Yuval Elovici
Provably Protecting Fine-Tuned LLMs from Training Data Extraction
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on sensitive datasets raises privacy concerns, as training data extraction (TDE) attacks can expose highly confidential information. Existing defenses against such attacks either lack formal privacy guarantees or incur substantial utility degradation. We observe that fine-tuning induces widespread probability shifts, yet preserving only a small subset of influential token-level deviations is sufficient; the remaining shifts can be aggressively smoothed with minimal impact on utility. Motivated by this insight, we propose SCP-$Δ_r$, a Near Access Freeness (NAF)-based algorithm that operates on relative probabilities and explicitly smooths low-impact tokens using a base model. SCP-$Δ_r$ achieves orders-of-magnitude better theoretical bounds than existing NAF based methods and provides strong empirical protection against TDE attacks with minimal performance loss.
AgentGuardian: Learning Access Control Policies to Govern AI Agent Behavior
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are increasingly used in a variety of domains to automate tasks, interact with users, and make decisions based on data inputs. Ensuring that AI agents perform only authorized actions and handle inputs appropriately is essential for maintaining system integrity and preventing misuse. In this study, we introduce the AgentGuardian, a novel security framework that governs and protects AI agent operations by enforcing context-aware access-control policies. During a controlled staging phase, the framework monitors execution traces to learn legitimate agent behaviors and input patterns. From this phase, it derives adaptive policies that regulate tool calls made by the agent, guided by both real-time input context and the control flow dependencies of multi-step agent actions. Evaluation across two real-world AI agent applications demonstrates that AgentGuardian effectively detects malicious or misleading inputs while preserving normal agent functionality. Moreover, its control-flow-based governance mechanism mitigates hallucination-driven errors and other orchestration-level malfunctions.
Real-World Adversarial Attacks on RF-Based Drone Detectors
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Radio frequency (RF) based systems are increasingly used to detect drones by analyzing their RF signal patterns, converting them into spectrogram images which are processed by object detection models. Existing RF attacks against image based models alter digital features, making over-the-air (OTA) implementation difficult due to the challenge of converting digital perturbations to transmittable waveforms that may introduce synchronization errors and interference, and encounter hardware limitations. We present the first physical attack on RF image based drone detectors, optimizing class-specific universal complex baseband (I/Q) perturbation waveforms that are transmitted alongside legitimate communications. We evaluated the attack using RF recordings and OTA experiments with four types of drones. Our results show that modest, structured I/Q perturbations are compatible with standard RF chains and reliably reduce target drone detection while preserving detection of legitimate drones.
MIA-EPT: Membership Inference Attack via Error Prediction for Tabular Data
Sep 16, 2025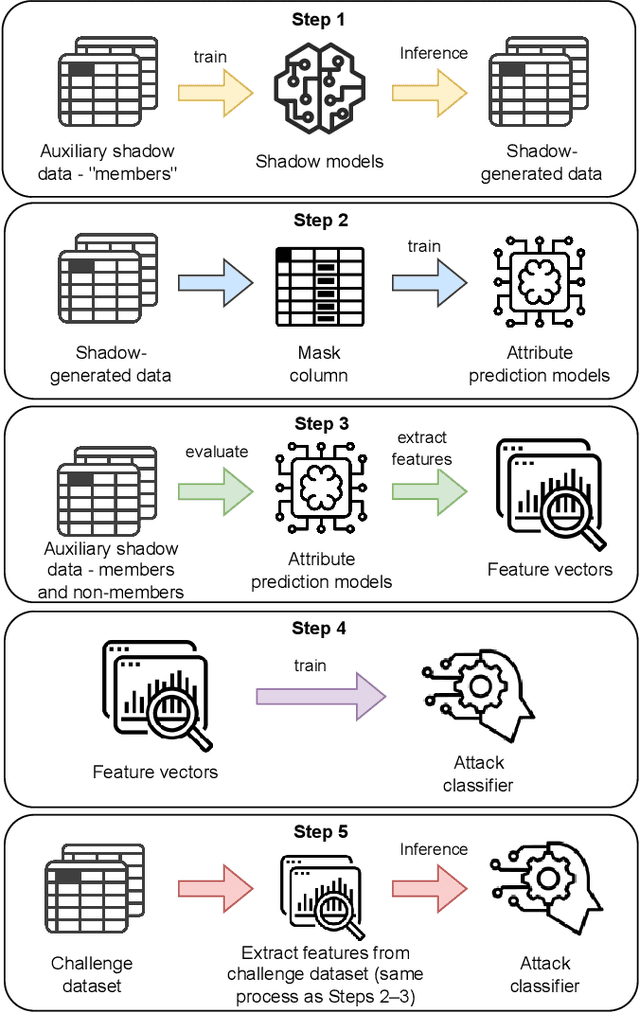
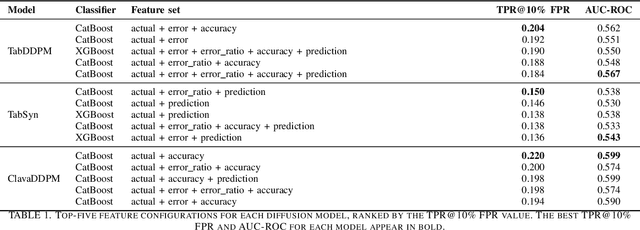
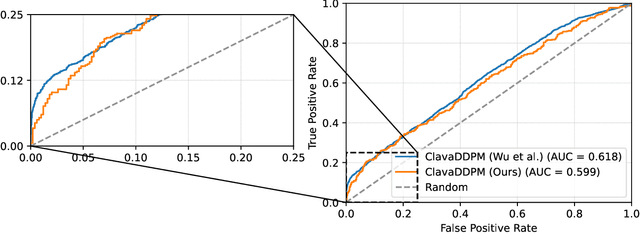
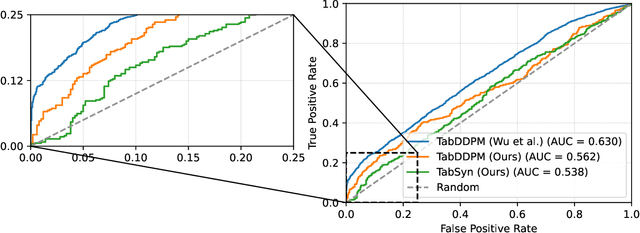
Abstract:Synthetic data generation plays an important role in enabling data sharing, particularly in sensitive domains like healthcare and finance. Recent advances in diffusion models have made it possible to generate realistic, high-quality tabular data, but they may also memorize training records and leak sensitive information. Membership inference attacks (MIAs) exploit this vulnerability by determining whether a record was used in training. While MIAs have been studied in images and text, their use against tabular diffusion models remains underexplored despite the unique risks of structured attributes and limited record diversity. In this paper, we introduce MIAEPT, Membership Inference Attack via Error Prediction for Tabular Data, a novel black-box attack specifically designed to target tabular diffusion models. MIA-EPT constructs errorbased feature vectors by masking and reconstructing attributes of target records, disclosing membership signals based on how well these attributes are predicted. MIA-EPT operates without access to the internal components of the generative model, relying only on its synthetic data output, and was shown to generalize across multiple state-of-the-art diffusion models. We validate MIA-EPT on three diffusion-based synthesizers, achieving AUC-ROC scores of up to 0.599 and TPR@10% FPR values of 22.0% in our internal tests. Under the MIDST 2025 competition conditions, MIA-EPT achieved second place in the Black-box Multi-Table track (TPR@10% FPR = 20.0%). These results demonstrate that our method can uncover substantial membership leakage in synthetic tabular data, challenging the assumption that synthetic data is inherently privacy-preserving. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/eyalgerman/MIA-EPT.
KubeGuard: LLM-Assisted Kubernetes Hardening via Configuration Files and Runtime Logs Analysis
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The widespread adoption of Kubernetes (K8s) for orchestrating cloud-native applications has introduced significant security challenges, such as misconfigured resources and overly permissive configurations. Failing to address these issues can result in unauthorized access, privilege escalation, and lateral movement within clusters. Most existing K8s security solutions focus on detecting misconfigurations, typically through static analysis or anomaly detection. In contrast, this paper presents KubeGuard, a novel runtime log-driven recommender framework aimed at mitigating risks by addressing overly permissive configurations. KubeGuard is designed to harden K8s environments through two complementary tasks: Resource Creation and Resource Refinement. It leverages large language models (LLMs) to analyze manifests and runtime logs reflecting actual system behavior, using modular prompt-chaining workflows. This approach enables KubeGuard to create least-privilege configurations for new resources and refine existing manifests to reduce the attack surface. KubeGuard's output manifests are presented as recommendations that users (e.g., developers and operators) can review and adopt to enhance cluster security. Our evaluation demonstrates that KubeGuard effectively generates and refines K8s manifests for Roles, NetworkPolicies, and Deployments, leveraging both proprietary and open-source LLMs. The high precision, recall, and F1-scores affirm KubeGuard's practicality as a framework that translates runtime observability into actionable, least-privilege configuration guidance.
SoK: Cybersecurity Assessment of Humanoid Ecosystem
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Humanoids are progressing toward practical deployment across healthcare, industrial, defense, and service sectors. While typically considered cyber-physical systems (CPSs), their dependence on traditional networked software stacks (e.g., Linux operating systems), robot operating system (ROS) middleware, and over-the-air update channels, creates a distinct security profile that exposes them to vulnerabilities conventional CPS models do not fully address. Prior studies have mainly examined specific threats, such as LiDAR spoofing or adversarial machine learning (AML). This narrow focus overlooks how an attack targeting one component can cascade harm throughout the robot's interconnected systems. We address this gap through a systematization of knowledge (SoK) that takes a comprehensive approach, consolidating fragmented research from robotics, CPS, and network security domains. We introduce a seven-layer security model for humanoid robots, organizing 39 known attacks and 35 defenses across the humanoid ecosystem-from hardware to human-robot interaction. Building on this security model, we develop a quantitative 39x35 attack-defense matrix with risk-weighted scoring, validated through Monte Carlo analysis. We demonstrate our method by evaluating three real-world robots: Pepper, G1 EDU, and Digit. The scoring analysis revealed varying security maturity levels, with scores ranging from 39.9% to 79.5% across the platforms. This work introduces a structured, evidence-based assessment method that enables systematic security evaluation, supports cross-platform benchmarking, and guides prioritization of security investments in humanoid robotics.
LumiMAS: A Comprehensive Framework for Real-Time Monitoring and Enhanced Observability in Multi-Agent Systems
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:The incorporation of large language models in multi-agent systems (MASs) has the potential to significantly improve our ability to autonomously solve complex problems. However, such systems introduce unique challenges in monitoring, interpreting, and detecting system failures. Most existing MAS observability frameworks focus on analyzing each individual agent separately, overlooking failures associated with the entire MAS. To bridge this gap, we propose LumiMAS, a novel MAS observability framework that incorporates advanced analytics and monitoring techniques. The proposed framework consists of three key components: a monitoring and logging layer, anomaly detection layer, and anomaly explanation layer. LumiMAS's first layer monitors MAS executions, creating detailed logs of the agents' activity. These logs serve as input to the anomaly detection layer, which detects anomalies across the MAS workflow in real time. Then, the anomaly explanation layer performs classification and root cause analysis (RCA) of the detected anomalies. LumiMAS was evaluated on seven different MAS applications, implemented using two popular MAS platforms, and a diverse set of possible failures. The applications include two novel failure-tailored applications that illustrate the effects of a hallucination or bias on the MAS. The evaluation results demonstrate LumiMAS's effectiveness in failure detection, classification, and RCA.
Tab-MIA: A Benchmark Dataset for Membership Inference Attacks on Tabular Data in LLMs
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly trained on tabular data, which, unlike unstructured text, often contains personally identifiable information (PII) in a highly structured and explicit format. As a result, privacy risks arise, since sensitive records can be inadvertently retained by the model and exposed through data extraction or membership inference attacks (MIAs). While existing MIA methods primarily target textual content, their efficacy and threat implications may differ when applied to structured data, due to its limited content, diverse data types, unique value distributions, and column-level semantics. In this paper, we present Tab-MIA, a benchmark dataset for evaluating MIAs on tabular data in LLMs and demonstrate how it can be used. Tab-MIA comprises five data collections, each represented in six different encoding formats. Using our Tab-MIA benchmark, we conduct the first evaluation of state-of-the-art MIA methods on LLMs finetuned with tabular data across multiple encoding formats. In the evaluation, we analyze the memorization behavior of pretrained LLMs on structured data derived from Wikipedia tables. Our findings show that LLMs memorize tabular data in ways that vary across encoding formats, making them susceptible to extraction via MIAs. Even when fine-tuned for as few as three epochs, models exhibit high vulnerability, with AUROC scores approaching 90% in most cases. Tab-MIA enables systematic evaluation of these risks and provides a foundation for developing privacy-preserving methods for tabular data in LLMs.
ImpReSS: Implicit Recommender System for Support Conversations
Jun 17, 2025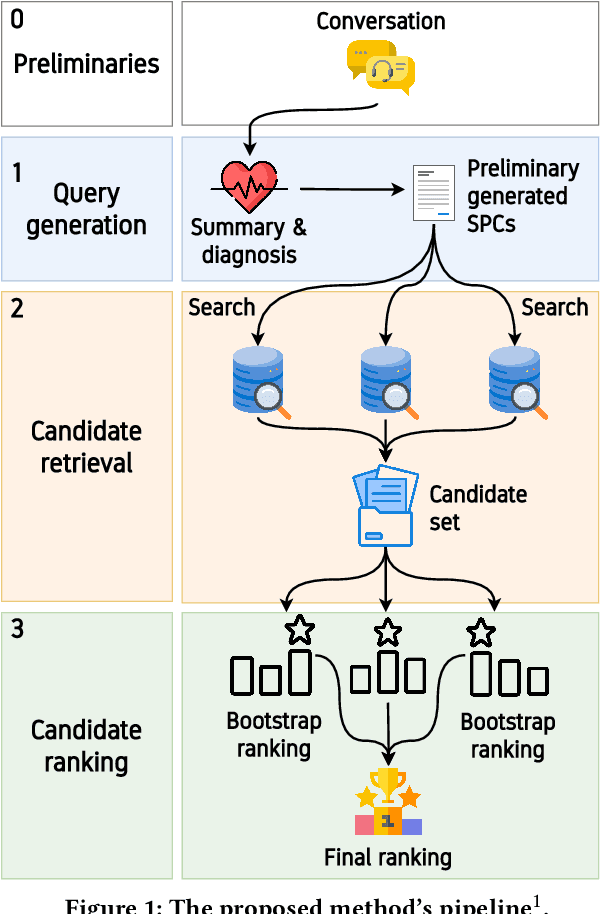


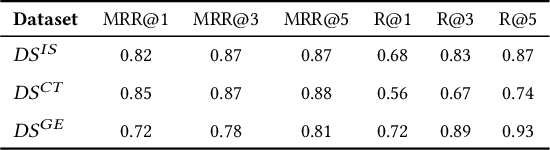
Abstract:Following recent advancements in large language models (LLMs), LLM-based chatbots have transformed customer support by automating interactions and providing consistent, scalable service. While LLM-based conversational recommender systems (CRSs) have attracted attention for their ability to enhance the quality of recommendations, limited research has addressed the implicit integration of recommendations within customer support interactions. In this work, we introduce ImpReSS, an implicit recommender system designed for customer support conversations. ImpReSS operates alongside existing support chatbots, where users report issues and chatbots provide solutions. Based on a customer support conversation, ImpReSS identifies opportunities to recommend relevant solution product categories (SPCs) that help resolve the issue or prevent its recurrence -- thereby also supporting business growth. Unlike traditional CRSs, ImpReSS functions entirely implicitly and does not rely on any assumption of a user's purchasing intent. Our empirical evaluation of ImpReSS's ability to recommend relevant SPCs that can help address issues raised in support conversations shows promising results, including an MRR@1 (and recall@3) of 0.72 (0.89) for general problem solving, 0.82 (0.83) for information security support, and 0.85 (0.67) for cybersecurity troubleshooting. To support future research, our data and code will be shared upon request.
LexiMark: Robust Watermarking via Lexical Substitutions to Enhance Membership Verification of an LLM's Textual Training Data
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can be trained or fine-tuned on data obtained without the owner's consent. Verifying whether a specific LLM was trained on particular data instances or an entire dataset is extremely challenging. Dataset watermarking addresses this by embedding identifiable modifications in training data to detect unauthorized use. However, existing methods often lack stealth, making them relatively easy to detect and remove. In light of these limitations, we propose LexiMark, a novel watermarking technique designed for text and documents, which embeds synonym substitutions for carefully selected high-entropy words. Our method aims to enhance an LLM's memorization capabilities on the watermarked text without altering the semantic integrity of the text. As a result, the watermark is difficult to detect, blending seamlessly into the text with no visible markers, and is resistant to removal due to its subtle, contextually appropriate substitutions that evade automated and manual detection. We evaluated our method using baseline datasets from recent studies and seven open-source models: LLaMA-1 7B, LLaMA-3 8B, Mistral 7B, Pythia 6.9B, as well as three smaller variants from the Pythia family (160M, 410M, and 1B). Our evaluation spans multiple training settings, including continued pretraining and fine-tuning scenarios. The results demonstrate significant improvements in AUROC scores compared to existing methods, underscoring our method's effectiveness in reliably verifying whether unauthorized watermarked data was used in LLM training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge