Sanchit Sinha
CASL: Concept-Aligned Sparse Latents for Interpreting Diffusion Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Internal activations of diffusion models encode rich semantic information, but interpreting such representations remains challenging. While Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) have shown promise in disentangling latent representations, existing SAE-based methods for diffusion model understanding rely on unsupervised approaches that fail to align sparse features with human-understandable concepts. This limits their ability to provide reliable semantic control over generated images. We introduce CASL (Concept-Aligned Sparse Latents), a supervised framework that aligns sparse latent dimensions of diffusion models with semantic concepts. CASL first trains an SAE on frozen U-Net activations to obtain disentangled latent representations, and then learns a lightweight linear mapping that associates each concept with a small set of relevant latent dimensions. To validate the semantic meaning of these aligned directions, we propose CASL-Steer, a controlled latent intervention that shifts activations along the learned concept axis. Unlike editing methods, CASL-Steer is used solely as a causal probe to reveal how concept-aligned latents influence generated content. We further introduce the Editing Precision Ratio (EPR), a metric that jointly measures concept specificity and the preservation of unrelated attributes. Experiments show that our method achieves superior editing precision and interpretability compared to existing approaches. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to achieve supervised alignment between latent representations and semantic concepts in diffusion models.
Reasoning Beyond Chain-of-Thought: A Latent Computational Mode in Large Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has improved the reasoning performance of large language models (LLMs), but it remains unclear why it works and whether it is the unique mechanism for triggering reasoning in large language models. In this work, we study this question by directly analyzing and intervening on the internal representations of LLMs with Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs), identifying a small set of latent features that are causally associated with LLM reasoning behavior. Across multiple model families and reasoning benchmarks, we find that steering a single reasoning-related latent feature can substantially improve accuracy without explicit CoT prompting. For large models, latent steering achieves performance comparable to standard CoT prompting while producing more efficient outputs. We further observe that this reasoning-oriented internal state is triggered early in generation and can override prompt-level instructions that discourage explicit reasoning. Overall, our results suggest that multi-step reasoning in LLMs is supported by latent internal activations that can be externally activated, while CoT prompting is one effective, but not unique, way of activating this mechanism rather than its necessary cause.
Toward Faithful Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Sparse Autoencoders
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) improves the factuality of large language models (LLMs) by grounding outputs in retrieved evidence, but faithfulness failures, where generations contradict or extend beyond the provided sources, remain a critical challenge. Existing hallucination detection methods for RAG often rely either on large-scale detector training, which requires substantial annotated data, or on querying external LLM judges, which leads to high inference costs. Although some approaches attempt to leverage internal representations of LLMs for hallucination detection, their accuracy remains limited. Motivated by recent advances in mechanistic interpretability, we employ sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to disentangle internal activations, successfully identifying features that are specifically triggered during RAG hallucinations. Building on a systematic pipeline of information-based feature selection and additive feature modeling, we introduce RAGLens, a lightweight hallucination detector that accurately flags unfaithful RAG outputs using LLM internal representations. RAGLens not only achieves superior detection performance compared to existing methods, but also provides interpretable rationales for its decisions, enabling effective post-hoc mitigation of unfaithful RAG. Finally, we justify our design choices and reveal new insights into the distribution of hallucination-related signals within LLMs. The code is available at https://github.com/Teddy-XiongGZ/RAGLens.
Concept-RuleNet: Grounded Multi-Agent Neurosymbolic Reasoning in Vision Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Modern vision-language models (VLMs) deliver impressive predictive accuracy yet offer little insight into 'why' a decision is reached, frequently hallucinating facts, particularly when encountering out-of-distribution data. Neurosymbolic frameworks address this by pairing black-box perception with interpretable symbolic reasoning, but current methods extract their symbols solely from task labels, leaving them weakly grounded in the underlying visual data. In this paper, we introduce a multi-agent system - Concept-RuleNet that reinstates visual grounding while retaining transparent reasoning. Specifically, a multimodal concept generator first mines discriminative visual concepts directly from a representative subset of training images. Next, these visual concepts are utilized to condition symbol discovery, anchoring the generations in real image statistics and mitigating label bias. Subsequently, symbols are composed into executable first-order rules by a large language model reasoner agent - yielding interpretable neurosymbolic rules. Finally, during inference, a vision verifier agent quantifies the degree of presence of each symbol and triggers rule execution in tandem with outputs of black-box neural models, predictions with explicit reasoning pathways. Experiments on five benchmarks, including two challenging medical-imaging tasks and three underrepresented natural-image datasets, show that our system augments state-of-the-art neurosymbolic baselines by an average of 5% while also reducing the occurrence of hallucinated symbols in rules by up to 50%.
GCAV: A Global Concept Activation Vector Framework for Cross-Layer Consistency in Interpretability
Aug 28, 2025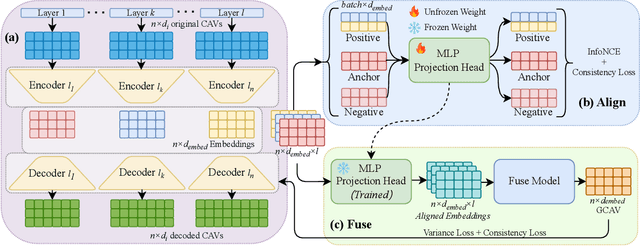
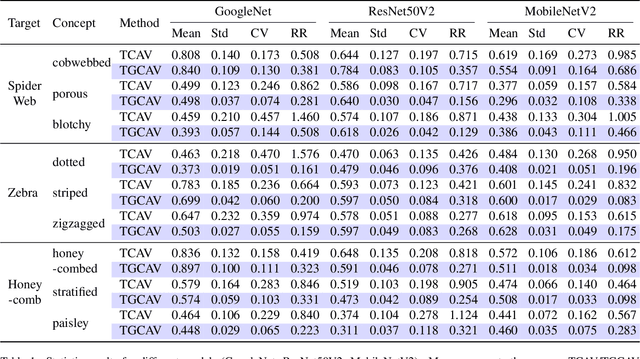
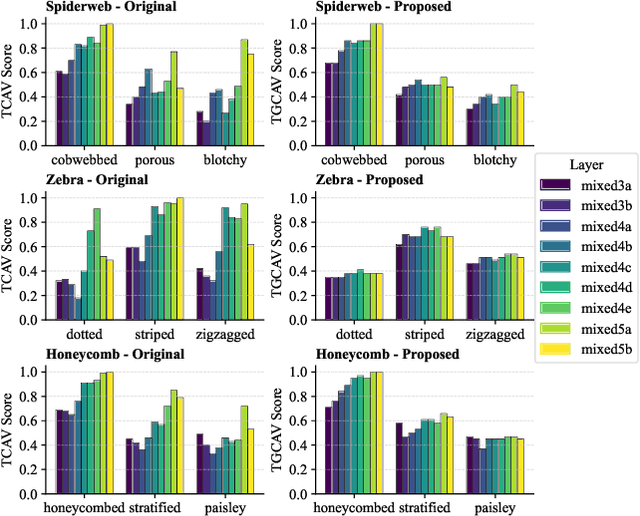

Abstract:Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs) provide a powerful approach for interpreting deep neural networks by quantifying their sensitivity to human-defined concepts. However, when computed independently at different layers, CAVs often exhibit inconsistencies, making cross-layer comparisons unreliable. To address this issue, we propose the Global Concept Activation Vector (GCAV), a novel framework that unifies CAVs into a single, semantically consistent representation. Our method leverages contrastive learning to align concept representations across layers and employs an attention-based fusion mechanism to construct a globally integrated CAV. By doing so, our method significantly reduces the variance in TCAV scores while preserving concept relevance, ensuring more stable and reliable concept attributions. To evaluate the effectiveness of GCAV, we introduce Testing with Global Concept Activation Vectors (TGCAV) as a method to apply TCAV to GCAV-based representations. We conduct extensive experiments on multiple deep neural networks, demonstrating that our method effectively mitigates concept inconsistency across layers, enhances concept localization, and improves robustness against adversarial perturbations. By integrating cross-layer information into a coherent framework, our method offers a more comprehensive and interpretable understanding of how deep learning models encode human-defined concepts. Code and models are available at https://github.com/Zhenghao-He/GCAV.
Leveraging Scale-aware Representations for improved Concept-Representation Alignment in ViTs
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) are increasingly being adopted in various sensitive vision applications - like medical diagnosis, facial recognition, etc. To improve the interpretability of such models, many approaches attempt to forward-align them with carefully annotated abstract, human-understandable semantic entities - concepts. Concepts provide global rationales to the model predictions and can be quickly understood/intervened on by domain experts. Most current research focuses on designing model-agnostic, plug-and-play generic concept-based explainability modules that do not incorporate the inner workings of foundation models (e.g., inductive biases, scale invariance, etc.) during training. To alleviate this issue for ViTs, in this paper, we propose a novel Concept Representation Alignment Module (CRAM) which learns both scale and position-aware representations from multi-scale feature pyramids and patch representations respectively. CRAM further aligns these representations with concept annotations through an attention matrix. The proposed CRAM module improves the predictive performance of ViT architectures and also provides accurate and robust concept explanations as demonstrated on five datasets - including three widely used benchmarks (CUB, Pascal APY, Concept-MNIST) and 2 real-world datasets (AWA2, KITS).
Structural Causality-based Generalizable Concept Discovery Models
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:The rising need for explainable deep neural network architectures has utilized semantic concepts as explainable units. Several approaches utilizing disentangled representation learning estimate the generative factors and utilize them as concepts for explaining DNNs. However, even though the generative factors for a dataset remain fixed, concepts are not fixed entities and vary based on downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a disentanglement mechanism utilizing a variational autoencoder (VAE) for learning mutually independent generative factors for a given dataset and subsequently learning task-specific concepts using a structural causal model (SCM). Our method assumes generative factors and concepts to form a bipartite graph, with directed causal edges from generative factors to concepts. Experiments are conducted on datasets with known generative factors: D-sprites and Shapes3D. On specific downstream tasks, our proposed method successfully learns task-specific concepts which are explained well by the causal edges from the generative factors. Lastly, separate from current causal concept discovery methods, our methodology is generalizable to an arbitrary number of concepts and flexible to any downstream tasks.
ProtoNAM: Prototypical Neural Additive Models for Interpretable Deep Tabular Learning
Oct 07, 2024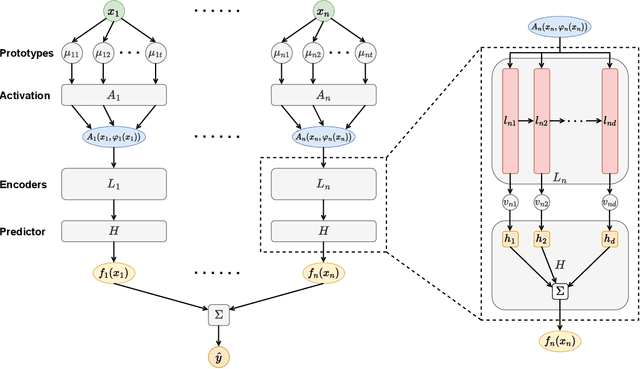
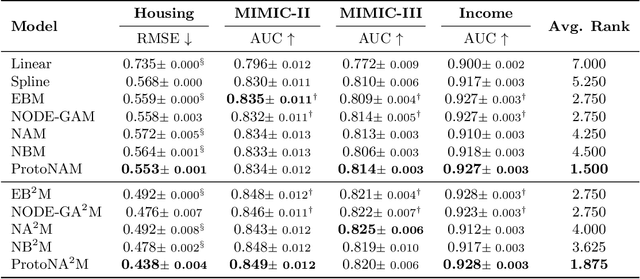
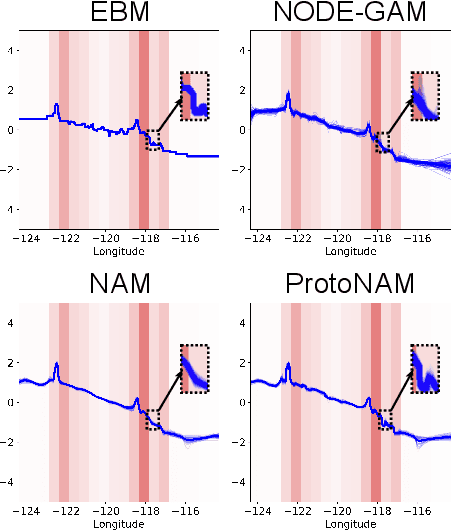
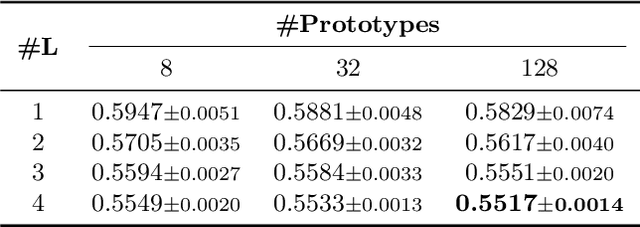
Abstract:Generalized additive models (GAMs) have long been a powerful white-box tool for the intelligible analysis of tabular data, revealing the influence of each feature on the model predictions. Despite the success of neural networks (NNs) in various domains, their application as NN-based GAMs in tabular data analysis remains suboptimal compared to tree-based ones, and the opacity of encoders in NN-GAMs also prevents users from understanding how networks learn the functions. In this work, we propose a new deep tabular learning method, termed Prototypical Neural Additive Model (ProtoNAM), which introduces prototypes into neural networks in the framework of GAMs. With the introduced prototype-based feature activation, ProtoNAM can flexibly model the irregular mapping from tabular features to the outputs while maintaining the explainability of the final prediction. We also propose a gradient-boosting inspired hierarchical shape function modeling method, facilitating the discovery of complex feature patterns and bringing transparency into the learning process of each network layer. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate that ProtoNAM outperforms all existing NN-based GAMs, while providing additional insights into the shape function learned for each feature. The source code of ProtoNAM is available at \url{https://github.com/Teddy-XiongGZ/ProtoNAM}.
CoLiDR: Concept Learning using Aggregated Disentangled Representations
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:Interpretability of Deep Neural Networks using concept-based models offers a promising way to explain model behavior through human-understandable concepts. A parallel line of research focuses on disentangling the data distribution into its underlying generative factors, in turn explaining the data generation process. While both directions have received extensive attention, little work has been done on explaining concepts in terms of generative factors to unify mathematically disentangled representations and human-understandable concepts as an explanation for downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel method CoLiDR - which utilizes a disentangled representation learning setup for learning mutually independent generative factors and subsequently learns to aggregate the said representations into human-understandable concepts using a novel aggregation/decomposition module. Experiments are conducted on datasets with both known and unknown latent generative factors. Our method successfully aggregates disentangled generative factors into concepts while maintaining parity with state-of-the-art concept-based approaches. Quantitative and visual analysis of the learned aggregation procedure demonstrates the advantages of our work compared to commonly used concept-based models over four challenging datasets. Lastly, our work is generalizable to an arbitrary number of concepts and generative factors - making it flexible enough to be suitable for various types of data.
MAML-en-LLM: Model Agnostic Meta-Training of LLMs for Improved In-Context Learning
May 19, 2024



Abstract:Adapting large language models (LLMs) to unseen tasks with in-context training samples without fine-tuning remains an important research problem. To learn a robust LLM that adapts well to unseen tasks, multiple meta-training approaches have been proposed such as MetaICL and MetaICT, which involve meta-training pre-trained LLMs on a wide variety of diverse tasks. These meta-training approaches essentially perform in-context multi-task fine-tuning and evaluate on a disjointed test set of tasks. Even though they achieve impressive performance, their goal is never to compute a truly general set of parameters. In this paper, we propose MAML-en-LLM, a novel method for meta-training LLMs, which can learn truly generalizable parameters that not only perform well on disjointed tasks but also adapts to unseen tasks. We see an average increase of 2% on unseen domains in the performance while a massive 4% improvement on adaptation performance. Furthermore, we demonstrate that MAML-en-LLM outperforms baselines in settings with limited amount of training data on both seen and unseen domains by an average of 2%. Finally, we discuss the effects of type of tasks, optimizers and task complexity, an avenue barely explored in meta-training literature. Exhaustive experiments across 7 task settings along with two data settings demonstrate that models trained with MAML-en-LLM outperform SOTA meta-training approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge