Xinyu Xu
PhysSFI-Net: Physics-informed Geometric Learning of Skeletal and Facial Interactions for Orthognathic Surgical Outcome Prediction
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Orthognathic surgery repositions jaw bones to restore occlusion and enhance facial aesthetics. Accurate simulation of postoperative facial morphology is essential for preoperative planning. However, traditional biomechanical models are computationally expensive, while geometric deep learning approaches often lack interpretability. In this study, we develop and validate a physics-informed geometric deep learning framework named PhysSFI-Net for precise prediction of soft tissue deformation following orthognathic surgery. PhysSFI-Net consists of three components: a hierarchical graph module with craniofacial and surgical plan encoders combined with attention mechanisms to extract skeletal-facial interaction features; a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-based sequential predictor for incremental soft tissue deformation; and a biomechanics-inspired module for high-resolution facial surface reconstruction. Model performance was assessed using point cloud shape error (Hausdorff distance), surface deviation error, and landmark localization error (Euclidean distances of craniomaxillofacial landmarks) between predicted facial shapes and corresponding ground truths. A total of 135 patients who underwent combined orthodontic and orthognathic treatment were included for model training and validation. Quantitative analysis demonstrated that PhysSFI-Net achieved a point cloud shape error of 1.070 +/- 0.088 mm, a surface deviation error of 1.296 +/- 0.349 mm, and a landmark localization error of 2.445 +/- 1.326 mm. Comparative experiments indicated that PhysSFI-Net outperformed the state-of-the-art method ACMT-Net in prediction accuracy. In conclusion, PhysSFI-Net enables interpretable, high-resolution prediction of postoperative facial morphology with superior accuracy, showing strong potential for clinical application in orthognathic surgical planning and simulation.
Rotation Perturbation Robustness in Point Cloud Analysis: A Perspective of Manifold Distillation
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:Point cloud is often regarded as a discrete sampling of Riemannian manifold and plays a pivotal role in the 3D image interpretation. Particularly, rotation perturbation, an unexpected small change in rotation caused by various factors (like equipment offset, system instability, measurement errors and so on), can easily lead to the inferior results in point cloud learning tasks. However, classical point cloud learning methods are sensitive to rotation perturbation, and the existing networks with rotation robustness also have much room for improvements in terms of performance and noise tolerance. Given these, this paper remodels the point cloud from the perspective of manifold as well as designs a manifold distillation method to achieve the robustness of rotation perturbation without any coordinate transformation. In brief, during the training phase, we introduce a teacher network to learn the rotation robustness information and transfer this information to the student network through online distillation. In the inference phase, the student network directly utilizes the original 3D coordinate information to achieve the robustness of rotation perturbation. Experiments carried out on four different datasets verify the effectiveness of our method. Averagely, on the Modelnet40 and ScanobjectNN classification datasets with random rotation perturbations, our classification accuracy has respectively improved by 4.92% and 4.41%, compared to popular rotation-robust networks; on the ShapeNet and S3DIS segmentation datasets, compared to the rotation-robust networks, the improvements of mIoU are 7.36% and 4.82%, respectively. Besides, from the experimental results, the proposed algorithm also shows excellent performance in resisting noise and outliers.
PreCM: The Padding-based Rotation Equivariant Convolution Mode for Semantic Segmentation
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Semantic segmentation is an important branch of image processing and computer vision. With the popularity of deep learning, various deep semantic segmentation networks have been proposed for pixel-level classification and segmentation tasks. However, the imaging angles are often arbitrary in real world, such as water body images in remote sensing, and capillary and polyp images in medical field, and we usually cannot obtain prior orientation information to guide these networks to extract more effective features. Additionally, learning the features of objects with multiple orientation information is also challenging, as most CNN-based semantic segmentation networks do not have rotation equivariance to resist the disturbance from orientation information. To address the same, in this paper, we first establish a universal convolution-group framework to more fully utilize the orientation information and make the networks rotation equivariant. Then, we mathematically construct the padding-based rotation equivariant convolution mode (PreCM), which can be used not only for multi-scale images and convolution kernels, but also as a replacement component to replace multiple convolutions, like dilated convolution, transposed convolution, variable stride convolution, etc. In order to verify the realization of rotation equivariance, a new evaluation metric named rotation difference (RD) is finally proposed. The experiments carried out on the datesets Satellite Images of Water Bodies, DRIVE and Floodnet show that the PreCM-based networks can achieve better segmentation performance than the original and data augmentation-based networks. In terms of the average RD value, the former is 0% and the latter two are respectively 7.0503% and 3.2606%. Last but not least, PreCM also effectively enhances the robustness of networks to rotation perturbations.
DISCO: Embodied Navigation and Interaction via Differentiable Scene Semantics and Dual-level Control
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:Building a general-purpose intelligent home-assistant agent skilled in diverse tasks by human commands is a long-term blueprint of embodied AI research, which poses requirements on task planning, environment modeling, and object interaction. In this work, we study primitive mobile manipulations for embodied agents, i.e. how to navigate and interact based on an instructed verb-noun pair. We propose DISCO, which features non-trivial advancements in contextualized scene modeling and efficient controls. In particular, DISCO incorporates differentiable scene representations of rich semantics in object and affordance, which is dynamically learned on the fly and facilitates navigation planning. Besides, we propose dual-level coarse-to-fine action controls leveraging both global and local cues to accomplish mobile manipulation tasks efficiently. DISCO easily integrates into embodied tasks such as embodied instruction following. To validate our approach, we take the ALFRED benchmark of large-scale long-horizon vision-language navigation and interaction tasks as a test bed. In extensive experiments, we make comprehensive evaluations and demonstrate that DISCO outperforms the art by a sizable +8.6% success rate margin in unseen scenes, even without step-by-step instructions. Our code is publicly released at https://github.com/AllenXuuu/DISCO.
A Secure and Efficient Distributed Semantic Communication System for Heterogeneous Internet of Things Devices
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:Semantic communications have emerged as a promising solution to address the challenge of efficient communication in rapidly evolving and increasingly complex Internet of Things (IoT) networks. However, protecting the security of semantic communication systems within the distributed and heterogeneous IoT networks is critical issues that need to be addressed. We develop a secure and efficient distributed semantic communication system in IoT scenarios, focusing on three aspects: secure system maintenance, efficient system update, and privacy-preserving system usage. Firstly, we propose a blockchain-based interaction framework that ensures the integrity, authentication, and availability of interactions among IoT devices to securely maintain system. This framework includes a novel digital signature verification mechanism designed for semantic communications, enabling secure and efficient interactions with semantic communications. Secondly, to improve the efficiency of interactions, we develop a flexible semantic communication scheme that leverages compressed semantic knowledge bases. This scheme reduces the data exchange required for system update and is adapt to dynamic task requirements and the diversity of device capabilities. Thirdly, we exploit the integration of differential privacy into semantic communications. We analyze the implementation of differential privacy taking into account the lossy nature of semantic communications and wireless channel distortions. An joint model-channel noise mechanism is introduced to achieve differential privacy preservation in semantic communications without compromising the system's functionality. Experiments show that the system is able to achieve integrity, availability, efficiency and the preservation of privacy.
HumanVLA: Towards Vision-Language Directed Object Rearrangement by Physical Humanoid
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:Physical Human-Scene Interaction (HSI) plays a crucial role in numerous applications. However, existing HSI techniques are limited to specific object dynamics and privileged information, which prevents the development of more comprehensive applications. To address this limitation, we introduce HumanVLA for general object rearrangement directed by practical vision and language. A teacher-student framework is utilized to develop HumanVLA. A state-based teacher policy is trained first using goal-conditioned reinforcement learning and adversarial motion prior. Then, it is distilled into a vision-language-action model via behavior cloning. We propose several key insights to facilitate the large-scale learning process. To support general object rearrangement by physical humanoid, we introduce a novel Human-in-the-Room dataset encompassing various rearrangement tasks. Through extensive experiments and analysis, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Beyond Object Recognition: A New Benchmark towards Object Concept Learning
Dec 06, 2022



Abstract:Understanding objects is a central building block of artificial intelligence, especially for embodied AI. Even though object recognition excels with deep learning, current machines still struggle to learn higher-level knowledge, e.g., what attributes an object has, and what can we do with an object. In this work, we propose a challenging Object Concept Learning (OCL) task to push the envelope of object understanding. It requires machines to reason out object affordances and simultaneously give the reason: what attributes make an object possesses these affordances. To support OCL, we build a densely annotated knowledge base including extensive labels for three levels of object concept (category, attribute, affordance), and the causal relations of three levels. By analyzing the causal structure of OCL, we present a baseline, Object Concept Reasoning Network (OCRN). It leverages causal intervention and concept instantiation to infer the three levels following their causal relations. In experiments, OCRN effectively infers the object knowledge while following the causalities well. Our data and code are available at https://mvig-rhos.com/ocl.
PAI3D: Painting Adaptive Instance-Prior for 3D Object Detection
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:3D object detection is a critical task in autonomous driving. Recently multi-modal fusion-based 3D object detection methods, which combine the complementary advantages of LiDAR and camera, have shown great performance improvements over mono-modal methods. However, so far, no methods have attempted to utilize the instance-level contextual image semantics to guide the 3D object detection. In this paper, we propose a simple and effective Painting Adaptive Instance-prior for 3D object detection (PAI3D) to fuse instance-level image semantics flexibly with point cloud features. PAI3D is a multi-modal sequential instance-level fusion framework. It first extracts instance-level semantic information from images, the extracted information, including objects categorical label, point-to-object membership and object position, are then used to augment each LiDAR point in the subsequent 3D detection network to guide and improve detection performance. PAI3D outperforms the state-of-the-art with a large margin on the nuScenes dataset, achieving 71.4 in mAP and 74.2 in NDS on the test split. Our comprehensive experiments show that instance-level image semantics contribute the most to the performance gain, and PAI3D works well with any good-quality instance segmentation models and any modern point cloud 3D encoders, making it a strong candidate for deployment on autonomous vehicles.
Learning to Anticipate Future with Dynamic Context Removal
Apr 06, 2022



Abstract:Anticipating future events is an essential feature for intelligent systems and embodied AI. However, compared to the traditional recognition task, the uncertainty of future and reasoning ability requirement make the anticipation task very challenging and far beyond solved. In this filed, previous methods usually care more about the model architecture design or but few attention has been put on how to train an anticipation model with a proper learning policy. To this end, in this work, we propose a novel training scheme called Dynamic Context Removal (DCR), which dynamically schedules the visibility of observed future in the learning procedure. It follows the human-like curriculum learning process, i.e., gradually removing the event context to increase the anticipation difficulty till satisfying the final anticipation target. Our learning scheme is plug-and-play and easy to integrate any reasoning model including transformer and LSTM, with advantages in both effectiveness and efficiency. In extensive experiments, the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art on four widely-used benchmarks. Our code and models are publicly released at https://github.com/AllenXuuu/DCR.
Learning Single/Multi-Attribute of Object with Symmetry and Group
Oct 09, 2021
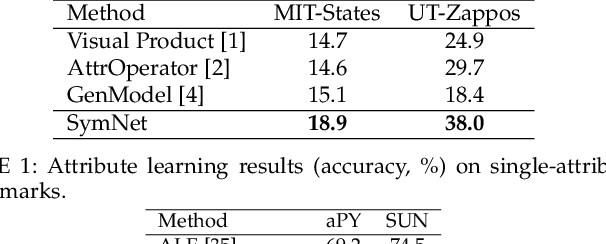
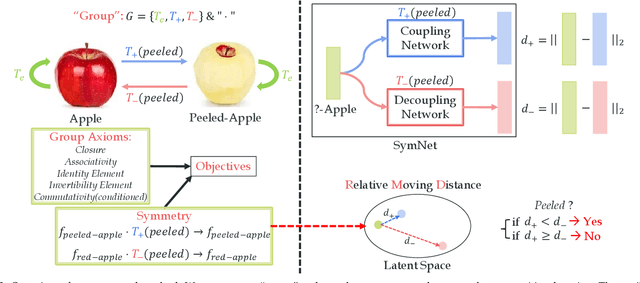

Abstract:Attributes and objects can compose diverse compositions. To model the compositional nature of these concepts, it is a good choice to learn them as transformations, e.g., coupling and decoupling. However, complex transformations need to satisfy specific principles to guarantee rationality. Here, we first propose a previously ignored principle of attribute-object transformation: Symmetry. For example, coupling peeled-apple with attribute peeled should result in peeled-apple, and decoupling peeled from apple should still output apple. Incorporating the symmetry, we propose a transformation framework inspired by group theory, i.e., SymNet. It consists of two modules: Coupling Network and Decoupling Network. We adopt deep neural networks to implement SymNet and train it in an end-to-end paradigm with the group axioms and symmetry as objectives. Then, we propose a Relative Moving Distance (RMD) based method to utilize the attribute change instead of the attribute pattern itself to classify attributes. Besides the compositions of single-attribute and object, our RMD is also suitable for complex compositions of multiple attributes and objects when incorporating attribute correlations. SymNet can be utilized for attribute learning, compositional zero-shot learning and outperforms the state-of-the-art on four widely-used benchmarks. Code is at https://github.com/DirtyHarryLYL/SymNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge