Longquan Jiang
Ontology-Guided, Hybrid Prompt Learning for Generalization in Knowledge Graph Question Answering
Feb 06, 2025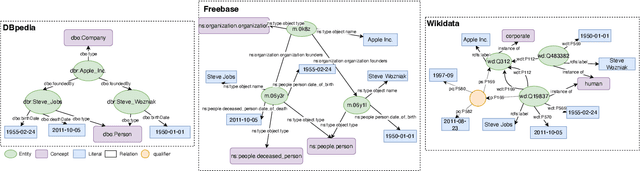
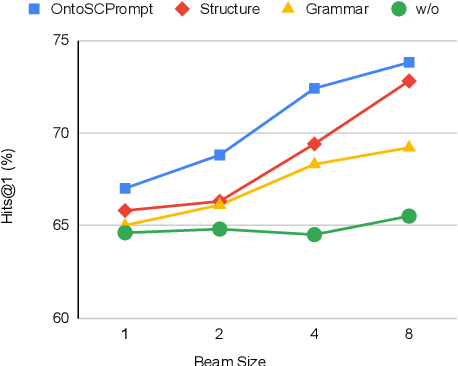


Abstract:Most existing Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) approaches are designed for a specific KG, such as Wikidata, DBpedia or Freebase. Due to the heterogeneity of the underlying graph schema, topology and assertions, most KGQA systems cannot be transferred to unseen Knowledge Graphs (KGs) without resource-intensive training data. We present OntoSCPrompt, a novel Large Language Model (LLM)-based KGQA approach with a two-stage architecture that separates semantic parsing from KG-dependent interactions. OntoSCPrompt first generates a SPARQL query structure (including SPARQL keywords such as SELECT, ASK, WHERE and placeholders for missing tokens) and then fills them with KG-specific information. To enhance the understanding of the underlying KG, we present an ontology-guided, hybrid prompt learning strategy that integrates KG ontology into the learning process of hybrid prompts (e.g., discrete and continuous vectors). We also present several task-specific decoding strategies to ensure the correctness and executability of generated SPARQL queries in both stages. Experimental results demonstrate that OntoSCPrompt performs as well as SOTA approaches without retraining on a number of KGQA datasets such as CWQ, WebQSP and LC-QuAD 1.0 in a resource-efficient manner and can generalize well to unseen domain-specific KGs like DBLP-QuAD and CoyPu KG Code: \href{https://github.com/LongquanJiang/OntoSCPrompt}{https://github.com/LongquanJiang/OntoSCPrompt}
MOSMOS: Multi-organ segmentation facilitated by medical report supervision
Sep 04, 2024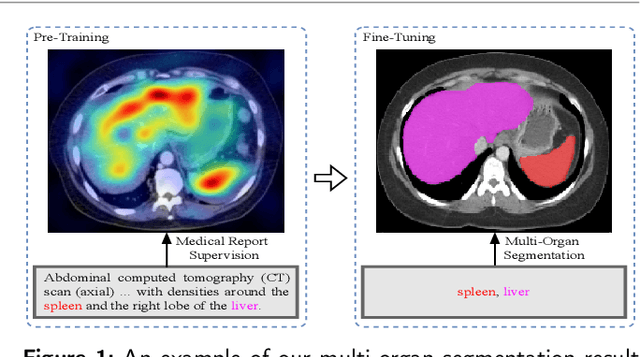
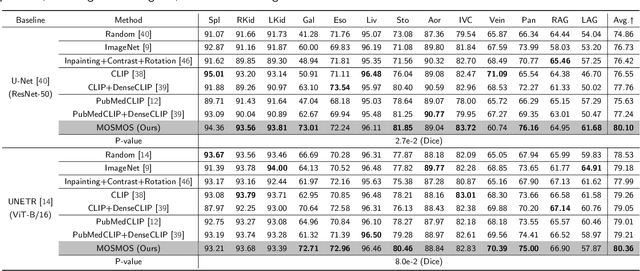
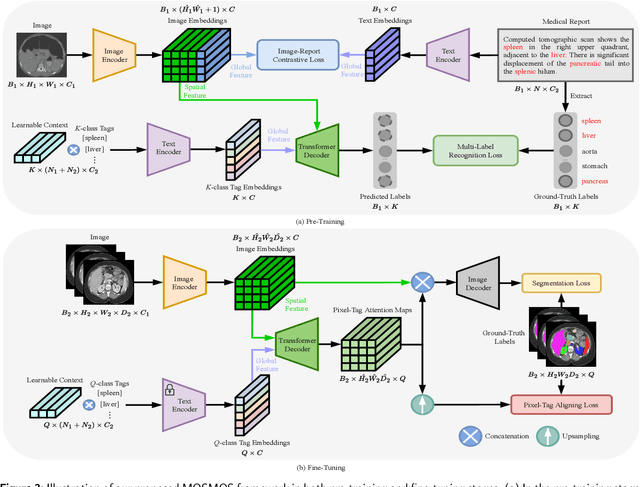
Abstract:Owing to a large amount of multi-modal data in modern medical systems, such as medical images and reports, Medical Vision-Language Pre-training (Med-VLP) has demonstrated incredible achievements in coarse-grained downstream tasks (i.e., medical classification, retrieval, and visual question answering). However, the problem of transferring knowledge learned from Med-VLP to fine-grained multi-organ segmentation tasks has barely been investigated. Multi-organ segmentation is challenging mainly due to the lack of large-scale fully annotated datasets and the wide variation in the shape and size of the same organ between individuals with different diseases. In this paper, we propose a novel pre-training & fine-tuning framework for Multi-Organ Segmentation by harnessing Medical repOrt Supervision (MOSMOS). Specifically, we first introduce global contrastive learning to maximally align the medical image-report pairs in the pre-training stage. To remedy the granularity discrepancy, we further leverage multi-label recognition to implicitly learn the semantic correspondence between image pixels and organ tags. More importantly, our pre-trained models can be transferred to any segmentation model by introducing the pixel-tag attention maps. Different network settings, i.e., 2D U-Net and 3D UNETR, are utilized to validate the generalization. We have extensively evaluated our approach using different diseases and modalities on BTCV, AMOS, MMWHS, and BRATS datasets. Experimental results in various settings demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework. This framework can serve as the foundation to facilitate future research on automatic annotation tasks under the supervision of medical reports.
Knowledge Graph Question Answering Datasets and Their Generalizability: Are They Enough for Future Research?
May 13, 2022



Abstract:Existing approaches on Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs (KGQA) have weak generalizability. That is often due to the standard i.i.d. assumption on the underlying dataset. Recently, three levels of generalization for KGQA were defined, namely i.i.d., compositional, zero-shot. We analyze 25 well-known KGQA datasets for 5 different Knowledge Graphs (KGs). We show that according to this definition many existing and online available KGQA datasets are either not suited to train a generalizable KGQA system or that the datasets are based on discontinued and out-dated KGs. Generating new datasets is a costly process and, thus, is not an alternative to smaller research groups and companies. In this work, we propose a mitigation method for re-splitting available KGQA datasets to enable their applicability to evaluate generalization, without any cost and manual effort. We test our hypothesis on three KGQA datasets, i.e., LC-QuAD, LC-QuAD 2.0 and QALD-9). Experiments on re-splitted KGQA datasets demonstrate its effectiveness towards generalizability. The code and a unified way to access 18 available datasets is online at https://github.com/semantic-systems/KGQA-datasets as well as https://github.com/semantic-systems/KGQA-datasets-generalization.
Knowledge Graph Question Answering Leaderboard: A Community Resource to Prevent a Replication Crisis
Jan 20, 2022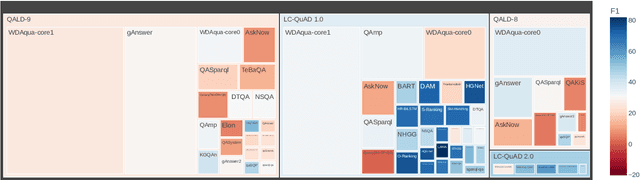
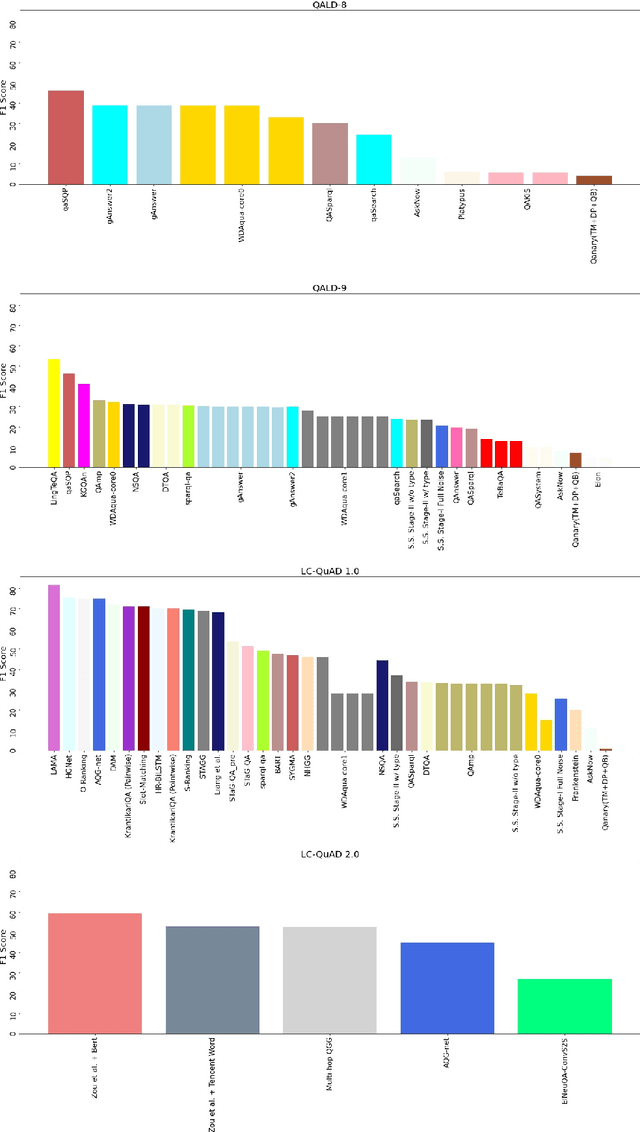
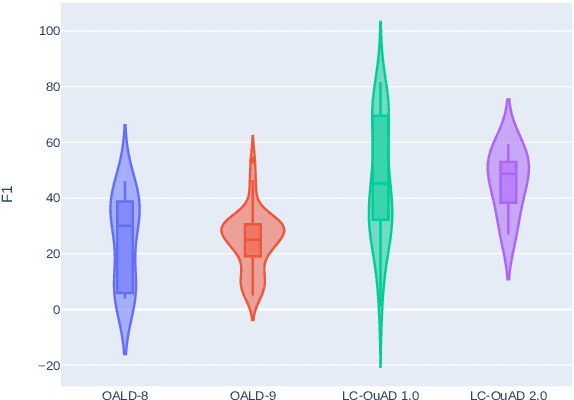
Abstract:Data-driven systems need to be evaluated to establish trust in the scientific approach and its applicability. In particular, this is true for Knowledge Graph (KG) Question Answering (QA), where complex data structures are made accessible via natural-language interfaces. Evaluating the capabilities of these systems has been a driver for the community for more than ten years while establishing different KGQA benchmark datasets. However, comparing different approaches is cumbersome. The lack of existing and curated leaderboards leads to a missing global view over the research field and could inject mistrust into the results. In particular, the latest and most-used datasets in the KGQA community, LC-QuAD and QALD, miss providing central and up-to-date points of trust. In this paper, we survey and analyze a wide range of evaluation results with significant coverage of 100 publications and 98 systems from the last decade. We provide a new central and open leaderboard for any KGQA benchmark dataset as a focal point for the community - https://kgqa.github.io/leaderboard. Our analysis highlights existing problems during the evaluation of KGQA systems. Thus, we will point to possible improvements for future evaluations.
Siamese Networks for Semantic Pattern Similarity
Dec 17, 2018



Abstract:Semantic Pattern Similarity is an interesting, though not often encountered NLP task where two sentences are compared not by their specific meaning, but by their more abstract semantic pattern (e.g., preposition or frame). We utilize Siamese Networks to model this task, and show its usefulness in determining SQL patterns for unseen questions in a database-backed question answering scenario. Our approach achieves high accuracy and contains a built-in proxy for confidence, which can be used to keep precision arbitrarily high.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge