Yonghao He
Efficient Task-specific Conditional Diffusion Policies: Shortcut Model Acceleration and SO(3) Optimization
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Imitation learning, particularly Diffusion Policies based methods, has recently gained significant traction in embodied AI as a powerful approach to action policy generation. These models efficiently generate action policies by learning to predict noise. However, conventional Diffusion Policy methods rely on iterative denoising, leading to inefficient inference and slow response times, which hinder real-time robot control. To address these limitations, we propose a Classifier-Free Shortcut Diffusion Policy (CF-SDP) that integrates classifier-free guidance with shortcut-based acceleration, enabling efficient task-specific action generation while significantly improving inference speed. Furthermore, we extend diffusion modeling to the SO(3) manifold in shortcut model, defining the forward and reverse processes in its tangent space with an isotropic Gaussian distribution. This ensures stable and accurate rotational estimation, enhancing the effectiveness of diffusion-based control. Our approach achieves nearly 5x acceleration in diffusion inference compared to DDIM-based Diffusion Policy while maintaining task performance. Evaluations both on the RoboTwin simulation platform and real-world scenarios across various tasks demonstrate the superiority of our method.
A Light-Weight Framework for Open-Set Object Detection with Decoupled Feature Alignment in Joint Space
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Open-set object detection (OSOD) is highly desirable for robotic manipulation in unstructured environments. However, existing OSOD methods often fail to meet the requirements of robotic applications due to their high computational burden and complex deployment. To address this issue, this paper proposes a light-weight framework called Decoupled OSOD (DOSOD), which is a practical and highly efficient solution to support real-time OSOD tasks in robotic systems. Specifically, DOSOD builds upon the YOLO-World pipeline by integrating a vision-language model (VLM) with a detector. A Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) adaptor is developed to transform text embeddings extracted by the VLM into a joint space, within which the detector learns the region representations of class-agnostic proposals. Cross-modality features are directly aligned in the joint space, avoiding the complex feature interactions and thereby improving computational efficiency. DOSOD operates like a traditional closed-set detector during the testing phase, effectively bridging the gap between closed-set and open-set detection. Compared to the baseline YOLO-World, the proposed DOSOD significantly enhances real-time performance while maintaining comparable accuracy. The slight DOSOD-S model achieves a Fixed AP of $26.7\%$, compared to $26.2\%$ for YOLO-World-v1-S and $22.7\%$ for YOLO-World-v2-S, using similar backbones on the LVIS minival dataset. Meanwhile, the FPS of DOSOD-S is $57.1\%$ higher than YOLO-World-v1-S and $29.6\%$ higher than YOLO-World-v2-S. Meanwhile, we demonstrate that the DOSOD model facilitates the deployment of edge devices. The codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/D-Robotics-AI-Lab/DOSOD.
The Second-place Solution for CVPR VISION 23 Challenge Track 1 -- Data Effificient Defect Detection
Jun 25, 2023



Abstract:The Vision Challenge Track 1 for Data-Effificient Defect Detection requires competitors to instance segment 14 industrial inspection datasets in a data-defificient setting. This report introduces the technical details of the team Aoi-overfifitting-Team for this challenge. Our method focuses on the key problem of segmentation quality of defect masks in scenarios with limited training samples. Based on the Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) instance segmentation algorithm, we connect the transformer backbone (Swin-B) through composite connections inspired by CBNetv2 to enhance the baseline results. Additionally, we propose two model ensemble methods to further enhance the segmentation effect: one incorporates semantic segmentation into instance segmentation, while the other employs multi-instance segmentation fusion algorithms. Finally, using multi-scale training and test-time augmentation (TTA), we achieve an average mAP@0.50:0.95 of more than 48.49% and an average mAR@0.50:0.95 of 66.71% on the test set of the Data Effificient Defect Detection Challenge. The code is available at https://github.com/love6tao/Aoi-overfitting-team
DSLA: Dynamic smooth label assignment for efficient anchor-free object detection
Aug 01, 2022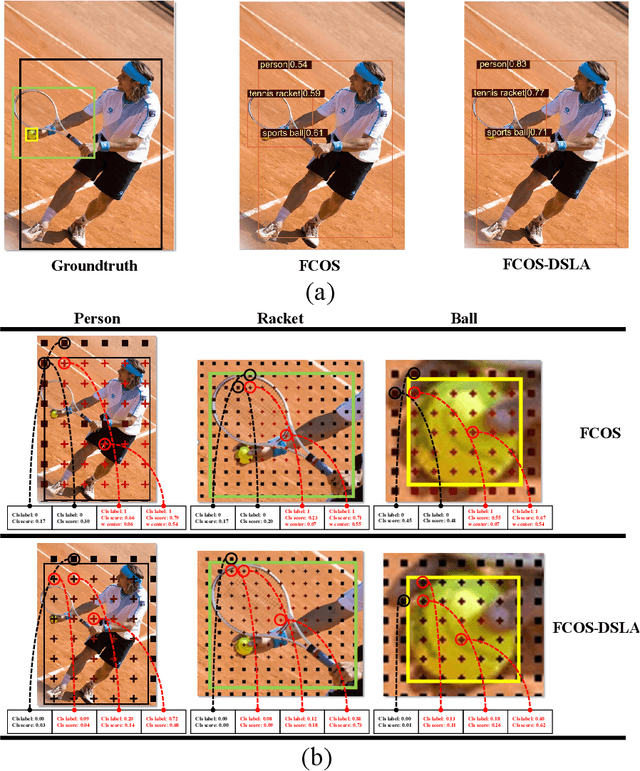
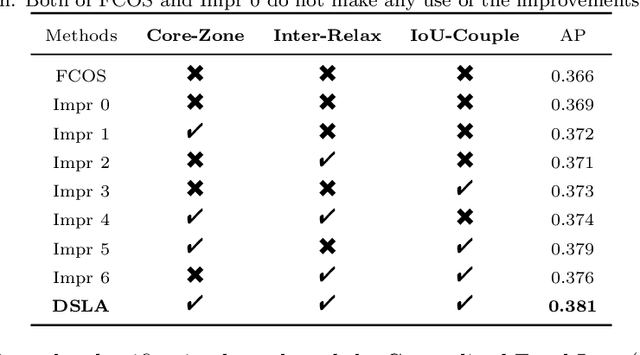
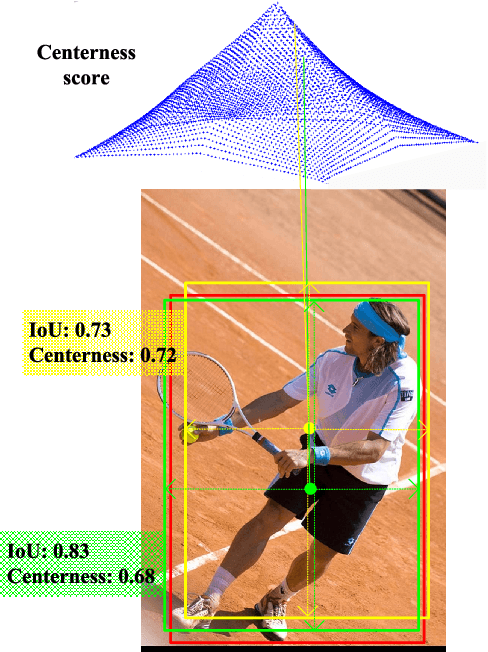

Abstract:Anchor-free detectors basically formulate object detection as dense classification and regression. For popular anchor-free detectors, it is common to introduce an individual prediction branch to estimate the quality of localization. The following inconsistencies are observed when we delve into the practices of classification and quality estimation. Firstly, for some adjacent samples which are assigned completely different labels, the trained model would produce similar classification scores. This violates the training objective and leads to performance degradation. Secondly, it is found that detected bounding boxes with higher confidences contrarily have smaller overlaps with the corresponding ground-truth. Accurately localized bounding boxes would be suppressed by less accurate ones in the Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) procedure. To address the inconsistency problems, the Dynamic Smooth Label Assignment (DSLA) method is proposed. Based on the concept of centerness originally developed in FCOS, a smooth assignment strategy is proposed. The label is smoothed to a continuous value in [0, 1] to make a steady transition between positive and negative samples. Intersection-of-Union (IoU) is predicted dynamically during training and is coupled with the smoothed label. The dynamic smooth label is assigned to supervise the classification branch. Under such supervision, quality estimation branch is naturally merged into the classification branch, which simplifies the architecture of anchor-free detector. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on the MS COCO benchmark. It is demonstrated that, DSLA can significantly boost the detection accuracy by alleviating the above inconsistencies for anchor-free detectors. Our codes are released at https://github.com/YonghaoHe/DSLA.
LFFD: A Light and Fast Face Detector for Edge Devices
May 09, 2019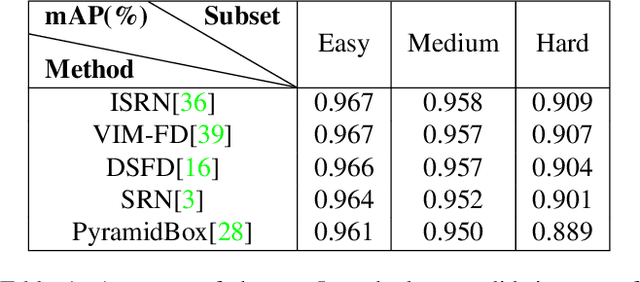
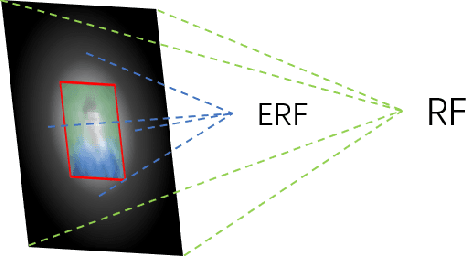
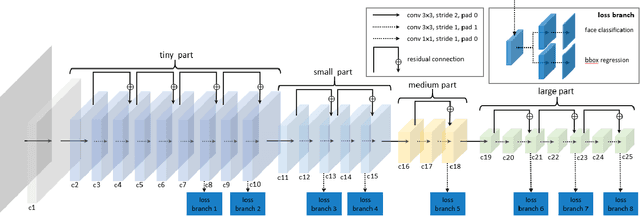
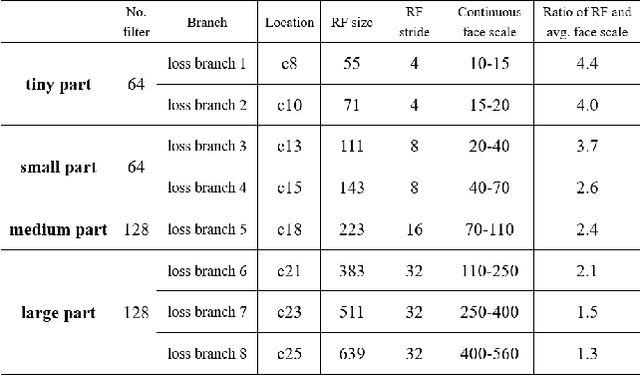
Abstract:Face detection, as a fundamental technology for various applications, is always deployed on edge devices. There-fore, face detectors are supposed to have limited model size and fast inference speed. This paper introduces a Light and Fast Face Detector (LFFD) for edge devices. We rethink the receptive field (RF) in context of face detection and find that RFs can be used as inherent anchors instead of manually construction. Combining RF anchors and appropriate strides, the proposed method can cover a large range of continuous face scales with nearly 100% hit rate, rather than discrete scales. The insightful understanding of relations between effective receptive field (ERF) and face scales motivates an efficient backbone for one-stage detection. The backbone is characterized by eight detection branches and common building blocks, resulting in efficient computation. Comprehensive and extensive experiments on popular benchmarks: WIDER FACE and FDDB are conducted. A new evaluation schema is proposed for practical applications. Under the new schema, the proposed method can achieve superior accuracy (WIDER FACE Val/Test - Easy: 0.910/0.896, Medium: 0.880/0.865, Hard: 0.780/0.770; FDDB - discontinuous: 0.965, continuous: 0.719). Multiple hardware platforms are introduced to evaluate the running efficiency. The proposed methods can obtain fast inference speed (NVIDIA TITAN Xp: 131.45 FPS at 640480; NVIDIA TX2: 136.99 FPS at 160120; Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+: 8.44 FPS at 160120) with model size of 9 MB.
Cross-Modal Similarity Learning : A Low Rank Bilinear Formulation
Dec 17, 2015
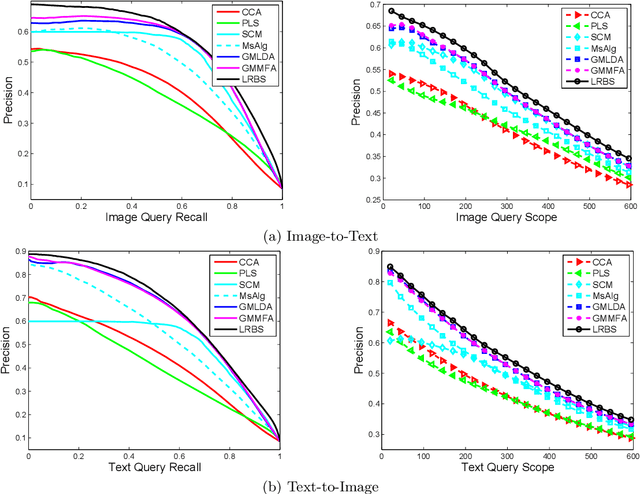


Abstract:The cross-media retrieval problem has received much attention in recent years due to the rapid increasing of multimedia data on the Internet. A new approach to the problem has been raised which intends to match features of different modalities directly. In this research, there are two critical issues: how to get rid of the heterogeneity between different modalities and how to match the cross-modal features of different dimensions. Recently metric learning methods show a good capability in learning a distance metric to explore the relationship between data points. However, the traditional metric learning algorithms only focus on single-modal features, which suffer difficulties in addressing the cross-modal features of different dimensions. In this paper, we propose a cross-modal similarity learning algorithm for the cross-modal feature matching. The proposed method takes a bilinear formulation, and with the nuclear-norm penalization, it achieves low-rank representation. Accordingly, the accelerated proximal gradient algorithm is successfully imported to find the optimal solution with a fast convergence rate O(1/t^2). Experiments on three well known image-text cross-media retrieval databases show that the proposed method achieves the best performance compared to the state-of-the-art algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge