Jiabin Zhang
Highly Efficient No-reference 4K Video Quality Assessment with Full-Pixel Covering Sampling and Training Strategy
Jul 30, 2024



Abstract:Deep Video Quality Assessment (VQA) methods have shown impressive high-performance capabilities. Notably, no-reference (NR) VQA methods play a vital role in situations where obtaining reference videos is restricted or not feasible. Nevertheless, as more streaming videos are being created in ultra-high definition (e.g., 4K) to enrich viewers' experiences, the current deep VQA methods face unacceptable computational costs. Furthermore, the resizing, cropping, and local sampling techniques employed in these methods can compromise the details and content of original 4K videos, thereby negatively impacting quality assessment. In this paper, we propose a highly efficient and novel NR 4K VQA technology. Specifically, first, a novel data sampling and training strategy is proposed to tackle the problem of excessive resolution. This strategy allows the VQA Swin Transformer-based model to effectively train and make inferences using the full data of 4K videos on standard consumer-grade GPUs without compromising content or details. Second, a weighting and scoring scheme is developed to mimic the human subjective perception mode, which is achieved by considering the distinct impact of each sub-region within a 4K frame on the overall perception. Third, we incorporate the frequency domain information of video frames to better capture the details that affect video quality, consequently further improving the model's generalizability. To our knowledge, this is the first technology for the NR 4K VQA task. Thorough empirical studies demonstrate it not only significantly outperforms existing methods on a specialized 4K VQA dataset but also achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple open-source NR video quality datasets.
DSLA: Dynamic smooth label assignment for efficient anchor-free object detection
Aug 01, 2022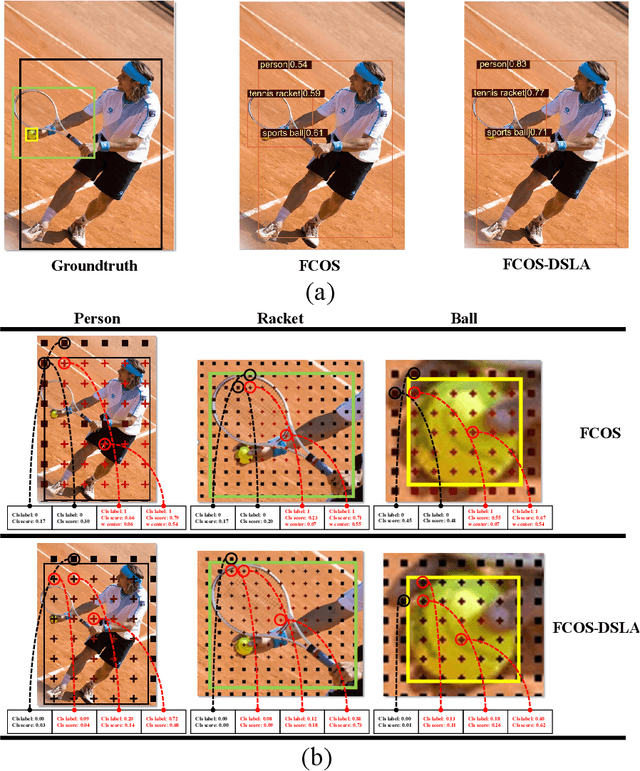
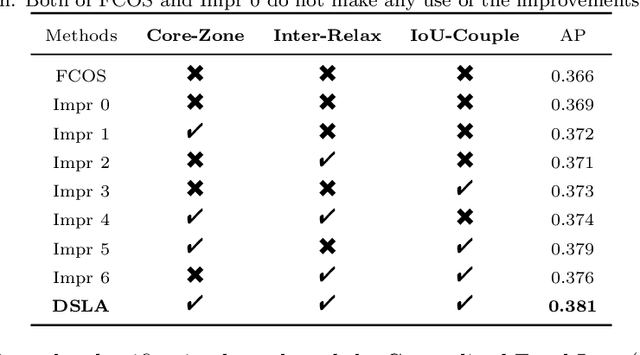
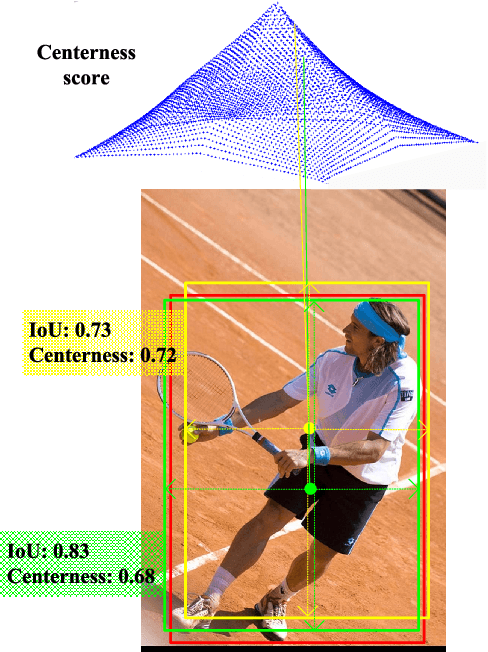

Abstract:Anchor-free detectors basically formulate object detection as dense classification and regression. For popular anchor-free detectors, it is common to introduce an individual prediction branch to estimate the quality of localization. The following inconsistencies are observed when we delve into the practices of classification and quality estimation. Firstly, for some adjacent samples which are assigned completely different labels, the trained model would produce similar classification scores. This violates the training objective and leads to performance degradation. Secondly, it is found that detected bounding boxes with higher confidences contrarily have smaller overlaps with the corresponding ground-truth. Accurately localized bounding boxes would be suppressed by less accurate ones in the Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) procedure. To address the inconsistency problems, the Dynamic Smooth Label Assignment (DSLA) method is proposed. Based on the concept of centerness originally developed in FCOS, a smooth assignment strategy is proposed. The label is smoothed to a continuous value in [0, 1] to make a steady transition between positive and negative samples. Intersection-of-Union (IoU) is predicted dynamically during training and is coupled with the smoothed label. The dynamic smooth label is assigned to supervise the classification branch. Under such supervision, quality estimation branch is naturally merged into the classification branch, which simplifies the architecture of anchor-free detector. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on the MS COCO benchmark. It is demonstrated that, DSLA can significantly boost the detection accuracy by alleviating the above inconsistencies for anchor-free detectors. Our codes are released at https://github.com/YonghaoHe/DSLA.
SIMPLE: SIngle-network with Mimicking and Point Learning for Bottom-up Human Pose Estimation
Apr 07, 2021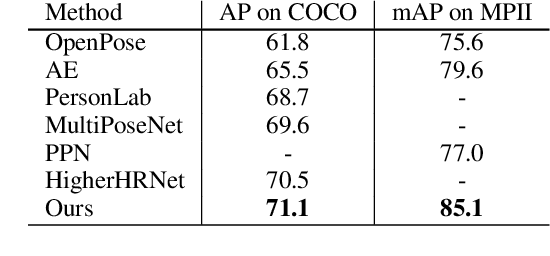
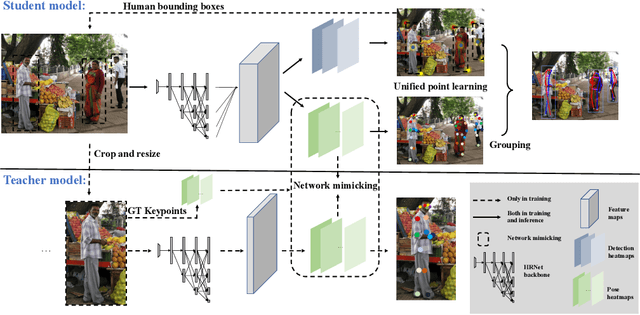
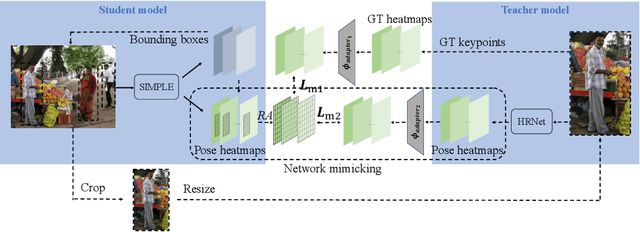
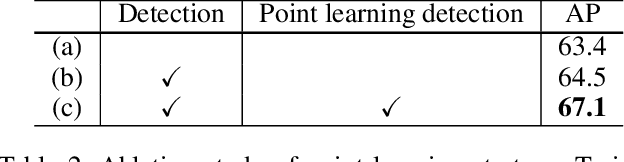
Abstract:The practical application requests both accuracy and efficiency on multi-person pose estimation algorithms. But the high accuracy and fast inference speed are dominated by top-down methods and bottom-up methods respectively. To make a better trade-off between accuracy and efficiency, we propose a novel multi-person pose estimation framework, SIngle-network with Mimicking and Point Learning for Bottom-up Human Pose Estimation (SIMPLE). Specifically, in the training process, we enable SIMPLE to mimic the pose knowledge from the high-performance top-down pipeline, which significantly promotes SIMPLE's accuracy while maintaining its high efficiency during inference. Besides, SIMPLE formulates human detection and pose estimation as a unified point learning framework to complement each other in single-network. This is quite different from previous works where the two tasks may interfere with each other. To the best of our knowledge, both mimicking strategy between different method types and unified point learning are firstly proposed in pose estimation. In experiments, our approach achieves the new state-of-the-art performance among bottom-up methods on the COCO, MPII and PoseTrack datasets. Compared with the top-down approaches, SIMPLE has comparable accuracy and faster inference speed.
FastPose: Towards Real-time Pose Estimation and Tracking via Scale-normalized Multi-task Networks
Aug 15, 2019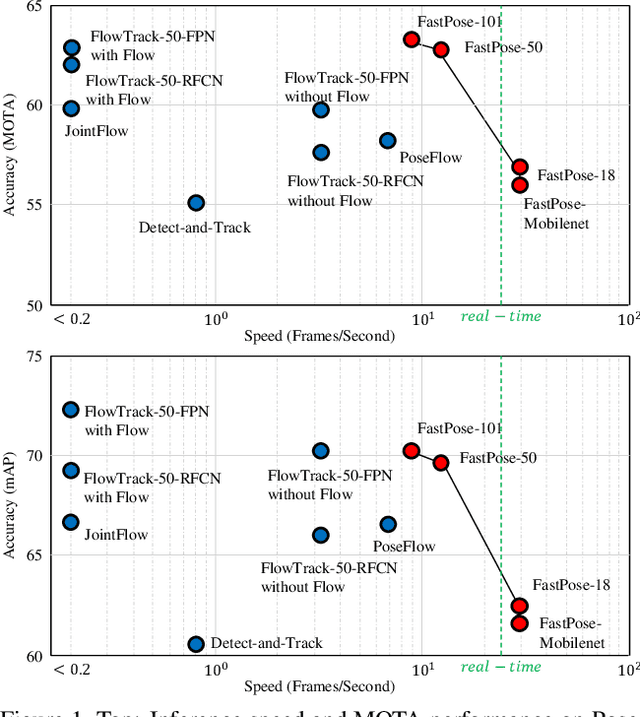
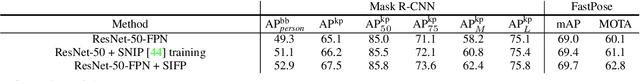
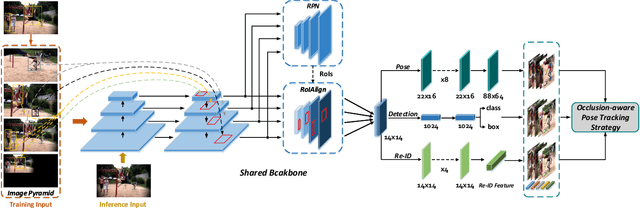
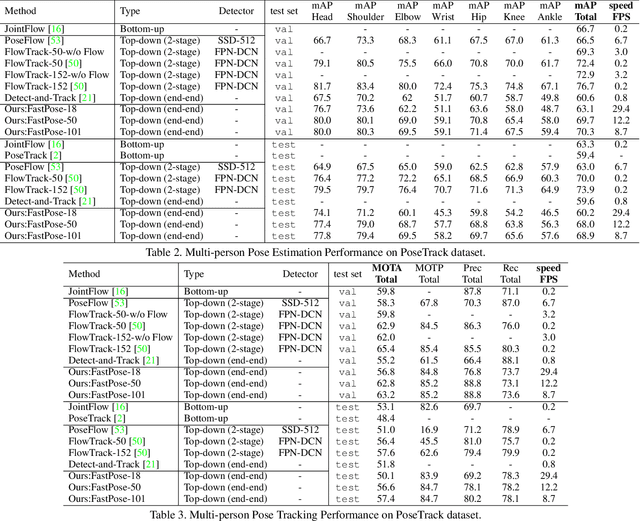
Abstract:Both accuracy and efficiency are significant for pose estimation and tracking in videos. State-of-the-art performance is dominated by two-stages top-down methods. Despite the leading results, these methods are impractical for real-world applications due to their separated architectures and complicated calculation. This paper addresses the task of articulated multi-person pose estimation and tracking towards real-time speed. An end-to-end multi-task network (MTN) is designed to perform human detection, pose estimation, and person re-identification (Re-ID) tasks simultaneously. To alleviate the performance bottleneck caused by scale variation problem, a paradigm which exploits scale-normalized image and feature pyramids (SIFP) is proposed to boost both performance and speed. Given the results of MTN, we adopt an occlusion-aware Re-ID feature strategy in the pose tracking module, where pose information is utilized to infer the occlusion state to make better use of Re-ID feature. In experiments, we demonstrate that the pose estimation and tracking performance improves steadily utilizing SIFP through different backbones. Using ResNet-18 and ResNet-50 as backbones, the overall pose tracking framework achieves competitive performance with 29.4 FPS and 12.2 FPS, respectively. Additionally, occlusion-aware Re-ID feature decreases the identification switches by 37% in the pose tracking process.
State-aware Re-identification Feature for Multi-target Multi-camera Tracking
Jun 04, 2019
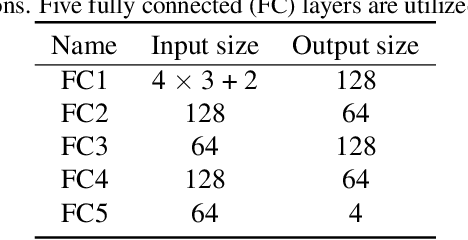
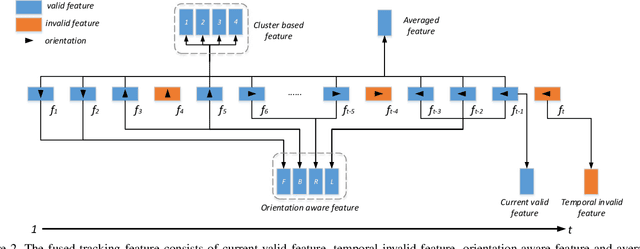
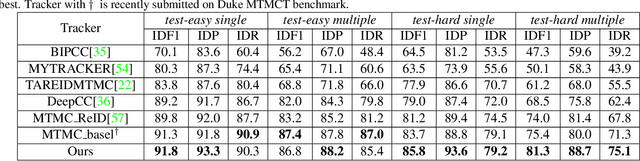
Abstract:Multi-target Multi-camera Tracking (MTMCT) aims to extract the trajectories from videos captured by a set of cameras. Recently, the tracking performance of MTMCT is significantly enhanced with the employment of re-identification (Re-ID) model. However, the appearance feature usually becomes unreliable due to the occlusion and orientation variance of the targets. Directly applying Re-ID model in MTMCT will encounter the problem of identity switches (IDS) and tracklet fragment caused by occlusion. To solve these problems, we propose a novel tracking framework in this paper. In this framework, the occlusion status and orientation information are utilized in Re-ID model with human pose information considered. In addition, the tracklet association using the proposed fused tracking feature is adopted to handle the fragment problem. The proposed tracker achieves 81.3\% IDF1 on the multiple-camera hard sequence, which outperforms all other reference methods by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge