Yangang Ren
Smoothing Policy Iteration for Zero-sum Markov Games
Dec 03, 2022



Abstract:Zero-sum Markov Games (MGs) has been an efficient framework for multi-agent systems and robust control, wherein a minimax problem is constructed to solve the equilibrium policies. At present, this formulation is well studied under tabular settings wherein the maximum operator is primarily and exactly solved to calculate the worst-case value function. However, it is non-trivial to extend such methods to handle complex tasks, as finding the maximum over large-scale action spaces is usually cumbersome. In this paper, we propose the smoothing policy iteration (SPI) algorithm to solve the zero-sum MGs approximately, where the maximum operator is replaced by the weighted LogSumExp (WLSE) function to obtain the nearly optimal equilibrium policies. Specially, the adversarial policy is served as the weight function to enable an efficient sampling over action spaces.We also prove the convergence of SPI and analyze its approximation error in $\infty -$norm based on the contraction mapping theorem. Besides, we propose a model-based algorithm called Smooth adversarial Actor-critic (SaAC) by extending SPI with the function approximations. The target value related to WLSE function is evaluated by the sampled trajectories and then mean square error is constructed to optimize the value function, and the gradient-ascent-descent methods are adopted to optimize the protagonist and adversarial policies jointly. In addition, we incorporate the reparameterization technique in model-based gradient back-propagation to prevent the gradient vanishing due to sampling from the stochastic policies. We verify our algorithm in both tabular and function approximation settings. Results show that SPI can approximate the worst-case value function with a high accuracy and SaAC can stabilize the training process and improve the adversarial robustness in a large margin.
Integrated Decision and Control for High-Level Automated Vehicles by Mixed Policy Gradient and Its Experiment Verification
Oct 19, 2022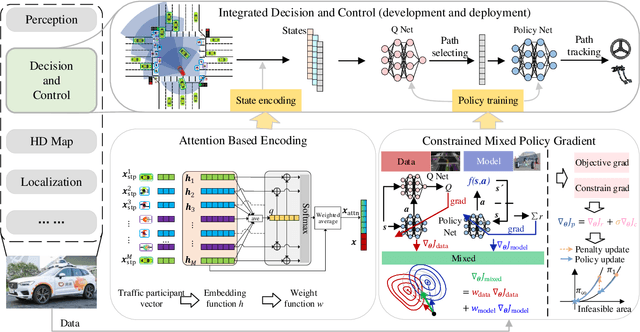
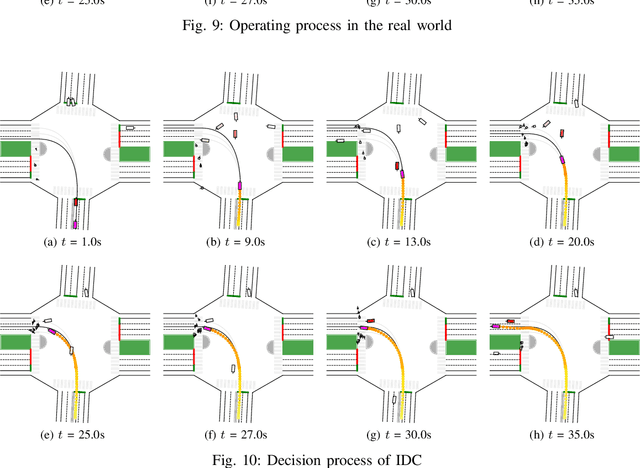
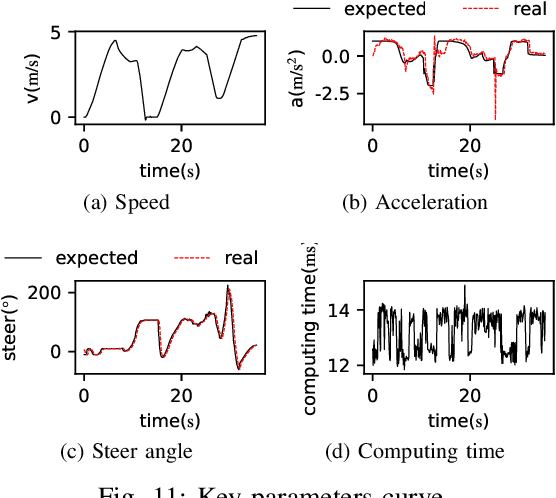
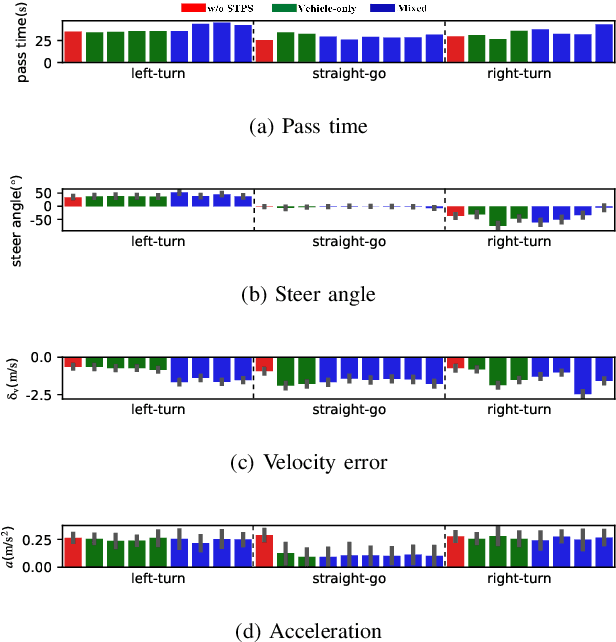
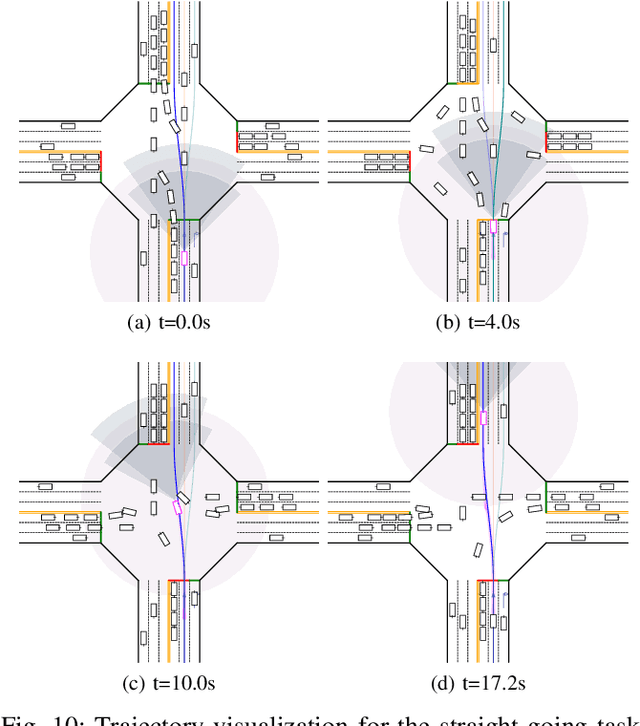
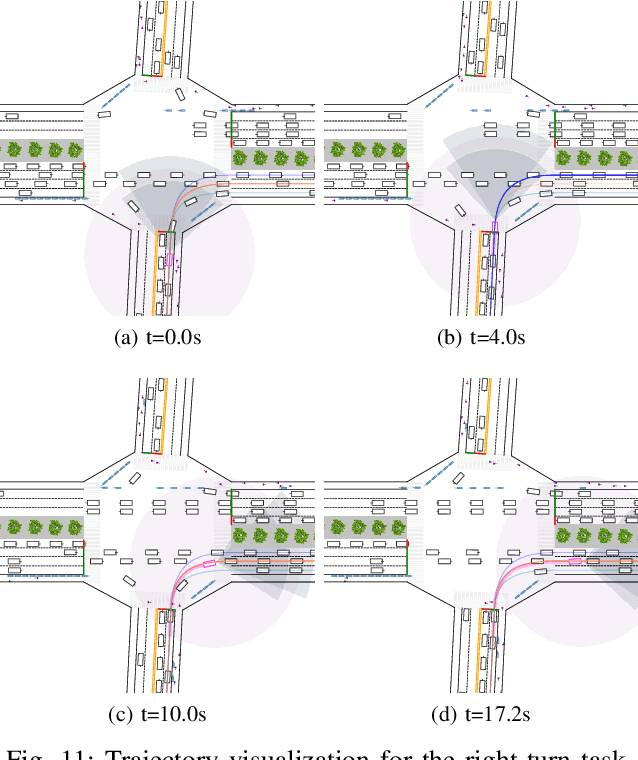
Abstract:Self-evolution is indispensable to realize full autonomous driving. This paper presents a self-evolving decision-making system based on the Integrated Decision and Control (IDC), an advanced framework built on reinforcement learning (RL). First, an RL algorithm called constrained mixed policy gradient (CMPG) is proposed to consistently upgrade the driving policy of the IDC. It adapts the MPG under the penalty method so that it can solve constrained optimization problems using both the data and model. Second, an attention-based encoding (ABE) method is designed to tackle the state representation issue. It introduces an embedding network for feature extraction and a weighting network for feature fusion, fulfilling order-insensitive encoding and importance distinguishing of road users. Finally, by fusing CMPG and ABE, we develop the first data-driven decision and control system under the IDC architecture, and deploy the system on a fully-functional self-driving vehicle running in daily operation. Experiment results show that boosting by data, the system can achieve better driving ability over model-based methods. It also demonstrates safe, efficient and smart driving behavior in various complex scenes at a signalized intersection with real mixed traffic flow.
Enhance Sample Efficiency and Robustness of End-to-end Urban Autonomous Driving via Semantic Masked World Model
Oct 08, 2022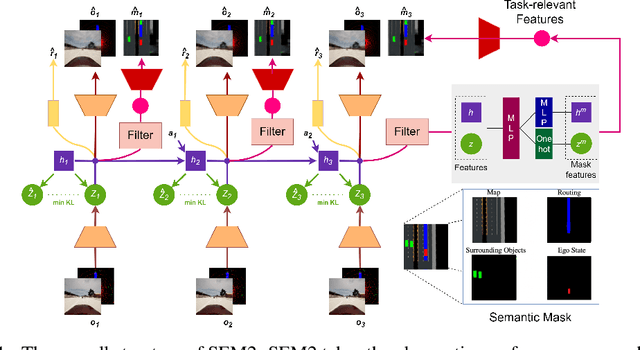
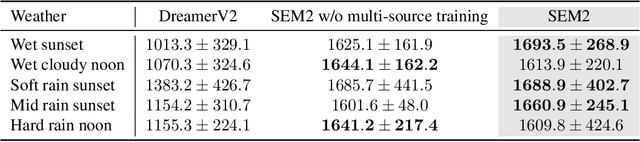
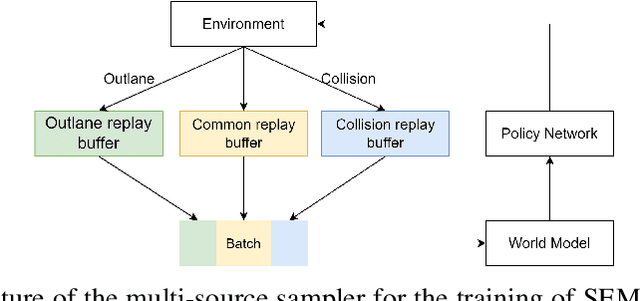
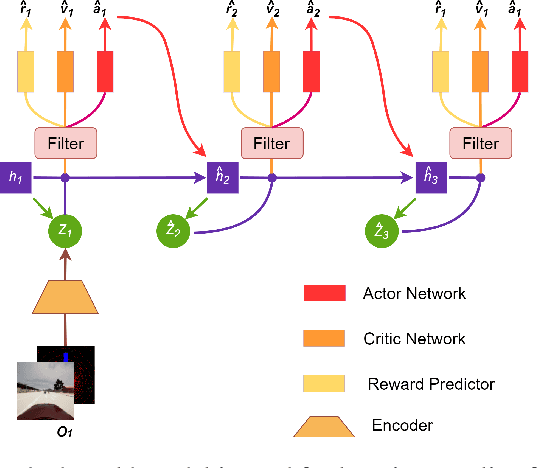
Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving provides a feasible way to automatically maximize overall driving system performance by directly mapping the raw pixels from a front-facing camera to control signals. Recent advanced methods construct a latent world model to map the high dimensional observations into compact latent space. However, the latent states embedded by the world model proposed in previous works may contain a large amount of task-irrelevant information, resulting in low sampling efficiency and poor robustness to input perturbations. Meanwhile, the training data distribution is usually unbalanced, and the learned policy is hard to cope with the corner cases during the driving process. To solve the above challenges, we present a semantic masked recurrent world model (SEM2), which introduces a latent filter to extract key task-relevant features and reconstruct a semantic mask via the filtered features, and is trained with a multi-source data sampler, which aggregates common data and multiple corner case data in a single batch, to balance the data distribution. Extensive experiments on CARLA show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in terms of sample efficiency and robustness to input permutations.
Improve Generalization of Driving Policy at Signalized Intersections with Adversarial Learning
Apr 09, 2022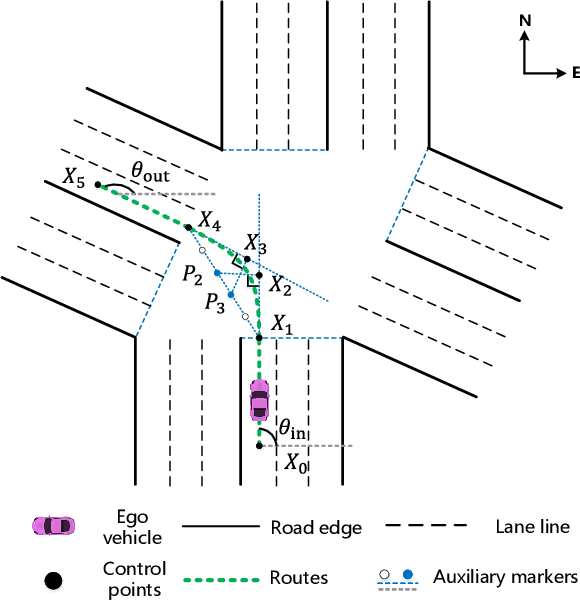
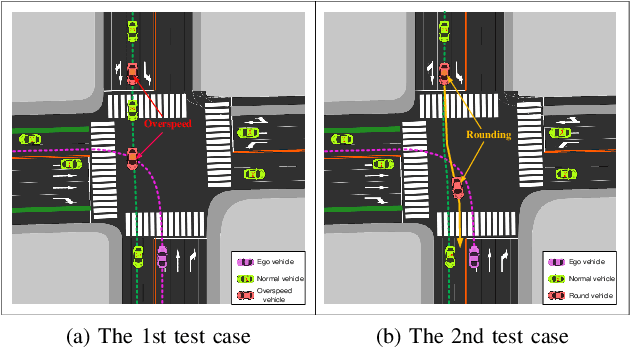
Abstract:Intersections are quite challenging among various driving scenes wherein the interaction of signal lights and distinct traffic actors poses great difficulty to learn a wise and robust driving policy. Current research rarely considers the diversity of intersections and stochastic behaviors of traffic participants. For practical applications, the randomness usually leads to some devastating events, which should be the focus of autonomous driving. This paper introduces an adversarial learning paradigm to boost the intelligence and robustness of driving policy for signalized intersections with dense traffic flow. Firstly, we design a static path planner which is capable of generating trackable candidate paths for multiple intersections with diversified topology. Next, a constrained optimal control problem (COCP) is built based on these candidate paths wherein the bounded uncertainty of dynamic models is considered to capture the randomness of driving environment. We propose adversarial policy gradient (APG) to solve the COCP wherein the adversarial policy is introduced to provide disturbances by seeking the most severe uncertainty while the driving policy learns to handle this situation by competition. Finally, a comprehensive system is established to conduct training and testing wherein the perception module is introduced and the human experience is incorporated to solve the yellow light dilemma. Experiments indicate that the trained policy can handle the signal lights flexibly meanwhile realizing the smooth and efficient passing with a humanoid paradigm. Besides, APG enables a large-margin improvement of the resistance to the abnormal behaviors and thus ensures a high safety level for the autonomous vehicle.
Self-learned Intelligence for Integrated Decision and Control of Automated Vehicles at Signalized Intersections
Nov 10, 2021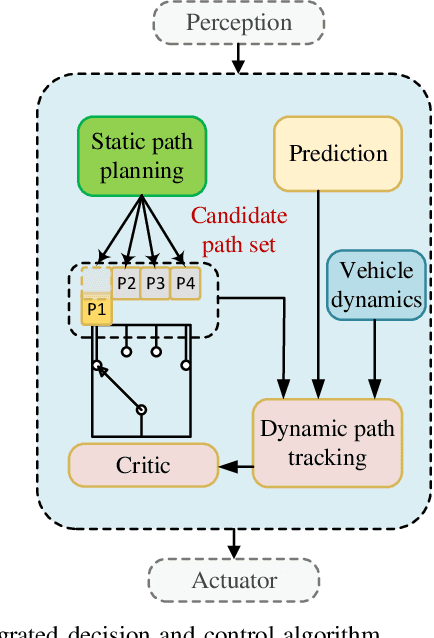
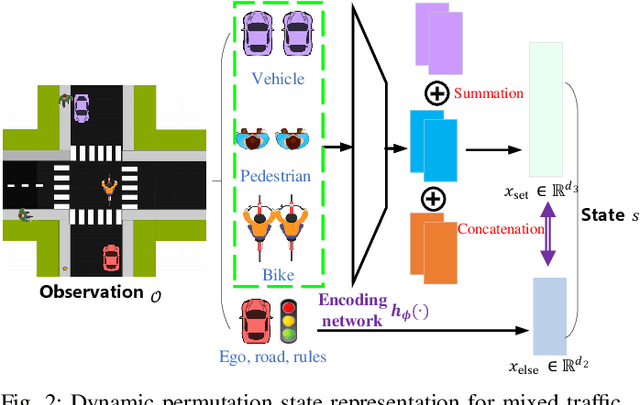
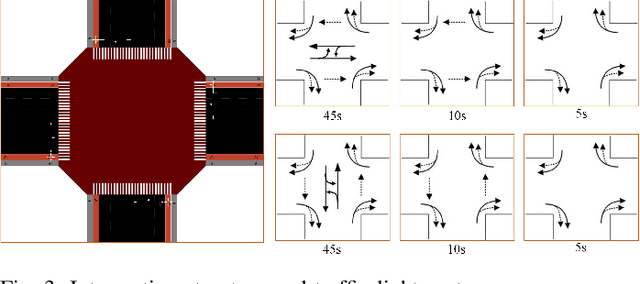
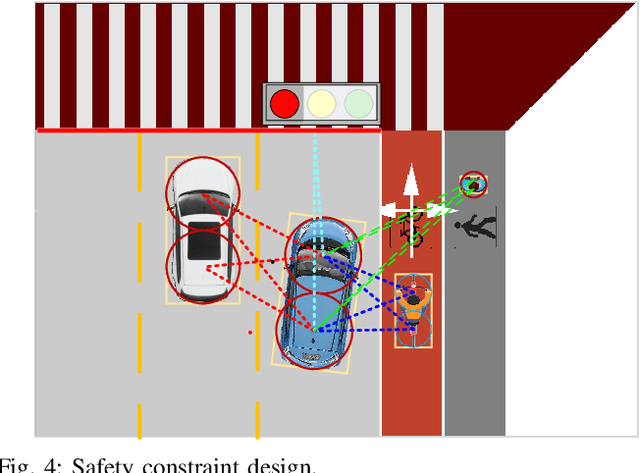
Abstract:Intersection is one of the most complex and accident-prone urban scenarios for autonomous driving wherein making safe and computationally efficient decisions is non-trivial. Current research mainly focuses on the simplified traffic conditions while ignoring the existence of mixed traffic flows, i.e., vehicles, cyclists and pedestrians. For urban roads, different participants leads to a quite dynamic and complex interaction, posing great difficulty to learn an intelligent policy. This paper develops the dynamic permutation state representation in the framework of integrated decision and control (IDC) to handle signalized intersections with mixed traffic flows. Specially, this representation introduces an encoding function and summation operator to construct driving states from environmental observation, capable of dealing with different types and variant number of traffic participants. A constrained optimal control problem is built wherein the objective involves tracking performance and the constraints for different participants and signal lights are designed respectively to assure safety. We solve this problem by offline optimizing encoding function, value function and policy function, wherein the reasonable state representation will be given by the encoding function and then served as the input of policy and value function. An off-policy training is designed to reuse observations from driving environment and backpropagation through time is utilized to update the policy function and encoding function jointly. Verification result shows that the dynamic permutation state representation can enhance the driving performance of IDC, including comfort, decision compliance and safety with a large margin. The trained driving policy can realize efficient and smooth passing in the complex intersection, guaranteeing driving intelligence and safety simultaneously.
Encoding Distributional Soft Actor-Critic for Autonomous Driving in Multi-lane Scenarios
Sep 12, 2021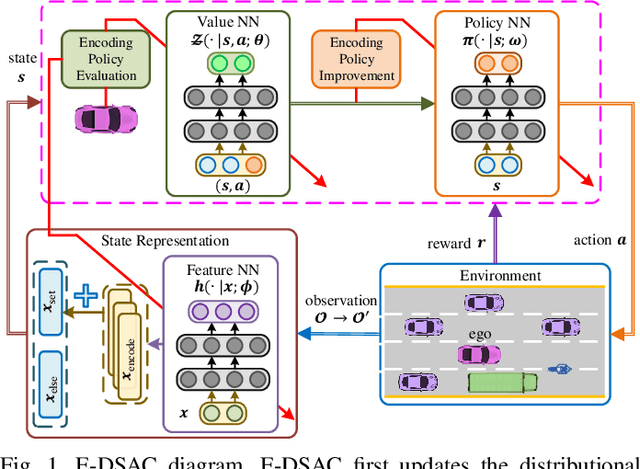
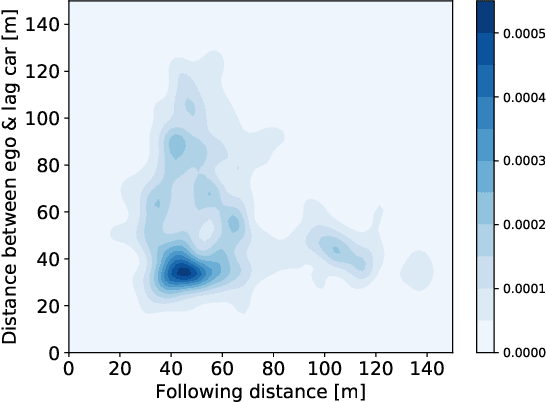
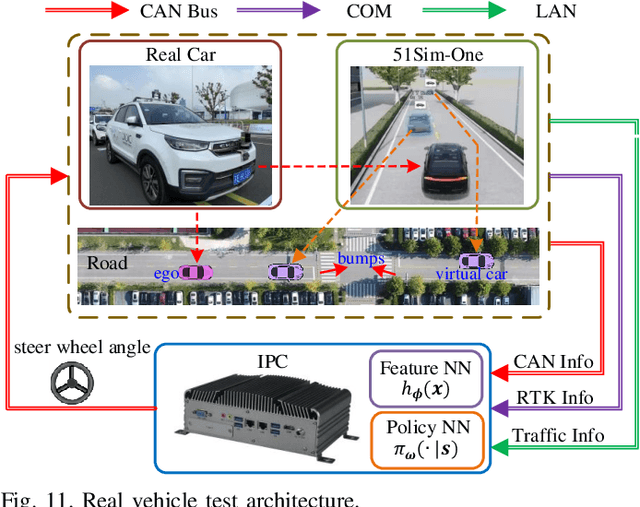
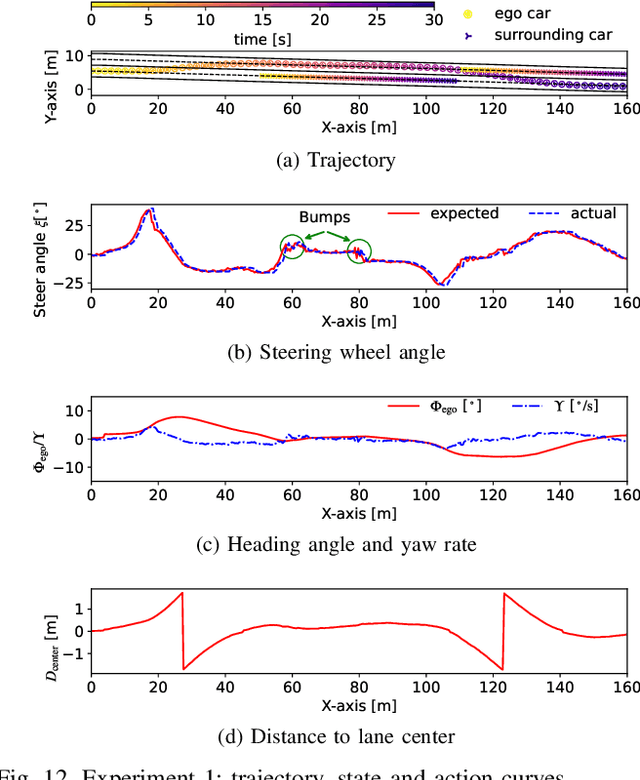
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm, called encoding distributional soft actor-critic (E-DSAC), for decision-making in autonomous driving. Unlike existing RL-based decision-making methods, E-DSAC is suitable for situations where the number of surrounding vehicles is variable and eliminates the requirement for manually pre-designed sorting rules, resulting in higher policy performance and generality. We first develop an encoding distributional policy iteration (DPI) framework by embedding a permutation invariant module, which employs a feature neural network (NN) to encode the indicators of each vehicle, in the distributional RL framework. The proposed DPI framework is proved to exhibit important properties in terms of convergence and global optimality. Next, based on the developed encoding DPI framework, we propose the E-DSAC algorithm by adding the gradient-based update rule of the feature NN to the policy evaluation process of the DSAC algorithm. Then, the multi-lane driving task and the corresponding reward function are designed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Results show that the policy learned by E-DSAC can realize efficient, smooth, and relatively safe autonomous driving in the designed scenario. And the final policy performance learned by E-DSAC is about three times that of DSAC. Furthermore, its effectiveness has also been verified in real vehicle experiments.
Integrated Decision and Control at Multi-Lane Intersections with Mixed Traffic Flow
Aug 30, 2021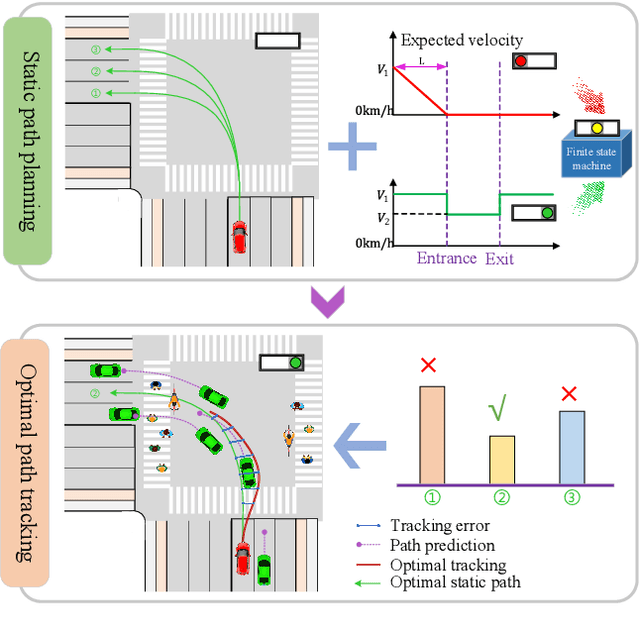
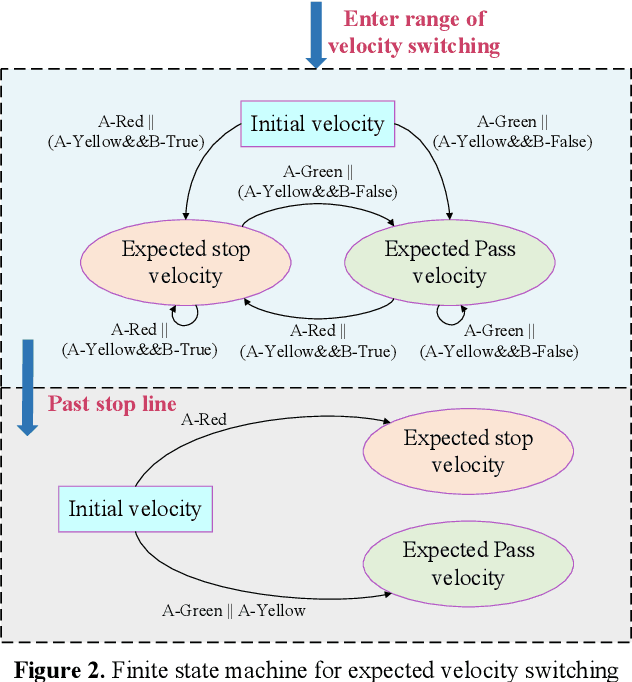
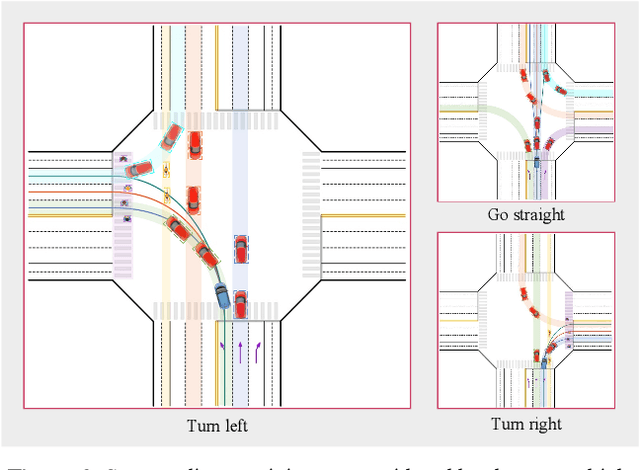
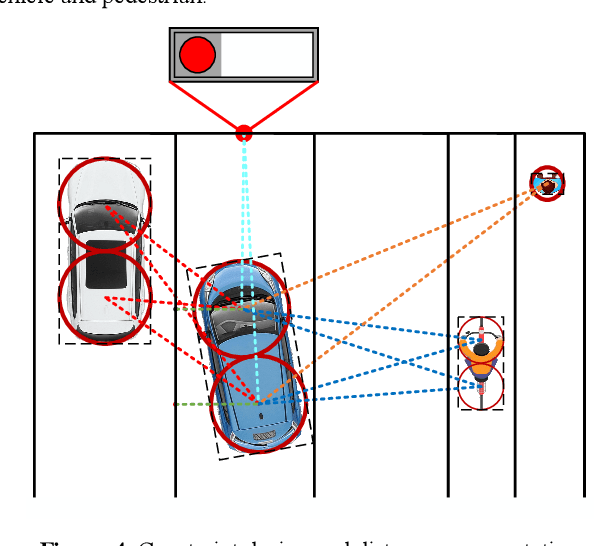
Abstract:Autonomous driving at intersections is one of the most complicated and accident-prone traffic scenarios, especially with mixed traffic participants such as vehicles, bicycles and pedestrians. The driving policy should make safe decisions to handle the dynamic traffic conditions and meet the requirements of on-board computation. However, most of the current researches focuses on simplified intersections considering only the surrounding vehicles and idealized traffic lights. This paper improves the integrated decision and control framework and develops a learning-based algorithm to deal with complex intersections with mixed traffic flows, which can not only take account of realistic characteristics of traffic lights, but also learn a safe policy under different safety constraints. We first consider different velocity models for green and red lights in the training process and use a finite state machine to handle different modes of light transformation. Then we design different types of distance constraints for vehicles, traffic lights, pedestrians, bicycles respectively and formulize the constrained optimal control problems (OCPs) to be optimized. Finally, reinforcement learning (RL) with value and policy networks is adopted to solve the series of OCPs. In order to verify the safety and efficiency of the proposed method, we design a multi-lane intersection with the existence of large-scale mixed traffic participants and set practical traffic light phases. The simulation results indicate that the trained decision and control policy can well balance safety and tracking performance. Compared with model predictive control (MPC), the computational time is three orders of magnitude lower.
Fixed-Dimensional and Permutation Invariant State Representation of Autonomous Driving
May 24, 2021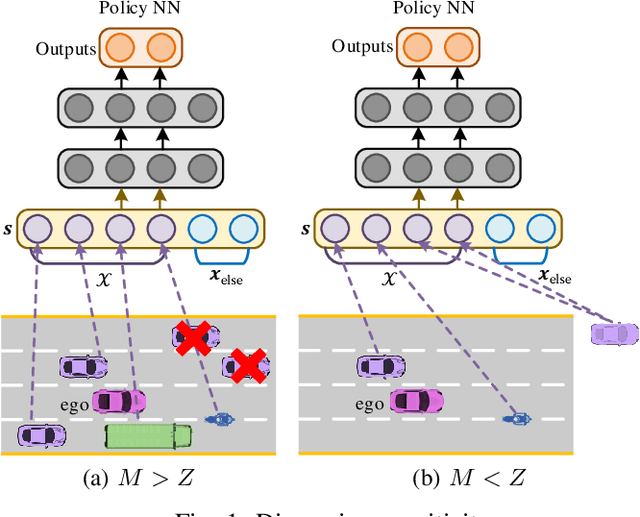
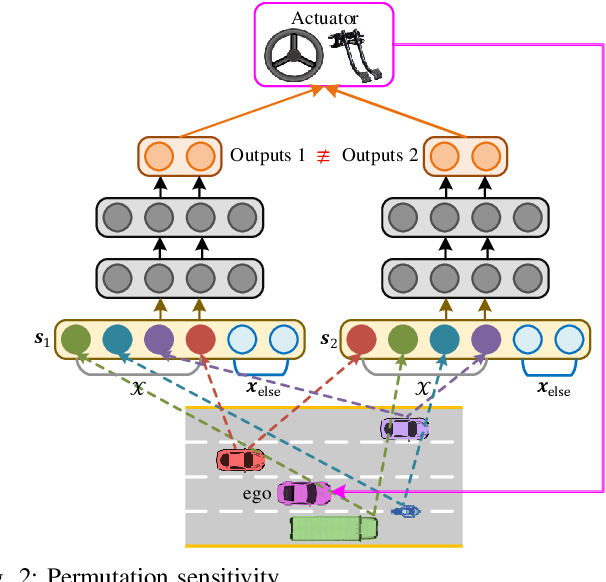
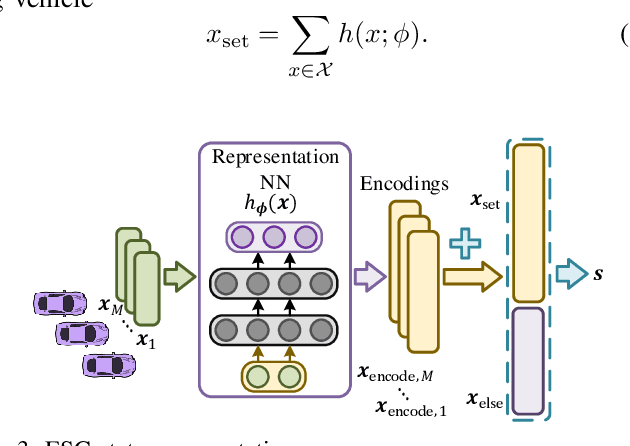
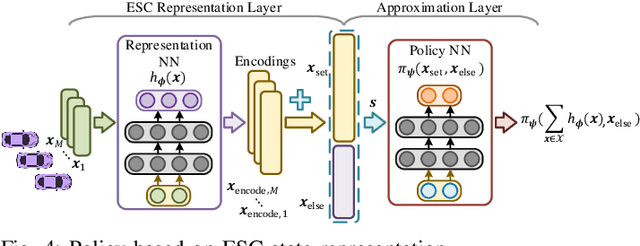
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new state representation method, called encoding sum and concatenation (ESC), for the state representation of decision-making in autonomous driving. Unlike existing state representation methods, ESC is applicable to a variable number of surrounding vehicles and eliminates the need for manually pre-designed sorting rules, leading to higher representation ability and generality. The proposed ESC method introduces a representation neural network (NN) to encode each surrounding vehicle into an encoding vector, and then adds these vectors to obtain the representation vector of the set of surrounding vehicles. By concatenating the set representation with other variables, such as indicators of the ego vehicle and road, we realize the fixed-dimensional and permutation invariant state representation. This paper has further proved that the proposed ESC method can realize the injective representation if the output dimension of the representation NN is greater than the number of variables of all surrounding vehicles. This means that by taking the ESC representation as policy inputs, we can find the nearly optimal representation NN and policy NN by simultaneously optimizing them using gradient-based updating. Experiments demonstrate that compared with the fixed-permutation representation method, the proposed method improves the representation ability of the surrounding vehicles, and the corresponding approximation error is reduced by 62.2%.
Integrated Decision and Control: Towards Interpretable and Efficient Driving Intelligence
Mar 18, 2021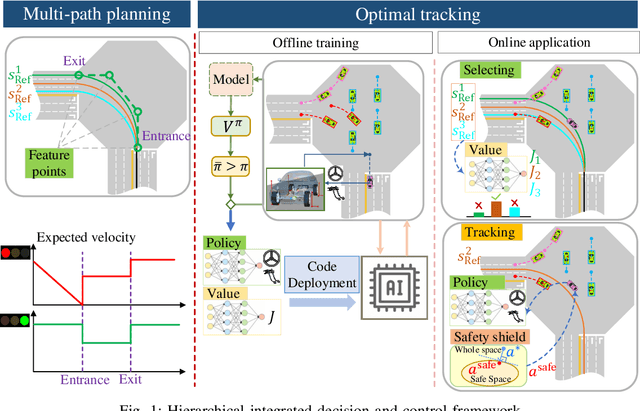
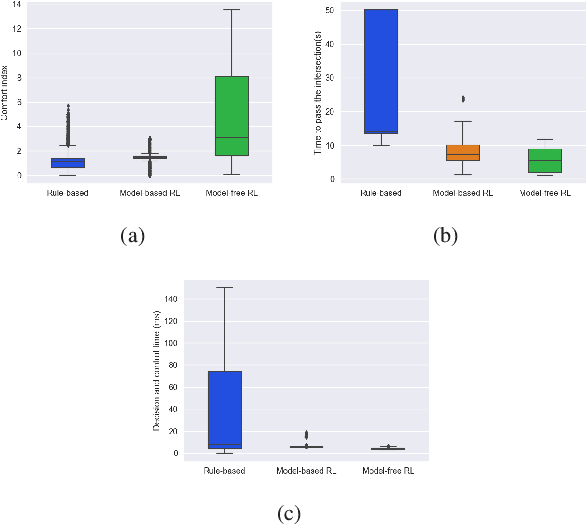
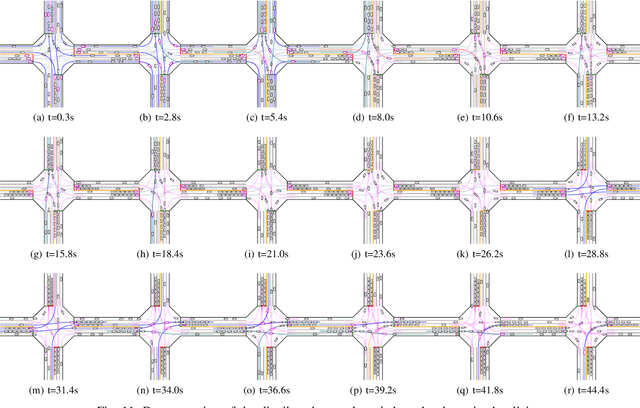
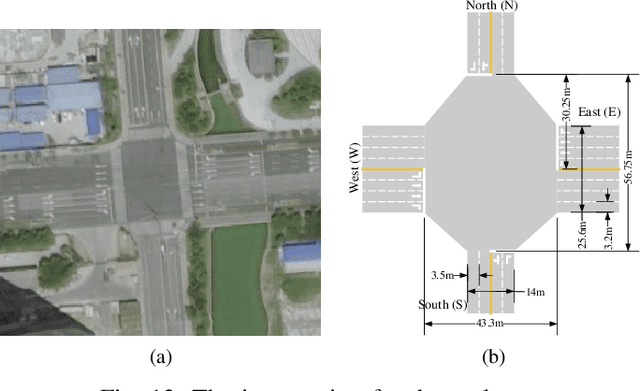
Abstract:Decision and control are two of the core functionalities of high-level automated vehicles. Current mainstream methods, such as functionality decomposition or end-to-end reinforcement learning (RL), either suffer high time complexity or poor interpretability and limited safety performance in real-world complex autonomous driving tasks. In this paper, we present an interpretable and efficient decision and control framework for automated vehicles, which decomposes the driving task into multi-path planning and optimal tracking that are structured hierarchically. First, the multi-path planning is to generate several paths only considering static constraints. Then, the optimal tracking is designed to track the optimal path while considering the dynamic obstacles. To that end, in theory, we formulate a constrained optimal control problem (OCP) for each candidate path, optimize them separately and choose the one with the best tracking performance to follow. More importantly, we propose a model-based reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm, which is served as an approximate constrained OCP solver, to unload the heavy computation by the paradigm of offline training and online application. Specifically, the OCPs for all paths are considered together to construct a multi-task RL problem and then solved offline by our algorithm into value and policy networks, for real-time online path selecting and tracking respectively. We verify our framework in both simulation and the real world. Results show that our method has better online computing efficiency and driving performance including traffic efficiency and safety compared with baseline methods. In addition, it yields great interpretability and adaptability among different driving tasks. The real road test also suggests that it is applicable in complicated traffic scenarios without even tuning.
Model-based Constrained Reinforcement Learning using Generalized Control Barrier Function
Mar 05, 2021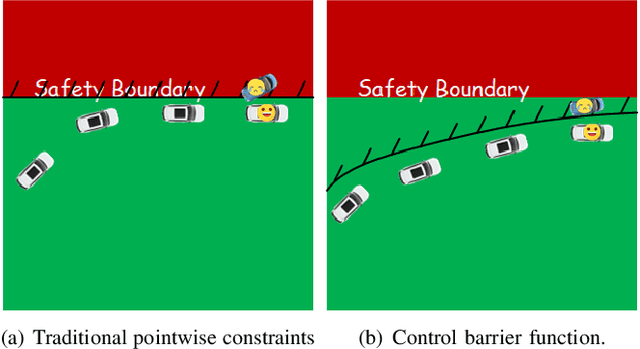
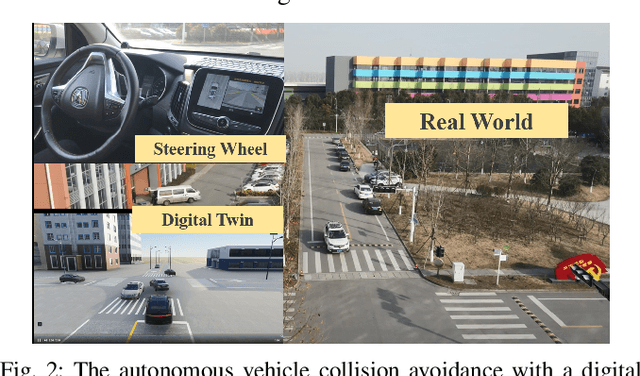
Abstract:Model information can be used to predict future trajectories, so it has huge potential to avoid dangerous region when implementing reinforcement learning (RL) on real-world tasks, like autonomous driving. However, existing studies mostly use model-free constrained RL, which causes inevitable constraint violations. This paper proposes a model-based feasibility enhancement technique of constrained RL, which enhances the feasibility of policy using generalized control barrier function (GCBF) defined on the distance to constraint boundary. By using the model information, the policy can be optimized safely without violating actual safety constraints, and the sample efficiency is increased. The major difficulty of infeasibility in solving the constrained policy gradient is handled by an adaptive coefficient mechanism. We evaluate the proposed method in both simulations and real vehicle experiments in a complex autonomous driving collision avoidance task. The proposed method achieves up to four times fewer constraint violations and converges 3.36 times faster than baseline constrained RL approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge