Xuan Guo
Beyond GEMM-Centric NPUs: Enabling Efficient Diffusion LLM Sampling
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) introduce iterative denoising to enable parallel token generation, but their sampling phase displays fundamentally different characteristics compared to GEMM-centric transformer layers. Profiling on modern GPUs reveals that sampling can account for up to 70% of total model inference latency-primarily due to substantial memory loads and writes from vocabulary-wide logits, reduction-based token selection, and iterative masked updates. These processes demand large on-chip SRAM and involve irregular memory accesses that conventional NPUs struggle to handle efficiently. To address this, we identify a set of critical instructions that an NPU architecture must specifically optimize for dLLM sampling. Our design employs lightweight non-GEMM vector primitives, in-place memory reuse strategies, and a decoupled mixed-precision memory hierarchy. Together, these optimizations deliver up to a 2.53x speedup over the NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPU under an equivalent nm technology node. We also open-source our cycle-accurate simulation and post-synthesis RTL verification code, confirming functional equivalence with current dLLM PyTorch implementations.
HGMP:Heterogeneous Graph Multi-Task Prompt Learning
Jul 10, 2025



Abstract:The pre-training and fine-tuning methods have gained widespread attention in the field of heterogeneous graph neural networks due to their ability to leverage large amounts of unlabeled data during the pre-training phase, allowing the model to learn rich structural features. However, these methods face the issue of a mismatch between the pre-trained model and downstream tasks, leading to suboptimal performance in certain application scenarios. Prompt learning methods have emerged as a new direction in heterogeneous graph tasks, as they allow flexible adaptation of task representations to address target inconsistency. Building on this idea, this paper proposes a novel multi-task prompt framework for the heterogeneous graph domain, named HGMP. First, to bridge the gap between the pre-trained model and downstream tasks, we reformulate all downstream tasks into a unified graph-level task format. Next, we address the limitations of existing graph prompt learning methods, which struggle to integrate contrastive pre-training strategies in the heterogeneous graph domain. We design a graph-level contrastive pre-training strategy to better leverage heterogeneous information and enhance performance in multi-task scenarios. Finally, we introduce heterogeneous feature prompts, which enhance model performance by refining the representation of input graph features. Experimental results on public datasets show that our proposed method adapts well to various tasks and significantly outperforms baseline methods.
A Survey on Temporal Interaction Graph Representation Learning: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities
May 07, 2025Abstract:Temporal interaction graphs (TIGs), defined by sequences of timestamped interaction events, have become ubiquitous in real-world applications due to their capability to model complex dynamic system behaviors. As a result, temporal interaction graph representation learning (TIGRL) has garnered significant attention in recent years. TIGRL aims to embed nodes in TIGs into low-dimensional representations that effectively preserve both structural and temporal information, thereby enhancing the performance of downstream tasks such as classification, prediction, and clustering within constantly evolving data environments. In this paper, we begin by introducing the foundational concepts of TIGs and emphasize the critical role of temporal dependencies. We then propose a comprehensive taxonomy of state-of-the-art TIGRL methods, systematically categorizing them based on the types of information utilized during the learning process to address the unique challenges inherent to TIGs. To facilitate further research and practical applications, we curate the source of datasets and benchmarks, providing valuable resources for empirical investigations. Finally, we examine key open challenges and explore promising research directions in TIGRL, laying the groundwork for future advancements that have the potential to shape the evolution of this field.
GiGL: Large-Scale Graph Neural Networks at Snapchat
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in graph machine learning (ML) with the introduction of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have led to a widespread interest in applying these approaches to business applications at scale. GNNs enable differentiable end-to-end (E2E) learning of model parameters given graph structure which enables optimization towards popular node, edge (link) and graph-level tasks. While the research innovation in new GNN layers and training strategies has been rapid, industrial adoption and utility of GNNs has lagged considerably due to the unique scale challenges that large-scale graph ML problems create. In this work, we share our approach to training, inference, and utilization of GNNs at Snapchat. To this end, we present GiGL (Gigantic Graph Learning), an open-source library to enable large-scale distributed graph ML to the benefit of researchers, ML engineers, and practitioners. We use GiGL internally at Snapchat to manage the heavy lifting of GNN workflows, including graph data preprocessing from relational DBs, subgraph sampling, distributed training, inference, and orchestration. GiGL is designed to interface cleanly with open-source GNN modeling libraries prominent in academia like PyTorch Geometric (PyG), while handling scaling and productionization challenges that make it easier for internal practitioners to focus on modeling. GiGL is used in multiple production settings, and has powered over 35 launches across multiple business domains in the last 2 years in the contexts of friend recommendation, content recommendation and advertising. This work details high-level design and tools the library provides, scaling properties, case studies in diverse business settings with industry-scale graphs, and several key lessons learned in employing graph ML at scale on large social data. GiGL is open-sourced at https://github.com/snap-research/GiGL.
Retrieval Augmented Spelling Correction for E-Commerce Applications
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:The rapid introduction of new brand names into everyday language poses a unique challenge for e-commerce spelling correction services, which must distinguish genuine misspellings from novel brand names that use unconventional spelling. We seek to address this challenge via Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). On this approach, product names are retrieved from a catalog and incorporated into the context used by a large language model (LLM) that has been fine-tuned to do contextual spelling correction. Through quantitative evaluation and qualitative error analyses, we find improvements in spelling correction utilizing the RAG framework beyond a stand-alone LLM. We also demonstrate the value of additional finetuning of the LLM to incorporate retrieved context.
Transformer-based de novo peptide sequencing for data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry
Feb 17, 2024



Abstract:Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) stands as the predominant high-throughput technique for comprehensively analyzing protein content within biological samples. This methodology is a cornerstone driving the advancement of proteomics. In recent years, substantial strides have been made in Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) strategies, facilitating impartial and non-targeted fragmentation of precursor ions. The DIA-generated MS/MS spectra present a formidable obstacle due to their inherent high multiplexing nature. Each spectrum encapsulates fragmented product ions originating from multiple precursor peptides. This intricacy poses a particularly acute challenge in de novo peptide/protein sequencing, where current methods are ill-equipped to address the multiplexing conundrum. In this paper, we introduce Casanovo-DIA, a deep-learning model based on transformer architecture. It deciphers peptide sequences from DIA mass spectrometry data. Our results show significant improvements over existing STOA methods, including DeepNovo-DIA and PepNet. Casanovo-DIA enhances precision by 15.14% to 34.8%, recall by 11.62% to 31.94% at the amino acid level, and boosts precision by 59% to 81.36% at the peptide level. Integrating DIA data and our Casanovo-DIA model holds considerable promise to uncover novel peptides and more comprehensive profiling of biological samples. Casanovo-DIA is freely available under the GNU GPL license at https://github.com/Biocomputing-Research-Group/Casanovo-DIA.
Multi-teacher Distillation for Multilingual Spelling Correction
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:Accurate spelling correction is a critical step in modern search interfaces, especially in an era of mobile devices and speech-to-text interfaces. For services that are deployed around the world, this poses a significant challenge for multilingual NLP: spelling errors need to be caught and corrected in all languages, and even in queries that use multiple languages. In this paper, we tackle this challenge using multi-teacher distillation. On our approach, a monolingual teacher model is trained for each language/locale, and these individual models are distilled into a single multilingual student model intended to serve all languages/locales. In experiments using open-source data as well as user data from a worldwide search service, we show that this leads to highly effective spelling correction models that can meet the tight latency requirements of deployed services.
Representation Learning on Heterostructures via Heterogeneous Anonymous Walks
Jan 18, 2022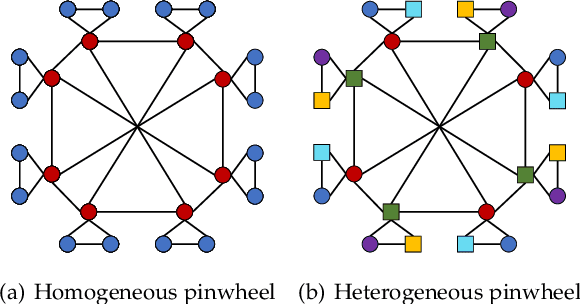
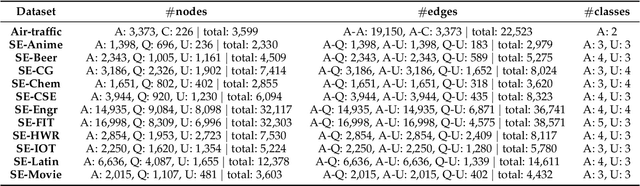
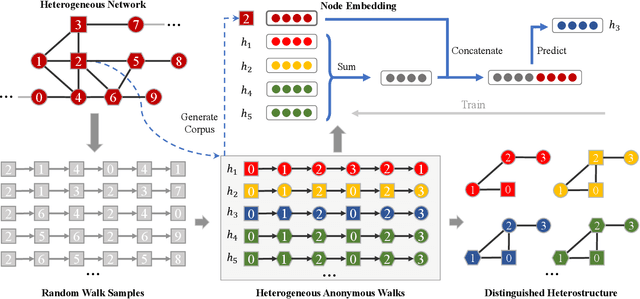
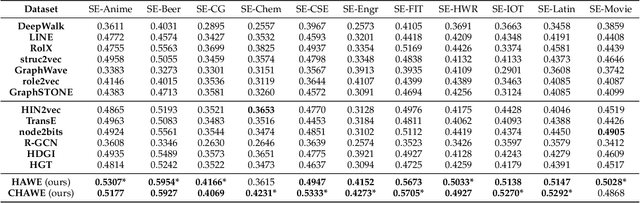
Abstract:Capturing structural similarity has been a hot topic in the field of network embedding recently due to its great help in understanding the node functions and behaviors. However, existing works have paid very much attention to learning structures on homogeneous networks while the related study on heterogeneous networks is still a void. In this paper, we try to take the first step for representation learning on heterostructures, which is very challenging due to their highly diverse combinations of node types and underlying structures. To effectively distinguish diverse heterostructures, we firstly propose a theoretically guaranteed technique called heterogeneous anonymous walk (HAW) and its variant coarse HAW (CHAW). Then, we devise the heterogeneous anonymous walk embedding (HAWE) and its variant coarse HAWE in a data-driven manner to circumvent using an extremely large number of possible walks and train embeddings by predicting occurring walks in the neighborhood of each node. Finally, we design and apply extensive and illustrative experiments on synthetic and real-world networks to build a benchmark on heterostructure learning and evaluate the effectiveness of our methods. The results demonstrate our methods achieve outstanding performance compared with both homogeneous and heterogeneous classic methods, and can be applied on large-scale networks.
A Survey on Role-Oriented Network Embedding
Jul 18, 2021



Abstract:Recently, Network Embedding (NE) has become one of the most attractive research topics in machine learning and data mining. NE approaches have achieved promising performance in various of graph mining tasks including link prediction and node clustering and classification. A wide variety of NE methods focus on the proximity of networks. They learn community-oriented embedding for each node, where the corresponding representations are similar if two nodes are closer to each other in the network. Meanwhile, there is another type of structural similarity, i.e., role-based similarity, which is usually complementary and completely different from the proximity. In order to preserve the role-based structural similarity, the problem of role-oriented NE is raised. However, compared to community-oriented NE problem, there are only a few role-oriented embedding approaches proposed recently. Although less explored, considering the importance of roles in analyzing networks and many applications that role-oriented NE can shed light on, it is necessary and timely to provide a comprehensive overview of existing role-oriented NE methods. In this review, we first clarify the differences between community-oriented and role-oriented network embedding. Afterwards, we propose a general framework for understanding role-oriented NE and a two-level categorization to better classify existing methods. Then, we select some representative methods according to the proposed categorization and briefly introduce them by discussing their motivation, development and differences. Moreover, we conduct comprehensive experiments to empirically evaluate these methods on a variety of role-related tasks including node classification and clustering (role discovery), top-k similarity search and visualization using some widely used synthetic and real-world datasets...
Automatic Generation of Multi-precision Multi-arithmetic CNN Accelerators for FPGAs
Oct 21, 2019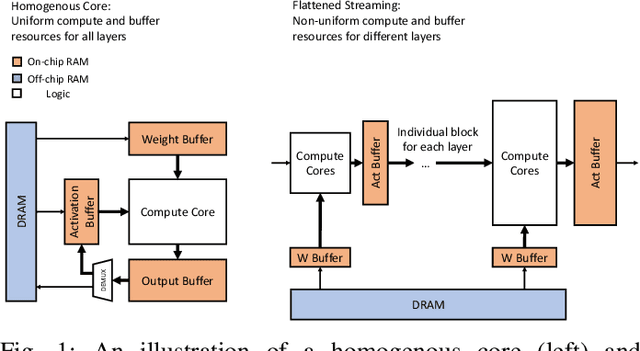
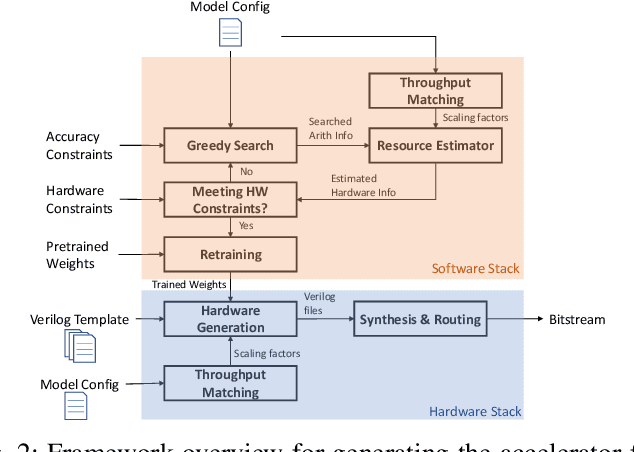
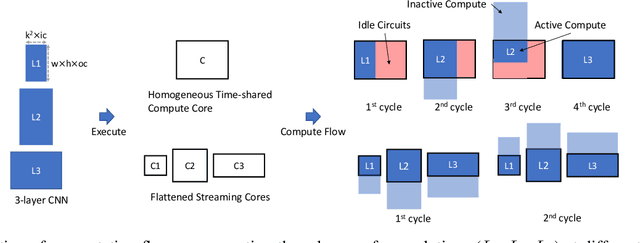
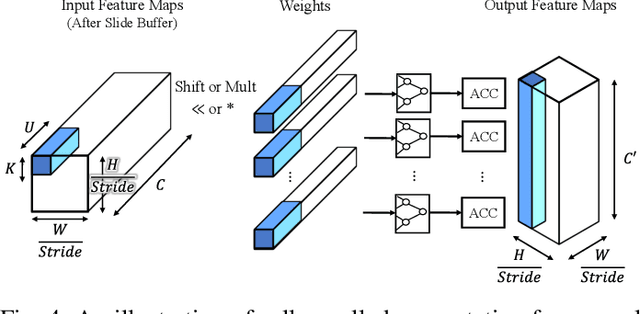
Abstract:Modern deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are computationally demanding, yet real applications often require high throughput and low latency. To help tackle these problems, we propose Tomato, a framework designed to automate the process of generating efficient CNN accelerators. The generated design is pipelined and each convolution layer uses different arithmetics at various precisions. Using Tomato, we showcase state-of-the-art multi-precision multi-arithmetic networks, including MobileNet-V1, running on FPGAs. To our knowledge, this is the first multi-precision multi-arithmetic auto-generation framework for CNNs. In software, Tomato fine-tunes pretrained networks to use a mixture of short powers-of-2 and fixed-point weights with a minimal loss in classification accuracy. The fine-tuned parameters are combined with the templated hardware designs to automatically produce efficient inference circuits in FPGAs. We demonstrate how our approach significantly reduces model sizes and computation complexities, and permits us to pack a complete ImageNet network onto a single FPGA without accessing off-chip memories for the first time. Furthermore, we show how Tomato produces implementations of networks with various sizes running on single or multiple FPGAs. To the best of our knowledge, our automatically generated accelerators outperform closest FPGA-based competitors by at least 2-4x for lantency and throughput; the generated accelerator runs ImageNet classification at a rate of more than 3000 frames per second.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge