Sravan Bodapati
Adaptive Video Understanding Agent: Enhancing efficiency with dynamic frame sampling and feedback-driven reasoning
Oct 26, 2024Abstract:Understanding long-form video content presents significant challenges due to its temporal complexity and the substantial computational resources required. In this work, we propose an agent-based approach to enhance both the efficiency and effectiveness of long-form video understanding by utilizing large language models (LLMs) and their tool-harnessing ability. A key aspect of our method is query-adaptive frame sampling, which leverages the reasoning capabilities of LLMs to process only the most relevant frames in real-time, and addresses an important limitation of existing methods which typically involve sampling redundant or irrelevant frames. To enhance the reasoning abilities of our video-understanding agent, we leverage the self-reflective capabilities of LLMs to provide verbal reinforcement to the agent, which leads to improved performance while minimizing the number of frames accessed. We evaluate our method across several video understanding benchmarks and demonstrate that not only it enhances state-of-the-art performance but also improves efficiency by reducing the number of frames sampled.
SeRA: Self-Reviewing and Alignment of Large Language Models using Implicit Reward Margins
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Direct alignment algorithms (DAAs), such as direct preference optimization (DPO), have become popular alternatives for Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) due to their simplicity, efficiency, and stability. However, the preferences used in DAAs are usually collected before the alignment training begins and remain unchanged (off-policy). This can lead to two problems where the policy model (1) picks up on spurious correlations in the dataset (as opposed to learning the intended alignment expressed in the human preference labels), and (2) overfits to feedback on off-policy trajectories that have less likelihood of being generated by an updated policy model. To address these issues, we introduce Self-Reviewing and Alignment (SeRA), a cost-efficient and effective method that can be readily combined with existing DAAs. SeRA comprises of two components: (1) sample selection using implicit reward margins, which helps alleviate over-fitting to some undesired features, and (2) preference bootstrapping using implicit rewards to augment preference data with updated policy models in a cost-efficient manner. Extensive experimentation, including some on instruction-following tasks, demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of SeRA in training LLMs on offline preference datasets with DAAs.
Beyond correlation: The impact of human uncertainty in measuring the effectiveness of automatic evaluation and LLM-as-a-judge
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:The effectiveness of automatic evaluation of generative models is typically measured by comparing it to human evaluation using correlation metrics. However, metrics like Krippendorff's $\alpha$ and Randolph's $\kappa$, originally designed to measure the reliability of human labeling, make assumptions about human behavior and the labeling process. In this paper, we show how *relying on a single aggregate correlation score* can obscure fundamental differences between human behavior and automatic evaluation methods, including LLM-as-a-Judge. Specifically, we demonstrate that when the proportion of samples with variation or uncertainty in human labels (gathered during human evaluation) is relatively high, machine labels (generated by automatic evaluation methods) may superficially appear to have similar or better correlation with the human majority label compared to human-to-human (HH) correlation. This can create the misleading impression that automatic evaluation is accurate enough to approximate the human majority label. However, as the proportion of samples with consistent human labels increases, the correlation between machine labels and human majority labels declines, falling below HH correlation. Based on these findings, we first propose stratifying results by human label uncertainty to provide a more robust analysis of automatic evaluation performance. Second, recognizing that uncertainty and variation are inherent in perception-based human evaluations, such as those involving attitudes or preferences, we introduce a new metric - *binned Jensen-Shannon Divergence for perception* for such scenarios to better measure the effectiveness of automatic evaluations. Third, we present visualization techniques -- *perception charts*, to compare the strengths and limitations of automatic evaluation and to contextualize correlation measures appropriately
ConSiDERS-The-Human Evaluation Framework: Rethinking Human Evaluation for Generative Large Language Models
May 28, 2024Abstract:In this position paper, we argue that human evaluation of generative large language models (LLMs) should be a multidisciplinary undertaking that draws upon insights from disciplines such as user experience research and human behavioral psychology to ensure that the experimental design and results are reliable. The conclusions from these evaluations, thus, must consider factors such as usability, aesthetics, and cognitive biases. We highlight how cognitive biases can conflate fluent information and truthfulness, and how cognitive uncertainty affects the reliability of rating scores such as Likert. Furthermore, the evaluation should differentiate the capabilities and weaknesses of increasingly powerful large language models -- which requires effective test sets. The scalability of human evaluation is also crucial to wider adoption. Hence, to design an effective human evaluation system in the age of generative NLP, we propose the ConSiDERS-The-Human evaluation framework consisting of 6 pillars --Consistency, Scoring Critera, Differentiating, User Experience, Responsible, and Scalability.
Multi-teacher Distillation for Multilingual Spelling Correction
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:Accurate spelling correction is a critical step in modern search interfaces, especially in an era of mobile devices and speech-to-text interfaces. For services that are deployed around the world, this poses a significant challenge for multilingual NLP: spelling errors need to be caught and corrected in all languages, and even in queries that use multiple languages. In this paper, we tackle this challenge using multi-teacher distillation. On our approach, a monolingual teacher model is trained for each language/locale, and these individual models are distilled into a single multilingual student model intended to serve all languages/locales. In experiments using open-source data as well as user data from a worldwide search service, we show that this leads to highly effective spelling correction models that can meet the tight latency requirements of deployed services.
Retrieve and Copy: Scaling ASR Personalization to Large Catalogs
Nov 14, 2023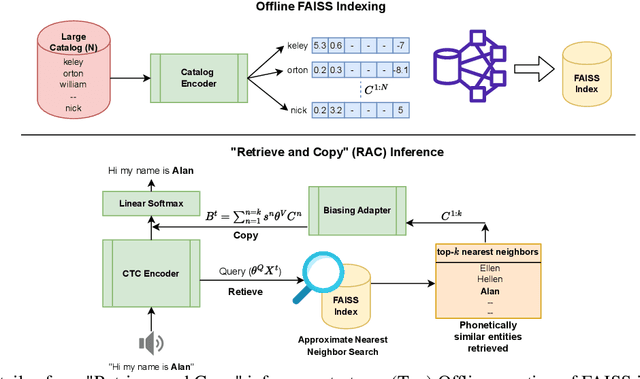

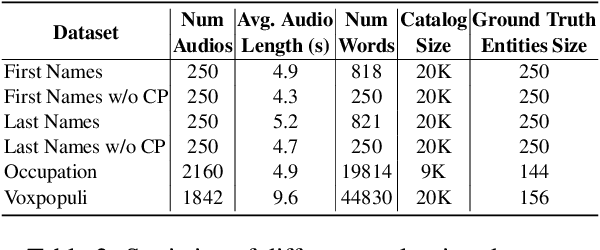
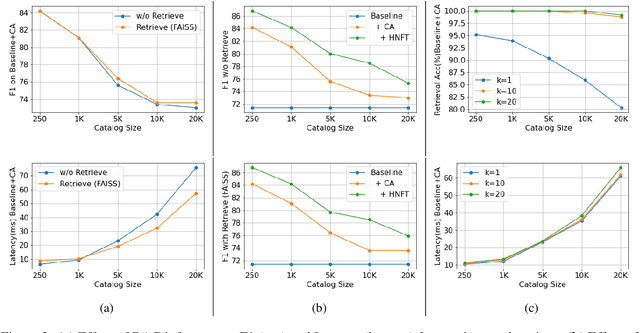
Abstract:Personalization of automatic speech recognition (ASR) models is a widely studied topic because of its many practical applications. Most recently, attention-based contextual biasing techniques are used to improve the recognition of rare words and domain specific entities. However, due to performance constraints, the biasing is often limited to a few thousand entities, restricting real-world usability. To address this, we first propose a "Retrieve and Copy" mechanism to improve latency while retaining the accuracy even when scaled to a large catalog. We also propose a training strategy to overcome the degradation in recall at such scale due to an increased number of confusing entities. Overall, our approach achieves up to 6% more Word Error Rate reduction (WERR) and 3.6% absolute improvement in F1 when compared to a strong baseline. Our method also allows for large catalog sizes of up to 20K without significantly affecting WER and F1-scores, while achieving at least 20% inference speedup per acoustic frame.
Generalized zero-shot audio-to-intent classification
Nov 04, 2023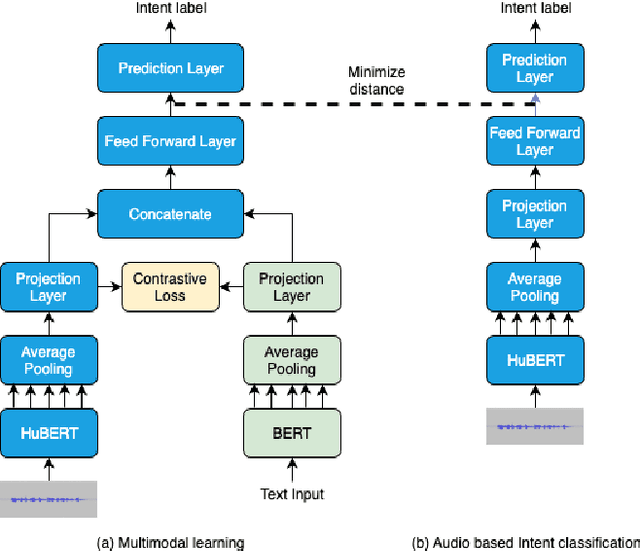
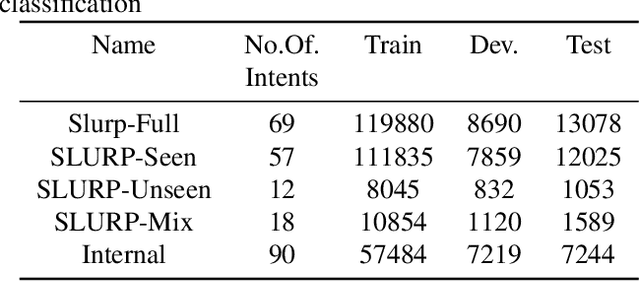
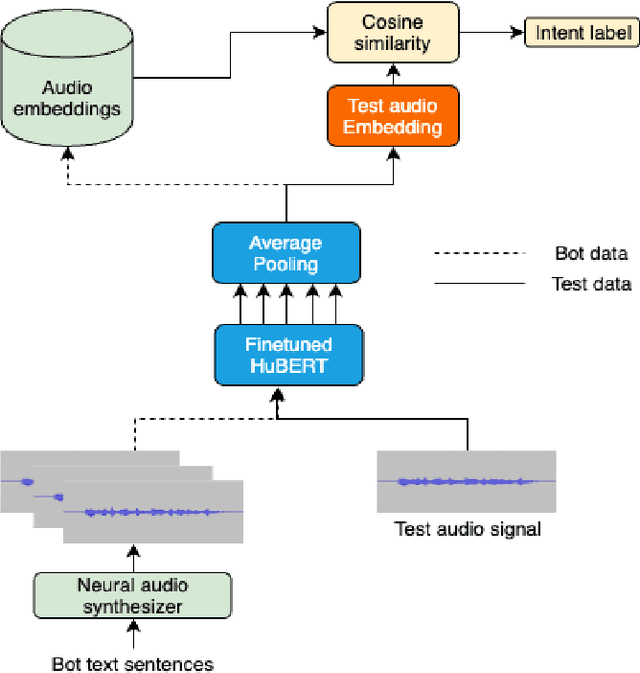
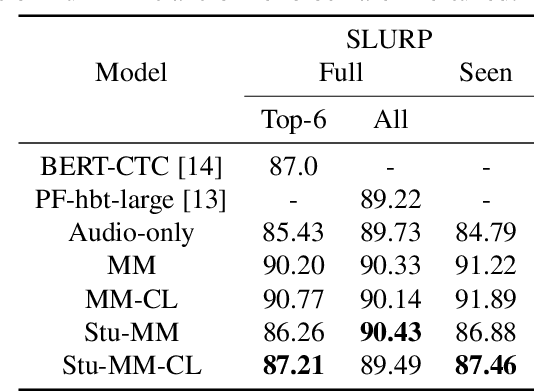
Abstract:Spoken language understanding systems using audio-only data are gaining popularity, yet their ability to handle unseen intents remains limited. In this study, we propose a generalized zero-shot audio-to-intent classification framework with only a few sample text sentences per intent. To achieve this, we first train a supervised audio-to-intent classifier by making use of a self-supervised pre-trained model. We then leverage a neural audio synthesizer to create audio embeddings for sample text utterances and perform generalized zero-shot classification on unseen intents using cosine similarity. We also propose a multimodal training strategy that incorporates lexical information into the audio representation to improve zero-shot performance. Our multimodal training approach improves the accuracy of zero-shot intent classification on unseen intents of SLURP by 2.75% and 18.2% for the SLURP and internal goal-oriented dialog datasets, respectively, compared to audio-only training.
Multilingual Contextual Adapters To Improve Custom Word Recognition In Low-resource Languages
Jul 03, 2023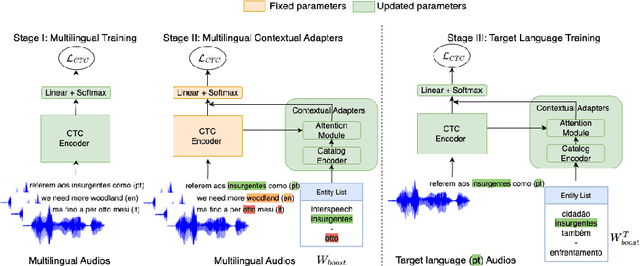


Abstract:Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) models are popular for their balance between speed and performance for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). However, these CTC models still struggle in other areas, such as personalization towards custom words. A recent approach explores Contextual Adapters, wherein an attention-based biasing model for CTC is used to improve the recognition of custom entities. While this approach works well with enough data, we showcase that it isn't an effective strategy for low-resource languages. In this work, we propose a supervision loss for smoother training of the Contextual Adapters. Further, we explore a multilingual strategy to improve performance with limited training data. Our method achieves 48% F1 improvement in retrieving unseen custom entities for a low-resource language. Interestingly, as a by-product of training the Contextual Adapters, we see a 5-11% Word Error Rate (WER) reduction in the performance of the base CTC model as well.
Don't Stop Self-Supervision: Accent Adaptation of Speech Representations via Residual Adapters
Jul 02, 2023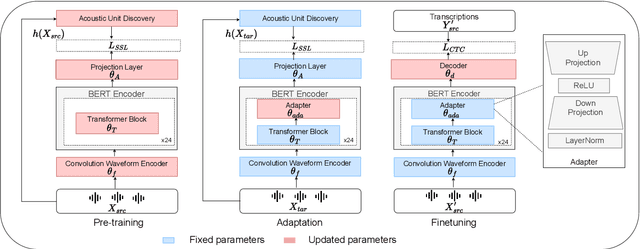
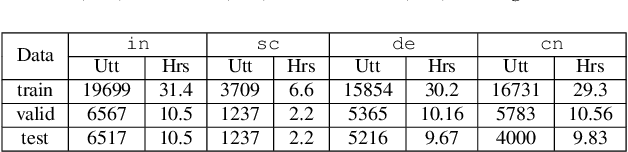
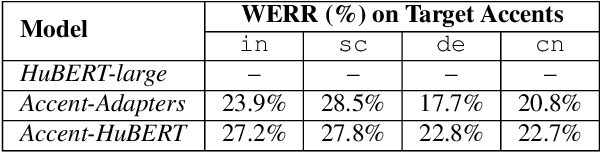
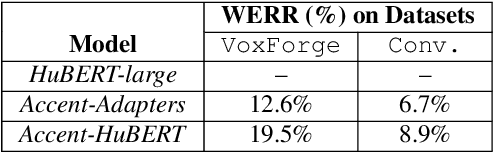
Abstract:Speech representations learned in a self-supervised fashion from massive unlabeled speech corpora have been adapted successfully toward several downstream tasks. However, such representations may be skewed toward canonical data characteristics of such corpora and perform poorly on atypical, non-native accented speaker populations. With the state-of-the-art HuBERT model as a baseline, we propose and investigate self-supervised adaptation of speech representations to such populations in a parameter-efficient way via training accent-specific residual adapters. We experiment with 4 accents and choose automatic speech recognition (ASR) as the downstream task of interest. We obtain strong word error rate reductions (WERR) over HuBERT-large for all 4 accents, with a mean WERR of 22.7% with accent-specific adapters and a mean WERR of 25.1% if the entire encoder is accent-adapted. While our experiments utilize HuBERT and ASR as the downstream task, our proposed approach is both model and task-agnostic.
DCTX-Conformer: Dynamic context carry-over for low latency unified streaming and non-streaming Conformer
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Conformer-based end-to-end models have become ubiquitous these days and are commonly used in both streaming and non-streaming automatic speech recognition (ASR). Techniques like dual-mode and dynamic chunk training helped unify streaming and non-streaming systems. However, there remains a performance gap between streaming with a full and limited past context. To address this issue, we propose the integration of a novel dynamic contextual carry-over mechanism in a state-of-the-art (SOTA) unified ASR system. Our proposed dynamic context Conformer (DCTX-Conformer) utilizes a non-overlapping contextual carry-over mechanism that takes into account both the left context of a chunk and one or more preceding context embeddings. We outperform the SOTA by a relative 25.0% word error rate, with a negligible latency impact due to the additional context embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge