Xinyu Wu
ProAct: A Benchmark and Multimodal Framework for Structure-Aware Proactive Response
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While passive agents merely follow instructions, proactive agents align with higher-level objectives, such as assistance and safety by continuously monitoring the environment to determine when and how to act. However, developing proactive agents is hindered by the lack of specialized resources. To address this, we introduce ProAct-75, a benchmark designed to train and evaluate proactive agents across diverse domains, including assistance, maintenance, and safety monitoring. Spanning 75 tasks, our dataset features 91,581 step-level annotations enriched with explicit task graphs. These graphs encode step dependencies and parallel execution possibilities, providing the structural grounding necessary for complex decision-making. Building on this benchmark, we propose ProAct-Helper, a reference baseline powered by a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that grounds decision-making in state detection, and leveraging task graphs to enable entropy-driven heuristic search for action selection, allowing agents to execute parallel threads independently rather than mirroring the human's next step. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ProAct-Helper outperforms strong closed-source models, improving trigger detection mF1 by 6.21%, saving 0.25 more steps in online one-step decision, and increasing the rate of parallel actions by 15.58%.
ESearch-R1: Learning Cost-Aware MLLM Agents for Interactive Embodied Search via Reinforcement Learning
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have empowered embodied agents with remarkable capabilities in planning and reasoning. However, when facing ambiguous natural language instructions (e.g., "fetch the tool" in a cluttered room), current agents often fail to balance the high cost of physical exploration against the cognitive cost of human interaction. They typically treat disambiguation as a passive perception problem, lacking the strategic reasoning to minimize total task execution costs. To bridge this gap, we propose ESearch-R1, a cost-aware embodied reasoning framework that unifies interactive dialogue (Ask), episodic memory retrieval (GetMemory), and physical navigation (Navigate) into a single decision process. We introduce HC-GRPO (Heterogeneous Cost-Aware Group Relative Policy Optimization). Unlike traditional PPO which relies on a separate value critic, HC-GRPO optimizes the MLLM by sampling groups of reasoning trajectories and reinforcing those that achieve the optimal trade-off between information gain and heterogeneous costs (e.g., navigate time, and human attention). Extensive experiments in AI2-THOR demonstrate that ESearch-R1 significantly outperforms standard ReAct-based agents. It improves task success rates while reducing total operational costs by approximately 50\%, validating the effectiveness of GRPO in aligning MLLM agents with physical world constraints.
GraspView: Active Perception Scoring and Best-View Optimization for Robotic Grasping in Cluttered Environments
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Robotic grasping is a fundamental capability for autonomous manipulation, yet remains highly challenging in cluttered environments where occlusion, poor perception quality, and inconsistent 3D reconstructions often lead to unstable or failed grasps. Conventional pipelines have widely relied on RGB-D cameras to provide geometric information, which fail on transparent or glossy objects and degrade at close range. We present GraspView, an RGB-only robotic grasping pipeline that achieves accurate manipulation in cluttered environments without depth sensors. Our framework integrates three key components: (i) global perception scene reconstruction, which provides locally consistent, up-to-scale geometry from a single RGB view and fuses multi-view projections into a coherent global 3D scene; (ii) a render-and-score active perception strategy, which dynamically selects next-best-views to reveal occluded regions; and (iii) an online metric alignment module that calibrates VGGT predictions against robot kinematics to ensure physical scale consistency. Building on these tailor-designed modules, GraspView performs best-view global grasping, fusing multi-view reconstructions and leveraging GraspNet for robust execution. Experiments on diverse tabletop objects demonstrate that GraspView significantly outperforms both RGB-D and single-view RGB baselines, especially under heavy occlusion, near-field sensing, and with transparent objects. These results highlight GraspView as a practical and versatile alternative to RGB-D pipelines, enabling reliable grasping in unstructured real-world environments.
VoxRole: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Speech-Based Role-Playing Agents
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Recent significant advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have greatly propelled the development of Role-Playing Conversational Agents (RPCAs). These systems aim to create immersive user experiences through consistent persona adoption. However, current RPCA research faces dual limitations. First, existing work predominantly focuses on the textual modality, entirely overlooking critical paralinguistic features including intonation, prosody, and rhythm in speech, which are essential for conveying character emotions and shaping vivid identities. Second, the speech-based role-playing domain suffers from a long-standing lack of standardized evaluation benchmarks. Most current spoken dialogue datasets target only fundamental capability assessments, featuring thinly sketched or ill-defined character profiles. Consequently, they fail to effectively quantify model performance on core competencies like long-term persona consistency. To address this critical gap, we introduce VoxRole, the first comprehensive benchmark specifically designed for the evaluation of speech-based RPCAs. The benchmark comprises 13335 multi-turn dialogues, totaling 65.6 hours of speech from 1228 unique characters across 261 movies. To construct this resource, we propose a novel two-stage automated pipeline that first aligns movie audio with scripts and subsequently employs an LLM to systematically build multi-dimensional profiles for each character. Leveraging VoxRole, we conduct a multi-dimensional evaluation of contemporary spoken dialogue models, revealing crucial insights into their respective strengths and limitations in maintaining persona consistency.
Growing Trees with an Agent: Accelerating RRTs with Learned, Multi-Step Episodic Exploration
Jul 09, 2025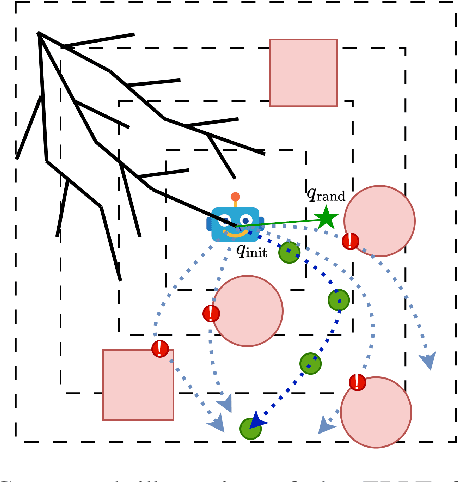
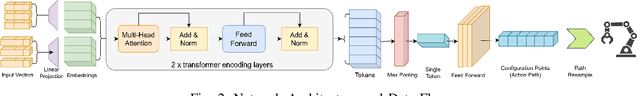
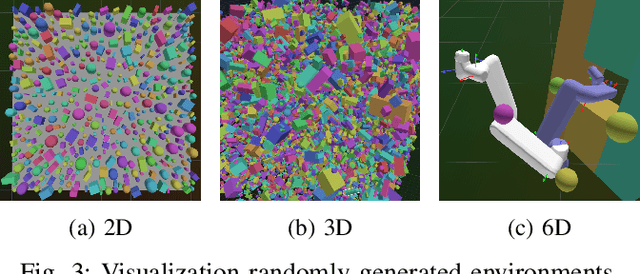
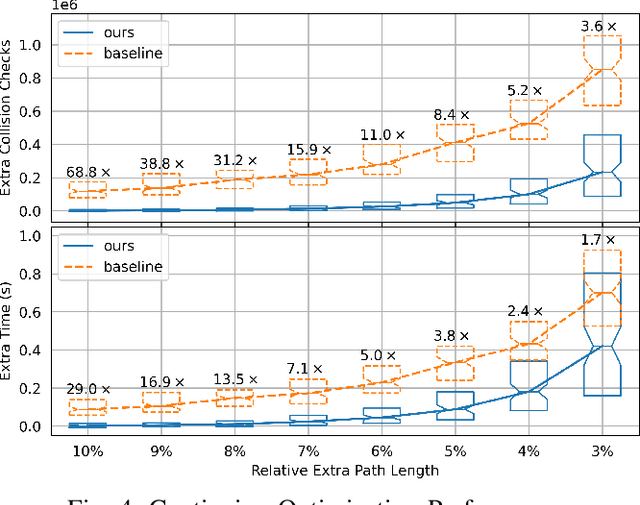
Abstract:Classical sampling-based motion planners like the RRTs suffer from inefficiencies, particularly in cluttered or high-dimensional spaces, due to their reliance on undirected, random sampling. This paper introduces the Episodic RRT, a novel hybrid planning framework that replaces the primitive of a random point with a learned, multi-step "exploratory episode" generated by a Deep Reinforcement Learning agent. By making the DRL agent the engine of exploration, ERRT transforms the search process from a diffuse, volumetric expansion into a directed, branch-like growth. This paradigm shift yields key advantages: it counters the curse of dimensionality with focused exploration, minimizes expensive collision checks by proactively proposing locally valid paths, and improves connectivity by generating inherently connected path segments. We demonstrate through extensive empirical evaluation across 2D, 3D, and 6D environments that ERRT and its variants consistently and significantly outperform their classical counterparts. In a challenging 6D robotic arm scenario, ERRT achieves a 98% success rate compared to 19% for RRT, is up to 107x faster, reduces collision checks by over 99.6%, and finds initial paths that are nearly 50% shorter. Furthermore, its asymptotically optimal variant, ERRT*, demonstrates vastly superior anytime performance, refining solutions to near-optimality up to 29x faster than standard RRT* in 3D environments. Code: https://xinyuwuu.github.io/Episodic_RRT/.
Multi-Modal Foundation Models for Computational Pathology: A Survey
Mar 12, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models have emerged as a powerful paradigm in computational pathology (CPath), enabling scalable and generalizable analysis of histopathological images. While early developments centered on uni-modal models trained solely on visual data, recent advances have highlighted the promise of multi-modal foundation models that integrate heterogeneous data sources such as textual reports, structured domain knowledge, and molecular profiles. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive and up-to-date review of multi-modal foundation models in CPath, with a particular focus on models built upon hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained whole slide images (WSIs) and tile-level representations. We categorize 32 state-of-the-art multi-modal foundation models into three major paradigms: vision-language, vision-knowledge graph, and vision-gene expression. We further divide vision-language models into non-LLM-based and LLM-based approaches. Additionally, we analyze 28 available multi-modal datasets tailored for pathology, grouped into image-text pairs, instruction datasets, and image-other modality pairs. Our survey also presents a taxonomy of downstream tasks, highlights training and evaluation strategies, and identifies key challenges and future directions. We aim for this survey to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of pathology and AI.
A Survey on Computational Pathology Foundation Models: Datasets, Adaptation Strategies, and Evaluation Tasks
Jan 27, 2025Abstract:Computational pathology foundation models (CPathFMs) have emerged as a powerful approach for analyzing histopathological data, leveraging self-supervised learning to extract robust feature representations from unlabeled whole-slide images. These models, categorized into uni-modal and multi-modal frameworks, have demonstrated promise in automating complex pathology tasks such as segmentation, classification, and biomarker discovery. However, the development of CPathFMs presents significant challenges, such as limited data accessibility, high variability across datasets, the necessity for domain-specific adaptation, and the lack of standardized evaluation benchmarks. This survey provides a comprehensive review of CPathFMs in computational pathology, focusing on datasets, adaptation strategies, and evaluation tasks. We analyze key techniques, such as contrastive learning and multi-modal integration, and highlight existing gaps in current research. Finally, we explore future directions from four perspectives for advancing CPathFMs. This survey serves as a valuable resource for researchers, clinicians, and AI practitioners, guiding the advancement of CPathFMs toward robust and clinically applicable AI-driven pathology solutions.
Power Failure Cascade Prediction using Graph Neural Networks
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:We consider the problem of predicting power failure cascades due to branch failures. We propose a flow-free model based on graph neural networks that predicts grid states at every generation of a cascade process given an initial contingency and power injection values. We train the proposed model using a cascade sequence data pool generated from simulations. We then evaluate our model at various levels of granularity. We present several error metrics that gauge the model's ability to predict the failure size, the final grid state, and the failure time steps of each branch within the cascade. We benchmark the graph neural network model against influence models. We show that, in addition to being generic over randomly scaled power injection values, the graph neural network model outperforms multiple influence models that are built specifically for their corresponding loading profiles. Finally, we show that the proposed model reduces the computational time by almost two orders of magnitude.
Rapid hyperspectral photothermal mid-infrared spectroscopic imaging from sparse data for gynecologic cancer tissue subtyping
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Ovarian cancer detection has traditionally relied on a multi-step process that includes biopsy, tissue staining, and morphological analysis by experienced pathologists. While widely practiced, this conventional approach suffers from several drawbacks: it is qualitative, time-intensive, and heavily dependent on the quality of staining. Mid-infrared (MIR) hyperspectral photothermal imaging is a label-free, biochemically quantitative technology that, when combined with machine learning algorithms, can eliminate the need for staining and provide quantitative results comparable to traditional histology. However, this technology is slow. This work presents a novel approach to MIR photothermal imaging that enhances its speed by an order of magnitude. Our method significantly accelerates data collection by capturing a combination of high-resolution and interleaved, lower-resolution infrared band images and applying computational techniques for data interpolation. We effectively minimize data collection requirements by leveraging sparse data acquisition and employing curvelet-based reconstruction algorithms. This method enables the reconstruction of high-quality, high-resolution images from undersampled datasets and achieving a 10X improvement in data acquisition time. We assessed the performance of our sparse imaging methodology using a variety of quantitative metrics, including mean squared error (MSE), structural similarity index (SSIM), and tissue subtype classification accuracies, employing both random forest and convolutional neural network (CNN) models, accompanied by ROC curves. Our statistically robust analysis, based on data from 100 ovarian cancer patient samples and over 65 million data points, demonstrates the method's capability to produce superior image quality and accurately distinguish between different gynecological tissue types with segmentation accuracy exceeding 95%.
Radarize: Large-Scale Radar SLAM for Indoor Environments
Nov 19, 2023



Abstract:We present Radarize, a self-contained SLAM pipeline for indoor environments that uses only a low-cost commodity single-chip mmWave radar. Our radar-native approach leverages phenomena unique to radio frequencies, such as doppler shift-based odometry, to improve performance. We evaluate our method on a large-scale dataset of 146 trajectories spanning 4 campus buildings, totaling approximately 4680m of travel distance. Our results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art radar-based approaches by approximately 5x in terms of odometry and 8x in terms of end-to-end SLAM, as measured by absolute trajectory error (ATE), without the need additional sensors such as IMUs or wheel odometry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge