Ke Zhan
Hyperlink-induced Pre-training for Passage Retrieval in Open-domain Question Answering
Apr 12, 2022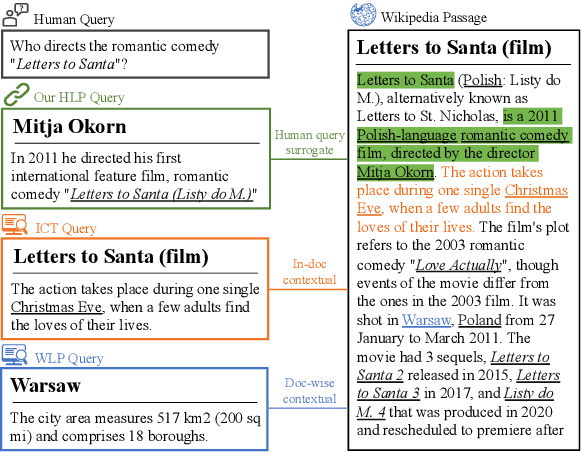

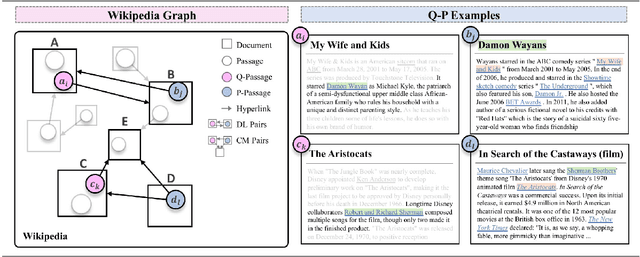

Abstract:To alleviate the data scarcity problem in training question answering systems, recent works propose additional intermediate pre-training for dense passage retrieval (DPR). However, there still remains a large discrepancy between the provided upstream signals and the downstream question-passage relevance, which leads to less improvement. To bridge this gap, we propose the HyperLink-induced Pre-training (HLP), a method to pre-train the dense retriever with the text relevance induced by hyperlink-based topology within Web documents. We demonstrate that the hyperlink-based structures of dual-link and co-mention can provide effective relevance signals for large-scale pre-training that better facilitate downstream passage retrieval. We investigate the effectiveness of our approach across a wide range of open-domain QA datasets under zero-shot, few-shot, multi-hop, and out-of-domain scenarios. The experiments show our HLP outperforms the BM25 by up to 7 points as well as other pre-training methods by more than 10 points in terms of top-20 retrieval accuracy under the zero-shot scenario. Furthermore, HLP significantly outperforms other pre-training methods under the other scenarios.
Towards More Effective and Economic Sparsely-Activated Model
Oct 14, 2021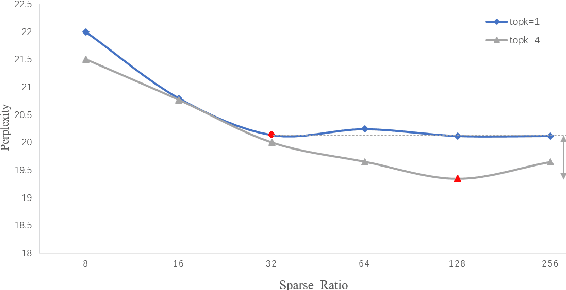
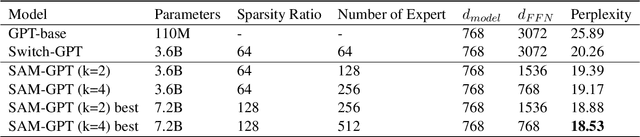
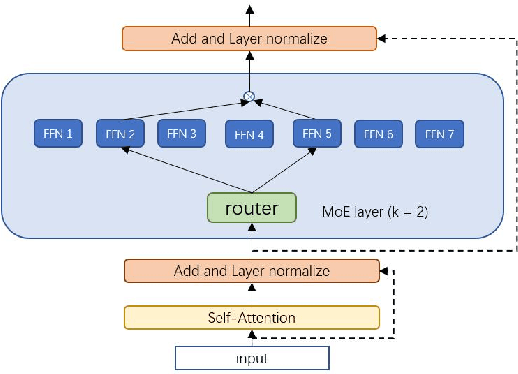
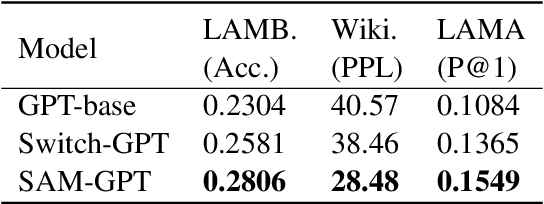
Abstract:The sparsely-activated models have achieved great success in natural language processing through large-scale parameters and relatively low computational cost, and gradually become a feasible technique for training and implementing extremely large models. Due to the limit of communication cost, activating multiple experts is hardly affordable during training and inference. Therefore, previous work usually activate just one expert at a time to alleviate additional communication cost. Such routing mechanism limits the upper bound of model performance. In this paper, we first investigate a phenomenon that increasing the number of activated experts can boost the model performance with higher sparse ratio. To increase the number of activated experts without an increase in computational cost, we propose SAM (Switch and Mixture) routing, an efficient hierarchical routing mechanism that activates multiple experts in a same device (GPU). Our methods shed light on the training of extremely large sparse models and experiments prove that our models can achieve significant performance gain with great efficiency improvement.
Directed-Weighting Group Lasso for Eltwise Blocked CNN Pruning
Oct 21, 2019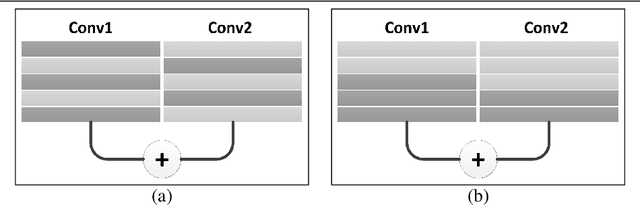
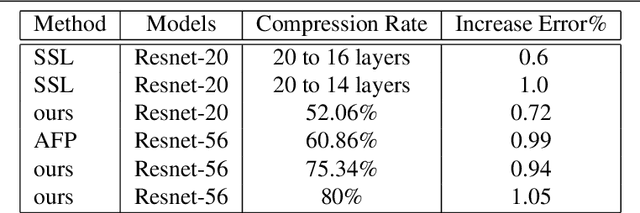
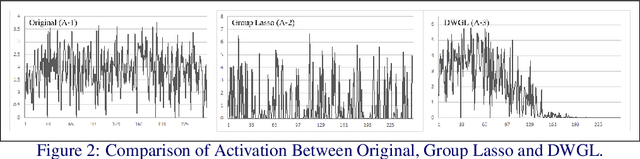
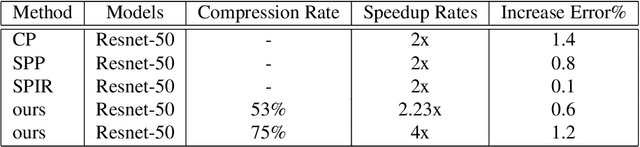
Abstract:Eltwise layer is a commonly used structure in the multi-branch deep learning network. In a filter-wise pruning procedure, due to the specific operation of the eltwise layer, all its previous convolutional layers should vote for which filters by index should be pruned. Since only an intersection of the voted filters is pruned, the compression rate is limited. This work proposes a method called Directed-Weighting Group Lasso (DWGL), which enforces an index-wise incremental (directed) coefficient on the filterlevel group lasso items, so that the low index filters getting high activation tend to be kept while the high index ones tend to be pruned. When using DWGL, much fewer filters are retained during the voting process and the compression rate can be boosted. The paper test the proposed method on the ResNet series networks. On CIFAR-10, it achieved a 75.34% compression rate on ResNet-56 with a 0.94% error increment, and a 52.06% compression rate on ResNet-20 with a 0.72% error increment. On ImageNet, it achieved a 53% compression rate with ResNet-50 with a 0.6% error increment, speeding up the network by 2.23 times. Furthermore, it achieved a 75% compression rate on ResNet-50 with a 1.2% error increment, speeding up the network by 4 times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge