Robert Belfer
Raising Student Completion Rates with Adaptive Curriculum and Contextual Bandits
Jul 28, 2022Abstract:We present an adaptive learning Intelligent Tutoring System, which uses model-based reinforcement learning in the form of contextual bandits to assign learning activities to students. The model is trained on the trajectories of thousands of students in order to maximize their exercise completion rates and continues to learn online, automatically adjusting itself to new activities. A randomized controlled trial with students shows that our model leads to superior completion rates and significantly improved student engagement when compared to other approaches. Our approach is fully-automated unlocking new opportunities for learning experience personalization.
Few-shot Question Generation for Personalized Feedback in Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Jun 08, 2022



Abstract:Existing work on generating hints in Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) focuses mostly on manual and non-personalized feedback. In this work, we explore automatically generated questions as personalized feedback in an ITS. Our personalized feedback can pinpoint correct and incorrect or missing phrases in student answers as well as guide them towards correct answer by asking a question in natural language. Our approach combines cause-effect analysis to break down student answers using text similarity-based NLP Transformer models to identify correct and incorrect or missing parts. We train a few-shot Neural Question Generation and Question Re-ranking models to show questions addressing components missing in the student answers which steers students towards the correct answer. Our model vastly outperforms both simple and strong baselines in terms of student learning gains by 45% and 23% respectively when tested in a real dialogue-based ITS. Finally, we show that our personalized corrective feedback system has the potential to improve Generative Question Answering systems.
A New Era: Intelligent Tutoring Systems Will Transform Online Learning for Millions
Mar 03, 2022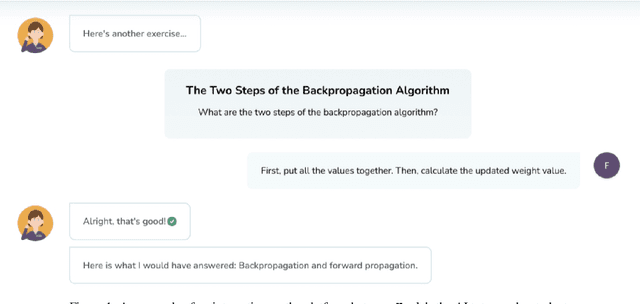
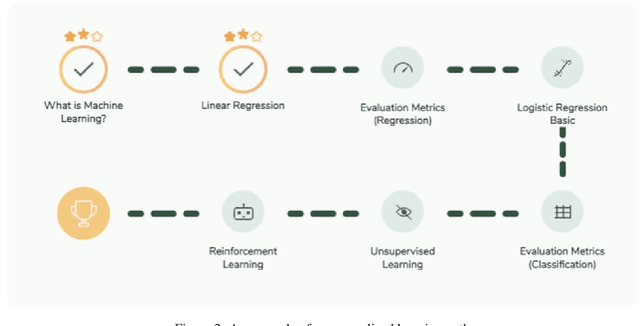
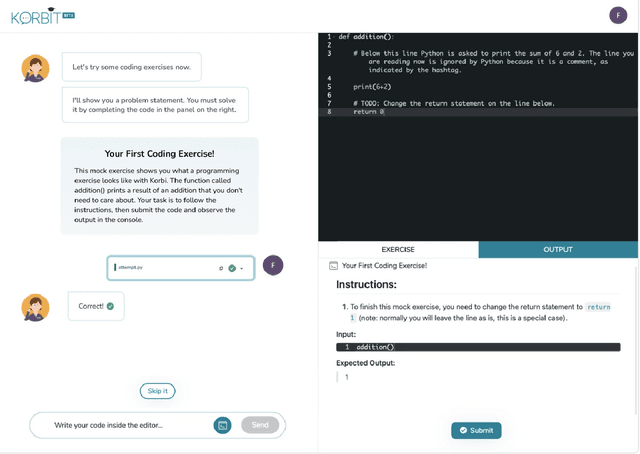
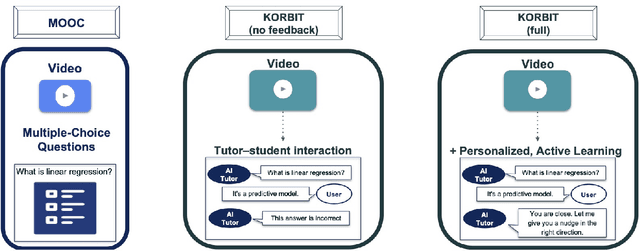
Abstract:Despite artificial intelligence (AI) having transformed major aspects of our society, less than a fraction of its potential has been explored, let alone deployed, for education. AI-powered learning can provide millions of learners with a highly personalized, active and practical learning experience, which is key to successful learning. This is especially relevant in the context of online learning platforms. In this paper, we present the results of a comparative head-to-head study on learning outcomes for two popular online learning platforms (n=199 participants): A MOOC platform following a traditional model delivering content using lecture videos and multiple-choice quizzes, and the Korbit learning platform providing a highly personalized, active and practical learning experience. We observe a huge and statistically significant increase in the learning outcomes, with students on the Korbit platform providing full feedback resulting in higher course completion rates and achieving learning gains 2 to 2.5 times higher than both students on the MOOC platform and students in a control group who don't receive personalized feedback on the Korbit platform. The results demonstrate the tremendous impact that can be achieved with a personalized, active learning AI-powered system. Making this technology and learning experience available to millions of learners around the world will represent a significant leap forward towards the democratization of education.
Back-Training excels Self-Training at Unsupervised Domain Adaptation of Question Generation and Passage Retrieval
Apr 18, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new domain adaptation method called $\textit{back-training}$, a superior alternative to self-training. While self-training results in synthetic training data of the form quality inputs aligned with noisy outputs, back-training results in noisy inputs aligned with quality outputs. Our experimental results on unsupervised domain adaptation of question generation and passage retrieval models from $\textit{Natural Questions}$ domain to the machine learning domain show that back-training outperforms self-training by a large margin: 9.3 BLEU-1 points on generation, and 7.9 accuracy points on top-1 retrieval. We release $\textit{MLQuestions}$, a domain-adaptation dataset for the machine learning domain containing 50K unaligned passages and 35K unaligned questions, and 3K aligned passage and question pairs. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/McGill-NLP/MLQuestions
Comparative Study of Learning Outcomes for Online Learning Platforms
Apr 15, 2021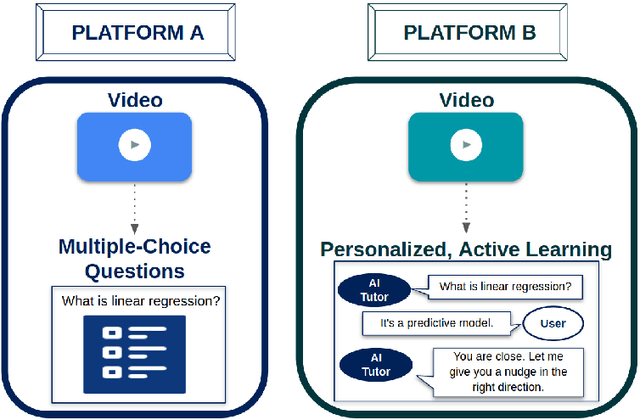
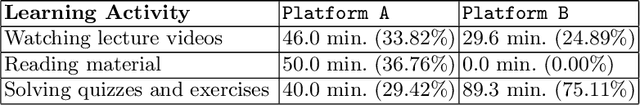
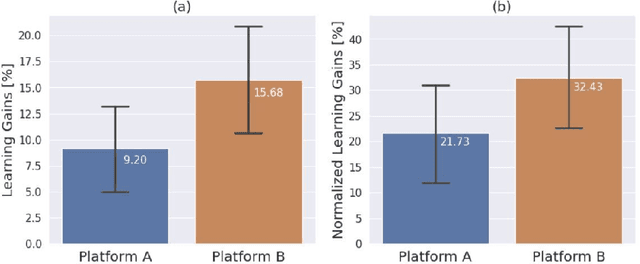
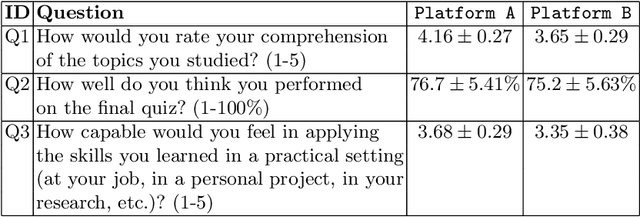
Abstract:Personalization and active learning are key aspects to successful learning. These aspects are important to address in intelligent educational applications, as they help systems to adapt and close the gap between students with varying abilities, which becomes increasingly important in the context of online and distance learning. We run a comparative head-to-head study of learning outcomes for two popular online learning platforms: Platform A, which follows a traditional model delivering content over a series of lecture videos and multiple-choice quizzes, and Platform B, which creates a personalized learning environment and provides problem-solving exercises and personalized feedback. We report on the results of our study using pre- and post-assessment quizzes with participants taking courses on an introductory data science topic on two platforms. We observe a statistically significant increase in the learning outcomes on Platform B, highlighting the impact of well-designed and well-engineered technology supporting active learning and problem-based learning in online education. Moreover, the results of the self-assessment questionnaire, where participants reported on perceived learning gains, suggest that participants using Platform B improve their metacognition.
Deep Discourse Analysis for Generating Personalized Feedback in Intelligent Tutor Systems
Mar 13, 2021
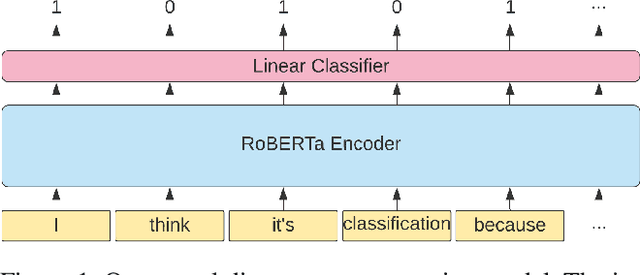
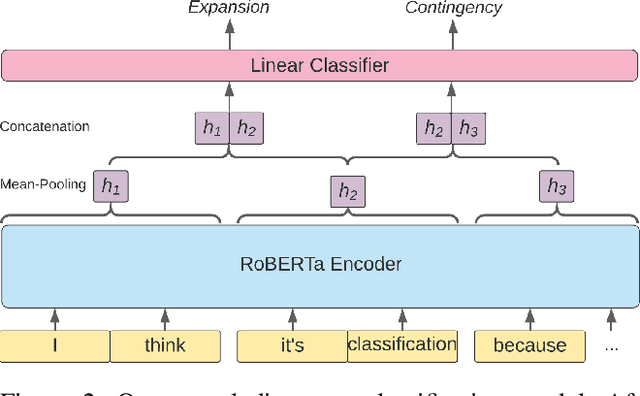
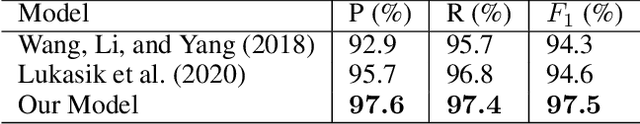
Abstract:We explore creating automated, personalized feedback in an intelligent tutoring system (ITS). Our goal is to pinpoint correct and incorrect concepts in student answers in order to achieve better student learning gains. Although automatic methods for providing personalized feedback exist, they do not explicitly inform students about which concepts in their answers are correct or incorrect. Our approach involves decomposing students answers using neural discourse segmentation and classification techniques. This decomposition yields a relational graph over all discourse units covered by the reference solutions and student answers. We use this inferred relational graph structure and a neural classifier to match student answers with reference solutions and generate personalized feedback. Although the process is completely automated and data-driven, the personalized feedback generated is highly contextual, domain-aware and effectively targets each student's misconceptions and knowledge gaps. We test our method in a dialogue-based ITS and demonstrate that our approach results in high-quality feedback and significantly improved student learning gains.
Automated Personalized Feedback Improves Learning Gains in an Intelligent Tutoring System
May 07, 2020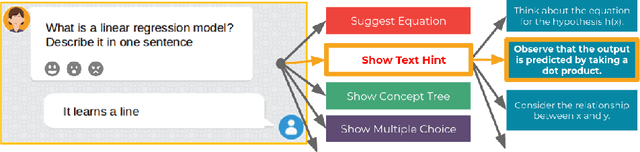
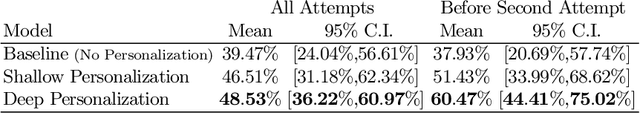
Abstract:We investigate how automated, data-driven, personalized feedback in a large-scale intelligent tutoring system (ITS) improves student learning outcomes. We propose a machine learning approach to generate personalized feedback, which takes individual needs of students into account. We utilize state-of-the-art machine learning and natural language processing techniques to provide the students with personalized hints, Wikipedia-based explanations, and mathematical hints. Our model is used in Korbit, a large-scale dialogue-based ITS with thousands of students launched in 2019, and we demonstrate that the personalized feedback leads to considerable improvement in student learning outcomes and in the subjective evaluation of the feedback.
A Large-Scale, Open-Domain, Mixed-Interface Dialogue-Based ITS for STEM
May 06, 2020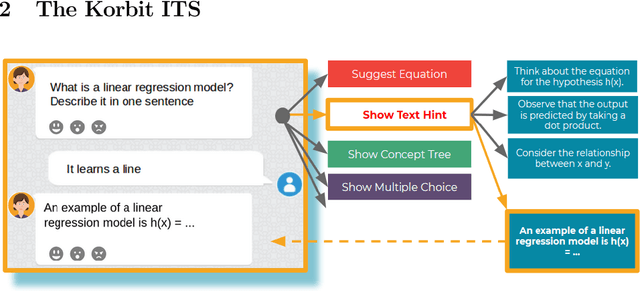
Abstract:We present Korbit, a large-scale, open-domain, mixed-interface, dialogue-based intelligent tutoring system (ITS). Korbit uses machine learning, natural language processing and reinforcement learning to provide interactive, personalized learning online. Korbit has been designed to easily scale to thousands of subjects, by automating, standardizing and simplifying the content creation process. Unlike other ITS, a teacher can develop new learning modules for Korbit in a matter of hours. To facilitate learning across a widerange of STEM subjects, Korbit uses a mixed-interface, which includes videos, interactive dialogue-based exercises, question-answering, conceptual diagrams, mathematical exercises and gamification elements. Korbit has been built to scale to millions of students, by utilizing a state-of-the-art cloud-based micro-service architecture. Korbit launched its first course in 2019 on machine learning, and since then over 7,000 students have enrolled. Although Korbit was designed to be open-domain and highly scalable, A/B testing experiments with real-world students demonstrate that both student learning outcomes and student motivation are substantially improved compared to typical online courses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge