Xinxing Zu
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025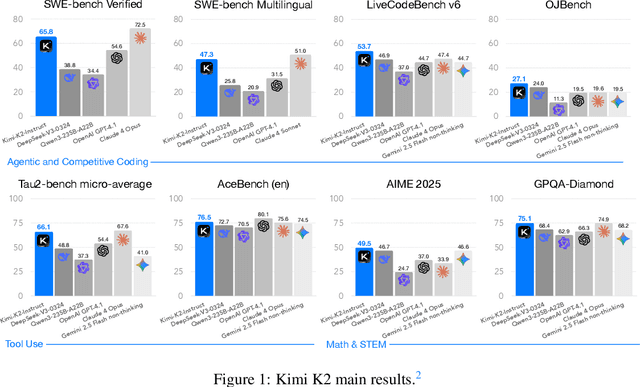
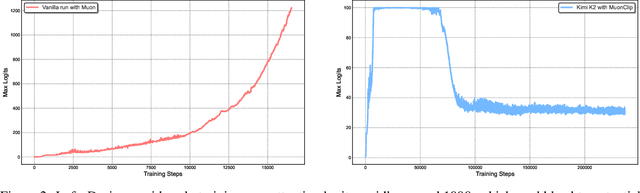
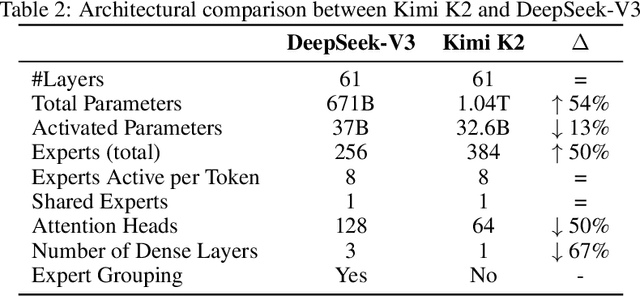
Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 32 billion activated parameters and 1 trillion total parameters. We propose the MuonClip optimizer, which improves upon Muon with a novel QK-clip technique to address training instability while enjoying the advanced token efficiency of Muon. Based on MuonClip, K2 was pre-trained on 15.5 trillion tokens with zero loss spike. During post-training, K2 undergoes a multi-stage post-training process, highlighted by a large-scale agentic data synthesis pipeline and a joint reinforcement learning (RL) stage, where the model improves its capabilities through interactions with real and synthetic environments. Kimi K2 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source non-thinking models, with strengths in agentic capabilities. Notably, K2 obtains 66.1 on Tau2-Bench, 76.5 on ACEBench (En), 65.8 on SWE-Bench Verified, and 47.3 on SWE-Bench Multilingual -- surpassing most open and closed-sourced baselines in non-thinking settings. It also exhibits strong capabilities in coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks, with a score of 53.7 on LiveCodeBench v6, 49.5 on AIME 2025, 75.1 on GPQA-Diamond, and 27.1 on OJBench, all without extended thinking. These results position Kimi K2 as one of the most capable open-source large language models to date, particularly in software engineering and agentic tasks. We release our base and post-trained model checkpoints to facilitate future research and applications of agentic intelligence.
Kimi-VL Technical Report
Apr 10, 2025
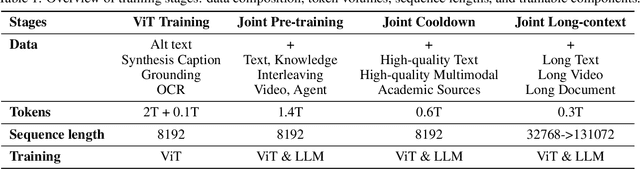
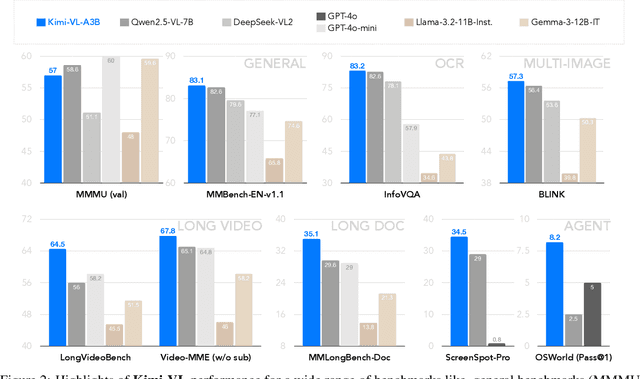
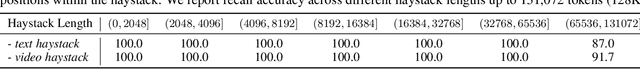
Abstract:We present Kimi-VL, an efficient open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) vision-language model (VLM) that offers advanced multimodal reasoning, long-context understanding, and strong agent capabilities - all while activating only 2.8B parameters in its language decoder (Kimi-VL-A3B). Kimi-VL demonstrates strong performance across challenging domains: as a general-purpose VLM, Kimi-VL excels in multi-turn agent tasks (e.g., OSWorld), matching flagship models. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable capabilities across diverse challenging vision language tasks, including college-level image and video comprehension, OCR, mathematical reasoning, and multi-image understanding. In comparative evaluations, it effectively competes with cutting-edge efficient VLMs such as GPT-4o-mini, Qwen2.5-VL-7B, and Gemma-3-12B-IT, while surpassing GPT-4o in several key domains. Kimi-VL also advances in processing long contexts and perceiving clearly. With a 128K extended context window, Kimi-VL can process diverse long inputs, achieving impressive scores of 64.5 on LongVideoBench and 35.1 on MMLongBench-Doc. Its native-resolution vision encoder, MoonViT, further allows it to see and understand ultra-high-resolution visual inputs, achieving 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on ScreenSpot-Pro, while maintaining lower computational cost for common tasks. Building upon Kimi-VL, we introduce an advanced long-thinking variant: Kimi-VL-Thinking. Developed through long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL), this model exhibits strong long-horizon reasoning capabilities. It achieves scores of 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista while maintaining the compact 2.8B activated LLM parameters, setting a new standard for efficient multimodal thinking models. Code and models are publicly accessible at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-VL.
VK-G2T: Vision and Context Knowledge enhanced Gloss2Text
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Existing sign language translation methods follow a two-stage pipeline: first converting the sign language video to a gloss sequence (i.e. Sign2Gloss) and then translating the generated gloss sequence into a spoken language sentence (i.e. Gloss2Text). While previous studies have focused on boosting the performance of the Sign2Gloss stage, we emphasize the optimization of the Gloss2Text stage. However, this task is non-trivial due to two distinct features of Gloss2Text: (1) isolated gloss input and (2) low-capacity gloss vocabulary. To address these issues, we propose a vision and context knowledge enhanced Gloss2Text model, named VK-G2T, which leverages the visual content of the sign language video to learn the properties of the target sentence and exploit the context knowledge to facilitate the adaptive translation of gloss words. Extensive experiments conducted on a Chinese benchmark validate the superiority of our model.
OneStop QAMaker: Extract Question-Answer Pairs from Text in a One-Stop Approach
Feb 24, 2021Abstract:Large-scale question-answer (QA) pairs are critical for advancing research areas like machine reading comprehension and question answering. To construct QA pairs from documents requires determining how to ask a question and what is the corresponding answer. Existing methods for QA pair generation usually follow a pipeline approach. Namely, they first choose the most likely candidate answer span and then generate the answer-specific question. This pipeline approach, however, is undesired in mining the most appropriate QA pairs from documents since it ignores the connection between question generation and answer extraction, which may lead to incompatible QA pair generation, i.e., the selected answer span is inappropriate for question generation. However, for human annotators, we take the whole QA pair into account and consider the compatibility between question and answer. Inspired by such motivation, instead of the conventional pipeline approach, we propose a model named OneStop generate QA pairs from documents in a one-stop approach. Specifically, questions and their corresponding answer span is extracted simultaneously and the process of question generation and answer extraction mutually affect each other. Additionally, OneStop is much more efficient to be trained and deployed in industrial scenarios since it involves only one model to solve the complex QA generation task. We conduct comprehensive experiments on three large-scale machine reading comprehension datasets: SQuAD, NewsQA, and DuReader. The experimental results demonstrate that our OneStop model outperforms the baselines significantly regarding the quality of generated questions, quality of generated question-answer pairs, and model efficiency.
MLR: A Two-stage Conversational Query Rewriting Model with Multi-task Learning
Apr 13, 2020

Abstract:Conversational context understanding aims to recognize the real intention of user from the conversation history, which is critical for building the dialogue system. However, the multi-turn conversation understanding in open domain is still quite challenging, which requires the system extracting the important information and resolving the dependencies in contexts among a variety of open topics. In this paper, we propose the conversational query rewriting model - MLR, which is a Multi-task model on sequence Labeling and query Rewriting. MLR reformulates the multi-turn conversational queries into a single turn query, which conveys the true intention of users concisely and alleviates the difficulty of the multi-turn dialogue modeling. In the model, we formulate the query rewriting as a sequence generation problem and introduce word category information via the auxiliary word category label predicting task. To train our model, we construct a new Chinese query rewriting dataset and conduct experiments on it. The experimental results show that our model outperforms compared models, and prove the effectiveness of the word category information in improving the rewriting performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge