Devang Kulshreshtha
Multi-Turn Jailbreaking of Aligned LLMs via Lexical Anchor Tree Search
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Most jailbreak methods achieve high attack success rates (ASR) but require attacker LLMs to craft adversarial queries and/or demand high query budgets. These resource limitations make jailbreaking expensive, and the queries generated by attacker LLMs often consist of non-interpretable random prefixes. This paper introduces Lexical Anchor Tree Search (), addressing these limitations through an attacker-LLM-free method that operates purely via lexical anchor injection. LATS reformulates jailbreaking as a breadth-first tree search over multi-turn dialogues, where each node incrementally injects missing content words from the attack goal into benign prompts. Evaluations on AdvBench and HarmBench demonstrate that LATS achieves 97-100% ASR on latest GPT, Claude, and Llama models with an average of only ~6.4 queries, compared to 20+ queries required by other methods. These results highlight conversational structure as a potent and under-protected attack surface, while demonstrating superior query efficiency in an era where high ASR is readily achievable. Our code will be released to support reproducibility.
Sequential Editing for Lifelong Training of Speech Recognition Models
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) traditionally assumes known domains, but adding data from a new domain raises concerns about computational inefficiencies linked to retraining models on both existing and new domains. Fine-tuning solely on new domain risks Catastrophic Forgetting (CF). To address this, Lifelong Learning (LLL) algorithms have been proposed for ASR. Prior research has explored techniques such as Elastic Weight Consolidation, Knowledge Distillation, and Replay, all of which necessitate either additional parameters or access to prior domain data. We propose Sequential Model Editing as a novel method to continually learn new domains in ASR systems. Different than previous methods, our approach does not necessitate access to prior datasets or the introduction of extra parameters. Our study demonstrates up to 15% Word Error Rate Reduction (WERR) over fine-tuning baseline, and superior efficiency over other LLL techniques on CommonVoice English multi-accent dataset.
Retrieve and Copy: Scaling ASR Personalization to Large Catalogs
Nov 14, 2023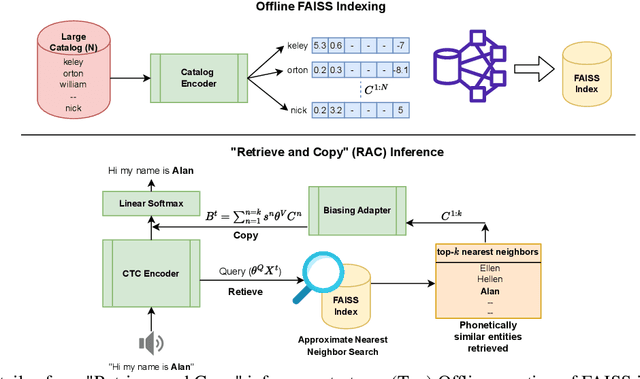

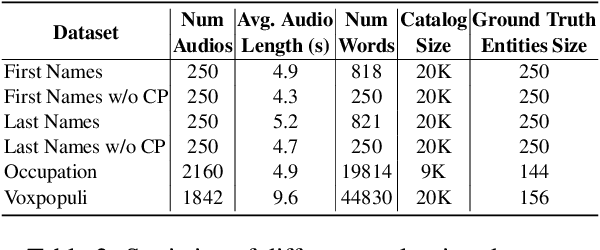
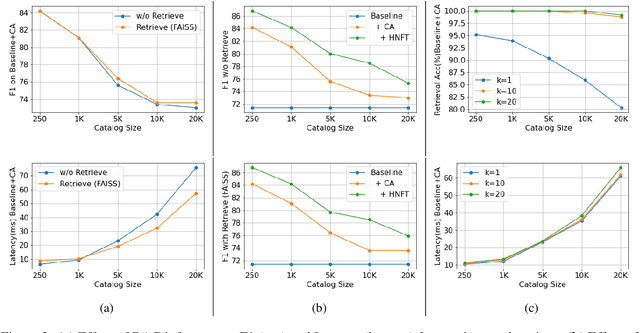
Abstract:Personalization of automatic speech recognition (ASR) models is a widely studied topic because of its many practical applications. Most recently, attention-based contextual biasing techniques are used to improve the recognition of rare words and domain specific entities. However, due to performance constraints, the biasing is often limited to a few thousand entities, restricting real-world usability. To address this, we first propose a "Retrieve and Copy" mechanism to improve latency while retaining the accuracy even when scaled to a large catalog. We also propose a training strategy to overcome the degradation in recall at such scale due to an increased number of confusing entities. Overall, our approach achieves up to 6% more Word Error Rate reduction (WERR) and 3.6% absolute improvement in F1 when compared to a strong baseline. Our method also allows for large catalog sizes of up to 20K without significantly affecting WER and F1-scores, while achieving at least 20% inference speedup per acoustic frame.
Generalized zero-shot audio-to-intent classification
Nov 04, 2023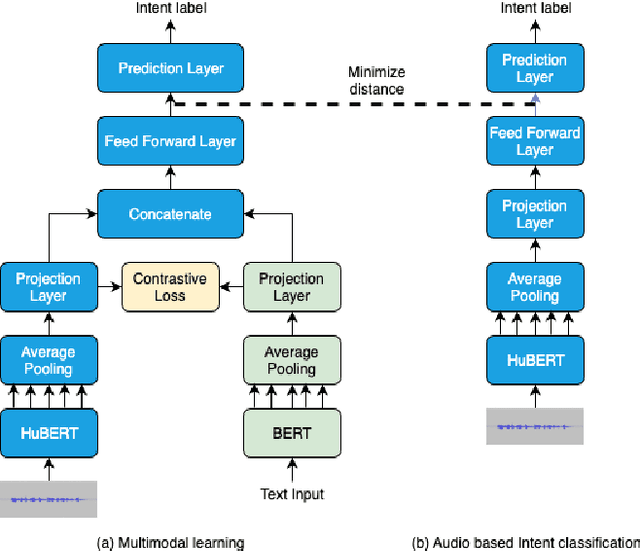
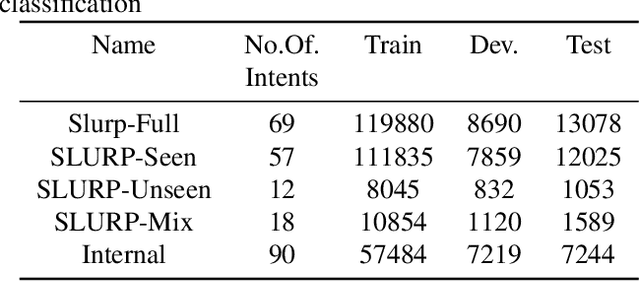
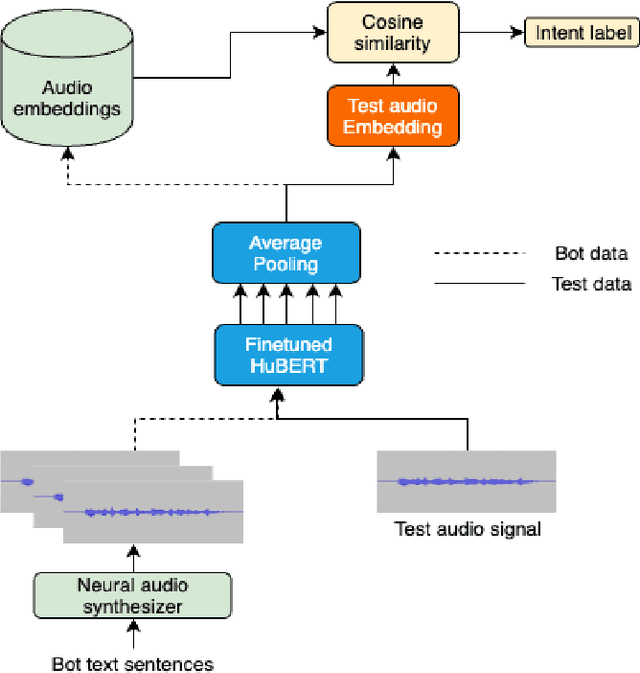
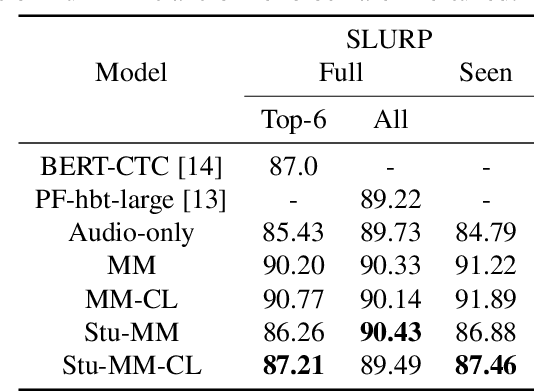
Abstract:Spoken language understanding systems using audio-only data are gaining popularity, yet their ability to handle unseen intents remains limited. In this study, we propose a generalized zero-shot audio-to-intent classification framework with only a few sample text sentences per intent. To achieve this, we first train a supervised audio-to-intent classifier by making use of a self-supervised pre-trained model. We then leverage a neural audio synthesizer to create audio embeddings for sample text utterances and perform generalized zero-shot classification on unseen intents using cosine similarity. We also propose a multimodal training strategy that incorporates lexical information into the audio representation to improve zero-shot performance. Our multimodal training approach improves the accuracy of zero-shot intent classification on unseen intents of SLURP by 2.75% and 18.2% for the SLURP and internal goal-oriented dialog datasets, respectively, compared to audio-only training.
Multilingual Contextual Adapters To Improve Custom Word Recognition In Low-resource Languages
Jul 03, 2023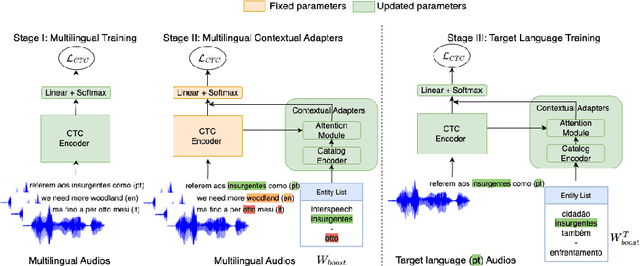


Abstract:Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) models are popular for their balance between speed and performance for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). However, these CTC models still struggle in other areas, such as personalization towards custom words. A recent approach explores Contextual Adapters, wherein an attention-based biasing model for CTC is used to improve the recognition of custom entities. While this approach works well with enough data, we showcase that it isn't an effective strategy for low-resource languages. In this work, we propose a supervision loss for smoother training of the Contextual Adapters. Further, we explore a multilingual strategy to improve performance with limited training data. Our method achieves 48% F1 improvement in retrieving unseen custom entities for a low-resource language. Interestingly, as a by-product of training the Contextual Adapters, we see a 5-11% Word Error Rate (WER) reduction in the performance of the base CTC model as well.
Mask The Bias: Improving Domain-Adaptive Generalization of CTC-based ASR with Internal Language Model Estimation
May 05, 2023
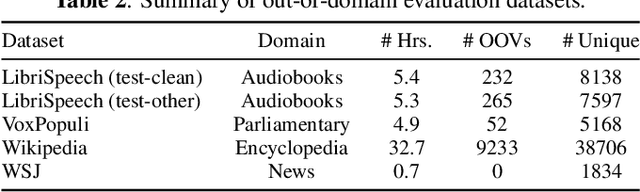
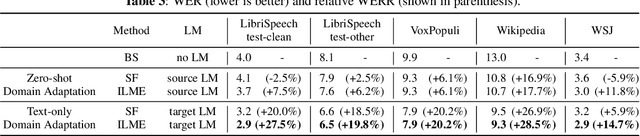
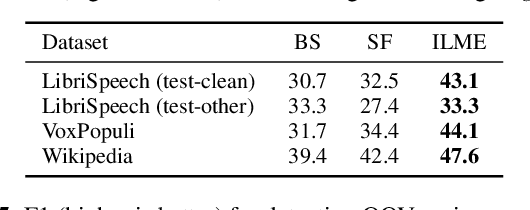
Abstract:End-to-end ASR models trained on large amount of data tend to be implicitly biased towards language semantics of the training data. Internal language model estimation (ILME) has been proposed to mitigate this bias for autoregressive models such as attention-based encoder-decoder and RNN-T. Typically, ILME is performed by modularizing the acoustic and language components of the model architecture, and eliminating the acoustic input to perform log-linear interpolation with the text-only posterior. However, for CTC-based ASR, it is not as straightforward to decouple the model into such acoustic and language components, as CTC log-posteriors are computed in a non-autoregressive manner. In this work, we propose a novel ILME technique for CTC-based ASR models. Our method iteratively masks the audio timesteps to estimate a pseudo log-likelihood of the internal LM by accumulating log-posteriors for only the masked timesteps. Extensive evaluation across multiple out-of-domain datasets reveals that the proposed approach improves WER by up to 9.8% and OOV F1-score by up to 24.6% relative to Shallow Fusion, when only text data from target domain is available. In the case of zero-shot domain adaptation, with no access to any target domain data, we demonstrate that removing the source domain bias with ILME can still outperform Shallow Fusion to improve WER by up to 9.3% relative.
Few-shot Question Generation for Personalized Feedback in Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Jun 08, 2022



Abstract:Existing work on generating hints in Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) focuses mostly on manual and non-personalized feedback. In this work, we explore automatically generated questions as personalized feedback in an ITS. Our personalized feedback can pinpoint correct and incorrect or missing phrases in student answers as well as guide them towards correct answer by asking a question in natural language. Our approach combines cause-effect analysis to break down student answers using text similarity-based NLP Transformer models to identify correct and incorrect or missing parts. We train a few-shot Neural Question Generation and Question Re-ranking models to show questions addressing components missing in the student answers which steers students towards the correct answer. Our model vastly outperforms both simple and strong baselines in terms of student learning gains by 45% and 23% respectively when tested in a real dialogue-based ITS. Finally, we show that our personalized corrective feedback system has the potential to improve Generative Question Answering systems.
Back-Training excels Self-Training at Unsupervised Domain Adaptation of Question Generation and Passage Retrieval
Apr 18, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new domain adaptation method called $\textit{back-training}$, a superior alternative to self-training. While self-training results in synthetic training data of the form quality inputs aligned with noisy outputs, back-training results in noisy inputs aligned with quality outputs. Our experimental results on unsupervised domain adaptation of question generation and passage retrieval models from $\textit{Natural Questions}$ domain to the machine learning domain show that back-training outperforms self-training by a large margin: 9.3 BLEU-1 points on generation, and 7.9 accuracy points on top-1 retrieval. We release $\textit{MLQuestions}$, a domain-adaptation dataset for the machine learning domain containing 50K unaligned passages and 35K unaligned questions, and 3K aligned passage and question pairs. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/McGill-NLP/MLQuestions
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge