Brady Houston
Zero-resource Speech Translation and Recognition with LLMs
Dec 24, 2024


Abstract:Despite recent advancements in speech processing, zero-resource speech translation (ST) and automatic speech recognition (ASR) remain challenging problems. In this work, we propose to leverage a multilingual Large Language Model (LLM) to perform ST and ASR in languages for which the model has never seen paired audio-text data. We achieve this by using a pre-trained multilingual speech encoder, a multilingual LLM, and a lightweight adaptation module that maps the audio representations to the token embedding space of the LLM. We perform several experiments both in ST and ASR to understand how to best train the model and what data has the most impact on performance in previously unseen languages. In ST, our best model is capable to achieve BLEU scores over 23 in CoVoST2 for two previously unseen languages, while in ASR, we achieve WERs of up to 28.2\%. We finally show that the performance of our system is bounded by the ability of the LLM to output text in the desired language.
Improving Lip-synchrony in Direct Audio-Visual Speech-to-Speech Translation
Dec 21, 2024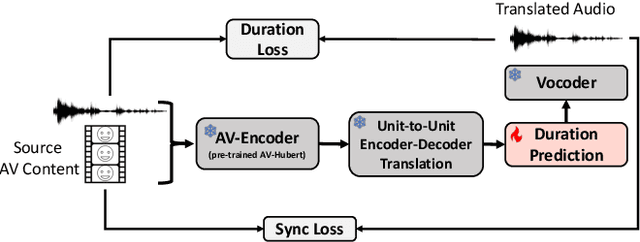

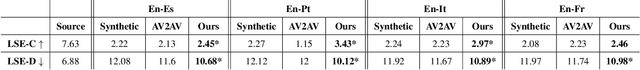

Abstract:Audio-Visual Speech-to-Speech Translation typically prioritizes improving translation quality and naturalness. However, an equally critical aspect in audio-visual content is lip-synchrony-ensuring that the movements of the lips match the spoken content-essential for maintaining realism in dubbed videos. Despite its importance, the inclusion of lip-synchrony constraints in AVS2S models has been largely overlooked. This study addresses this gap by integrating a lip-synchrony loss into the training process of AVS2S models. Our proposed method significantly enhances lip-synchrony in direct audio-visual speech-to-speech translation, achieving an average LSE-D score of 10.67, representing a 9.2% reduction in LSE-D over a strong baseline across four language pairs. Additionally, it maintains the naturalness and high quality of the translated speech when overlaid onto the original video, without any degradation in translation quality.
Sequential Editing for Lifelong Training of Speech Recognition Models
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) traditionally assumes known domains, but adding data from a new domain raises concerns about computational inefficiencies linked to retraining models on both existing and new domains. Fine-tuning solely on new domain risks Catastrophic Forgetting (CF). To address this, Lifelong Learning (LLL) algorithms have been proposed for ASR. Prior research has explored techniques such as Elastic Weight Consolidation, Knowledge Distillation, and Replay, all of which necessitate either additional parameters or access to prior domain data. We propose Sequential Model Editing as a novel method to continually learn new domains in ASR systems. Different than previous methods, our approach does not necessitate access to prior datasets or the introduction of extra parameters. Our study demonstrates up to 15% Word Error Rate Reduction (WERR) over fine-tuning baseline, and superior efficiency over other LLL techniques on CommonVoice English multi-accent dataset.
Multilingual Contextual Adapters To Improve Custom Word Recognition In Low-resource Languages
Jul 03, 2023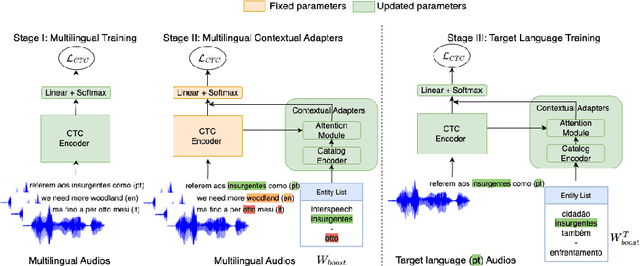


Abstract:Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) models are popular for their balance between speed and performance for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). However, these CTC models still struggle in other areas, such as personalization towards custom words. A recent approach explores Contextual Adapters, wherein an attention-based biasing model for CTC is used to improve the recognition of custom entities. While this approach works well with enough data, we showcase that it isn't an effective strategy for low-resource languages. In this work, we propose a supervision loss for smoother training of the Contextual Adapters. Further, we explore a multilingual strategy to improve performance with limited training data. Our method achieves 48% F1 improvement in retrieving unseen custom entities for a low-resource language. Interestingly, as a by-product of training the Contextual Adapters, we see a 5-11% Word Error Rate (WER) reduction in the performance of the base CTC model as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge