Wanzheng Zhu
Euphemistic Phrase Detection by Masked Language Model
Sep 10, 2021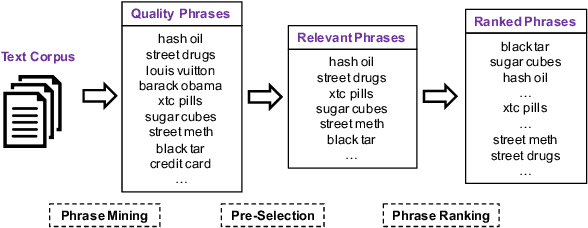
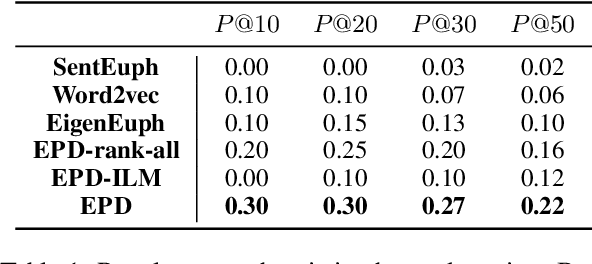

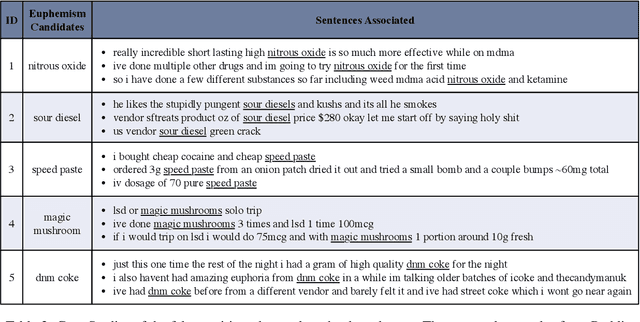
Abstract:It is a well-known approach for fringe groups and organizations to use euphemisms -- ordinary-sounding and innocent-looking words with a secret meaning -- to conceal what they are discussing. For instance, drug dealers often use "pot" for marijuana and "avocado" for heroin. From a social media content moderation perspective, though recent advances in NLP have enabled the automatic detection of such single-word euphemisms, no existing work is capable of automatically detecting multi-word euphemisms, such as "blue dream" (marijuana) and "black tar" (heroin). Our paper tackles the problem of euphemistic phrase detection without human effort for the first time, as far as we are aware. We first perform phrase mining on a raw text corpus (e.g., social media posts) to extract quality phrases. Then, we utilize word embedding similarities to select a set of euphemistic phrase candidates. Finally, we rank those candidates by a masked language model -- SpanBERT. Compared to strong baselines, we report 20-50% higher detection accuracies using our algorithm for detecting euphemistic phrases.
Generate, Prune, Select: A Pipeline for Counterspeech Generation against Online Hate Speech
Jun 03, 2021
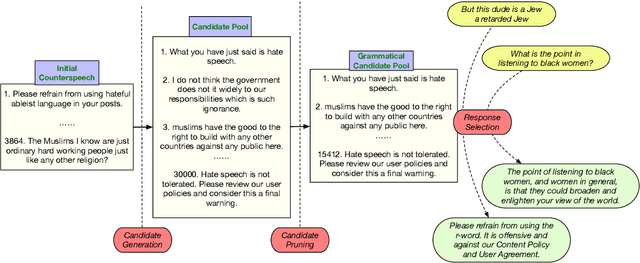
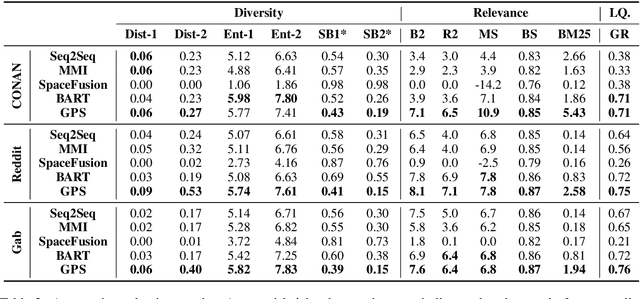
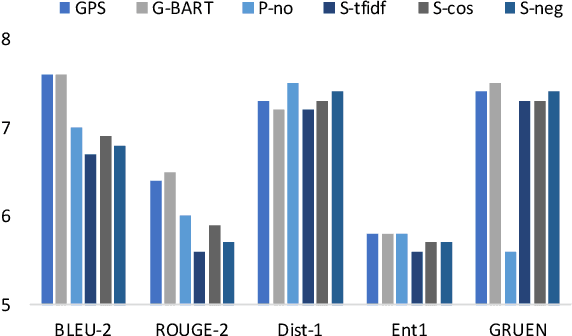
Abstract:Countermeasures to effectively fight the ever increasing hate speech online without blocking freedom of speech is of great social interest. Natural Language Generation (NLG), is uniquely capable of developing scalable solutions. However, off-the-shelf NLG methods are primarily sequence-to-sequence neural models and they are limited in that they generate commonplace, repetitive and safe responses regardless of the hate speech (e.g., "Please refrain from using such language.") or irrelevant responses, making them ineffective for de-escalating hateful conversations. In this paper, we design a three-module pipeline approach to effectively improve the diversity and relevance. Our proposed pipeline first generates various counterspeech candidates by a generative model to promote diversity, then filters the ungrammatical ones using a BERT model, and finally selects the most relevant counterspeech response using a novel retrieval-based method. Extensive Experiments on three representative datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in generating diverse and relevant counterspeech.
Self-Supervised Euphemism Detection and Identification for Content Moderation
Mar 31, 2021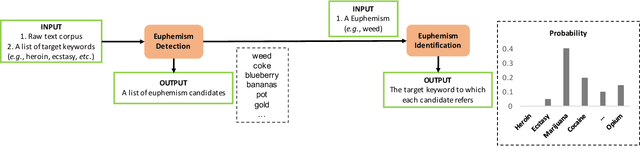
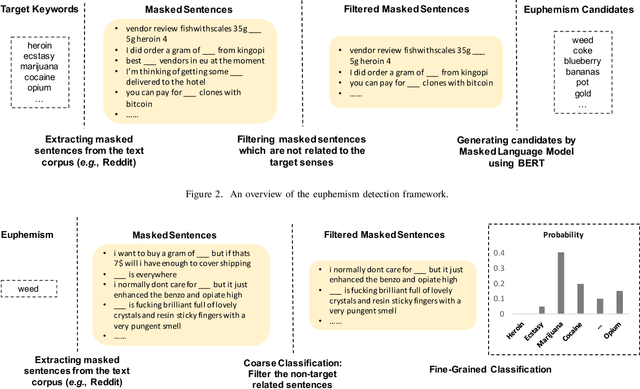
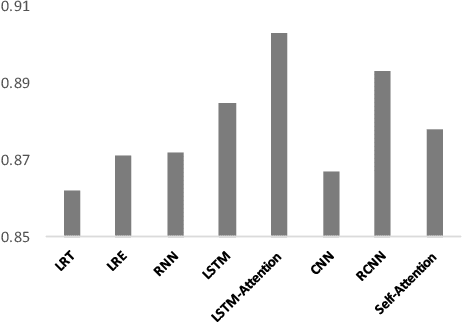
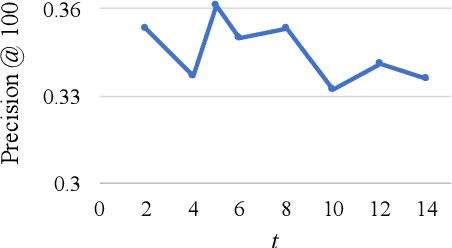
Abstract:Fringe groups and organizations have a long history of using euphemisms--ordinary-sounding words with a secret meaning--to conceal what they are discussing. Nowadays, one common use of euphemisms is to evade content moderation policies enforced by social media platforms. Existing tools for enforcing policy automatically rely on keyword searches for words on a "ban list", but these are notoriously imprecise: even when limited to swearwords, they can still cause embarrassing false positives. When a commonly used ordinary word acquires a euphemistic meaning, adding it to a keyword-based ban list is hopeless: consider "pot" (storage container or marijuana?) or "heater" (household appliance or firearm?) The current generation of social media companies instead hire staff to check posts manually, but this is expensive, inhumane, and not much more effective. It is usually apparent to a human moderator that a word is being used euphemistically, but they may not know what the secret meaning is, and therefore whether the message violates policy. Also, when a euphemism is banned, the group that used it need only invent another one, leaving moderators one step behind. This paper will demonstrate unsupervised algorithms that, by analyzing words in their sentence-level context, can both detect words being used euphemistically, and identify the secret meaning of each word. Compared to the existing state of the art, which uses context-free word embeddings, our algorithm for detecting euphemisms achieves 30-400% higher detection accuracies of unlabeled euphemisms in a text corpus. Our algorithm for revealing euphemistic meanings of words is the first of its kind, as far as we are aware. In the arms race between content moderators and policy evaders, our algorithms may help shift the balance in the direction of the moderators.
GRUEN for Evaluating Linguistic Quality of Generated Text
Oct 06, 2020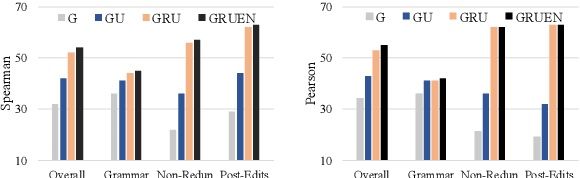
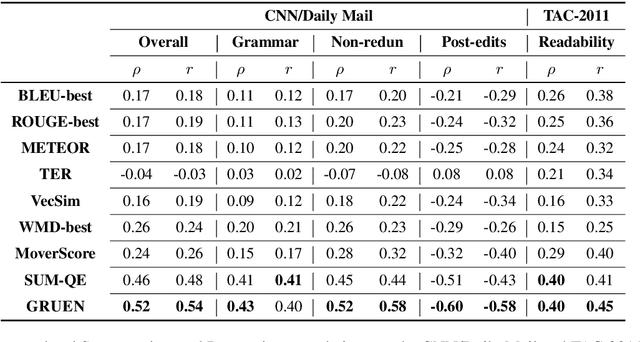
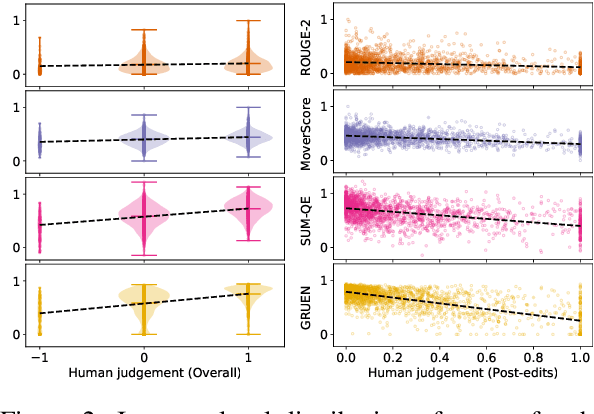
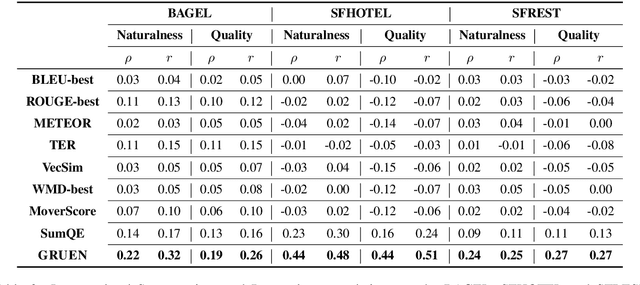
Abstract:Automatic evaluation metrics are indispensable for evaluating generated text. To date, these metrics have focused almost exclusively on the content selection aspect of the system output, ignoring the linguistic quality aspect altogether. We bridge this gap by proposing GRUEN for evaluating Grammaticality, non-Redundancy, focUs, structure and coherENce of generated text. GRUEN utilizes a BERT-based model and a class of syntactic, semantic, and contextual features to examine the system output. Unlike most existing evaluation metrics which require human references as an input, GRUEN is reference-less and requires only the system output. Besides, it has the advantage of being unsupervised, deterministic, and adaptable to various tasks. Experiments on seven datasets over four language generation tasks show that the proposed metric correlates highly with human judgments.
A Spherical Hidden Markov Model for Semantics-Rich Human Mobility Modeling
Oct 05, 2020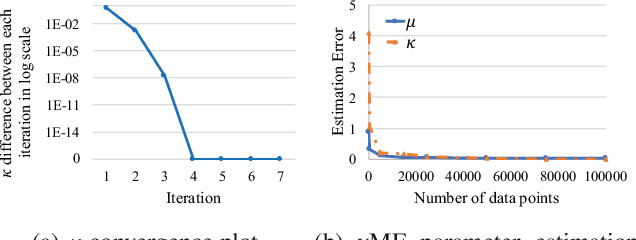
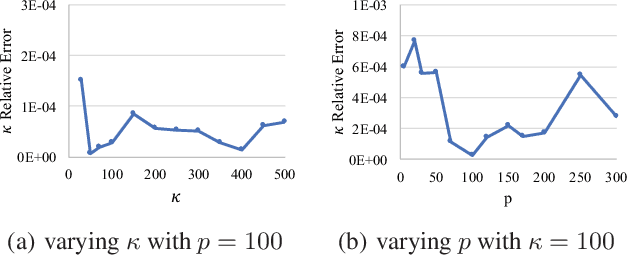
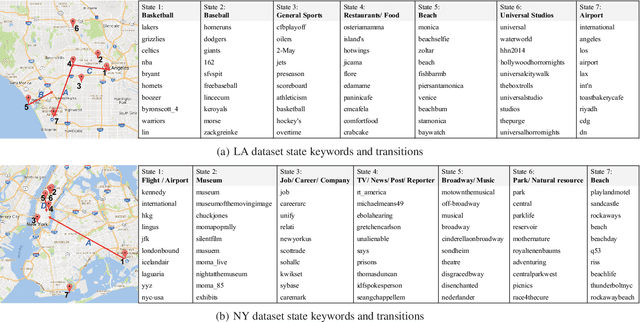
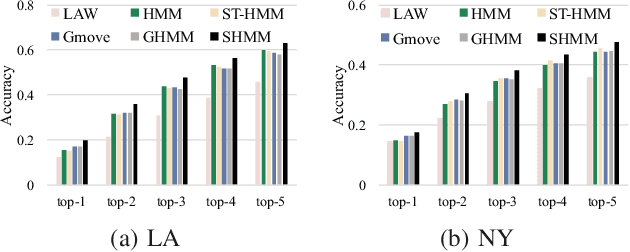
Abstract:We study the problem of modeling human mobility from semantic trace data, wherein each GPS record in a trace is associated with a text message that describes the user's activity. Existing methods fall short in unveiling human movement regularities, because they either do not model the text data at all or suffer from text sparsity severely. We propose SHMM, a multi-modal spherical hidden Markov model for semantics-rich human mobility modeling. Under the hidden Markov assumption, SHMM models the generation process of a given trace by jointly considering the observed location, time, and text at each step of the trace. The distinguishing characteristic of SHMM is the text modeling part. We use fixed-size vector representations to encode the semantics of the text messages, and model the generation of the l2-normalized text embeddings on a unit sphere with the von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distribution. Compared with other alternatives like multi-variate Gaussian, our choice of the vMF distribution not only incurs much fewer parameters, but also better leverages the discriminative power of text embeddings in a directional metric space. The parameter inference for the vMF distribution is non-trivial since it involves functional inversion of ratios of Bessel functions. We theoretically prove that: 1) the classical Expectation-Maximization algorithm can work with vMF distributions; and 2) while closed-form solutions are hard to be obtained for the M-step, Newton's method is guaranteed to converge to the optimal solution with quadratic convergence rate. We have performed extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-life data. The results on synthetic data verify our theoretical analysis; while the results on real-life data demonstrate that SHMM learns meaningful semantics-rich mobility models, outperforms state-of-the-art mobility models for next location prediction, and incurs lower training cost.
FUSE: Multi-Faceted Set Expansion by Coherent Clustering of Skip-grams
Oct 22, 2019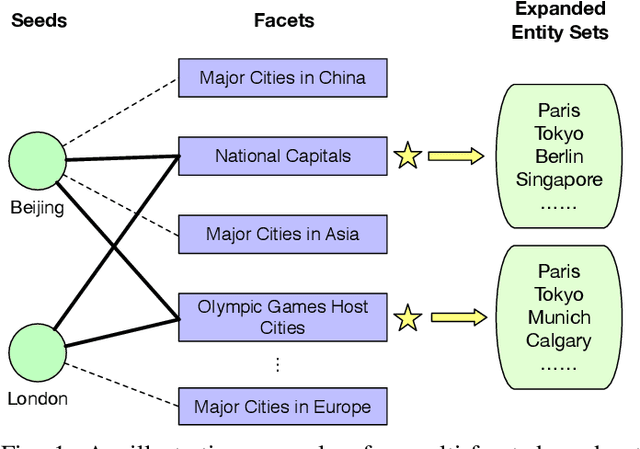
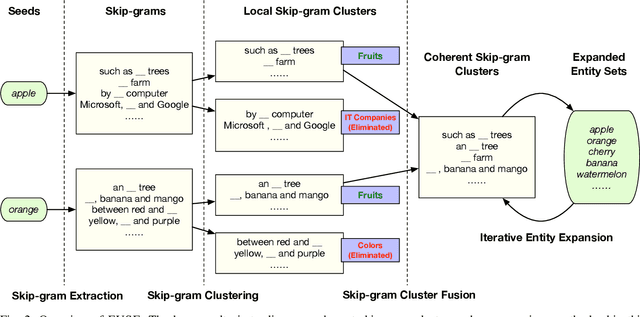
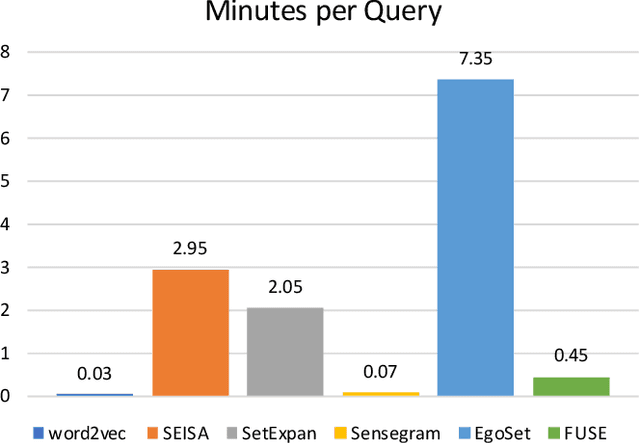
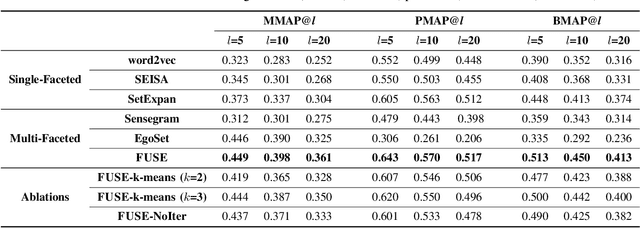
Abstract:Set expansion aims to expand a small set of seed entities into a complete set of relevant entities. Most existing approaches assume the input seed set is unambiguous and completely ignore the multi-faceted semantics of seed entities. As a result, given the seed set {"Canon", "Sony", "Nikon"}, previous methods return one mixed set of entities that are either Camera Brands or Japanese Companies. In this paper, we study the task of multi-faceted set expansion, which aims to capture all semantic facets in the seed set and return multiple sets of entities, one for each semantic facet. We propose an unsupervised framework, FUSE, which consists of three major components: (1) facet discovery module: identifies all semantic facets of each seed entity by extracting and clustering its skip-grams, and (2) facet fusion module: discovers shared semantic facets of the entire seed set by an optimization formulation, and (3) entity expansion module: expands each semantic facet by utilizing an iterative algorithm robust to skip-gram noise. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our algorithm, FUSE, can accurately identify multiple semantic facets of the seed set and generate quality entities for each facet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge