Yifan Zhan
Visionary: The World Model Carrier Built on WebGPU-Powered Gaussian Splatting Platform
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Neural rendering, particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has evolved rapidly and become a key component for building world models. However, existing viewer solutions remain fragmented, heavy, or constrained by legacy pipelines, resulting in high deployment friction and limited support for dynamic content and generative models. In this work, we present Visionary, an open, web-native platform for real-time various Gaussian Splatting and meshes rendering. Built on an efficient WebGPU renderer with per-frame ONNX inference, Visionary enables dynamic neural processing while maintaining a lightweight, "click-to-run" browser experience. It introduces a standardized Gaussian Generator contract, which not only supports standard 3DGS rendering but also allows plug-and-play algorithms to generate or update Gaussians each frame. Such inference also enables us to apply feedforward generative post-processing. The platform further offers a plug in three.js library with a concise TypeScript API for seamless integration into existing web applications. Experiments show that, under identical 3DGS assets, Visionary achieves superior rendering efficiency compared to current Web viewers due to GPU-based primitive sorting. It already supports multiple variants, including MLP-based 3DGS, 4DGS, neural avatars, and style transformation or enhancement networks. By unifying inference and rendering directly in the browser, Visionary significantly lowers the barrier to reproduction, comparison, and deployment of 3DGS-family methods, serving as a unified World Model Carrier for both reconstructive and generative paradigms.
AniCrafter: Customizing Realistic Human-Centric Animation via Avatar-Background Conditioning in Video Diffusion Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in video diffusion models have significantly improved character animation techniques. However, current approaches rely on basic structural conditions such as DWPose or SMPL-X to animate character images, limiting their effectiveness in open-domain scenarios with dynamic backgrounds or challenging human poses. In this paper, we introduce $\textbf{AniCrafter}$, a diffusion-based human-centric animation model that can seamlessly integrate and animate a given character into open-domain dynamic backgrounds while following given human motion sequences. Built on cutting-edge Image-to-Video (I2V) diffusion architectures, our model incorporates an innovative "avatar-background" conditioning mechanism that reframes open-domain human-centric animation as a restoration task, enabling more stable and versatile animation outputs. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our method. Codes will be available at https://github.com/MyNiuuu/AniCrafter.
Tree-NeRV: A Tree-Structured Neural Representation for Efficient Non-Uniform Video Encoding
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations for Videos (NeRV) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for video representation, enabling direct mappings from frame indices to video frames. However, existing NeRV-based methods do not fully exploit temporal redundancy, as they rely on uniform sampling along the temporal axis, leading to suboptimal rate-distortion (RD) performance. To address this limitation, we propose Tree-NeRV, a novel tree-structured feature representation for efficient and adaptive video encoding. Unlike conventional approaches, Tree-NeRV organizes feature representations within a Binary Search Tree (BST), enabling non-uniform sampling along the temporal axis. Additionally, we introduce an optimization-driven sampling strategy, dynamically allocating higher sampling density to regions with greater temporal variation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Tree-NeRV achieves superior compression efficiency and reconstruction quality, outperforming prior uniform sampling-based methods. Code will be released.
All-in-One Transferring Image Compression from Human Perception to Multi-Machine Perception
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Efficiently transferring Learned Image Compression (LIC) model from human perception to machine perception is an emerging challenge in vision-centric representation learning. Existing approaches typically adapt LIC to downstream tasks in a single-task manner, which is inefficient, lacks task interaction, and results in multiple task-specific bitstreams. To address these limitations, we propose an asymmetric adaptor framework that supports multi-task adaptation within a single model. Our method introduces a shared adaptor to learn general semantic features and task-specific adaptors to preserve task-level distinctions. With only lightweight plug-in modules and a frozen base codec, our method achieves strong performance across multiple tasks while maintaining compression efficiency. Experiments on the PASCAL-Context benchmark demonstrate that our method outperforms both Fully Fine-Tuned and other Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuned (PEFT) baselines, and validating the effectiveness of multi-vision transferring.
R3-Avatar: Record and Retrieve Temporal Codebook for Reconstructing Photorealistic Human Avatars
Mar 17, 2025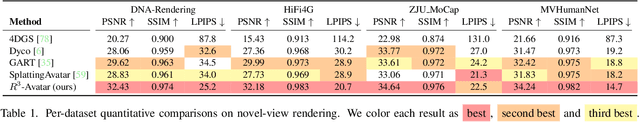
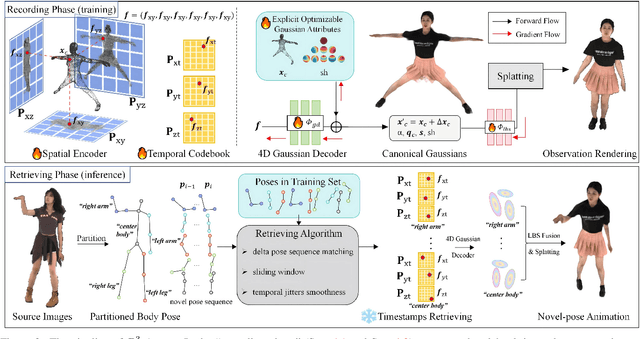
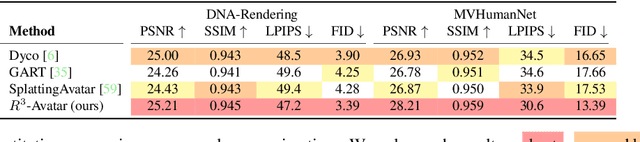

Abstract:We present R3-Avatar, incorporating a temporal codebook, to overcome the inability of human avatars to be both animatable and of high-fidelity rendering quality. Existing video-based reconstruction of 3D human avatars either focuses solely on rendering, lacking animation support, or learns a pose-appearance mapping for animating, which degrades under limited training poses or complex clothing. In this paper, we adopt a "record-retrieve-reconstruct" strategy that ensures high-quality rendering from novel views while mitigating degradation in novel poses. Specifically, disambiguating timestamps record temporal appearance variations in a codebook, ensuring high-fidelity novel-view rendering, while novel poses retrieve corresponding timestamps by matching the most similar training poses for augmented appearance. Our R3-Avatar outperforms cutting-edge video-based human avatar reconstruction, particularly in overcoming visual quality degradation in extreme scenarios with limited training human poses and complex clothing.
Robustifying Fourier Features Embeddings for Implicit Neural Representations
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) employ neural networks to represent continuous functions by mapping coordinates to the corresponding values of the target function, with applications e.g., inverse graphics. However, INRs face a challenge known as spectral bias when dealing with scenes containing varying frequencies. To overcome spectral bias, the most common approach is the Fourier features-based methods such as positional encoding. However, Fourier features-based methods will introduce noise to output, which degrades their performances when applied to downstream tasks. In response, this paper initially hypothesizes that combining multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) with Fourier feature embeddings mutually enhances their strengths, yet simultaneously introduces limitations inherent in Fourier feature embeddings. By presenting a simple theorem, we validate our hypothesis, which serves as a foundation for the design of our solution. Leveraging these insights, we propose the use of multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) without additive
MaskGaussian: Adaptive 3D Gaussian Representation from Probabilistic Masks
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated remarkable performance in novel view synthesis and real-time rendering, the high memory consumption due to the use of millions of Gaussians limits its practicality. To mitigate this issue, improvements have been made by pruning unnecessary Gaussians, either through a hand-crafted criterion or by using learned masks. However, these methods deterministically remove Gaussians based on a snapshot of the pruning moment, leading to sub-optimized reconstruction performance from a long-term perspective. To address this issue, we introduce MaskGaussian, which models Gaussians as probabilistic entities rather than permanently removing them, and utilize them according to their probability of existence. To achieve this, we propose a masked-rasterization technique that enables unused yet probabilistically existing Gaussians to receive gradients, allowing for dynamic assessment of their contribution to the evolving scene and adjustment of their probability of existence. Hence, the importance of Gaussians iteratively changes and the pruned Gaussians are selected diversely. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in achieving better rendering quality with fewer Gaussians than previous pruning methods, pruning over 60% of Gaussians on average with only a 0.02 PSNR decline. Our code can be found at: https://github.com/kaikai23/MaskGaussian
Physics-Based Adversarial Attack on Near-Infrared Human Detector for Nighttime Surveillance Camera Systems
Dec 18, 2024
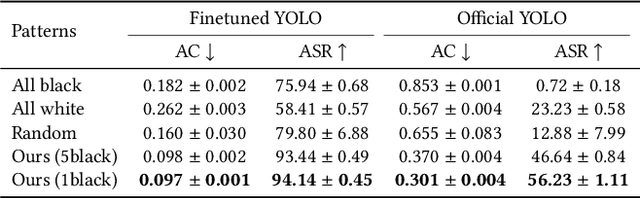


Abstract:Many surveillance cameras switch between daytime and nighttime modes based on illuminance levels. During the day, the camera records ordinary RGB images through an enabled IR-cut filter. At night, the filter is disabled to capture near-infrared (NIR) light emitted from NIR LEDs typically mounted around the lens. While RGB-based AI algorithm vulnerabilities have been widely reported, the vulnerabilities of NIR-based AI have rarely been investigated. In this paper, we identify fundamental vulnerabilities in NIR-based image understanding caused by color and texture loss due to the intrinsic characteristics of clothes' reflectance and cameras' spectral sensitivity in the NIR range. We further show that the nearly co-located configuration of illuminants and cameras in existing surveillance systems facilitates concealing and fully passive attacks in the physical world. Specifically, we demonstrate how retro-reflective and insulation plastic tapes can manipulate the intensity distribution of NIR images. We showcase an attack on the YOLO-based human detector using binary patterns designed in the digital space (via black-box query and searching) and then physically realized using tapes pasted onto clothes. Our attack highlights significant reliability concerns for nighttime surveillance systems, which are intended to enhance security. Codes Available: https://github.com/MyNiuuu/AdvNIR
SUICA: Learning Super-high Dimensional Sparse Implicit Neural Representations for Spatial Transcriptomics
Dec 02, 2024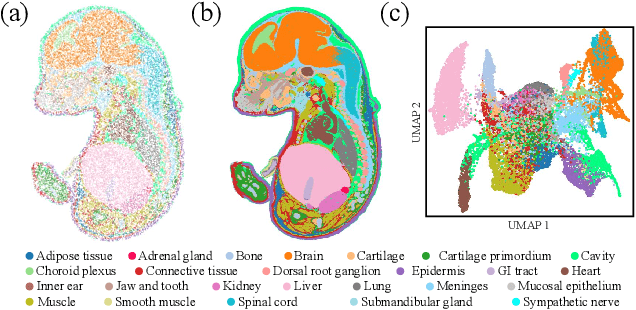
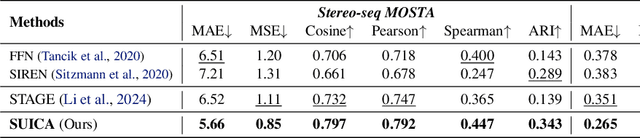
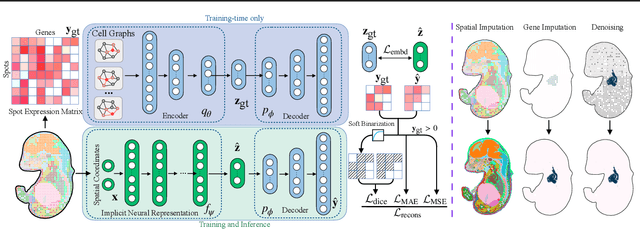
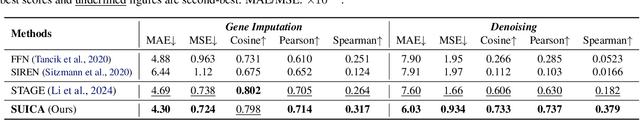
Abstract:Spatial Transcriptomics (ST) is a method that captures spatial gene expression profiles within histological sections. The discrete spatial distribution and the super-high dimensional sequencing results make ST data challenging to be modeled effectively. In this paper, we manage to model ST in a continuous and compact manner by the proposed tool, SUICA, empowered by the great approximation capability of Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) that can improve both the spatial resolution and the gene expression. Concretely within the proposed SUICA, we incorporate a graph-augmented Autoencoder to effectively model the context information of the unstructured spots and provide informative embeddings that are structure-aware for spatial mapping. We also tackle the extremely skewed distribution in a regression-by-classification fashion and enforce classification-based loss functions for the optimization of SUICA. By extensive experiments of a wide range of common ST platforms, SUICA outperforms both conventional INR variants and SOTA methods for ST super-resolution regarding numerical fidelity, statistical correlation, and bio-conservation. The prediction by SUICA also showcases amplified gene signatures that enriches the bio-conservation of the raw data and benefits subsequent analysis. The code is available at https://github.com/Szym29/SUICA.
GAST: Sequential Gaussian Avatars with Hierarchical Spatio-temporal Context
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:3D human avatars, through the use of canonical radiance fields and per-frame observed warping, enable high-fidelity rendering and animating. However, existing methods, which rely on either spatial SMPL(-X) poses or temporal embeddings, respectively suffer from coarse rendering quality or limited animation flexibility. To address these challenges, we propose GAST, a framework that unifies 3D human modeling with 3DGS by hierarchically integrating both spatial and temporal information. Specifically, we design a sequential conditioning framework for the non-rigid warping of the human body, under whose guidance more accurate 3D Gaussians can be obtained in the observation space. Moreover, the explicit properties of Gaussians allow us to embed richer sequential information, encompassing both the coarse sequence of human poses and finer per-vertex motion details. These sequence conditions are further sampled across different temporal scales, in a coarse-to-fine manner, ensuring unbiased inputs for non-rigid warping. Experimental results demonstrate that our method combined with hierarchical spatio-temporal modeling surpasses concurrent baselines, delivering both high-quality rendering and flexible animating capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge