Yuankai Wu
Aeolus: A Multi-structural Flight Delay Dataset
Oct 30, 2025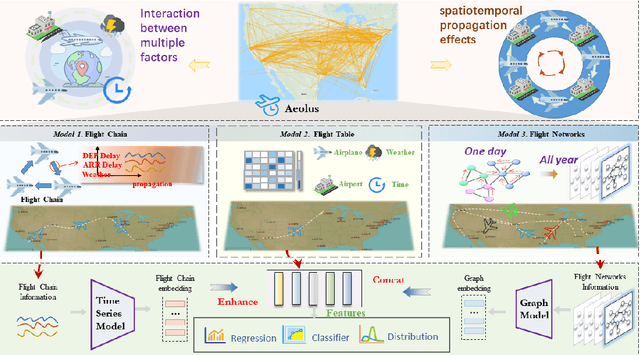
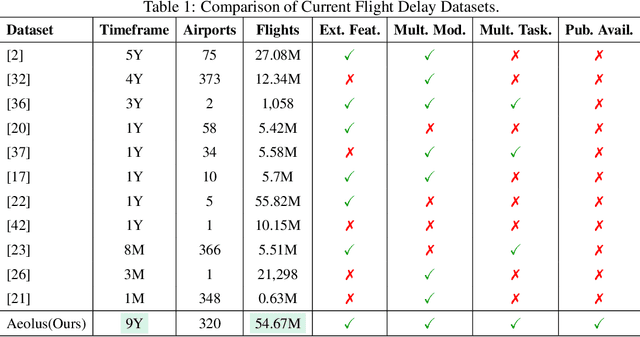
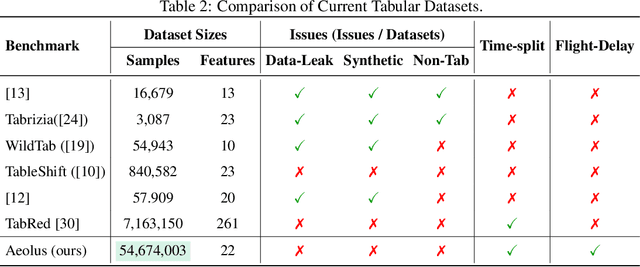
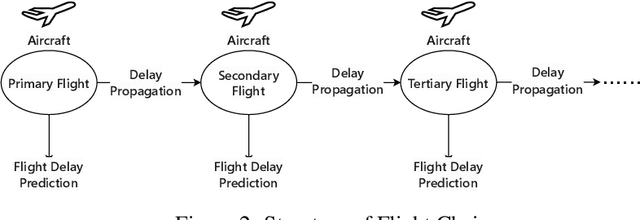
Abstract:We introduce Aeolus, a large-scale Multi-modal Flight Delay Dataset designed to advance research on flight delay prediction and support the development of foundation models for tabular data. Existing datasets in this domain are typically limited to flat tabular structures and fail to capture the spatiotemporal dynamics inherent in delay propagation. Aeolus addresses this limitation by providing three aligned modalities: (i) a tabular dataset with rich operational, meteorological, and airportlevel features for over 50 million flights; (ii) a flight chain module that models delay propagation along sequential flight legs, capturing upstream and downstream dependencies; and (iii) a flight network graph that encodes shared aircraft, crew, and airport resource connections, enabling cross-flight relational reasoning. The dataset is carefully constructed with temporal splits, comprehensive features, and strict leakage prevention to support realistic and reproducible machine learning evaluation. Aeolus supports a broad range of tasks, including regression, classification, temporal structure modeling, and graph learning, serving as a unified benchmark across tabular, sequential, and graph modalities. We release baseline experiments and preprocessing tools to facilitate adoption. Aeolus fills a key gap for both domain-specific modeling and general-purpose structured data research.Our source code and data can be accessed at https://github.com/Flnny/Delay-data
GeoSR: Cognitive-Agentic Framework for Probing Geospatial Knowledge Boundaries via Iterative Self-Refinement
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have extended the application of large language models (LLMs) to geographic problems, revealing surprising geospatial competence even without explicit spatial supervision. However, LLMs still face challenges in spatial consistency, multi-hop reasoning, and geographic bias. To address these issues, we propose GeoSR, a self-refining agentic reasoning framework that embeds core geographic principles -- most notably Tobler's First Law of Geography -- into an iterative prediction loop. In GeoSR, the reasoning process is decomposed into three collaborating agents: (1) a variable-selection agent that selects relevant covariates from the same location; (2) a point-selection agent that chooses reference predictions at nearby locations generated by the LLM in previous rounds; and (3) a refine agent that coordinates the iterative refinement process by evaluating prediction quality and triggering further rounds when necessary. This agentic loop progressively improves prediction quality by leveraging both spatial dependencies and inter-variable relationships. We validate GeoSR on tasks ranging from physical-world property estimation to socioeconomic prediction. Experimental results show consistent improvements over standard prompting strategies, demonstrating that incorporating geostatistical priors and spatially structured reasoning into LLMs leads to more accurate and equitable geospatial predictions. The code of GeoSR is available at https://github.com/JinfanTang/GeoSR.
Technical Report for Egocentric Mistake Detection for the HoloAssist Challenge
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:In this report, we address the task of online mistake detection, which is vital in domains like industrial automation and education, where real-time video analysis allows human operators to correct errors as they occur. While previous work focuses on procedural errors involving action order, broader error types must be addressed for real-world use. We introduce an online mistake detection framework that handles both procedural and execution errors (e.g., motor slips or tool misuse). Upon detecting an error, we use a large language model (LLM) to generate explanatory feedback. Experiments on the HoloAssist benchmark confirm the effectiveness of our approach, where our approach is placed second on the mistake detection task.
Evaluating Temporal Plasticity in Foundation Time Series Models for Incremental Fine-tuning
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Time series foundation models excel at diverse time series forecasting tasks, but their capacity for continuous improvement through incremental learning remains unexplored. We present the first comprehensive study investigating these models' temporal plasticity - their ability to progressively enhance performance through continual learning while maintaining existing capabilities. Through experiments on real-world datasets exhibiting distribution shifts, we evaluate both conventional deep learning models and foundation models using a novel continual learning framework. Our findings reveal that while traditional models struggle with performance deterioration during incremental fine-tuning, foundation models like Time-MoE and Chronos demonstrate sustained improvement in predictive accuracy. This suggests that optimizing foundation model fine-tuning strategies may be more valuable than developing domain-specific small models. Our research introduces new evaluation methodologies and insights for developing foundation time series models with robust continuous learning capabilities.
Memory-based Ensemble Learning in CMR Semantic Segmentation
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Existing models typically segment either the entire 3D frame or 2D slices independently to derive clinical functional metrics from ventricular segmentation in cardiac cine sequences. While performing well overall, they struggle at the end slices. To address this, we leverage spatial continuity to extract global uncertainty from segmentation variance and use it as memory in our ensemble learning method, Streaming, for classifier weighting, balancing overall and end-slice performance. Additionally, we introduce the End Coefficient (EC) to quantify end-slice accuracy. Experiments on ACDC and M\&Ms datasets show that our framework achieves near-state-of-the-art Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and outperforms all models on end-slice performance, improving patient-specific segmentation accuracy.
ForecastGrapher: Redefining Multivariate Time Series Forecasting with Graph Neural Networks
May 28, 2024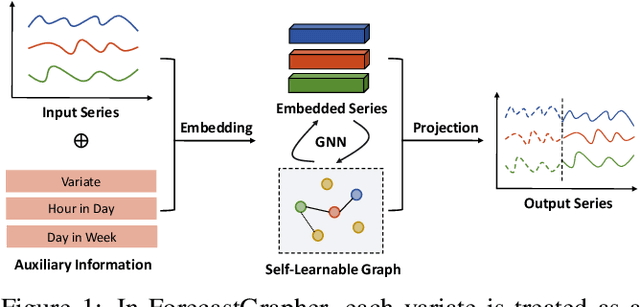
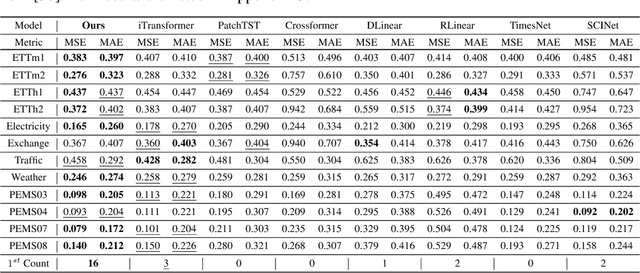
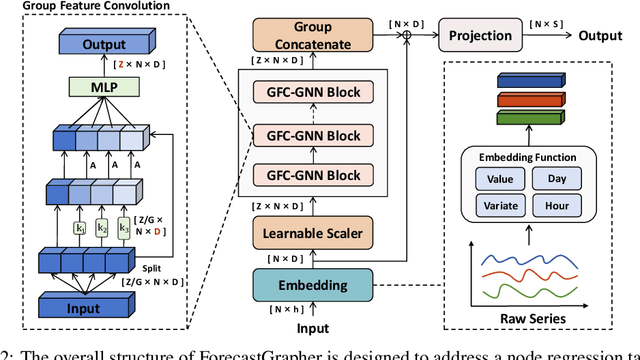
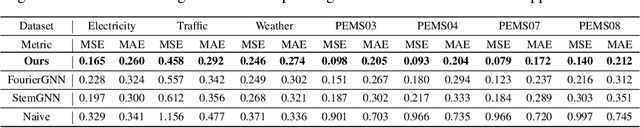
Abstract:The challenge of effectively learning inter-series correlations for multivariate time series forecasting remains a substantial and unresolved problem. Traditional deep learning models, which are largely dependent on the Transformer paradigm for modeling long sequences, often fail to integrate information from multiple time series into a coherent and universally applicable model. To bridge this gap, our paper presents ForecastGrapher, a framework reconceptualizes multivariate time series forecasting as a node regression task, providing a unique avenue for capturing the intricate temporal dynamics and inter-series correlations. Our approach is underpinned by three pivotal steps: firstly, generating custom node embeddings to reflect the temporal variations within each series; secondly, constructing an adaptive adjacency matrix to encode the inter-series correlations; and thirdly, augmenting the GNNs' expressive power by diversifying the node feature distribution. To enhance this expressive power, we introduce the Group Feature Convolution GNN (GFC-GNN). This model employs a learnable scaler to segment node features into multiple groups and applies one-dimensional convolutions with different kernel lengths to each group prior to the aggregation phase. Consequently, the GFC-GNN method enriches the diversity of node feature distribution in a fully end-to-end fashion. Through extensive experiments and ablation studies, we show that ForecastGrapher surpasses strong baselines and leading published techniques in the domain of multivariate time series forecasting.
NuwaTS: a Foundation Model Mending Every Incomplete Time Series
May 27, 2024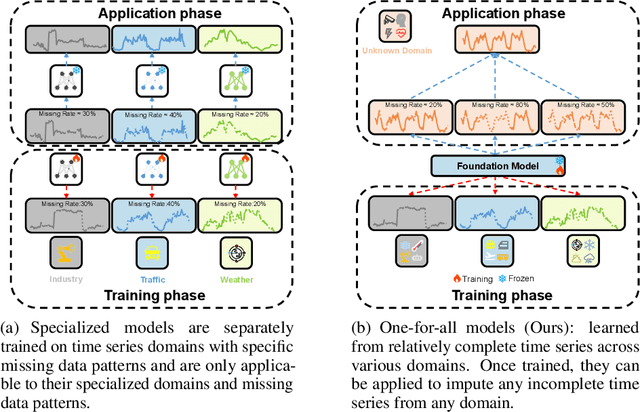

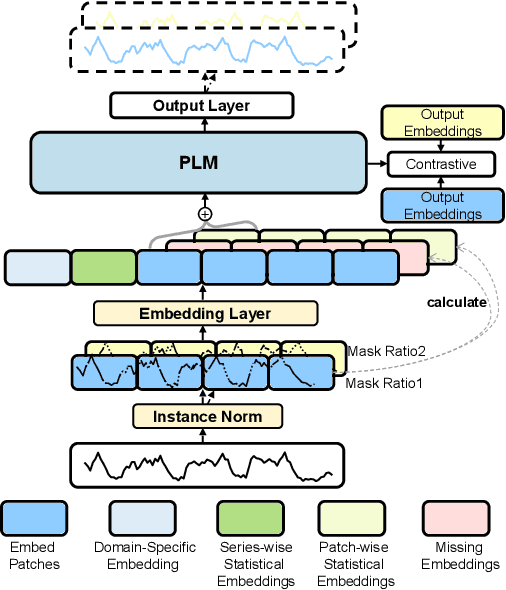
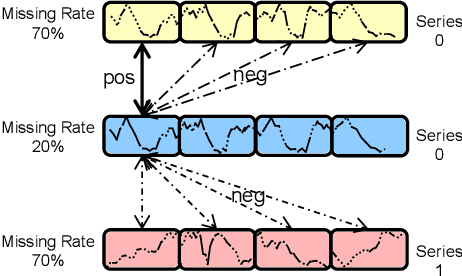
Abstract:Time series imputation plays a crucial role in various real-world systems and has been extensively explored. Models for time series imputation often require specialization, necessitating distinct designs for different domains and missing patterns. In this study, we introduce NuwaTS, a framework to repurpose Pre-trained Language Model (PLM) for general time series imputation. Once trained, this model can be applied to imputation tasks on incomplete time series from any domain with any missing patterns. We begin by devising specific embeddings for each sub-series patch of the incomplete time series. These embeddings encapsulate information about the patch itself, the missing data patterns within the patch, and the patch's statistical characteristics. To enhance the model's adaptability to different missing patterns, we propose a contrastive learning approach to make representations of the same patch more similar across different missing patterns. By combining this contrastive loss with the missing data imputation task, we train PLMs to obtain a one-for-all imputation model. Furthermore, we utilize a plug-and-play layer-wise fine-tuning approach to train domain-specific models. Experimental results demonstrate that leveraging a dataset of over seventeen million time series from diverse domains, we obtain a one-for-all imputation model which outperforms existing domain-specific models across various datasets and missing patterns. Additionally, we find that NuwaTS can be generalized to other time series tasks such as forecasting. Our codes are available at https://github.com/Chengyui/NuwaTS.
ADL4D: Towards A Contextually Rich Dataset for 4D Activities of Daily Living
Feb 27, 2024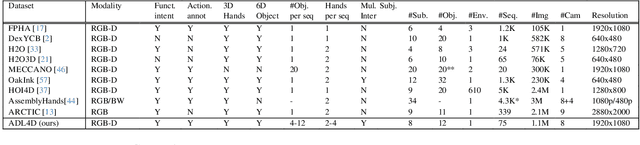
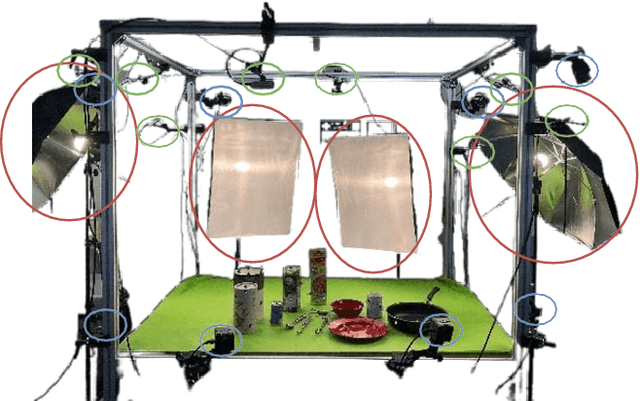
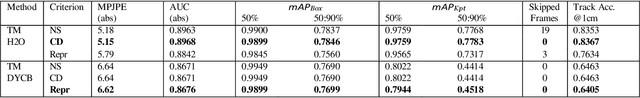

Abstract:Hand-Object Interactions (HOIs) are conditioned on spatial and temporal contexts like surrounding objects, pre- vious actions, and future intents (for example, grasping and handover actions vary greatly based on objects proximity and trajectory obstruction). However, existing datasets for 4D HOI (3D HOI over time) are limited to one subject inter- acting with one object only. This restricts the generalization of learning-based HOI methods trained on those datasets. We introduce ADL4D, a dataset of up to two subjects inter- acting with different sets of objects performing Activities of Daily Living (ADL) like breakfast or lunch preparation ac- tivities. The transition between multiple objects to complete a certain task over time introduces a unique context lacking in existing datasets. Our dataset consists of 75 sequences with a total of 1.1M RGB-D frames, hand and object poses, and per-hand fine-grained action annotations. We develop an automatic system for multi-view multi-hand 3D pose an- notation capable of tracking hand poses over time. We inte- grate and test it against publicly available datasets. Finally, we evaluate our dataset on the tasks of Hand Mesh Recov- ery (HMR) and Hand Action Segmentation (HAS).
Modeling Spatio-temporal Dynamical Systems with Neural Discrete Learning and Levels-of-Experts
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we address the issue of modeling and estimating changes in the state of the spatio-temporal dynamical systems based on a sequence of observations like video frames. Traditional numerical simulation systems depend largely on the initial settings and correctness of the constructed partial differential equations (PDEs). Despite recent efforts yielding significant success in discovering data-driven PDEs with neural networks, the limitations posed by singular scenarios and the absence of local insights prevent them from performing effectively in a broader real-world context. To this end, this paper propose the universal expert module -- that is, optical flow estimation component, to capture the evolution laws of general physical processes in a data-driven fashion. To enhance local insight, we painstakingly design a finer-grained physical pipeline, since local characteristics may be influenced by various internal contextual information, which may contradict the macroscopic properties of the whole system. Further, we harness currently popular neural discrete learning to unveil the underlying important features in its latent space, this process better injects interpretability, which can help us obtain a powerful prior over these discrete random variables. We conduct extensive experiments and ablations to demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves large performance margins, compared with the existing SOTA baselines.
MSGNet: Learning Multi-Scale Inter-Series Correlations for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting
Dec 31, 2023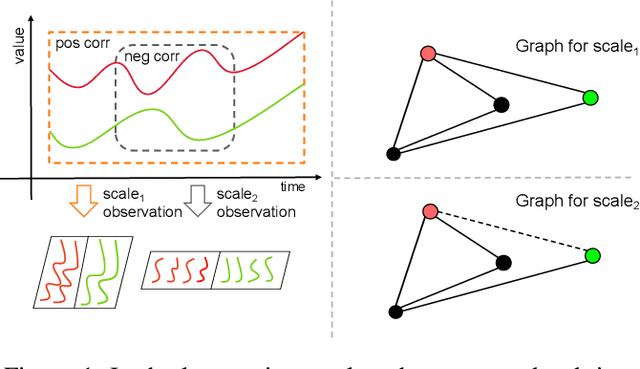
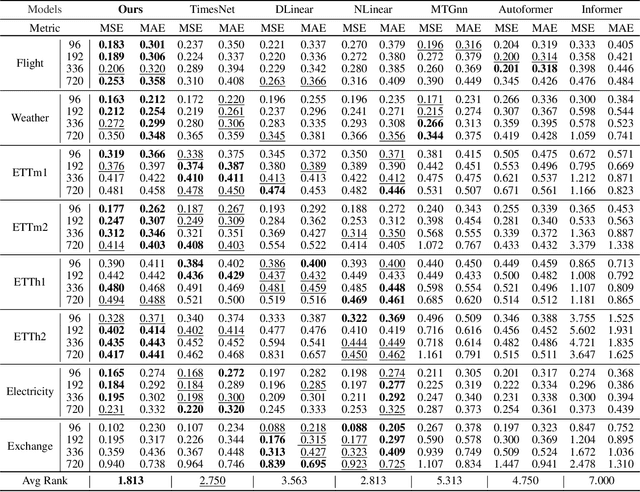
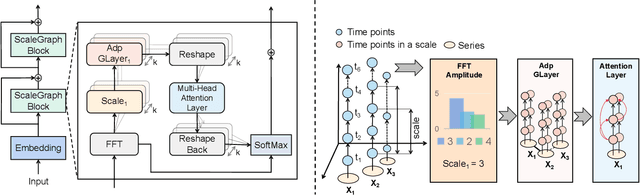
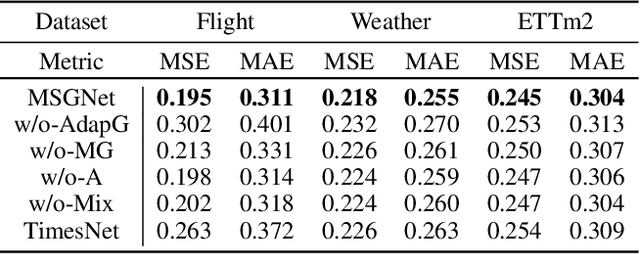
Abstract:Multivariate time series forecasting poses an ongoing challenge across various disciplines. Time series data often exhibit diverse intra-series and inter-series correlations, contributing to intricate and interwoven dependencies that have been the focus of numerous studies. Nevertheless, a significant research gap remains in comprehending the varying inter-series correlations across different time scales among multiple time series, an area that has received limited attention in the literature. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces MSGNet, an advanced deep learning model designed to capture the varying inter-series correlations across multiple time scales using frequency domain analysis and adaptive graph convolution. By leveraging frequency domain analysis, MSGNet effectively extracts salient periodic patterns and decomposes the time series into distinct time scales. The model incorporates a self-attention mechanism to capture intra-series dependencies, while introducing an adaptive mixhop graph convolution layer to autonomously learn diverse inter-series correlations within each time scale. Extensive experiments are conducted on several real-world datasets to showcase the effectiveness of MSGNet. Furthermore, MSGNet possesses the ability to automatically learn explainable multi-scale inter-series correlations, exhibiting strong generalization capabilities even when applied to out-of-distribution samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge