Zhuoran Xu
Multimodal Integrated Knowledge Transfer to Large Language Models through Preference Optimization with Biomedical Applications
May 09, 2025Abstract:The scarcity of high-quality multimodal biomedical data limits the ability to effectively fine-tune pretrained Large Language Models (LLMs) for specialized biomedical tasks. To address this challenge, we introduce MINT (Multimodal Integrated kNowledge Transfer), a framework that aligns unimodal large decoder models with domain-specific decision patterns from multimodal biomedical data through preference optimization. While MINT supports different optimization techniques, we primarily implement it with the Odds Ratio Preference Optimization (ORPO) framework as its backbone. This strategy enables the aligned LLMs to perform predictive tasks using text-only or image-only inputs while retaining knowledge learnt from multimodal data. MINT leverages an upstream multimodal machine learning (MML) model trained on high-quality multimodal data to transfer domain-specific insights to downstream text-only or image-only LLMs. We demonstrate its effectiveness through two key applications: (1) Rare genetic disease prediction from texts, where MINT uses a multimodal encoder model, trained on facial photos and clinical notes, to generate a preference dataset for aligning a lightweight Llama 3.2-3B-Instruct. Despite relying on text input only, the MINT-derived model outperforms models trained with SFT, RAG, or DPO, and even outperforms Llama 3.1-405B-Instruct. (2) Tissue type classification using cell nucleus images, where MINT uses a vision-language foundation model as the preference generator, containing knowledge learnt from both text and histopathological images to align downstream image-only models. The resulting MINT-derived model significantly improves the performance of Llama 3.2-Vision-11B-Instruct on tissue type classification. In summary, MINT provides an effective strategy to align unimodal LLMs with high-quality multimodal expertise through preference optimization.
HiP-AD: Hierarchical and Multi-Granularity Planning with Deformable Attention for Autonomous Driving in a Single Decoder
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Although end-to-end autonomous driving (E2E-AD) technologies have made significant progress in recent years, there remains an unsatisfactory performance on closed-loop evaluation. The potential of leveraging planning in query design and interaction has not yet been fully explored. In this paper, we introduce a multi-granularity planning query representation that integrates heterogeneous waypoints, including spatial, temporal, and driving-style waypoints across various sampling patterns. It provides additional supervision for trajectory prediction, enhancing precise closed-loop control for the ego vehicle. Additionally, we explicitly utilize the geometric properties of planning trajectories to effectively retrieve relevant image features based on physical locations using deformable attention. By combining these strategies, we propose a novel end-to-end autonomous driving framework, termed HiP-AD, which simultaneously performs perception, prediction, and planning within a unified decoder. HiP-AD enables comprehensive interaction by allowing planning queries to iteratively interact with perception queries in the BEV space while dynamically extracting image features from perspective views. Experiments demonstrate that HiP-AD outperforms all existing end-to-end autonomous driving methods on the closed-loop benchmark Bench2Drive and achieves competitive performance on the real-world dataset nuScenes.
PAI3D: Painting Adaptive Instance-Prior for 3D Object Detection
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:3D object detection is a critical task in autonomous driving. Recently multi-modal fusion-based 3D object detection methods, which combine the complementary advantages of LiDAR and camera, have shown great performance improvements over mono-modal methods. However, so far, no methods have attempted to utilize the instance-level contextual image semantics to guide the 3D object detection. In this paper, we propose a simple and effective Painting Adaptive Instance-prior for 3D object detection (PAI3D) to fuse instance-level image semantics flexibly with point cloud features. PAI3D is a multi-modal sequential instance-level fusion framework. It first extracts instance-level semantic information from images, the extracted information, including objects categorical label, point-to-object membership and object position, are then used to augment each LiDAR point in the subsequent 3D detection network to guide and improve detection performance. PAI3D outperforms the state-of-the-art with a large margin on the nuScenes dataset, achieving 71.4 in mAP and 74.2 in NDS on the test split. Our comprehensive experiments show that instance-level image semantics contribute the most to the performance gain, and PAI3D works well with any good-quality instance segmentation models and any modern point cloud 3D encoders, making it a strong candidate for deployment on autonomous vehicles.
Knowledge accumulating: The general pattern of learning
Aug 09, 2021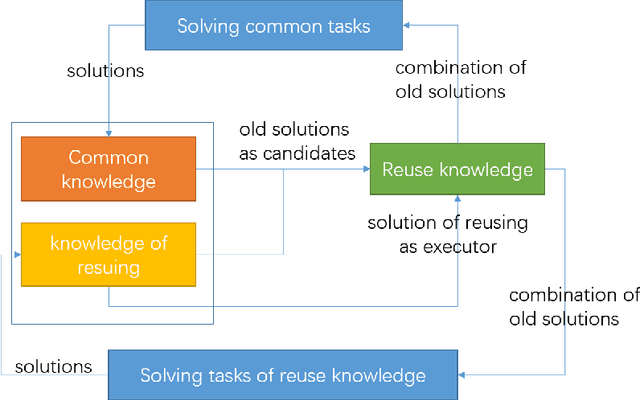
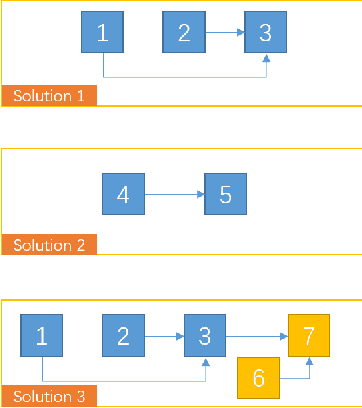
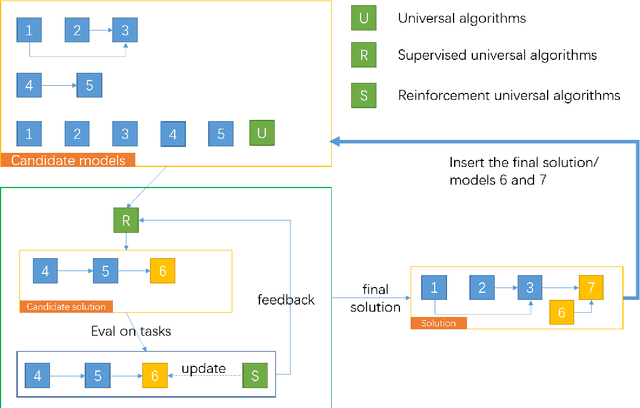
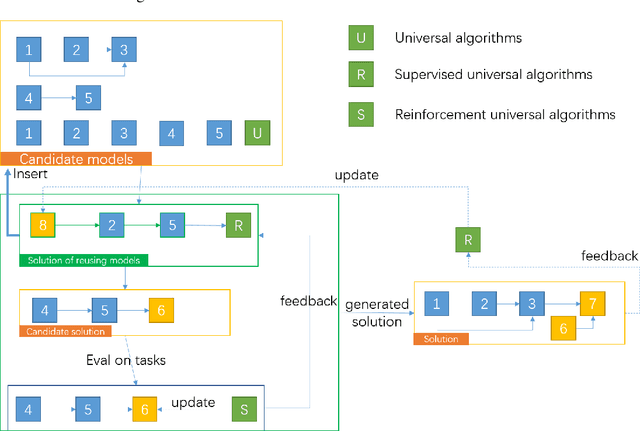
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence has been developed for decades with the achievement of great progress. Recently, deep learning shows its ability to solve many real world problems, e.g. image classification and detection, natural language processing, playing GO. Theoretically speaking, an artificial neural network can fit any function and reinforcement learning can learn from any delayed reward. But in solving real world tasks, we still need to spend a lot of effort to adjust algorithms to fit task unique features. This paper proposes that the reason of this phenomenon is the sparse feedback feature of the nature, and a single algorithm, no matter how we improve it, can only solve dense feedback tasks or specific sparse feedback tasks. This paper first analyses how sparse feedback affects algorithm perfomance, and then proposes a pattern that explains how to accumulate knowledge to solve sparse feedback problems.
Multi-modal Trajectory Prediction for Autonomous Driving with Semantic Map and Dynamic Graph Attention Network
Mar 30, 2021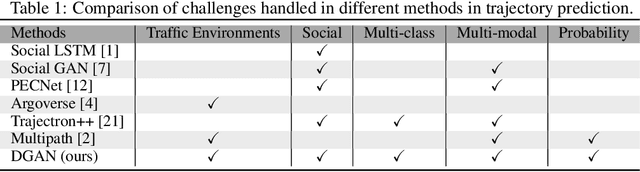
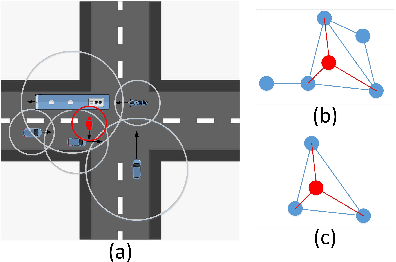
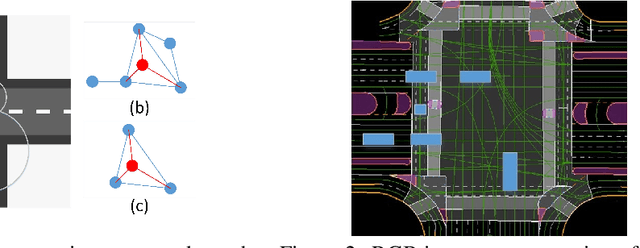
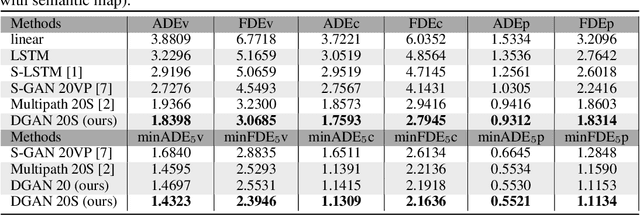
Abstract:Predicting future trajectories of surrounding obstacles is a crucial task for autonomous driving cars to achieve a high degree of road safety. There are several challenges in trajectory prediction in real-world traffic scenarios, including obeying traffic rules, dealing with social interactions, handling traffic of multi-class movement, and predicting multi-modal trajectories with probability. Inspired by people's natural habit of navigating traffic with attention to their goals and surroundings, this paper presents a unique dynamic graph attention network to solve all those challenges. The network is designed to model the dynamic social interactions among agents and conform to traffic rules with a semantic map. By extending the anchor-based method to multiple types of agents, the proposed method can predict multi-modal trajectories with probabilities for multi-class movements using a single model. We validate our approach on the proprietary autonomous driving dataset for the logistic delivery scenario and two publicly available datasets. The results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques and demonstrates the potential for trajectory prediction in real-world traffic.
Directed-Weighting Group Lasso for Eltwise Blocked CNN Pruning
Oct 21, 2019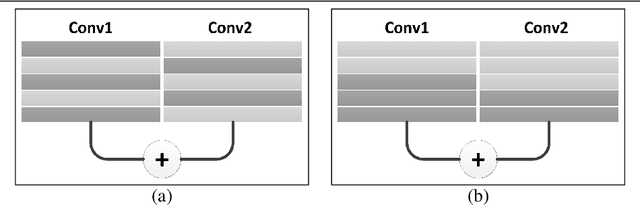
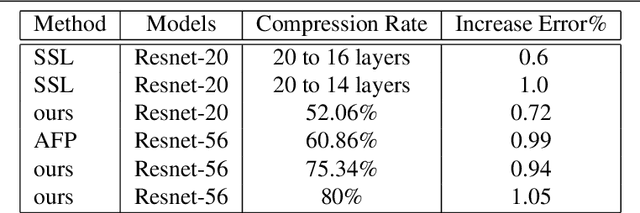
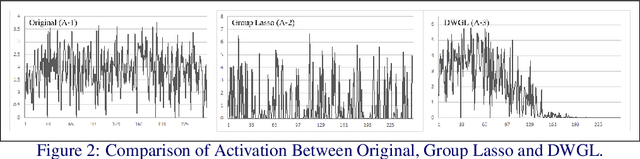
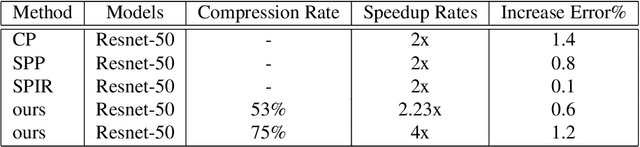
Abstract:Eltwise layer is a commonly used structure in the multi-branch deep learning network. In a filter-wise pruning procedure, due to the specific operation of the eltwise layer, all its previous convolutional layers should vote for which filters by index should be pruned. Since only an intersection of the voted filters is pruned, the compression rate is limited. This work proposes a method called Directed-Weighting Group Lasso (DWGL), which enforces an index-wise incremental (directed) coefficient on the filterlevel group lasso items, so that the low index filters getting high activation tend to be kept while the high index ones tend to be pruned. When using DWGL, much fewer filters are retained during the voting process and the compression rate can be boosted. The paper test the proposed method on the ResNet series networks. On CIFAR-10, it achieved a 75.34% compression rate on ResNet-56 with a 0.94% error increment, and a 52.06% compression rate on ResNet-20 with a 0.72% error increment. On ImageNet, it achieved a 53% compression rate with ResNet-50 with a 0.6% error increment, speeding up the network by 2.23 times. Furthermore, it achieved a 75% compression rate on ResNet-50 with a 1.2% error increment, speeding up the network by 4 times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge