Xinchi Qiu
Rethinking Rubric Generation for Improving LLM Judge and Reward Modeling for Open-ended Tasks
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Recently, rubrics have been used to guide LLM judges in capturing subjective, nuanced, multi-dimensional human preferences, and have been extended from evaluation to reward signals for reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT). However, rubric generation remains hard to control: rubrics often lack coverage, conflate dimensions, misalign preference direction, and contain redundant or highly correlated criteria, degrading judge accuracy and producing suboptimal rewards during RFT. We propose RRD, a principled framework for rubric refinement built on a recursive decompose-filter cycle. RRD decomposes coarse rubrics into fine-grained, discriminative criteria, expanding coverage while sharpening separation between responses. A complementary filtering mechanism removes misaligned and redundant rubrics, and a correlation-aware weighting scheme prevents over-representing highly correlated criteria, yielding rubric sets that are informative, comprehensive, and non-redundant. Empirically, RRD delivers large, consistent gains across both evaluation and training: it improves preference-judgment accuracy on JudgeBench and PPE for both GPT-4o and Llama3.1-405B judges, achieving top performance in all settings with up to +17.7 points on JudgeBench. When used as the reward source for RFT on WildChat, it yields substantially stronger and more stable learning signals, boosting reward by up to 160% (Qwen3-4B) and 60% (Llama3.1-8B) versus 10-20% for prior rubric baselines, with gains that transfer to HealthBench-Hard and BiGGen Bench. Overall, RRD establishes recursive rubric refinement as a scalable and interpretable foundation for LLM judging and reward modeling in open-ended domains.
LoRDO: Distributed Low-Rank Optimization with Infrequent Communication
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Distributed training of foundation models via $\texttt{DDP}$ is limited by interconnect bandwidth. While infrequent communication strategies reduce synchronization frequency, they remain bottlenecked by the memory and communication requirements of optimizer states. Low-rank optimizers can alleviate these constraints; however, in the local-update regime, workers lack access to the full-batch gradients required to compute low-rank projections, which degrades performance. We propose $\texttt{LoRDO}$, a principled framework unifying low-rank optimization with infrequent synchronization. We first demonstrate that, while global projections based on pseudo-gradients are theoretically superior, they permanently restrict the optimization trajectory to a low-rank subspace. To restore subspace exploration, we introduce a full-rank quasi-hyperbolic update. $\texttt{LoRDO}$ achieves near-parity with low-rank $\texttt{DDP}$ in language modeling and downstream tasks at model scales of $125$M--$720$M, while reducing communication by $\approx 10 \times$. Finally, we show that $\texttt{LoRDO}$ improves performance even more in very low-memory settings with small rank/batch size.
Don't Make It Up: Preserving Ignorance Awareness in LLM Fine-Tuning
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Existing work on mitigating catastrophic forgetting in large language model (LLM) fine-tuning has primarily focused on preserving specific data or tasks, while critically overlooking the degradation of essential capabilities instilled through safety alignment, particularly the model's ability to faithfully express ignorance. In this work, we show that this capability is significantly degraded during conventional fine-tuning, leading to undesired behaviors such as hallucinations. To address this novel but highly practical problem, we propose SEAT, a simple and effective fine-tuning approach that preserves both fine-tuning performance and the model's inherent ability to acknowledge its ignorance. SEAT integrates two key components: (1) sparse training that constrains activation drift, and (2) a novel entity perturbation method with KL-divergence regularization, designed to counter knowledge entanglement. Experimental results demonstrate that SEAT significantly outperforms baselines in preserving ignorance awareness while retaining fine-tuning performance, offering a more robust solution for LLM fine-tuning.
DES-LOC: Desynced Low Communication Adaptive Optimizers for Training Foundation Models
May 28, 2025Abstract:Scaling foundation model training with Distributed Data Parallel (DDP) methods is bandwidth-limited. Existing infrequent communication methods like Local SGD were designed to synchronize only model parameters and cannot be trivially applied to adaptive optimizers due to additional optimizer states. Current approaches extending Local SGD either lack convergence guarantees or require synchronizing all optimizer states, tripling communication costs. We propose Desynced Low Communication Adaptive Optimizers (DES-LOC), a family of optimizers assigning independent synchronization periods to parameters and momenta, enabling lower communication costs while preserving convergence. Through extensive experiments on language models of up to 1.7B, we show that DES-LOC can communicate 170x less than DDP and 2x less than the previous state-of-the-art Local ADAM. Furthermore, unlike previous heuristic approaches, DES-LOC is suited for practical training scenarios prone to system failures. DES-LOC offers a scalable, bandwidth-efficient, and fault-tolerant solution for foundation model training.
Editing as Unlearning: Are Knowledge Editing Methods Strong Baselines for Large Language Model Unlearning?
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large language Model (LLM) unlearning, i.e., selectively removing information from LLMs, is vital for responsible model deployment. Differently, LLM knowledge editing aims to modify LLM knowledge instead of removing it. Though editing and unlearning seem to be two distinct tasks, we find there is a tight connection between them. In this paper, we conceptualize unlearning as a special case of editing where information is modified to a refusal or "empty set" $\emptyset$ response, signifying its removal. This paper thus investigates if knowledge editing techniques are strong baselines for LLM unlearning. We evaluate state-of-the-art (SOTA) editing methods (e.g., ROME, MEMIT, GRACE, WISE, and AlphaEdit) against existing unlearning approaches on pretrained and finetuned knowledge. Results show certain editing methods, notably WISE and AlphaEdit, are effective unlearning baselines, especially for pretrained knowledge, and excel in generating human-aligned refusal answers. To better adapt editing methods for unlearning applications, we propose practical recipes including self-improvement and query merging. The former leverages the LLM's own in-context learning ability to craft a more human-aligned unlearning target, and the latter enables ROME and MEMIT to perform well in unlearning longer sample sequences. We advocate for the unlearning community to adopt SOTA editing methods as baselines and explore unlearning from an editing perspective for more holistic LLM memory control.
LUNAR: LLM Unlearning via Neural Activation Redirection
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) benefit from training on ever larger amounts of textual data, but as a result, they increasingly incur the risk of leaking private information. The ability to selectively remove knowledge from LLMs is, therefore, a highly desirable capability. In this paper, we propose LUNAR, a novel unlearning methodology grounded in the Linear Representation Hypothesis. LUNAR operates by redirecting the representations of unlearned data to regions that trigger the model's inherent ability to express its inability to answer. LUNAR achieves state-of-the-art unlearning performance while significantly enhancing the controllability of the unlearned model during inference. Specifically, LUNAR achieves between 2.9x to 11.7x improvements on combined "unlearning efficacy" and "model utility" score ("Deviation Score") on the PISTOL dataset across various base models. We also demonstrate, through quantitative analysis and qualitative examples, LUNAR's superior controllability in generating coherent and contextually aware responses, mitigating undesired side effects of existing methods. Moreover, we demonstrate that LUNAR is robust against white-box adversarial attacks and versatile in handling real-world scenarios, such as processing sequential unlearning requests.
Photon: Federated LLM Pre-Training
Nov 05, 2024



Abstract:Scaling large language models (LLMs) demands extensive data and computing resources, which are traditionally constrained to data centers by the high-bandwidth requirements of distributed training. Low-bandwidth methods like federated learning (FL) could enable collaborative training of larger models across weakly-connected GPUs if they can effectively be used for pre-training. To achieve this, we introduce Photon, the first complete system for federated end-to-end LLM training, leveraging cross-silo FL for global-scale training with minimal communication overheads. Using Photon, we train the first federated family of decoder-only LLMs from scratch. We show that: (1) Photon can train model sizes up to 7B in a federated fashion while reaching an even better perplexity than centralized pre-training; (2) Photon model training time decreases with available compute, achieving a similar compute-time trade-off to centralized; and (3) Photon outperforms the wall-time of baseline distributed training methods by 35% via communicating 64x-512xless. Our proposal is robust to data heterogeneity and converges twice as fast as previous methods like DiLoCo. This surprising data efficiency stems from a unique approach combining small client batch sizes with extremely high learning rates, enabled by federated averaging's robustness to hyperparameters. Photon thus represents the first economical system for global internet-wide LLM pre-training.
DEPT: Decoupled Embeddings for Pre-training Language Models
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Language Model pre-training benefits from a broader data mixture to enhance performance across domains and languages. However, training on such heterogeneous text corpora is complex, requiring extensive and cost-intensive efforts. Since these data sources vary in lexical, syntactic, and semantic aspects, they cause negative interference or the "curse of multilinguality". We propose a novel pre-training framework to alleviate this curse. Our method, DEPT, decouples the embedding layers from the transformer body while simultaneously training the latter in multiple contexts. DEPT enables the model to train without being bound to a shared global vocabulary. DEPT: (1) can train robustly and effectively under significant data heterogeneity, (2) reduces the parameter count of the token embeddings by up to 80% and the communication costs by 675x for billion-scale models (3) enhances model generalization and plasticity in adapting to new languages and domains, and (4) allows training with custom optimized vocabulary per data source. We prove DEPT's potential by performing the first vocabulary-agnostic federated multilingual pre-training of a 1.3 billion-parameter model across high and low-resource languages, reducing its parameter count by 409 million.
PISTOL: Dataset Compilation Pipeline for Structural Unlearning of LLMs
Jun 24, 2024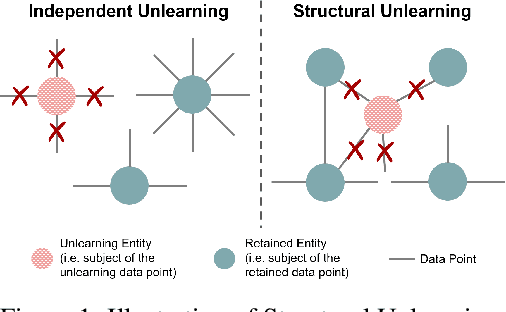
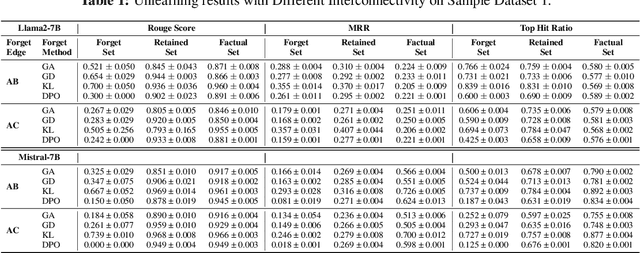

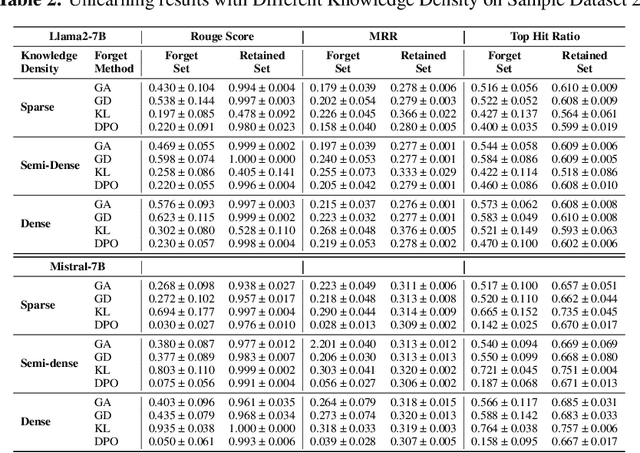
Abstract:Recently, machine unlearning, which seeks to erase specific data stored in the pre-trained or fine-tuned models, has emerged as a crucial protective measure for LLMs. However, unlearning approaches for LLMs that have been considered thus far have focused on the removal of independent data points and have not taken into account that the stored facts are logically connected to one another and form an implicit knowledge graph. To facilitate the development of structural unlearning methods, which are essential for the practical application of unlearning, we propose PISTOL, a pipeline for compiling multi-scenario datasets for benchmarking structural LLM unlearning. Additionally, leveraging sample datasets synthesized using PISTOL, we conducted benchmarks with four distinct unlearning methods on both Llama2-7B and Mistral-7B models. This analysis helps to illustrate the prevailing challenges in effectively and robustly removing highly inter-connected data, batched data, or data skewed towards a specific domain. It also highlights the choice of pre-trained model can impact unlearning performance. This work not only advances our understandings on the limitation of current LLMs unlearning methods and proposes future research directions, but also provides a replicable framework for ongoing exploration and validation in the field.
FLea: Addressing Data Scarcity and Label Skew in Federated Learning via Privacy-preserving Feature Augmentation
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables model development by leveraging data distributed across numerous edge devices without transferring local data to a central server. However, existing FL methods still face challenges when dealing with scarce and label-skewed data across devices, resulting in local model overfitting and drift, consequently hindering the performance of the global model. In response to these challenges, we propose a pioneering framework called FLea, incorporating the following key components: i) A global feature buffer that stores activation-target pairs shared from multiple clients to support local training. This design mitigates local model drift caused by the absence of certain classes; ii) A feature augmentation approach based on local and global activation mix-ups for local training. This strategy enlarges the training samples, thereby reducing the risk of local overfitting; iii) An obfuscation method to minimize the correlation between intermediate activations and the source data, enhancing the privacy of shared features. To verify the superiority of FLea, we conduct extensive experiments using a wide range of data modalities, simulating different levels of local data scarcity and label skew. The results demonstrate that FLea consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FL counterparts (among 13 of the experimented 18 settings, the improvement is over 5% while concurrently mitigating the privacy vulnerabilities associated with shared features. Code is available at https://github.com/XTxiatong/FLea.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge