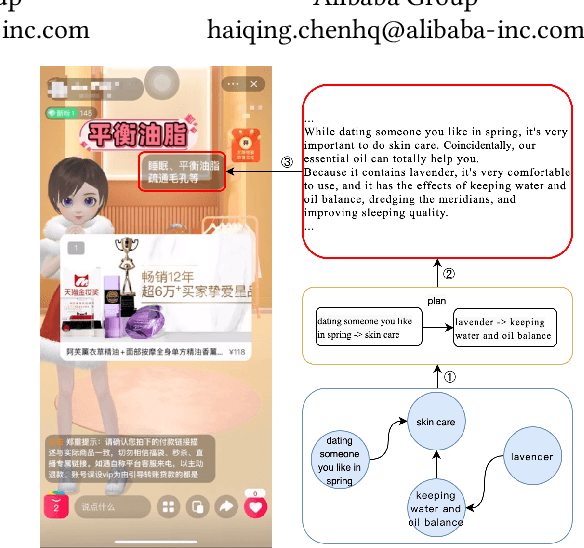

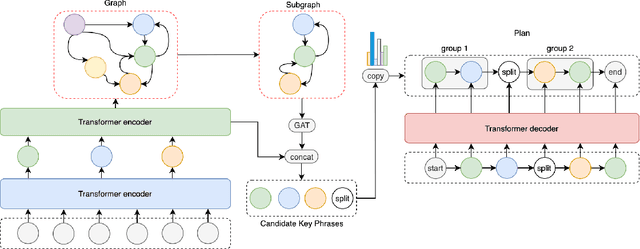
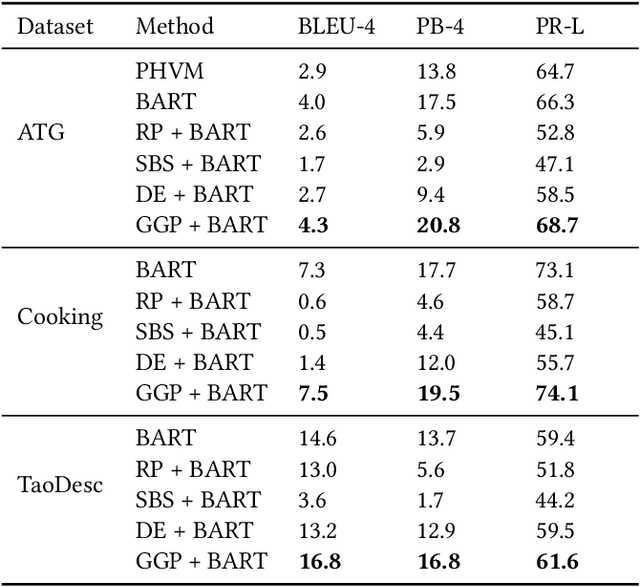
Abstract:Existing data-driven methods can well handle short text generation. However, when applied to the long-text generation scenarios such as story generation or advertising text generation in the commercial scenario, these methods may generate illogical and uncontrollable texts. To address these aforementioned issues, we propose a graph-based grouping planner(GGP) following the idea of first-plan-then-generate. Specifically, given a collection of key phrases, GGP firstly encodes these phrases into an instance-level sequential representation and a corpus-level graph-based representation separately. With these two synergic representations, we then regroup these phrases into a fine-grained plan, based on which we generate the final long text. We conduct our experiments on three long text generation datasets and the experimental results reveal that GGP significantly outperforms baselines, which proves that GGP can control the long text generation by knowing how to say and in what order.
SPMoE: Generate Multiple Pattern-Aware Outputs with Sparse Pattern Mixture of Experts
Aug 18, 2021Abstract:Many generation tasks follow a one-to-many mapping relationship: each input could be associated with multiple outputs. Existing methods like Conditional Variational AutoEncoder(CVAE) employ a latent variable to model this one-to-many relationship. However, this high-dimensional and dense latent variable lacks explainability and usually leads to poor and uncontrollable generations. In this paper, we innovatively introduce the linguistic concept of pattern to decompose the one-to-many mapping into multiple one-to-one mappings and further propose a model named Sparse Pattern Mixture of Experts(SPMoE). Each one-to-one mapping is associated with a conditional generation pattern and is modeled with an expert in SPMoE. To ensure each language pattern can be exclusively handled with an expert model for better explainability and diversity, a sparse mechanism is employed to coordinate all the expert models in SPMoE. We assess the performance of our SPMoE on the paraphrase generation task and the experiment results prove that SPMoE can achieve a good balance in terms of quality, pattern-level diversity, and corpus-level diversity.
ROSITA: Enhancing Vision-and-Language Semantic Alignments via Cross- and Intra-modal Knowledge Integration
Aug 16, 2021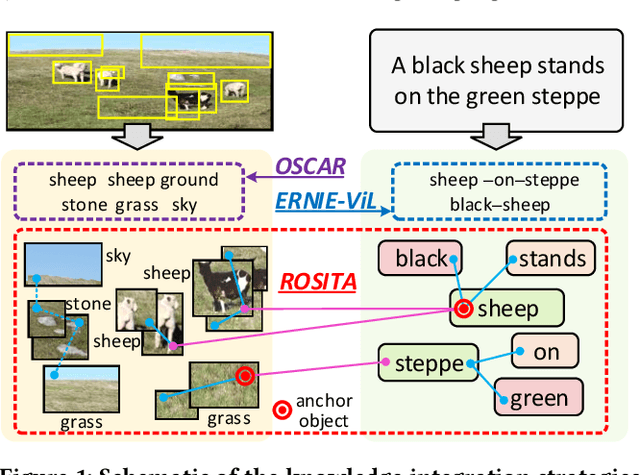
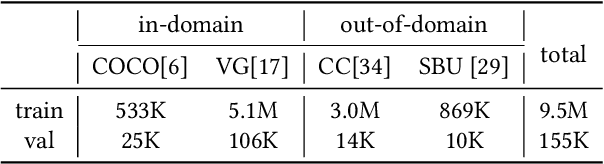
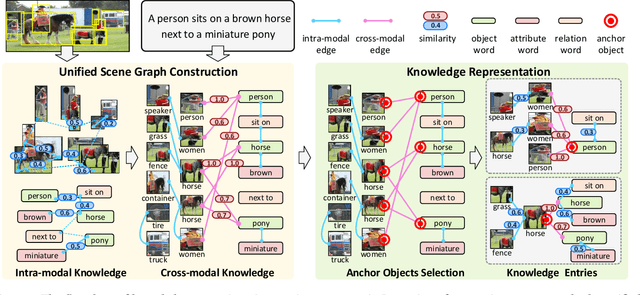
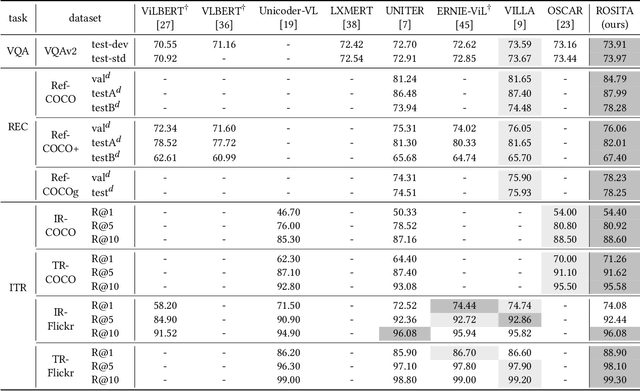
Abstract:Vision-and-language pretraining (VLP) aims to learn generic multimodal representations from massive image-text pairs. While various successful attempts have been proposed, learning fine-grained semantic alignments between image-text pairs plays a key role in their approaches. Nevertheless, most existing VLP approaches have not fully utilized the intrinsic knowledge within the image-text pairs, which limits the effectiveness of the learned alignments and further restricts the performance of their models. To this end, we introduce a new VLP method called ROSITA, which integrates the cross- and intra-modal knowledge in a unified scene graph to enhance the semantic alignments. Specifically, we introduce a novel structural knowledge masking (SKM) strategy to use the scene graph structure as a priori to perform masked language (region) modeling, which enhances the semantic alignments by eliminating the interference information within and across modalities. Extensive ablation studies and comprehensive analysis verifies the effectiveness of ROSITA in semantic alignments. Pretrained with both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets, ROSITA significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art VLP methods on three typical vision-and-language tasks over six benchmark datasets.
OneStop QAMaker: Extract Question-Answer Pairs from Text in a One-Stop Approach
Feb 24, 2021Abstract:Large-scale question-answer (QA) pairs are critical for advancing research areas like machine reading comprehension and question answering. To construct QA pairs from documents requires determining how to ask a question and what is the corresponding answer. Existing methods for QA pair generation usually follow a pipeline approach. Namely, they first choose the most likely candidate answer span and then generate the answer-specific question. This pipeline approach, however, is undesired in mining the most appropriate QA pairs from documents since it ignores the connection between question generation and answer extraction, which may lead to incompatible QA pair generation, i.e., the selected answer span is inappropriate for question generation. However, for human annotators, we take the whole QA pair into account and consider the compatibility between question and answer. Inspired by such motivation, instead of the conventional pipeline approach, we propose a model named OneStop generate QA pairs from documents in a one-stop approach. Specifically, questions and their corresponding answer span is extracted simultaneously and the process of question generation and answer extraction mutually affect each other. Additionally, OneStop is much more efficient to be trained and deployed in industrial scenarios since it involves only one model to solve the complex QA generation task. We conduct comprehensive experiments on three large-scale machine reading comprehension datasets: SQuAD, NewsQA, and DuReader. The experimental results demonstrate that our OneStop model outperforms the baselines significantly regarding the quality of generated questions, quality of generated question-answer pairs, and model efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge