Xiaobin Gao
GiGL: Large-Scale Graph Neural Networks at Snapchat
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in graph machine learning (ML) with the introduction of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have led to a widespread interest in applying these approaches to business applications at scale. GNNs enable differentiable end-to-end (E2E) learning of model parameters given graph structure which enables optimization towards popular node, edge (link) and graph-level tasks. While the research innovation in new GNN layers and training strategies has been rapid, industrial adoption and utility of GNNs has lagged considerably due to the unique scale challenges that large-scale graph ML problems create. In this work, we share our approach to training, inference, and utilization of GNNs at Snapchat. To this end, we present GiGL (Gigantic Graph Learning), an open-source library to enable large-scale distributed graph ML to the benefit of researchers, ML engineers, and practitioners. We use GiGL internally at Snapchat to manage the heavy lifting of GNN workflows, including graph data preprocessing from relational DBs, subgraph sampling, distributed training, inference, and orchestration. GiGL is designed to interface cleanly with open-source GNN modeling libraries prominent in academia like PyTorch Geometric (PyG), while handling scaling and productionization challenges that make it easier for internal practitioners to focus on modeling. GiGL is used in multiple production settings, and has powered over 35 launches across multiple business domains in the last 2 years in the contexts of friend recommendation, content recommendation and advertising. This work details high-level design and tools the library provides, scaling properties, case studies in diverse business settings with industry-scale graphs, and several key lessons learned in employing graph ML at scale on large social data. GiGL is open-sourced at https://github.com/snap-research/GiGL.
A Spherical Hidden Markov Model for Semantics-Rich Human Mobility Modeling
Oct 05, 2020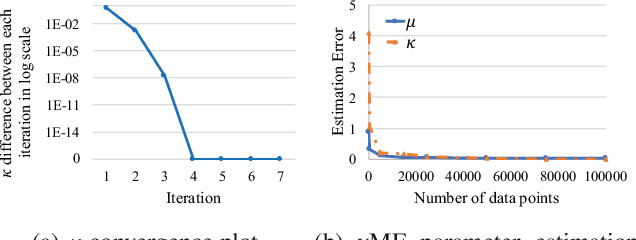
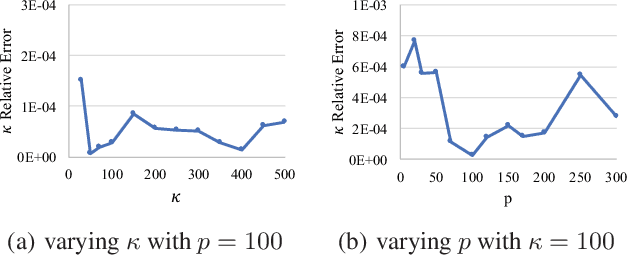
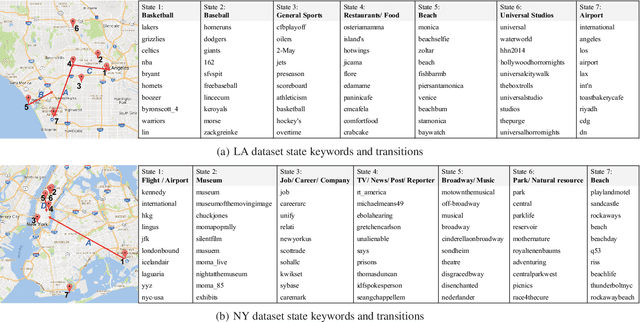
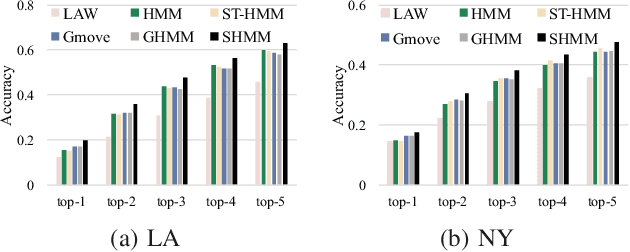
Abstract:We study the problem of modeling human mobility from semantic trace data, wherein each GPS record in a trace is associated with a text message that describes the user's activity. Existing methods fall short in unveiling human movement regularities, because they either do not model the text data at all or suffer from text sparsity severely. We propose SHMM, a multi-modal spherical hidden Markov model for semantics-rich human mobility modeling. Under the hidden Markov assumption, SHMM models the generation process of a given trace by jointly considering the observed location, time, and text at each step of the trace. The distinguishing characteristic of SHMM is the text modeling part. We use fixed-size vector representations to encode the semantics of the text messages, and model the generation of the l2-normalized text embeddings on a unit sphere with the von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distribution. Compared with other alternatives like multi-variate Gaussian, our choice of the vMF distribution not only incurs much fewer parameters, but also better leverages the discriminative power of text embeddings in a directional metric space. The parameter inference for the vMF distribution is non-trivial since it involves functional inversion of ratios of Bessel functions. We theoretically prove that: 1) the classical Expectation-Maximization algorithm can work with vMF distributions; and 2) while closed-form solutions are hard to be obtained for the M-step, Newton's method is guaranteed to converge to the optimal solution with quadratic convergence rate. We have performed extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-life data. The results on synthetic data verify our theoretical analysis; while the results on real-life data demonstrate that SHMM learns meaningful semantics-rich mobility models, outperforms state-of-the-art mobility models for next location prediction, and incurs lower training cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge