Yuejie Zhang
Dual Semantic-Aware Network for Noise Suppressed Ultrasound Video Segmentation
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Ultrasound imaging is a prevalent diagnostic tool known for its simplicity and non-invasiveness. However, its inherent characteristics often introduce substantial noise, posing considerable challenges for automated lesion or organ segmentation in ultrasound video sequences. To address these limitations, we propose the Dual Semantic-Aware Network (DSANet), a novel framework designed to enhance noise robustness in ultrasound video segmentation by fostering mutual semantic awareness between local and global features. Specifically, we introduce an Adjacent-Frame Semantic-Aware (AFSA) module, which constructs a channel-wise similarity matrix to guide feature fusion across adjacent frames, effectively mitigating the impact of random noise without relying on pixel-level relationships. Additionally, we propose a Local-and-Global Semantic-Aware (LGSA) module that reorganizes and fuses temporal unconditional local features, which capture spatial details independently at each frame, with conditional global features that incorporate temporal context from adjacent frames. This integration facilitates multi-level semantic representation, significantly improving the model's resilience to noise interference. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that DSANet substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods in segmentation accuracy. Moreover, since our model avoids pixel-level feature dependencies, it achieves significantly higher inference FPS than video-based methods, and even surpasses some image-based models. Code can be found in \href{https://github.com/ZhouL2001/DSANet}{DSANet}
Advancing Lung Disease Diagnosis in 3D CT Scans
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:To enable more accurate diagnosis of lung disease in chest CT scans, we propose a straightforward yet effective model. Firstly, we analyze the characteristics of 3D CT scans and remove non-lung regions, which helps the model focus on lesion-related areas and reduces computational cost. We adopt ResNeSt50 as a strong feature extractor, and use a weighted cross-entropy loss to mitigate class imbalance, especially for the underrepresented squamous cell carcinoma category. Our model achieves a Macro F1 Score of 0.80 on the validation set of the Fair Disease Diagnosis Challenge, demonstrating its strong performance in distinguishing between different lung conditions.
AOR: Anatomical Ontology-Guided Reasoning for Medical Large Multimodal Model in Chest X-Ray Interpretation
May 05, 2025Abstract:Chest X-rays (CXRs) are the most frequently performed imaging examinations in clinical settings. Recent advancements in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have enabled automated CXR interpretation, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. However, despite their strong visual understanding, current Medical LMMs (MLMMs) still face two major challenges: (1) Insufficient region-level understanding and interaction, and (2) Limited accuracy and interpretability due to single-step reasoning. In this paper, we empower MLMMs with anatomy-centric reasoning capabilities to enhance their interactivity and explainability. Specifically, we first propose an Anatomical Ontology-Guided Reasoning (AOR) framework, which centers on cross-modal region-level information to facilitate multi-step reasoning. Next, under the guidance of expert physicians, we develop AOR-Instruction, a large instruction dataset for MLMMs training. Our experiments demonstrate AOR's superior performance in both VQA and report generation tasks.
EgoExo-Gen: Ego-centric Video Prediction by Watching Exo-centric Videos
Apr 16, 2025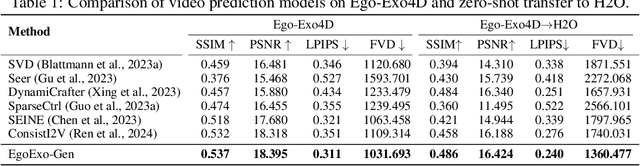
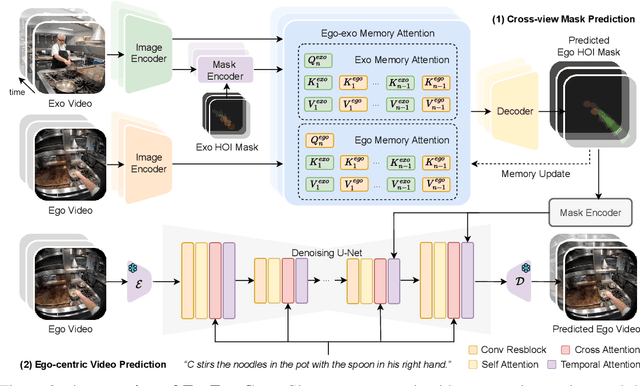
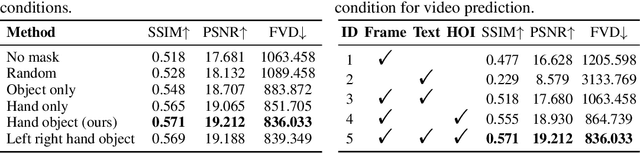
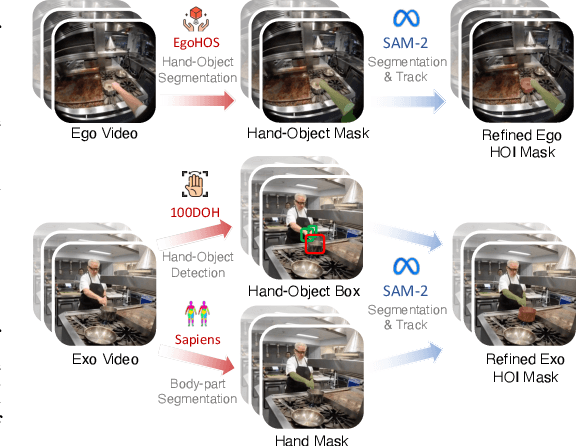
Abstract:Generating videos in the first-person perspective has broad application prospects in the field of augmented reality and embodied intelligence. In this work, we explore the cross-view video prediction task, where given an exo-centric video, the first frame of the corresponding ego-centric video, and textual instructions, the goal is to generate futur frames of the ego-centric video. Inspired by the notion that hand-object interactions (HOI) in ego-centric videos represent the primary intentions and actions of the current actor, we present EgoExo-Gen that explicitly models the hand-object dynamics for cross-view video prediction. EgoExo-Gen consists of two stages. First, we design a cross-view HOI mask prediction model that anticipates the HOI masks in future ego-frames by modeling the spatio-temporal ego-exo correspondence. Next, we employ a video diffusion model to predict future ego-frames using the first ego-frame and textual instructions, while incorporating the HOI masks as structural guidance to enhance prediction quality. To facilitate training, we develop an automated pipeline to generate pseudo HOI masks for both ego- and exo-videos by exploiting vision foundation models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed EgoExo-Gen achieves better prediction performance compared to previous video prediction models on the Ego-Exo4D and H2O benchmark datasets, with the HOI masks significantly improving the generation of hands and interactive objects in the ego-centric videos.
CT2C-QA: Multimodal Question Answering over Chinese Text, Table and Chart
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Question Answering (MMQA) is crucial as it enables comprehensive understanding and accurate responses by integrating insights from diverse data representations such as tables, charts, and text. Most existing researches in MMQA only focus on two modalities such as image-text QA, table-text QA and chart-text QA, and there remains a notable scarcity in studies that investigate the joint analysis of text, tables, and charts. In this paper, we present C$\text{T}^2$C-QA, a pioneering Chinese reasoning-based QA dataset that includes an extensive collection of text, tables, and charts, meticulously compiled from 200 selectively sourced webpages. Our dataset simulates real webpages and serves as a great test for the capability of the model to analyze and reason with multimodal data, because the answer to a question could appear in various modalities, or even potentially not exist at all. Additionally, we present AED (\textbf{A}llocating, \textbf{E}xpert and \textbf{D}esicion), a multi-agent system implemented through collaborative deployment, information interaction, and collective decision-making among different agents. Specifically, the Assignment Agent is in charge of selecting and activating expert agents, including those proficient in text, tables, and charts. The Decision Agent bears the responsibility of delivering the final verdict, drawing upon the analytical insights provided by these expert agents. We execute a comprehensive analysis, comparing AED with various state-of-the-art models in MMQA, including GPT-4. The experimental outcomes demonstrate that current methodologies, including GPT-4, are yet to meet the benchmarks set by our dataset.
MOSMOS: Multi-organ segmentation facilitated by medical report supervision
Sep 04, 2024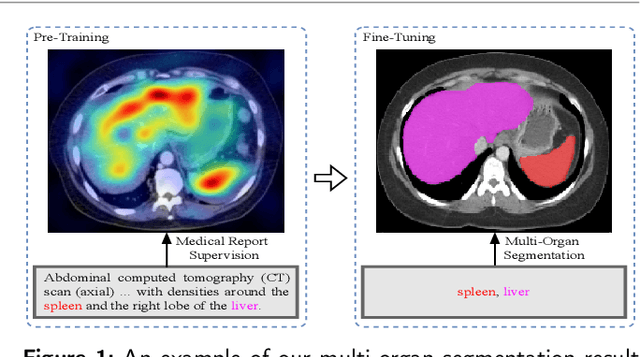
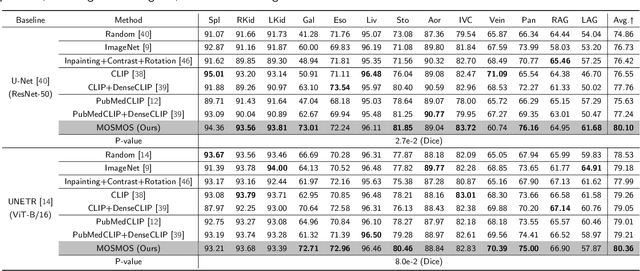
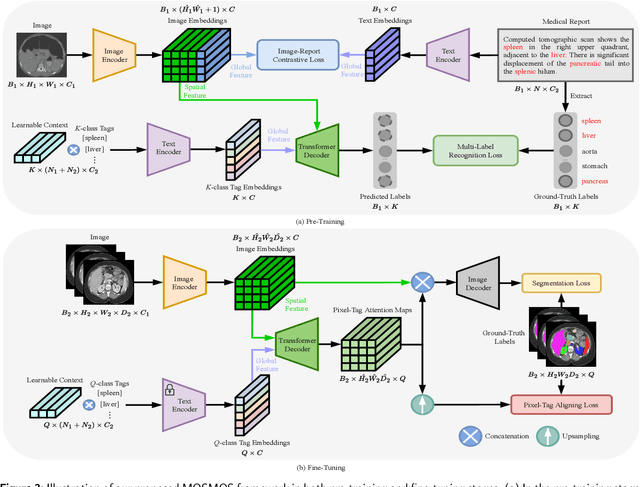
Abstract:Owing to a large amount of multi-modal data in modern medical systems, such as medical images and reports, Medical Vision-Language Pre-training (Med-VLP) has demonstrated incredible achievements in coarse-grained downstream tasks (i.e., medical classification, retrieval, and visual question answering). However, the problem of transferring knowledge learned from Med-VLP to fine-grained multi-organ segmentation tasks has barely been investigated. Multi-organ segmentation is challenging mainly due to the lack of large-scale fully annotated datasets and the wide variation in the shape and size of the same organ between individuals with different diseases. In this paper, we propose a novel pre-training & fine-tuning framework for Multi-Organ Segmentation by harnessing Medical repOrt Supervision (MOSMOS). Specifically, we first introduce global contrastive learning to maximally align the medical image-report pairs in the pre-training stage. To remedy the granularity discrepancy, we further leverage multi-label recognition to implicitly learn the semantic correspondence between image pixels and organ tags. More importantly, our pre-trained models can be transferred to any segmentation model by introducing the pixel-tag attention maps. Different network settings, i.e., 2D U-Net and 3D UNETR, are utilized to validate the generalization. We have extensively evaluated our approach using different diseases and modalities on BTCV, AMOS, MMWHS, and BRATS datasets. Experimental results in various settings demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework. This framework can serve as the foundation to facilitate future research on automatic annotation tasks under the supervision of medical reports.
Advancing COVID-19 Detection in 3D CT Scans
Mar 18, 2024


Abstract:To make a more accurate diagnosis of COVID-19, we propose a straightforward yet effective model. Firstly, we analyse the characteristics of 3D CT scans and remove the non-lung parts, facilitating the model to focus on lesion-related areas and reducing computational cost. We use ResNeSt50 as the strong feature extractor, initializing it with pretrained weights which have COVID-19-specific prior knowledge. Our model achieves a Macro F1 Score of 0.94 on the validation set of the 4th COV19D Competition Challenge $\mathrm{I}$, surpassing the baseline by 16%. This indicates its effectiveness in distinguishing between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 cases, making it a robust method for COVID-19 detection.
Domain Adaptation Using Pseudo Labels for COVID-19 Detection
Mar 18, 2024

Abstract:In response to the need for rapid and accurate COVID-19 diagnosis during the global pandemic, we present a two-stage framework that leverages pseudo labels for domain adaptation to enhance the detection of COVID-19 from CT scans. By utilizing annotated data from one domain and non-annotated data from another, the model overcomes the challenge of data scarcity and variability, common in emergent health crises. The innovative approach of generating pseudo labels enables the model to iteratively refine its learning process, thereby improving its accuracy and adaptability across different hospitals and medical centres. Experimental results on COV19-CT-DB database showcase the model's potential to achieve high diagnostic precision, significantly contributing to efficient patient management and alleviating the strain on healthcare systems. Our method achieves 0.92 Macro F1 Score on the validation set of Covid-19 domain adaptation challenge.
Anatomical Structure-Guided Medical Vision-Language Pre-training
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Learning medical visual representations through vision-language pre-training has reached remarkable progress. Despite the promising performance, it still faces challenges, i.e., local alignment lacks interpretability and clinical relevance, and the insufficient internal and external representation learning of image-report pairs. To address these issues, we propose an Anatomical Structure-Guided (ASG) framework. Specifically, we parse raw reports into triplets <anatomical region, finding, existence>, and fully utilize each element as supervision to enhance representation learning. For anatomical region, we design an automatic anatomical region-sentence alignment paradigm in collaboration with radiologists, considering them as the minimum semantic units to explore fine-grained local alignment. For finding and existence, we regard them as image tags, applying an image-tag recognition decoder to associate image features with their respective tags within each sample and constructing soft labels for contrastive learning to improve the semantic association of different image-report pairs. We evaluate the proposed ASG framework on two downstream tasks, including five public benchmarks. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
Retrieval-Augmented Egocentric Video Captioning
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:Understanding human actions from videos of first-person view poses significant challenges. Most prior approaches explore representation learning on egocentric videos only, while overlooking the potential benefit of exploiting existing large-scale third-person videos. In this paper, (1) we develop EgoInstructor, a retrieval-augmented multimodal captioning model that automatically retrieves semantically relevant third-person instructional videos to enhance the video captioning of egocentric videos. (2) For training the cross-view retrieval module, we devise an automatic pipeline to discover ego-exo video pairs from distinct large-scale egocentric and exocentric datasets. (3) We train the cross-view retrieval module with a novel EgoExoNCE loss that pulls egocentric and exocentric video features closer by aligning them to shared text features that describe similar actions. (4) Through extensive experiments, our cross-view retrieval module demonstrates superior performance across seven benchmarks. Regarding egocentric video captioning, EgoInstructor exhibits significant improvements by leveraging third-person videos as references.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge