Yueguo Chen
Balanced Anomaly-guided Ego-graph Diffusion Model for Inductive Graph Anomaly Detection
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Graph anomaly detection (GAD) is crucial in applications like fraud detection and cybersecurity. Despite recent advancements using graph neural networks (GNNs), two major challenges persist. At the model level, most methods adopt a transductive learning paradigm, which assumes static graph structures, making them unsuitable for dynamic, evolving networks. At the data level, the extreme class imbalance, where anomalous nodes are rare, leads to biased models that fail to generalize to unseen anomalies. These challenges are interdependent: static transductive frameworks limit effective data augmentation, while imbalance exacerbates model distortion in inductive learning settings. To address these challenges, we propose a novel data-centric framework that integrates dynamic graph modeling with balanced anomaly synthesis. Our framework features: (1) a discrete ego-graph diffusion model, which captures the local topology of anomalies to generate ego-graphs aligned with anomalous structural distribution, and (2) a curriculum anomaly augmentation mechanism, which dynamically adjusts synthetic data generation during training, focusing on underrepresented anomaly patterns to improve detection and generalization. Experiments on five datasets demonstrate that the effectiveness of our framework.
QKVQA: Question-Focused Filtering for Knowledge-based VQA
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering (KB-VQA) aims to answer questions by integrating images with external knowledge. Effective knowledge filtering is crucial for improving accuracy. Typical filtering methods use similarity metrics to locate relevant article sections from one article, leading to information selection errors at the article and intra-article levels. Although recent explorations of Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based filtering methods demonstrate superior semantic understanding and cross-article filtering capabilities, their high computational cost limits practical application. To address these issues, this paper proposes a question-focused filtering method. This approach can perform question-focused, cross-article filtering, efficiently obtaining high-quality filtered knowledge while keeping computational costs comparable to typical methods. Specifically, we design a trainable Question-Focused Filter (QFF) and a Chunk-based Dynamic Multi-Article Selection (CDA) module, which collectively alleviate information selection errors at both the article and intra-article levels. Experiments show that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art models by 4.9% on E-VQA and 3.8% on InfoSeek, validating its effectiveness. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/leaffeall/QKVQA.
T-Retriever: Tree-based Hierarchical Retrieval Augmented Generation for Textual Graphs
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has significantly enhanced Large Language Models' ability to access external knowledge, yet current graph-based RAG approaches face two critical limitations in managing hierarchical information: they impose rigid layer-specific compression quotas that damage local graph structures, and they prioritize topological structure while neglecting semantic content. We introduce T-Retriever, a novel framework that reformulates attributed graph retrieval as tree-based retrieval using a semantic and structure-guided encoding tree. Our approach features two key innovations: (1) Adaptive Compression Encoding, which replaces artificial compression quotas with a global optimization strategy that preserves the graph's natural hierarchical organization, and (2) Semantic-Structural Entropy ($S^2$-Entropy), which jointly optimizes for both structural cohesion and semantic consistency when creating hierarchical partitions. Experiments across diverse graph reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that T-Retriever significantly outperforms state-of-the-art RAG methods, providing more coherent and contextually relevant responses to complex queries.
MAJL: A Model-Agnostic Joint Learning Framework for Music Source Separation and Pitch Estimation
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Music source separation and pitch estimation are two vital tasks in music information retrieval. Typically, the input of pitch estimation is obtained from the output of music source separation. Therefore, existing methods have tried to perform these two tasks simultaneously, so as to leverage the mutually beneficial relationship between both tasks. However, these methods still face two critical challenges that limit the improvement of both tasks: the lack of labeled data and joint learning optimization. To address these challenges, we propose a Model-Agnostic Joint Learning (MAJL) framework for both tasks. MAJL is a generic framework and can use variant models for each task. It includes a two-stage training method and a dynamic weighting method named Dynamic Weights on Hard Samples (DWHS), which addresses the lack of labeled data and joint learning optimization, respectively. Experimental results on public music datasets show that MAJL outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both tasks, with significant improvements of 0.92 in Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (SDR) for music source separation and 2.71% in Raw Pitch Accuracy (RPA) for pitch estimation. Furthermore, comprehensive studies not only validate the effectiveness of each component of MAJL, but also indicate the great generality of MAJL in adapting to different model architectures.
YuLan: An Open-source Large Language Model
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have become the foundation of many applications, leveraging their extensive capabilities in processing and understanding natural language. While many open-source LLMs have been released with technical reports, the lack of training details hinders further research and development. This paper presents the development of YuLan, a series of open-source LLMs with $12$ billion parameters. The base model of YuLan is pre-trained on approximately $1.7$T tokens derived from a diverse corpus, including massive English, Chinese, and multilingual texts. We design a three-stage pre-training method to enhance YuLan's overall capabilities. Subsequent phases of training incorporate instruction-tuning and human alignment, employing a substantial volume of high-quality synthesized data. To facilitate the learning of complex and long-tail knowledge, we devise a curriculum-learning framework throughout across these stages, which helps LLMs learn knowledge in an easy-to-hard manner. YuLan's training is finished on Jan, 2024 and has achieved performance on par with state-of-the-art LLMs across various English and Chinese benchmarks. This paper outlines a comprehensive technical roadmap for developing LLMs from scratch. Our model and codes are available at https://github.com/RUC-GSAI/YuLan-Chat.
Large Language Model for Table Processing: A Survey
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Tables, typically two-dimensional and structured to store large amounts of data, are essential in daily activities like database queries, spreadsheet calculations, and generating reports from web tables. Automating these table-centric tasks with Large Language Models (LLMs) offers significant public benefits, garnering interest from academia and industry. This survey provides an extensive overview of table tasks, encompassing not only the traditional areas like table question answering (Table QA) and fact verification, but also newly emphasized aspects such as table manipulation and advanced table data analysis. Additionally, it goes beyond the early strategies of pre-training and fine-tuning small language models, to include recent paradigms in LLM usage. The focus here is particularly on instruction-tuning, prompting, and agent-based approaches within the realm of LLMs. Finally, we highlight several challenges, ranging from private deployment and efficient inference to the development of extensive benchmarks for table manipulation and advanced data analysis.
DJCM: A Deep Joint Cascade Model for Singing Voice Separation and Vocal Pitch Estimation
Jan 08, 2024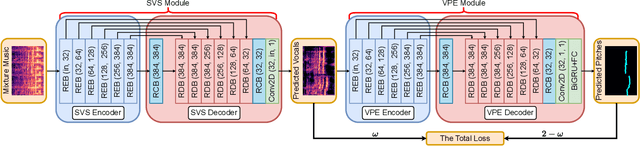



Abstract:Singing voice separation and vocal pitch estimation are pivotal tasks in music information retrieval. Existing methods for simultaneous extraction of clean vocals and vocal pitches can be classified into two categories: pipeline methods and naive joint learning methods. However, the efficacy of these methods is limited by the following problems: On the one hand, pipeline methods train models for each task independently, resulting a mismatch between the data distributions at the training and testing time. On the other hand, naive joint learning methods simply add the losses of both tasks, possibly leading to a misalignment between the distinct objectives of each task. To solve these problems, we propose a Deep Joint Cascade Model (DJCM) for singing voice separation and vocal pitch estimation. DJCM employs a novel joint cascade model structure to concurrently train both tasks. Moreover, task-specific weights are used to align different objectives of both tasks. Experimental results show that DJCM achieves state-of-the-art performance on both tasks, with great improvements of 0.45 in terms of Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (SDR) for singing voice separation and 2.86% in terms of Overall Accuracy (OA) for vocal pitch estimation. Furthermore, extensive ablation studies validate the effectiveness of each design of our proposed model. The code of DJCM is available at https://github.com/Dream-High/DJCM .
REAL: A Representative Error-Driven Approach for Active Learning
Jul 06, 2023



Abstract:Given a limited labeling budget, active learning (AL) aims to sample the most informative instances from an unlabeled pool to acquire labels for subsequent model training. To achieve this, AL typically measures the informativeness of unlabeled instances based on uncertainty and diversity. However, it does not consider erroneous instances with their neighborhood error density, which have great potential to improve the model performance. To address this limitation, we propose $REAL$, a novel approach to select data instances with $\underline{R}$epresentative $\underline{E}$rrors for $\underline{A}$ctive $\underline{L}$earning. It identifies minority predictions as \emph{pseudo errors} within a cluster and allocates an adaptive sampling budget for the cluster based on estimated error density. Extensive experiments on five text classification datasets demonstrate that $REAL$ consistently outperforms all best-performing baselines regarding accuracy and F1-macro scores across a wide range of hyperparameter settings. Our analysis also shows that $REAL$ selects the most representative pseudo errors that match the distribution of ground-truth errors along the decision boundary. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/withchencheng/ECML_PKDD_23_Real.
RMVPE: A Robust Model for Vocal Pitch Estimation in Polyphonic Music
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:Vocal pitch is an important high-level feature in music audio processing. However, extracting vocal pitch in polyphonic music is more challenging due to the presence of accompaniment. To eliminate the influence of the accompaniment, most previous methods adopt music source separation models to obtain clean vocals from polyphonic music before predicting vocal pitches. As a result, the performance of vocal pitch estimation is affected by the music source separation models. To address this issue and directly extract vocal pitches from polyphonic music, we propose a robust model named RMVPE. This model can extract effective hidden features and accurately predict vocal pitches from polyphonic music. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of RMVPE in terms of raw pitch accuracy (RPA) and raw chroma accuracy (RCA). Additionally, experiments conducted with different types of noise show that RMVPE is robust across all signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels. The code of RMVPE is available at https://github.com/Dream-High/RMVPE.
JEPOO: Highly Accurate Joint Estimation of Pitch, Onset and Offset for Music Information Retrieval
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:Melody extraction is a core task in music information retrieval, and the estimation of pitch, onset and offset are key sub-tasks in melody extraction. Existing methods have limited accuracy, and work for only one type of data, either single-pitch or multipitch. In this paper, we propose a highly accurate method for joint estimation of pitch, onset and offset, named JEPOO. We address the challenges of joint learning optimization and handling both single-pitch and multi-pitch data through novel model design and a new optimization technique named Pareto modulated loss with loss weight regularization. This is the first method that can accurately handle both single-pitch and multi-pitch music data, and even a mix of them. A comprehensive experimental study on a wide range of real datasets shows that JEPOO outperforms state-ofthe-art methods by up to 10.6%, 8.3% and 10.3% for the prediction of Pitch, Onset and Offset, respectively, and JEPOO is robust for various types of data and instruments. The ablation study shows the effectiveness of each component of JEPOO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge