Wen He
A Medical Multimodal Large Language Model for Pediatric Pneumonia
Sep 04, 2024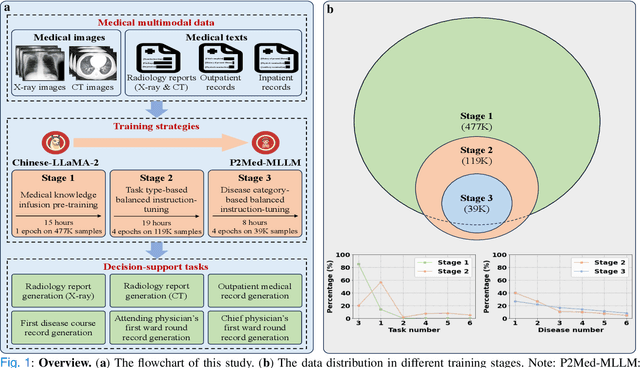

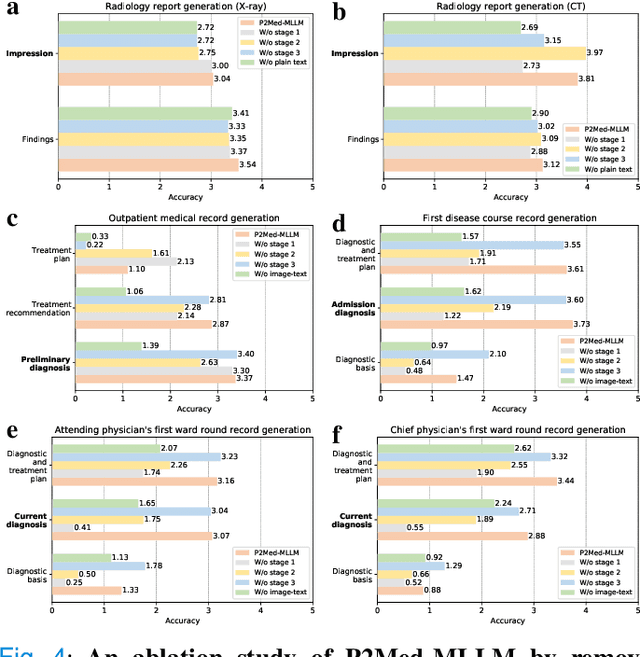
Abstract:Pediatric pneumonia is the leading cause of death among children under five years worldwide, imposing a substantial burden on affected families. Currently, there are three significant hurdles in diagnosing and treating pediatric pneumonia. Firstly, pediatric pneumonia shares similar symptoms with other respiratory diseases, making rapid and accurate differential diagnosis challenging. Secondly, primary hospitals often lack sufficient medical resources and experienced doctors. Lastly, providing personalized diagnostic reports and treatment recommendations is labor-intensive and time-consuming. To tackle these challenges, we proposed a Medical Multimodal Large Language Model for Pediatric Pneumonia (P2Med-MLLM). It was capable of handling diverse clinical tasks, such as generating free-text radiology reports and medical records within a unified framework. Specifically, P2Med-MLLM can process both pure text and image-text data, trained on an extensive and large-scale dataset (P2Med-MD), including real clinical information from 163,999 outpatient and 8,684 inpatient cases. This dataset comprised 2D chest X-ray images, 3D chest CT images, corresponding radiology reports, and outpatient and inpatient records. We designed a three-stage training strategy to enable P2Med-MLLM to comprehend medical knowledge and follow instructions for various clinical tasks. To rigorously evaluate P2Med-MLLM's performance, we developed P2Med-MBench, a benchmark consisting of 642 meticulously verified samples by pediatric pulmonology specialists, covering six clinical decision-support tasks and a balanced variety of diseases. The automated scoring results demonstrated the superiority of P2Med-MLLM. This work plays a crucial role in assisting primary care doctors with prompt disease diagnosis and treatment planning, reducing severe symptom mortality rates, and optimizing the allocation of medical resources.
Large Language Models are Complex Table Parsers
Dec 13, 2023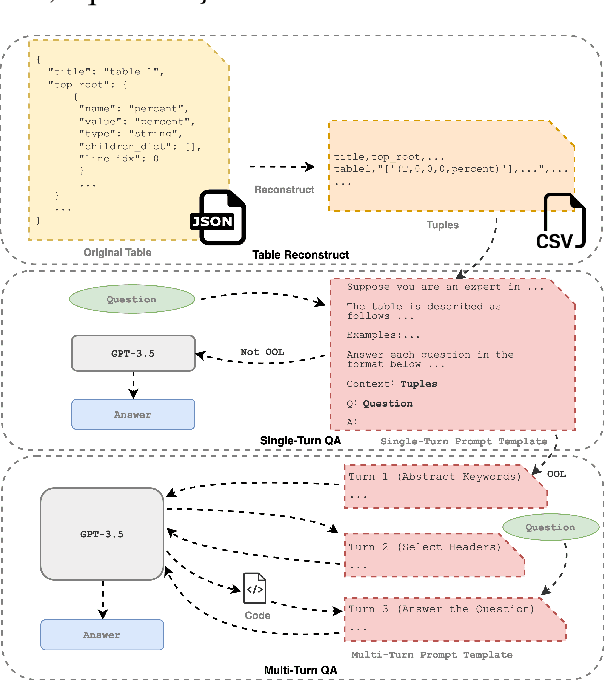
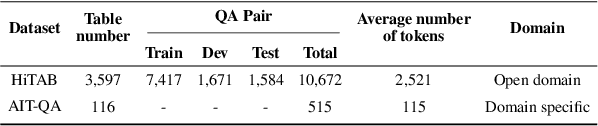
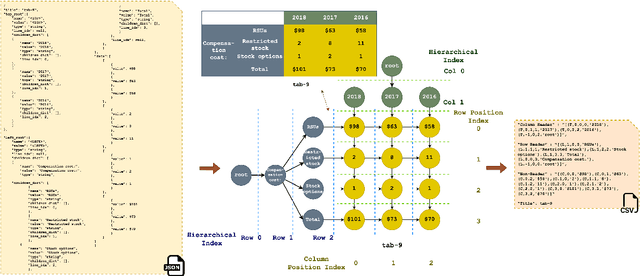
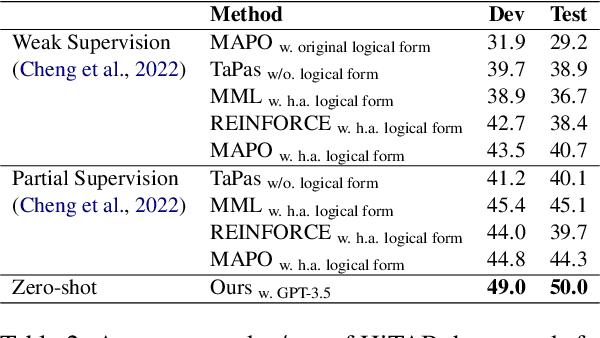
Abstract:With the Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3.5 (GPT-3.5) exhibiting remarkable reasoning and comprehension abilities in Natural Language Processing (NLP), most Question Answering (QA) research has primarily centered around general QA tasks based on GPT, neglecting the specific challenges posed by Complex Table QA. In this paper, we propose to incorporate GPT-3.5 to address such challenges, in which complex tables are reconstructed into tuples and specific prompt designs are employed for dialogues. Specifically, we encode each cell's hierarchical structure, position information, and content as a tuple. By enhancing the prompt template with an explanatory description of the meaning of each tuple and the logical reasoning process of the task, we effectively improve the hierarchical structure awareness capability of GPT-3.5 to better parse the complex tables. Extensive experiments and results on Complex Table QA datasets, i.e., the open-domain dataset HiTAB and the aviation domain dataset AIT-QA show that our approach significantly outperforms previous work on both datasets, leading to state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance.
E-Sports Talent Scouting Based on Multimodal Twitch Stream Data
Jul 02, 2019
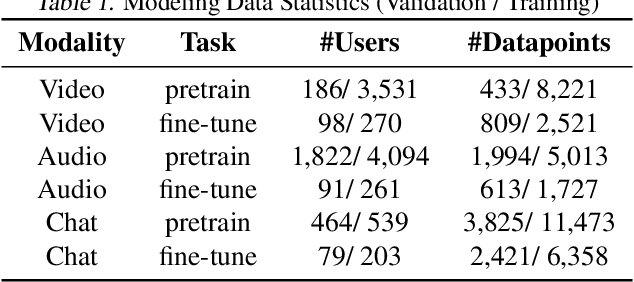
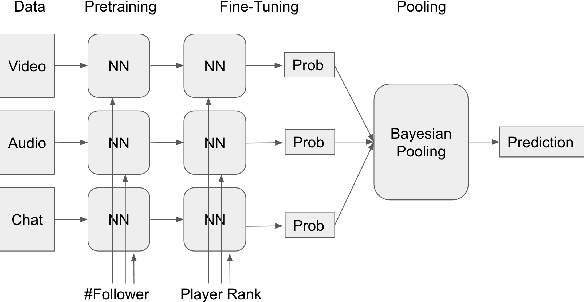
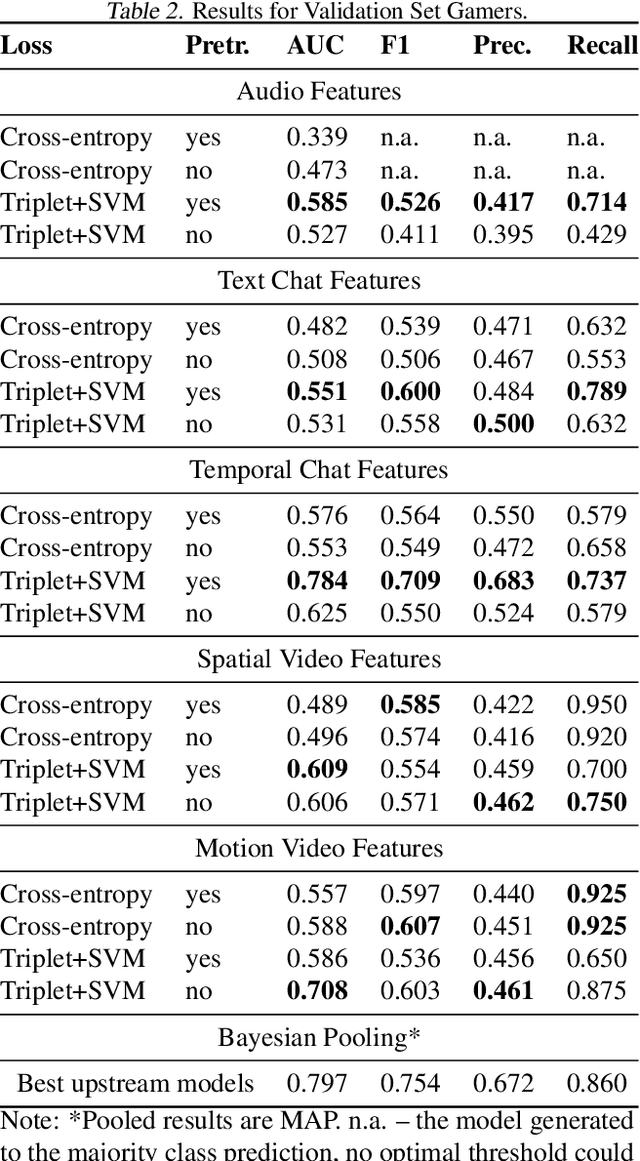
Abstract:We propose and investigate feasibility of a novel task that consists in finding e-sports talent using multimodal Twitch chat and video stream data. In that, we focus on predicting the ranks of Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO) gamers who broadcast their games on Twitch. During January 2019-April 2019, we have built two Twitch stream collections: One for 425 publicly ranked CS:GO gamers and one for 9,928 unranked CS:GO gamers. We extract neural features from video, audio and text chat data and estimate modality-specific probabilities for a gamer to be top-ranked during the data collection time-frame. A hierarchical Bayesian model is then used to pool the evidence across modalities and generate estimates of intrinsic skill for each gamer. Our modeling is validated through correlating the intrinsic skill predictions with May 2019 ranks of the publicly profiled gamers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge