Zaiwang Gu
Learning Intra-view and Cross-view Geometric Knowledge for Stereo Matching
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Geometric knowledge has been shown to be beneficial for the stereo matching task. However, prior attempts to integrate geometric insights into stereo matching algorithms have largely focused on geometric knowledge from single images while crucial cross-view factors such as occlusion and matching uniqueness have been overlooked. To address this gap, we propose a novel Intra-view and Cross-view Geometric knowledge learning Network (ICGNet), specifically crafted to assimilate both intra-view and cross-view geometric knowledge. ICGNet harnesses the power of interest points to serve as a channel for intra-view geometric understanding. Simultaneously, it employs the correspondences among these points to capture cross-view geometric relationships. This dual incorporation empowers the proposed ICGNet to leverage both intra-view and cross-view geometric knowledge in its learning process, substantially improving its ability to estimate disparities. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the ICGNet over contemporary leading models.
Semantic-Human: Neural Rendering of Humans from Monocular Video with Human Parsing
Aug 19, 2023Abstract:The neural rendering of humans is a topic of great research significance. However, previous works mostly focus on achieving photorealistic details, neglecting the exploration of human parsing. Additionally, classical semantic work are all limited in their ability to efficiently represent fine results in complex motions. Human parsing is inherently related to radiance reconstruction, as similar appearance and geometry often correspond to similar semantic part. Furthermore, previous works often design a motion field that maps from the observation space to the canonical space, while it tends to exhibit either underfitting or overfitting, resulting in limited generalization. In this paper, we present Semantic-Human, a novel method that achieves both photorealistic details and viewpoint-consistent human parsing for the neural rendering of humans. Specifically, we extend neural radiance fields (NeRF) to jointly encode semantics, appearance and geometry to achieve accurate 2D semantic labels using noisy pseudo-label supervision. Leveraging the inherent consistency and smoothness properties of NeRF, Semantic-Human achieves consistent human parsing in both continuous and novel views. We also introduce constraints derived from the SMPL surface for the motion field and regularization for the recovered volumetric geometry. We have evaluated the model using the ZJU-MoCap dataset, and the obtained highly competitive results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed Semantic-Human. We also showcase various compelling applications, including label denoising, label synthesis and image editing, and empirically validate its advantageous properties.
MOS: A Low Latency and Lightweight Framework for Face Detection, Landmark Localization, and Head Pose Estimation
Nov 01, 2021



Abstract:With the emergence of service robots and surveillance cameras, dynamic face recognition (DFR) in wild has received much attention in recent years. Face detection and head pose estimation are two important steps for DFR. Very often, the pose is estimated after the face detection. However, such sequential computations lead to higher latency. In this paper, we propose a low latency and lightweight network for simultaneous face detection, landmark localization and head pose estimation. Inspired by the observation that it is more challenging to locate the facial landmarks for faces with large angles, a pose loss is proposed to constrain the learning. Moreover, we also propose an uncertainty multi-task loss to learn the weights of individual tasks automatically. Another challenge is that robots often use low computational units like ARM based computing core and we often need to use lightweight networks instead of the heavy ones, which lead to performance drop especially for small and hard faces. In this paper, we propose online feedback sampling to augment the training samples across different scales, which increases the diversity of training data automatically. Through validation in commonly used WIDER FACE, AFLW and AFLW2000 datasets, the results show that the proposed method achieves the state-of-the-art performance in low computational resources. The code and data will be available at https://github.com/lyp-deeplearning/MOS-Multi-Task-Face-Detect.
Encoding Structure-Texture Relation with P-Net for Anomaly Detection in Retinal Images
Aug 09, 2020Abstract:Anomaly detection in retinal image refers to the identification of abnormality caused by various retinal diseases/lesions, by only leveraging normal images in training phase. Normal images from healthy subjects often have regular structures (e.g., the structured blood vessels in the fundus image, or structured anatomy in optical coherence tomography image). On the contrary, the diseases and lesions often destroy these structures. Motivated by this, we propose to leverage the relation between the image texture and structure to design a deep neural network for anomaly detection. Specifically, we first extract the structure of the retinal images, then we combine both the structure features and the last layer features extracted from original health image to reconstruct the original input healthy image. The image feature provides the texture information and guarantees the uniqueness of the image recovered from the structure. In the end, we further utilize the reconstructed image to extract the structure and measure the difference between structure extracted from original and the reconstructed image. On the one hand, minimizing the reconstruction difference behaves like a regularizer to guarantee that the image is corrected reconstructed. On the other hand, such structure difference can also be used as a metric for normality measurement. The whole network is termed as P-Net because it has a ``P'' shape. Extensive experiments on RESC dataset and iSee dataset validate the effectiveness of our approach for anomaly detection in retinal images. Further, our method also generalizes well to novel class discovery in retinal images and anomaly detection in real-world images.
Sparse-GAN: Sparsity-constrained Generative Adversarial Network for Anomaly Detection in Retinal OCT Image
Jan 07, 2020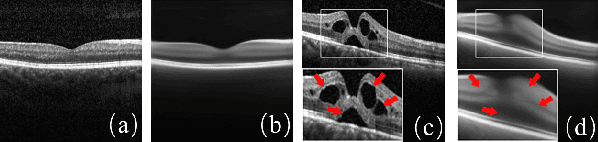
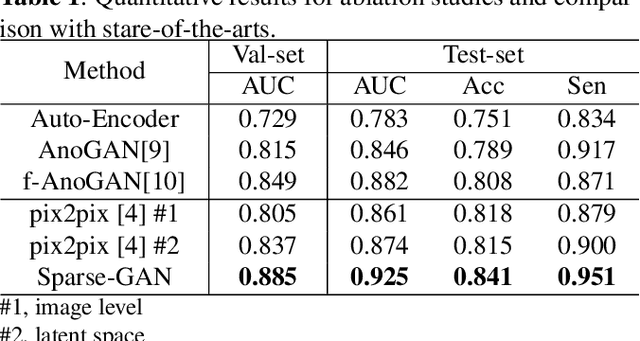
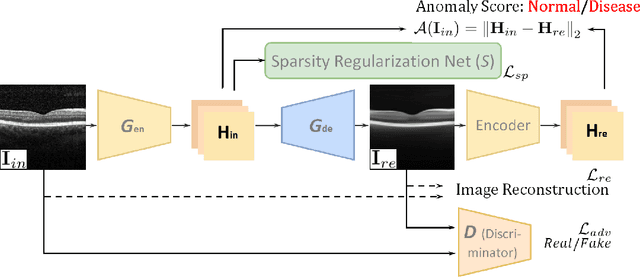
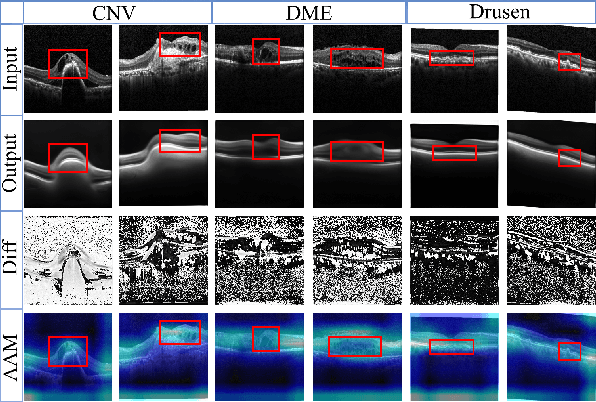
Abstract:With the development of convolutional neural network, deep learning has shown its success for retinal disease detection from optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. However, deep learning often relies on large scale labelled data for training, which is oftentimes challenging especially for disease with low occurrence. Moreover, a deep learning system trained from data-set with one or a few diseases is unable to detect other unseen diseases, which limits the practical usage of the system in disease screening. To address the limitation, we propose a novel anomaly detection framework termed Sparsity-constrained Generative Adversarial Network (Sparse-GAN) for disease screening where only healthy data are available in the training set. The contributions of Sparse-GAN are two-folds: 1) The proposed Sparse-GAN predicts the anomalies in latent space rather than image-level; 2) Sparse-GAN is constrained by a novel Sparsity Regularization Net. Furthermore, in light of the role of lesions for disease screening, we present to leverage on an anomaly activation map to show the heatmap of lesions. We evaluate our proposed Sparse-GAN on a publicly available dataset, and the results show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
Dense Dilated Network with Probability Regularized Walk for Vessel Detection
Oct 26, 2019



Abstract:The detection of retinal vessel is of great importance in the diagnosis and treatment of many ocular diseases. Many methods have been proposed for vessel detection. However, most of the algorithms neglect the connectivity of the vessels, which plays an important role in the diagnosis. In this paper, we propose a novel method for retinal vessel detection. The proposed method includes a dense dilated network to get an initial detection of the vessels and a probability regularized walk algorithm to address the fracture issue in the initial detection. The dense dilated network integrates newly proposed dense dilated feature extraction blocks into an encoder-decoder structure to extract and accumulate features at different scales. A multiscale Dice loss function is adopted to train the network. To improve the connectivity of the segmented vessels, we also introduce a probability regularized walk algorithm to connect the broken vessels. The proposed method has been applied on three public data sets: DRIVE, STARE and CHASE_DB1. The results show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and also are under receiver operating characteristic curve.
The Channel Attention based Context Encoder Network for Inner Limiting Membrane Detection
Aug 09, 2019


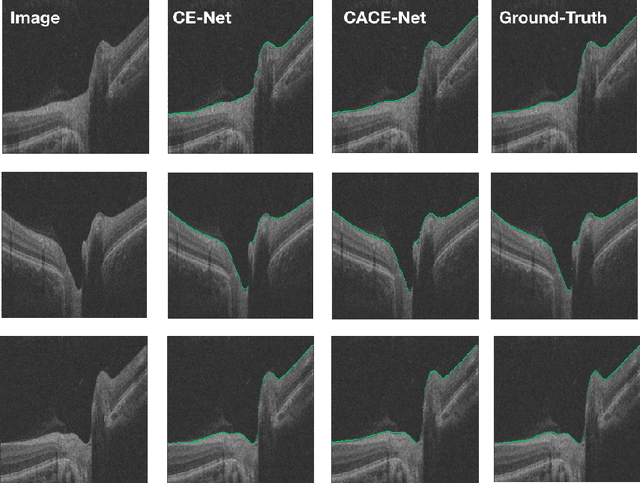
Abstract:The optic disc segmentation is an important step for retinal image-based disease diagnosis such as glaucoma. The inner limiting membrane (ILM) is the first boundary in the OCT, which can help to extract the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) through gradient edge information to locate the boundary of the optic disc. Thus, the ILM layer segmentation is of great importance for optic disc localization. In this paper, we build a new optic disc centered dataset from 20 volunteers and manually annotated the ILM boundary in each OCT scan as ground-truth. We also propose a channel attention based context encoder network modified from the CE-Net to segment the optic disc. It mainly contains three phases: the encoder module, the channel attention based context encoder module, and the decoder module. Finally, we demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art disc segmentation performance on our dataset mentioned above.
SkrGAN: Sketching-rendering Unconditional Generative Adversarial Networks for Medical Image Synthesis
Aug 06, 2019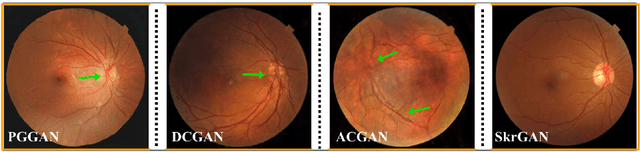
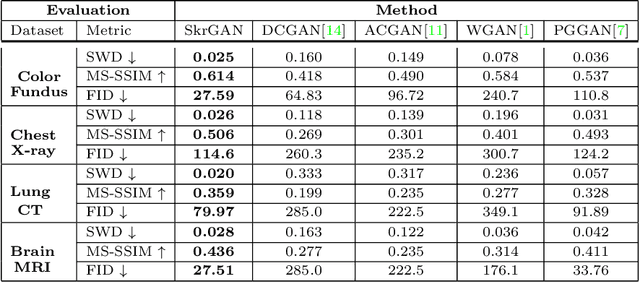
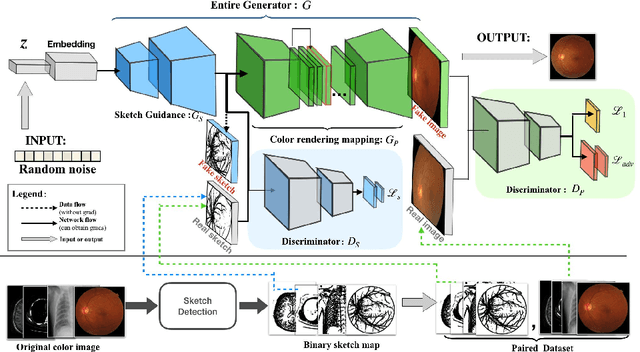
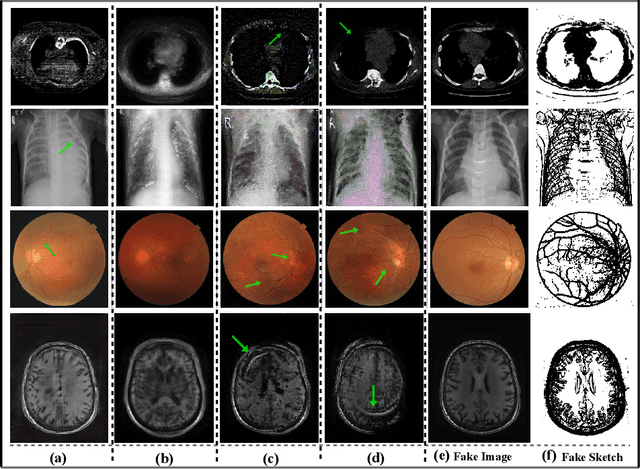
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have the capability of synthesizing images, which have been successfully applied to medical image synthesis tasks. However, most of existing methods merely consider the global contextual information and ignore the fine foreground structures, e.g., vessel, skeleton, which may contain diagnostic indicators for medical image analysis. Inspired by human painting procedure, which is composed of stroking and color rendering steps, we propose a Sketching-rendering Unconditional Generative Adversarial Network (SkrGAN) to introduce a sketch prior constraint to guide the medical image generation. In our SkrGAN, a sketch guidance module is utilized to generate a high quality structural sketch from random noise, then a color render mapping is used to embed the sketch-based representations and resemble the background appearances. Experimental results show that the proposed SkrGAN achieves the state-of-the-art results in synthesizing images for various image modalities, including retinal color fundus, X-Ray, Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). In addition, we also show that the performances of medical image segmentation method have been improved by using our synthesized images as data augmentation.
CE-Net: Context Encoder Network for 2D Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 07, 2019



Abstract:Medical image segmentation is an important step in medical image analysis. With the rapid development of convolutional neural network in image processing, deep learning has been used for medical image segmentation, such as optic disc segmentation, blood vessel detection, lung segmentation, cell segmentation, etc. Previously, U-net based approaches have been proposed. However, the consecutive pooling and strided convolutional operations lead to the loss of some spatial information. In this paper, we propose a context encoder network (referred to as CE-Net) to capture more high-level information and preserve spatial information for 2D medical image segmentation. CE-Net mainly contains three major components: a feature encoder module, a context extractor and a feature decoder module. We use pretrained ResNet block as the fixed feature extractor. The context extractor module is formed by a newly proposed dense atrous convolution (DAC) block and residual multi-kernel pooling (RMP) block. We applied the proposed CE-Net to different 2D medical image segmentation tasks. Comprehensive results show that the proposed method outperforms the original U-Net method and other state-of-the-art methods for optic disc segmentation, vessel detection, lung segmentation, cell contour segmentation and retinal optical coherence tomography layer segmentation.
Multi-Cell Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Networks for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading
Oct 11, 2018



Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a non-negligible eye disease among patients with Diabetes Mellitus, and automatic retinal image analysis algorithm for the DR screening is in high demand. Considering the resolution of retinal image is very high, where small pathological tissues can be detected only with large resolution image and large local receptive field are required to identify those late stage disease, but directly training a neural network with very deep architecture and high resolution image is both time computational expensive and difficult because of gradient vanishing/exploding problem, we propose a \textbf{Multi-Cell} architecture which gradually increases the depth of deep neural network and the resolution of input image, which both boosts the training time but also improves the classification accuracy. Further, considering the different stages of DR actually progress gradually, which means the labels of different stages are related. To considering the relationships of images with different stages, we propose a \textbf{Multi-Task} learning strategy which predicts the label with both classification and regression. Experimental results on the Kaggle dataset show that our method achieves a Kappa of 0.841 on test set which is the 4-th rank of all state-of-the-arts methods. Further, our Multi-Cell Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Networks (M$^2$CNN) solution is a general framework, which can be readily integrated with many other deep neural network architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge