Zhiwang Zhou
SciEvalKit: An Open-source Evaluation Toolkit for Scientific General Intelligence
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce SciEvalKit, a unified benchmarking toolkit designed to evaluate AI models for science across a broad range of scientific disciplines and task capabilities. Unlike general-purpose evaluation platforms, SciEvalKit focuses on the core competencies of scientific intelligence, including Scientific Multimodal Perception, Scientific Multimodal Reasoning, Scientific Multimodal Understanding, Scientific Symbolic Reasoning, Scientific Code Generation, Science Hypothesis Generation and Scientific Knowledge Understanding. It supports six major scientific domains, spanning from physics and chemistry to astronomy and materials science. SciEvalKit builds a foundation of expert-grade scientific benchmarks, curated from real-world, domain-specific datasets, ensuring that tasks reflect authentic scientific challenges. The toolkit features a flexible, extensible evaluation pipeline that enables batch evaluation across models and datasets, supports custom model and dataset integration, and provides transparent, reproducible, and comparable results. By bridging capability-based evaluation and disciplinary diversity, SciEvalKit offers a standardized yet customizable infrastructure to benchmark the next generation of scientific foundation models and intelligent agents. The toolkit is open-sourced and actively maintained to foster community-driven development and progress in AI4Science.
Omni-Weather: Unified Multimodal Foundation Model for Weather Generation and Understanding
Dec 25, 2025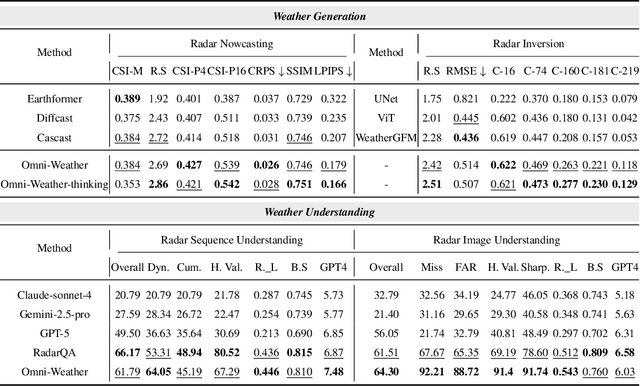
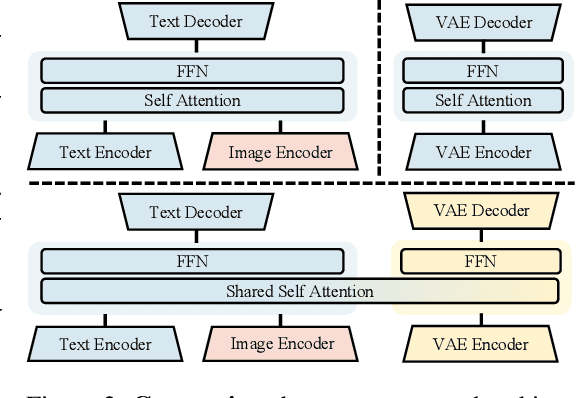
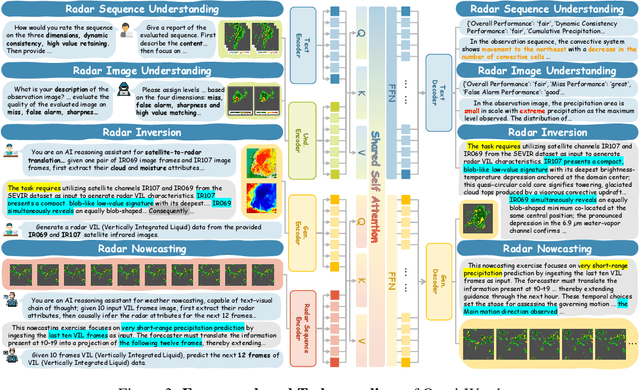
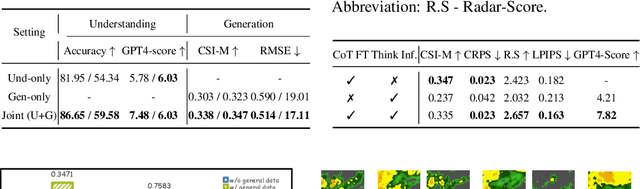
Abstract:Weather modeling requires both accurate prediction and mechanistic interpretation, yet existing methods treat these goals in isolation, separating generation from understanding. To address this gap, we present Omni-Weather, the first multimodal foundation model that unifies weather generation and understanding within a single architecture. Omni-Weather integrates a radar encoder for weather generation tasks, followed by unified processing using a shared self-attention mechanism. Moreover, we construct a Chain-of-Thought dataset for causal reasoning in weather generation, enabling interpretable outputs and improved perceptual quality. Extensive experiments show Omni-Weather achieves state-of-the-art performance in both weather generation and understanding. Our findings further indicate that generative and understanding tasks in the weather domain can mutually enhance each other. Omni-Weather also demonstrates the feasibility and value of unifying weather generation and understanding.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
SynWeather: Weather Observation Data Synthesis across Multiple Regions and Variables via a General Diffusion Transformer
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of meteorological instruments, abundant data has become available. Current approaches are typically focus on single-variable, single-region tasks and primarily rely on deterministic modeling. This limits unified synthesis across variables and regions, overlooks cross-variable complementarity and often leads to over-smoothed results. To address above challenges, we introduce SynWeather, the first dataset designed for Unified Multi-region and Multi-variable Weather Observation Data Synthesis. SynWeather covers four representative regions: the Continental United States, Europe, East Asia, and Tropical Cyclone regions, as well as provides high-resolution observations of key weather variables, including Composite Radar Reflectivity, Hourly Precipitation, Visible Light, and Microwave Brightness Temperature. In addition, we introduce SynWeatherDiff, a general and probabilistic weather synthesis model built upon the Diffusion Transformer framework to address the over-smoothed problem. Experiments on the SynWeather dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our network compared with both task-specific and general models.
DiffSR: Learning Radar Reflectivity Synthesis via Diffusion Model from Satellite Observations
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:Weather radar data synthesis can fill in data for areas where ground observations are missing. Existing methods often employ reconstruction-based approaches with MSE loss to reconstruct radar data from satellite observation. However, such methods lead to over-smoothing, which hinders the generation of high-frequency details or high-value observation areas associated with convective weather. To address this issue, we propose a two-stage diffusion-based method called DiffSR. We first pre-train a reconstruction model on global-scale data to obtain radar estimation and then synthesize radar reflectivity by combining radar estimation results with satellite data as conditions for the diffusion model. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results, demonstrating the ability to generate high-frequency details and high-value areas.
WeatherGFM: Learning A Weather Generalist Foundation Model via In-context Learning
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:The Earth's weather system encompasses intricate weather data modalities and diverse weather understanding tasks, which hold significant value to human life. Existing data-driven models focus on single weather understanding tasks (e.g., weather forecasting). Although these models have achieved promising results, they fail to tackle various complex tasks within a single and unified model. Moreover, the paradigm that relies on limited real observations for a single scenario hinders the model's performance upper bound. In response to these limitations, we draw inspiration from the in-context learning paradigm employed in state-of-the-art visual foundation models and large language models. In this paper, we introduce the first generalist weather foundation model (WeatherGFM), designed to address a wide spectrum of weather understanding tasks in a unified manner. More specifically, we initially unify the representation and definition of the diverse weather understanding tasks. Subsequently, we devised weather prompt formats to manage different weather data modalities, namely single, multiple, and temporal modalities. Finally, we adopt a visual prompting question-answering paradigm for the training of unified weather understanding tasks. Extensive experiments indicate that our WeatherGFM can effectively handle up to ten weather understanding tasks, including weather forecasting, super-resolution, weather image translation, and post-processing. Our method also showcases generalization ability on unseen tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge