Zhenxin Li
DriveSuprim: Towards Precise Trajectory Selection for End-to-End Planning
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:In complex driving environments, autonomous vehicles must navigate safely. Relying on a single predicted path, as in regression-based approaches, usually does not explicitly assess the safety of the predicted trajectory. Selection-based methods address this by generating and scoring multiple trajectory candidates and predicting the safety score for each, but face optimization challenges in precisely selecting the best option from thousands of possibilities and distinguishing subtle but safety-critical differences, especially in rare or underrepresented scenarios. We propose DriveSuprim to overcome these challenges and advance the selection-based paradigm through a coarse-to-fine paradigm for progressive candidate filtering, a rotation-based augmentation method to improve robustness in out-of-distribution scenarios, and a self-distillation framework to stabilize training. DriveSuprim achieves state-of-the-art performance, reaching 93.5% PDMS in NAVSIM v1 and 87.1% EPDMS in NAVSIM v2 without extra data, demonstrating superior safetycritical capabilities, including collision avoidance and compliance with rules, while maintaining high trajectory quality in various driving scenarios.
Generalized Trajectory Scoring for End-to-end Multimodal Planning
Jun 07, 2025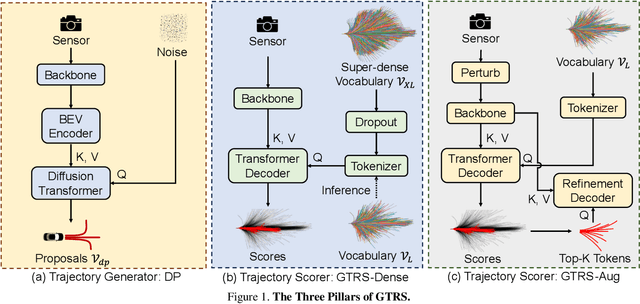
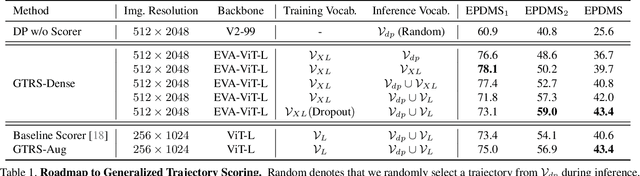
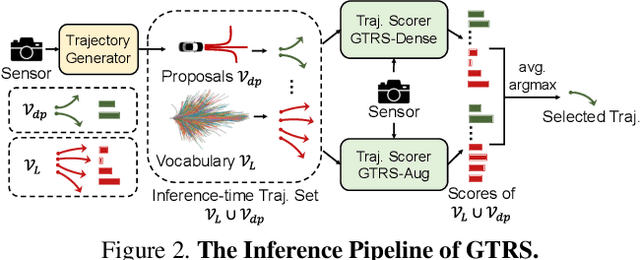
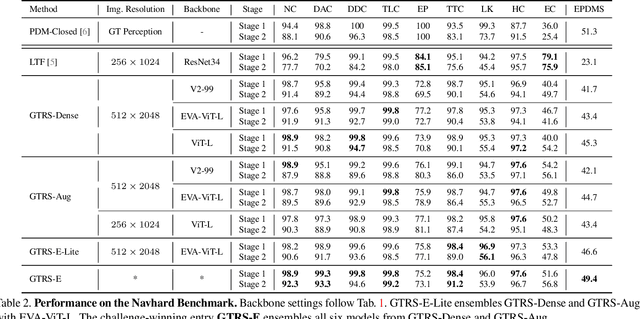
Abstract:End-to-end multi-modal planning is a promising paradigm in autonomous driving, enabling decision-making with diverse trajectory candidates. A key component is a robust trajectory scorer capable of selecting the optimal trajectory from these candidates. While recent trajectory scorers focus on scoring either large sets of static trajectories or small sets of dynamically generated ones, both approaches face significant limitations in generalization. Static vocabularies provide effective coarse discretization but struggle to make fine-grained adaptation, while dynamic proposals offer detailed precision but fail to capture broader trajectory distributions. To overcome these challenges, we propose GTRS (Generalized Trajectory Scoring), a unified framework for end-to-end multi-modal planning that combines coarse and fine-grained trajectory evaluation. GTRS consists of three complementary innovations: (1) a diffusion-based trajectory generator that produces diverse fine-grained proposals; (2) a vocabulary generalization technique that trains a scorer on super-dense trajectory sets with dropout regularization, enabling its robust inference on smaller subsets; and (3) a sensor augmentation strategy that enhances out-of-domain generalization while incorporating refinement training for critical trajectory discrimination. As the winning solution of the Navsim v2 Challenge, GTRS demonstrates superior performance even with sub-optimal sensor inputs, approaching privileged methods that rely on ground-truth perception. Code will be available at https://github.com/NVlabs/GTRS.
Hydra-MDP++: Advancing End-to-End Driving via Expert-Guided Hydra-Distillation
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Hydra-MDP++ introduces a novel teacher-student knowledge distillation framework with a multi-head decoder that learns from human demonstrations and rule-based experts. Using a lightweight ResNet-34 network without complex components, the framework incorporates expanded evaluation metrics, including traffic light compliance (TL), lane-keeping ability (LK), and extended comfort (EC) to address unsafe behaviors not captured by traditional NAVSIM-derived teachers. Like other end-to-end autonomous driving approaches, \hydra processes raw images directly without relying on privileged perception signals. Hydra-MDP++ achieves state-of-the-art performance by integrating these components with a 91.0% drive score on NAVSIM through scaling to a V2-99 image encoder, demonstrating its effectiveness in handling diverse driving scenarios while maintaining computational efficiency.
Hydra-NeXt: Robust Closed-Loop Driving with Open-Loop Training
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving research currently faces a critical challenge in bridging the gap between open-loop training and closed-loop deployment. Current approaches are trained to predict trajectories in an open-loop environment, which struggle with quick reactions to other agents in closed-loop environments and risk generating kinematically infeasible plans due to the gap between open-loop training and closed-loop driving. In this paper, we introduce Hydra-NeXt, a novel multi-branch planning framework that unifies trajectory prediction, control prediction, and a trajectory refinement network in one model. Unlike current open-loop trajectory prediction models that only handle general-case planning, Hydra-NeXt further utilizes a control decoder to focus on short-term actions, which enables faster responses to dynamic situations and reactive agents. Moreover, we propose the Trajectory Refinement module to augment and refine the planning decisions by effectively adhering to kinematic constraints in closed-loop environments. This unified approach bridges the gap between open-loop training and closed-loop driving, demonstrating superior performance of 65.89 Driving Score (DS) and 48.20% Success Rate (SR) on the Bench2Drive dataset without relying on external experts for data collection. Hydra-NeXt surpasses the previous state-of-the-art by 22.98 DS and 17.49 SR, marking a significant advancement in autonomous driving. Code will be available at https://github.com/woxihuanjiangguo/Hydra-NeXt.
Enhancing Autonomous Driving Safety with Collision Scenario Integration
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Autonomous vehicle safety is crucial for the successful deployment of self-driving cars. However, most existing planning methods rely heavily on imitation learning, which limits their ability to leverage collision data effectively. Moreover, collecting collision or near-collision data is inherently challenging, as it involves risks and raises ethical and practical concerns. In this paper, we propose SafeFusion, a training framework to learn from collision data. Instead of over-relying on imitation learning, SafeFusion integrates safety-oriented metrics during training to enable collision avoidance learning. In addition, to address the scarcity of collision data, we propose CollisionGen, a scalable data generation pipeline to generate diverse, high-quality scenarios using natural language prompts, generative models, and rule-based filtering. Experimental results show that our approach improves planning performance in collision-prone scenarios by 56\% over previous state-of-the-art planners while maintaining effectiveness in regular driving situations. Our work provides a scalable and effective solution for advancing the safety of autonomous driving systems.
Hydra-MDP: End-to-end Multimodal Planning with Multi-target Hydra-Distillation
Jun 11, 2024
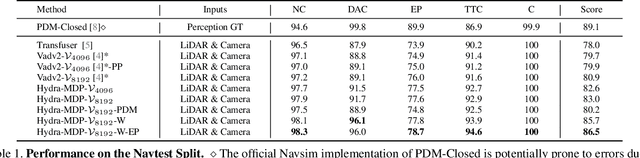
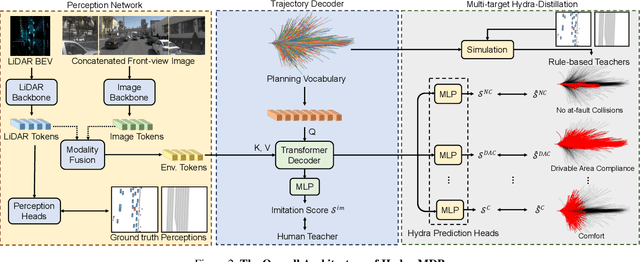
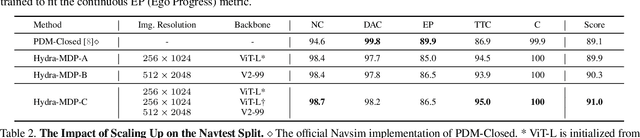
Abstract:We propose Hydra-MDP, a novel paradigm employing multiple teachers in a teacher-student model. This approach uses knowledge distillation from both human and rule-based teachers to train the student model, which features a multi-head decoder to learn diverse trajectory candidates tailored to various evaluation metrics. With the knowledge of rule-based teachers, Hydra-MDP learns how the environment influences the planning in an end-to-end manner instead of resorting to non-differentiable post-processing. This method achieves the $1^{st}$ place in the Navsim challenge, demonstrating significant improvements in generalization across diverse driving environments and conditions. Code will be available at \url{https://github.com/woxihuanjiangguo/Hydra-MDP}
BEVNeXt: Reviving Dense BEV Frameworks for 3D Object Detection
Dec 04, 2023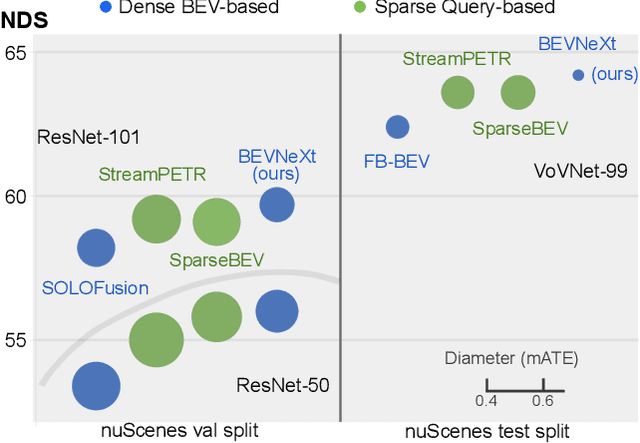
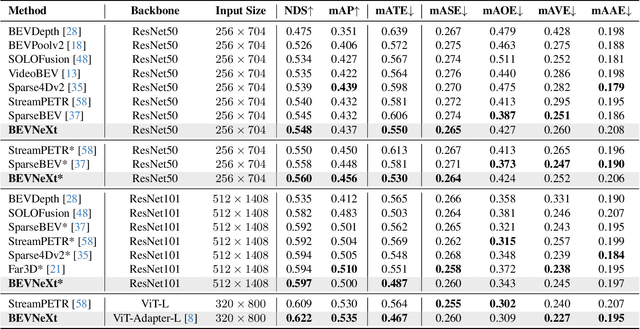
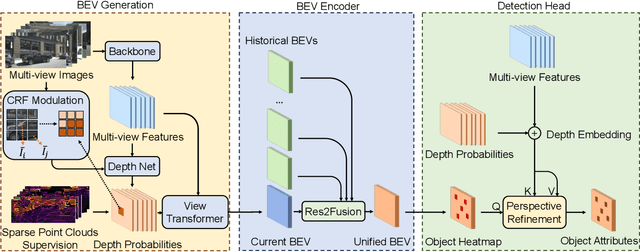
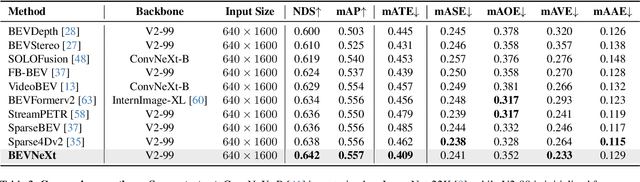
Abstract:Recently, the rise of query-based Transformer decoders is reshaping camera-based 3D object detection. These query-based decoders are surpassing the traditional dense BEV (Bird's Eye View)-based methods. However, we argue that dense BEV frameworks remain important due to their outstanding abilities in depth estimation and object localization, depicting 3D scenes accurately and comprehensively. This paper aims to address the drawbacks of the existing dense BEV-based 3D object detectors by introducing our proposed enhanced components, including a CRF-modulated depth estimation module enforcing object-level consistencies, a long-term temporal aggregation module with extended receptive fields, and a two-stage object decoder combining perspective techniques with CRF-modulated depth embedding. These enhancements lead to a "modernized" dense BEV framework dubbed BEVNeXt. On the nuScenes benchmark, BEVNeXt outperforms both BEV-based and query-based frameworks under various settings, achieving a state-of-the-art result of 64.2 NDS on the nuScenes test set.
Fighting Malicious Media Data: A Survey on Tampering Detection and Deepfake Detection
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:Online media data, in the forms of images and videos, are becoming mainstream communication channels. However, recent advances in deep learning, particularly deep generative models, open the doors for producing perceptually convincing images and videos at a low cost, which not only poses a serious threat to the trustworthiness of digital information but also has severe societal implications. This motivates a growing interest of research in media tampering detection, i.e., using deep learning techniques to examine whether media data have been maliciously manipulated. Depending on the content of the targeted images, media forgery could be divided into image tampering and Deepfake techniques. The former typically moves or erases the visual elements in ordinary images, while the latter manipulates the expressions and even the identity of human faces. Accordingly, the means of defense include image tampering detection and Deepfake detection, which share a wide variety of properties. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive review of the current media tampering detection approaches, and discuss the challenges and trends in this field for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge